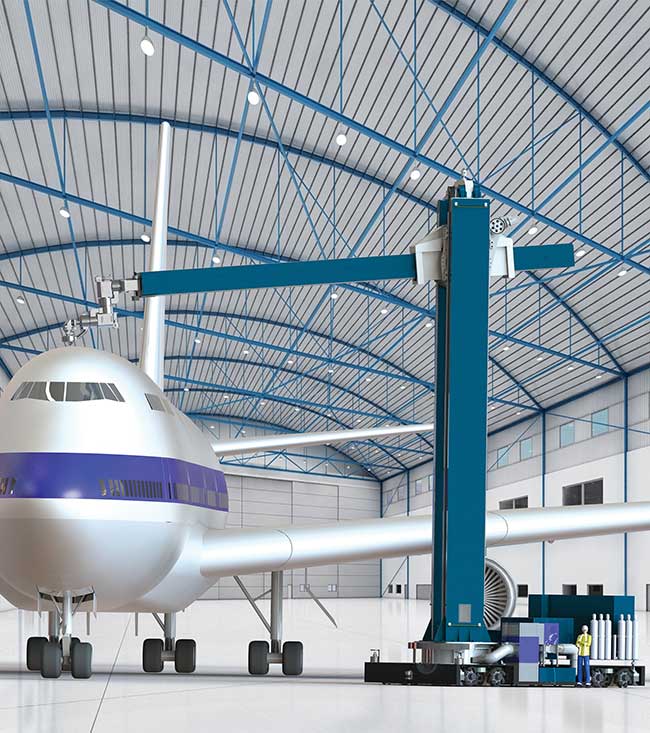
The global laser paint stripping market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for precision surface preparation in aerospace, automotive, and defense industries. According to Mordor Intelligence, the market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.8% from 2023 to 2028, fueled by the adoption of environmentally sustainable and non-abrasive de-coating technologies. Grand View Research further supports this trend, noting that the push for eco-friendly manufacturing processes and stringent regulations on chemical-based stripping methods are accelerating the shift toward laser solutions. As industries prioritize efficiency, safety, and repeatability, manufacturers of laser paint strippers are scaling innovation in power control, automation, and portability. In this evolving landscape, the following nine companies have emerged as leading manufacturers, combining technological excellence with proven performance across high-stakes applications.
Top 9 Laser Paint Strippers Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 China Laser Paint Stripper
Website: laserstripper.com
Key Highlights: Industrial-grade laser paint stripper and laser rust stripper with continuous wave technology for heavy-duty cleaning applications and large-scale operations….
#2 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: we engineer and manufacture the most advanced—and most powerful—pulsed industrial laser cleaning systems on the market, built for both manual and automated ……
#3 Laserax
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Laserax works with the world’s leading manufacturers to implement laser cleaning, welding, texturing, and marking solutions….
#4 Clean Laser Systems
Website: cleanlaser.de
Key Highlights: Our laser systems are primarily in operation with mold and tool cleaning, paint stripping and decoating as well as cleaning and modification of metallic ……
#5 Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: Explore PULSAR Laser P CL laser cleaning machines for industrial rust removal and paint stripping. Compare SHARK P CL, PANDA P CL and FOX P CL….
#6 Laser Photonics
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser Photonics manufactures reliable, safe, and eco-friendly Laser Cleaning, Laser Cutting, Laser Engraving, Laser Marking, and Laser Welding solutions….
#7 Laser Paint Removal
Website: keyence.com
Key Highlights: Achieve fast, precise laser paint removal with minimal waste. Discover advanced paint removal with laser for industrial and manufacturing needs….
#8 Argento Lux
Website: argentolux.com
Key Highlights: Our company provides state-of-the-art Industrial Laser Equipment Sales and Mobile Laser Cleaning Services for a wide range of applications and industries….
#9 Clean Laser Technologies
Website: cleanlasertechnologies.com
Key Highlights: Clean Laser Technologies is a Mississippi-based company specializing in laser cleaning technology, providing state-of-the-art laser cleaning machines, training ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Paint Strippers

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Laser Paint Strippers
The global market for laser paint strippers is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, increasing environmental regulations, and growing demand across key industries such as aerospace, automotive, and marine. As industries shift toward more sustainable and efficient surface preparation methods, laser-based solutions are emerging as a preferred alternative to traditional chemical and abrasive techniques.
