The global laser cleaning equipment market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for eco-friendly and precision-based surface treatment technologies across industrial sectors. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at approximately USD 380 million in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 12.5% through 2028. This expansion is fueled by the rising adoption of laser paint and rust removal systems in automotive, aerospace, and heritage conservation applications, where traditional abrasive methods are being phased out due to environmental and efficiency concerns. As industries shift toward sustainable maintenance practices, leading manufacturers are investing heavily in high-power, portable laser cleaning solutions. This data-driven momentum sets the stage for identifying the top 10 laser paint and rust remover manufacturers at the forefront of innovation, reliability, and market impact—companies shaping the future of non-contact surface decontamination.
Top 10 Laser Paint Rust Remover Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 FOX P CL – laser for removing rust
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: An innovative laser cleaner that revolutionizes the maintenance and restoration of large vehicles and industrial equipment….
#2 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: we engineer and manufacture the most advanced—and most powerful—pulsed industrial laser cleaning systems on the market, built for both manual and automated ……
#3 Laserax
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Our laser cleaning solutions are used to remove a range of contaminants from metal surfaces such as rust, oxide, paint, and electrolyte. As contaminants are ……
#4 Laser Photonics
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser Photonics manufactures reliable, safe, and eco-friendly Laser Cleaning, Laser Cutting, Laser Engraving, Laser Marking, and Laser Welding solutions….
#5 SFX Laser
Website: sfxlaser.com
Key Highlights: SFX Laser is a 20+ years professional laser equipment manufacturer including laser cleaning machine, laser welding machine, fiber laser engraver, ……
#6 Industrial 1500W 2000W CW Laser Cleaning Machine Rusty Remove
Website: xinglaser.com
Key Highlights: XING Laser (6am Life LLC, DBA XING Laser) specializes in the development and manufacture of high-performance handheld laser cleaning and rust removal equipment….
#7 Adapt Laser
Website: adapt-laser.com
Key Highlights: Specializing in custom laser processing solutions, we use advanced pulsed laser technology for superior surface treatment and material ablation….
#8 Laser cleaning
Website: p-laserusa.com
Key Highlights: Our laser machines are mainly used to remove the following contaminants: Rust – Paint – Coatings – Release Agents – Grease, Oils – Soot – Rubber- Organic ……
#9 Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: sltl.com
Key Highlights: This futuristic laser cleaning solution can capably remove rust, oil, paint, grease, colour and other particles from the surface of the metals….
#10 Laser Cleaning
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaning is used across a variety of industries to remove unwanted surface materials like coatings, paints, rust, oil, and for surface preparation for ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Paint Rust Remover

H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for Laser Paint and Rust Removers
The market for laser paint and rust removers is poised for significant transformation and growth by 2026, driven by technological advancements, increasing environmental and safety regulations, and shifting industrial demands. Here’s an analysis of the key trends shaping this sector:
1. Accelerated Adoption Across Industries:
By 2026, laser ablation technology is expected to gain stronger footholds beyond niche applications. Key industries such as aerospace, automotive restoration, maritime, and heritage preservation will increasingly adopt laser systems due to their precision, non-contact nature, and ability to preserve substrate integrity. The demand for efficient, repeatable surface preparation in high-value manufacturing and maintenance operations will be a major growth driver.
2. Technological Advancements Enhancing Efficiency and Accessibility:
Ongoing R&D will lead to more compact, energy-efficient, and user-friendly laser systems. Expect improvements in:
– Fiber Laser Dominance: High-power fiber lasers will continue to outperform older laser types, offering better reliability, lower maintenance, and increased portability.
– Automation and Robotics Integration: Greater integration with robotic arms and automated guided vehicles (AGVs) will enable scalable, consistent surface treatment in production environments, reducing labor costs and human error.
– Smart Features: AI-powered process monitoring, real-time feedback control, and predictive maintenance will enhance operational efficiency and reduce downtime.
3. Environmental and Regulatory Tailwinds:
Stringent global regulations on VOC emissions, hazardous waste disposal (e.g., from chemical strippers or abrasive blasting media), and worker safety will favor clean, dry laser ablation methods. As ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) criteria become central to corporate strategies, laser removers—producing no secondary waste and minimal airborne particulates (with proper filtration)—will be increasingly viewed as sustainable alternatives.
4. Cost-Benefit Justification Improving:
Although the upfront cost of laser systems remains higher than traditional methods, the total cost of ownership (TCO) is becoming more competitive. By 2026, reduced labor requirements, elimination of consumables (e.g., abrasives, chemicals), lower waste disposal costs, and extended equipment lifespan will improve ROI, making lasers a more attractive investment for mid-sized enterprises.
5. Expansion of Service-Based Business Models:
A growing trend will be the rise of laser surface treatment as a service (LaaS). Companies without capital for equipment purchase will increasingly contract specialized providers, expanding market reach and enabling faster adoption, especially in SMEs and infrastructure maintenance sectors.
6. Regional Market Diversification:
While North America and Western Europe lead in early adoption due to regulatory and technological maturity, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific (particularly China, Japan, and India) are expected to experience the fastest growth by 2026. Rising industrialization, infrastructure investment, and government support for green technologies will fuel demand in these regions.
7. Competitive Landscape Intensification:
The market will see increased competition as both established industrial equipment manufacturers and innovative startups enter the space. This will drive product differentiation, pricing pressures, and accelerated innovation, ultimately benefiting end users.
In conclusion, the 2026 outlook for laser paint and rust removers is highly positive, marked by technological maturity, regulatory support, and expanding industrial applications. As the technology becomes more efficient and cost-effective, it is set to transition from a premium solution to a mainstream surface preparation method across multiple high-value sectors.