Rising Demand for Eco-Friendly Solutions
One of the primary drivers of the 2026 market landscape is the global push for environmentally sustainable manufacturing practices. Regulatory bodies in North America and Europe are imposing stricter controls on volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and hazardous waste generated by chemical paint strippers. Laser paint stripping produces no chemical runoff and minimal particulate matter when paired with proper filtration systems, making it compliant with tightening environmental standards. This regulatory tailwind is accelerating adoption, particularly in environmentally sensitive regions.
Technological Advancements and Automation Integration
By 2026, laser paint stripper systems are expected to feature enhanced automation, artificial intelligence (AI)-driven targeting, and real-time monitoring capabilities. Integration with robotic arms and industrial IoT platforms enables precise, repeatable stripping with minimal operator intervention. These advancements reduce labor costs, improve safety, and increase throughput—key factors for large-scale industrial applications. Fiber lasers, in particular, are becoming more efficient and cost-effective, broadening their accessibility beyond high-end aerospace applications to mid-tier manufacturers.
Aerospace and Defense Leading Adoption
The aerospace and defense sector remains the largest adopter of laser paint stripping technology, driven by the need for non-damaging, precision surface preparation on aircraft fuselages and components. By 2026, nearly 60% of major aircraft maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) facilities are projected to incorporate laser systems into their workflows. The technology’s ability to remove coatings without harming underlying composites or metals is a critical advantage, especially with the rising use of advanced materials in modern aircraft.
Expansion into Automotive and Marine Sectors
While aerospace leads, the automotive and marine industries are expected to show the highest compound annual growth rate (CAGR) through 2026. In automotive, laser stripping is being used in restoration, custom fabrication, and electric vehicle (EV) manufacturing, where clean surface preparation is essential for adhesion and quality control. In the marine industry, shipyards are adopting laser systems to reduce dry-docking time and comply with anti-pollution regulations during hull maintenance.
Cost and Accessibility Challenges
Despite the positive outlook, high initial investment costs and the need for skilled operators remain barriers to widespread adoption, especially among small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). However, by 2026, leasing models, modular systems, and government incentives for green technology are expected to improve accessibility. Equipment costs are projected to decline by 15–20% due to economies of scale and increased competition among manufacturers in North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific.
Regional Market Dynamics
North America and Europe will continue to dominate the laser paint stripper market in 2026, supported by strong regulatory frameworks and advanced industrial infrastructure. Meanwhile, the Asia-Pacific region—particularly China, Japan, and South Korea—is expected to experience rapid growth due to expanding aerospace and automotive manufacturing sectors and increasing environmental awareness.
Conclusion
By 2026, the laser paint stripper market will be characterized by broader industrial adoption, enhanced technological integration, and strong growth fueled by environmental and efficiency demands. As innovation reduces costs and improves usability, laser-based systems are set to become a standard tool in sustainable surface engineering across multiple high-value industries.
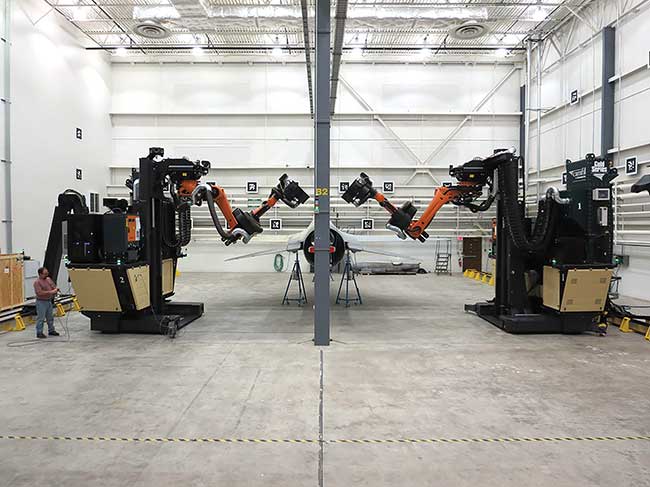

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Laser Paint Strippers (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing laser paint strippers presents unique challenges, particularly concerning product quality and intellectual property (IP) risks. Being aware of these pitfalls is essential for ensuring a reliable, legal, and effective solution.
Poor Build Quality and Inconsistent Performance
Many suppliers, especially those from regions with less stringent manufacturing standards, offer systems with subpar components. These may include low-grade optics, unreliable cooling systems, or poorly calibrated lasers, leading to inconsistent stripping results, frequent downtime, and shortened equipment lifespan. Buyers often discover these flaws only after deployment, resulting in costly repairs and operational delays.
Inadequate Safety Features and Compliance
Laser paint strippers must comply with international safety standards (e.g., IEC 60825). Some sourced units lack proper safety interlocks, beam shielding, or emergency shut-offs, posing serious risks to operators. Additionally, non-compliant systems may fail regulatory inspections, leading to project halts or liability issues, particularly in aerospace or defense applications.
Misrepresented Laser Specifications
A common issue is the exaggeration of key performance metrics such as laser power, pulse energy, or beam quality. Suppliers may quote peak power instead of average power or use misleading classifications. This results in underperforming equipment that fails to meet stripping requirements, especially on challenging substrates or thick coatings.
Lack of Intellectual Property Protection
Sourcing from manufacturers with questionable IP practices increases the risk of acquiring systems that infringe on patented technologies. This exposes the buyer to legal challenges, potential lawsuits, and forced equipment removal. It is crucial to verify that the supplier holds legitimate IP rights or proper licensing for critical components and control software.
Insufficient Technical Support and Documentation
Many low-cost suppliers provide minimal technical documentation, training, or after-sales support. Without detailed operating manuals, maintenance guides, or accessible engineering support, integrating and maintaining the system becomes difficult. This lack of support can lead to prolonged downtimes and increased total cost of ownership.
Hidden Costs from Incomplete System Integration
Some suppliers offer stripped-down configurations that exclude essential accessories—such as fume extraction, robotic arms, or safety enclosures. Buyers may face unexpected expenses when integrating the laser into their workflow, undermining the initial cost advantage.
Counterfeit or Reverse-Engineered Components
In extreme cases, sourced systems may contain counterfeit or reverse-engineered parts that mimic genuine components. These not only compromise performance and safety but also void warranties and create long-term reliability concerns.
To mitigate these risks, due diligence is essential: verify supplier credentials, request third-party testing, conduct factory audits, and ensure IP clearance through legal review. Prioritizing reputable manufacturers with proven track records helps secure a high-quality, legally sound laser paint stripping solution.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Paint Strippers
Regulatory Classification and Documentation
Laser paint strippers are specialized industrial tools that combine high-powered lasers with precision control systems for removing paint, coatings, and surface contaminants from substrates such as metal, concrete, and composites. Due to their laser technology, electrical components, and potential safety risks, they are subject to various international and national regulations. Proper classification under Harmonized System (HS) codes is essential for customs clearance. Typical HS codes for laser paint strippers may fall under 8515 (Electro-thermic appliances, including laser soldering or welding equipment) or 8479 (Machines having individual functions not elsewhere specified). Accurate technical specifications, including laser class, power output (in watts), wavelength, and intended use, must be provided to determine the correct classification. Accompanying documents should include commercial invoices, packing lists, certificates of origin, and product compliance certificates.
Safety and Laser Compliance Standards
Laser paint strippers must comply with stringent safety standards due to the inherent hazards of high-intensity laser radiation. In the United States, compliance with the FDA/CDRH (Center for Devices and Radiological Health) regulations under 21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11 is mandatory. These regulations require product certification, proper labeling (including warning labels and laser classification), and the inclusion of safety features such as interlocks, emergency shutoffs, and protective housings. Internationally, adherence to IEC 60825-1 (Safety of laser products – Part 1: Equipment classification and requirements) is critical. The laser system must be classified (typically Class 4 for industrial paint strippers), and users must be provided with appropriate safety training, protective eyewear, and operational manuals. Manufacturers and suppliers must ensure that equipment bears the CE marking when shipped to the European Union, confirming conformity with the EU’s health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
Packaging and Transportation Requirements
Due to their sensitive optical and electronic components, laser paint strippers require robust and secure packaging to prevent damage during transit. Packaging should include shock-absorbent materials, rigid outer containers, and internal bracing to immobilize components. Equipment must be protected from moisture, dust, and extreme temperatures. When shipping internationally, compliance with IATA (International Air Transport Association) regulations is necessary for air freight, especially if the equipment contains batteries or other regulated components. Lithium-ion batteries, if present in portable units, must be shipped in accordance with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations (DGR), including proper labeling, state-of-charge restrictions, and packaging requirements. For sea freight, adherence to the IMDG (International Maritime Dangerous Goods) Code may apply depending on ancillary components. Proper handling labels (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” “Protect from Moisture”) must be clearly displayed.
Import/Export Controls and Permits
Export and import of laser paint striippers may be subject to dual-use or strategic trade controls, particularly if the laser power exceeds certain thresholds or if the technology has potential military applications. In the United States, exports may require authorization from the Department of Commerce under the Export Administration Regulations (EAR), especially if the laser falls under ECCN (Export Control Classification Number) 6A003 or 6A005. Similarly, the Wassenaar Arrangement on Export Controls for Conventional Arms and Dual-Use Goods and Technologies governs international transfers of such technology in participating countries. Importers must verify if their country requires licenses or notifications for receiving laser systems. End-user documentation or statements may be necessary to confirm legitimate industrial use and prevent diversion to unauthorized applications.
Environmental and Disposal Compliance
Laser paint stripping generates ablated material, including paint particles, fumes, and debris, some of which may contain hazardous substances (e.g., lead, chromium). The system must be used in conjunction with appropriate fume extraction and filtration units compliant with local environmental and occupational health regulations (e.g., OSHA in the U.S., REACH and RoHS in the EU). End-of-life disposal of the laser unit must follow WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directives in the European Union and similar e-waste regulations elsewhere. Components such as laser diodes, circuit boards, and batteries must be recycled or disposed of through certified electronic waste handlers. Suppliers and users must retain documentation proving proper disposal to ensure regulatory compliance.
Training and Operational Compliance
Effective logistics and compliance extend beyond shipment and importation to include responsible use. Suppliers must provide comprehensive training materials and documentation to ensure safe and legal operation. This includes operator manuals, safety data sheets (SDS) for any consumables, and guidelines for compliance with local occupational safety regulations (e.g., ANSI Z136.1 in the U.S.). Facilities using laser paint strippers must implement laser safety programs, designate a Laser Safety Officer (LSO) where required, and maintain controlled access zones with appropriate signage. Regular equipment maintenance and calibration records must be kept to demonstrate ongoing compliance during audits or inspections.
Summary and Best Practices
To ensure smooth logistics and full compliance when handling laser paint strippers, stakeholders should:
– Verify accurate HS code classification and maintain complete shipping documentation.
– Confirm compliance with laser safety standards (FDA/CDRH, IEC 60825, CE marking).
– Use protective, environmentally stable packaging with proper hazard labeling.
– Obtain necessary export/import licenses for controlled laser technologies.
– Implement fume management and adhere to environmental regulations during use.
– Provide operator training and maintain documentation for audits.
Adherence to these guidelines minimizes delays, avoids penalties, and promotes the safe and legal deployment of laser paint stripping technology worldwide.
Conclusion on Sourcing Laser Paint Strippers
Sourcing laser paint strippers requires a strategic approach that balances technical capabilities, cost efficiency, safety compliance, and long-term operational needs. These advanced systems offer significant advantages over traditional paint removal methods—including precision, minimal substrate damage, reduced environmental impact, and elimination of chemical solvents—making them particularly valuable in industries such as aerospace, automotive restoration, and cultural heritage conservation.
However, the high initial investment, specialized training requirements, and maintenance demands necessitate careful supplier evaluation. Key considerations when sourcing include the laser’s power and wavelength compatibility with target materials, system portability, automation features, and adherence to international safety standards (e.g., IEC 60825). Engaging with reputable manufacturers or integrators with proven track records, strong technical support, and service agreements is crucial for successful implementation.
Additionally, conducting pilot testing, evaluating total cost of ownership (including energy consumption and maintenance), and aligning the technology with specific application requirements will ensure optimal performance and return on investment.
In conclusion, while laser paint strippers represent a premium solution, sourcing the right system from a reliable provider can deliver long-term efficiency gains, improved quality outcomes, and enhanced sustainability, making it a worthwhile investment for organizations committed to advanced surface preparation technologies.