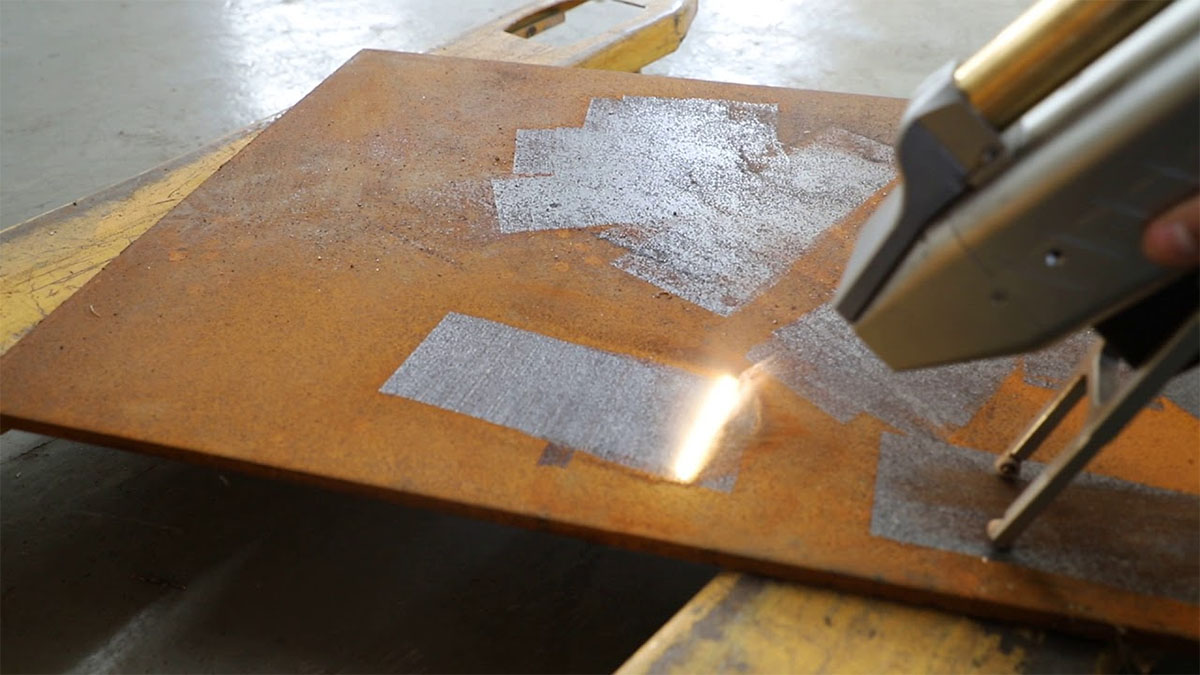

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Laser Paint and Rust Remover (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing a laser paint and rust remover involves significant technical, quality, and legal considerations. Overlooking these aspects can lead to subpar performance, safety risks, and intellectual property (IP) disputes. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
1. Overlooking Build Quality and Component Reliability
Many low-cost suppliers offer laser systems with inferior components, such as under-spec lasers, weak cooling systems, or flimsy mechanical frames. These compromises lead to inconsistent ablation, frequent breakdowns, and shortened equipment lifespan. Always verify the manufacturer’s build standards, materials used, and third-party certifications (e.g., CE, FDA, or IEC 60825 for laser safety).
2. Inadequate Power and Wavelength Specification
Not all lasers effectively remove paint and rust. Using underpowered systems (e.g., <100W fiber lasers) results in slow processing and incomplete removal. Additionally, incorrect wavelengths may damage the substrate or fail to ablate the coating efficiently. Ensure the laser’s power, pulse frequency, and wavelength (typically 1064 nm for fiber lasers) are suitable for industrial surface cleaning.
3. Lack of Real-World Performance Validation
Suppliers may provide ideal lab results that don’t reflect field conditions. Always request on-site demos or third-party test reports using materials and coatings similar to your application. Pay attention to cleaning speed, substrate damage, and ease of integration into existing workflows.
4. Ignoring Safety and Compliance Features
High-power lasers pose serious safety risks. Systems lacking essential safety features—such as emergency stops, interlocks, fume extraction, and enclosed operation—can endanger operators and violate OSHA or local regulations. Confirm compliance with laser safety standards and ensure proper training is provided.
5. Underestimating Maintenance and Operating Costs
Some laser removers require frequent maintenance, expensive replacement parts, or specialized technicians. Failing to assess total cost of ownership (TCO) can result in budget overruns. Review service contracts, spare parts availability, and expected maintenance intervals before procurement.
6. Overlooking Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Sourcing from manufacturers that infringe on patented laser technologies (e.g., beam delivery systems, scanning methods, or control software) exposes your company to legal liability. Conduct due diligence on the supplier’s IP portfolio, request proof of licensing for critical technologies, and include IP indemnity clauses in contracts.
7. Falling for Misleading Marketing Claims
Some vendors exaggerate cleaning speed, material compatibility, or automation capabilities. Be skeptical of vague performance metrics and demand verifiable data. Ask for customer references and case studies involving applications comparable to yours.
8. Poor Software and User Interface
An intuitive control system is essential for efficient operation. Systems with clunky or proprietary software can hinder usability and integration with existing manufacturing systems. Evaluate software flexibility, update availability, and compatibility with industry-standard protocols (e.g., Ethernet/IP, Modbus).
Avoiding these pitfalls requires thorough supplier vetting, technical evaluation, and legal review. Prioritize quality, safety, and IP integrity to ensure a reliable and compliant laser cleaning solution.
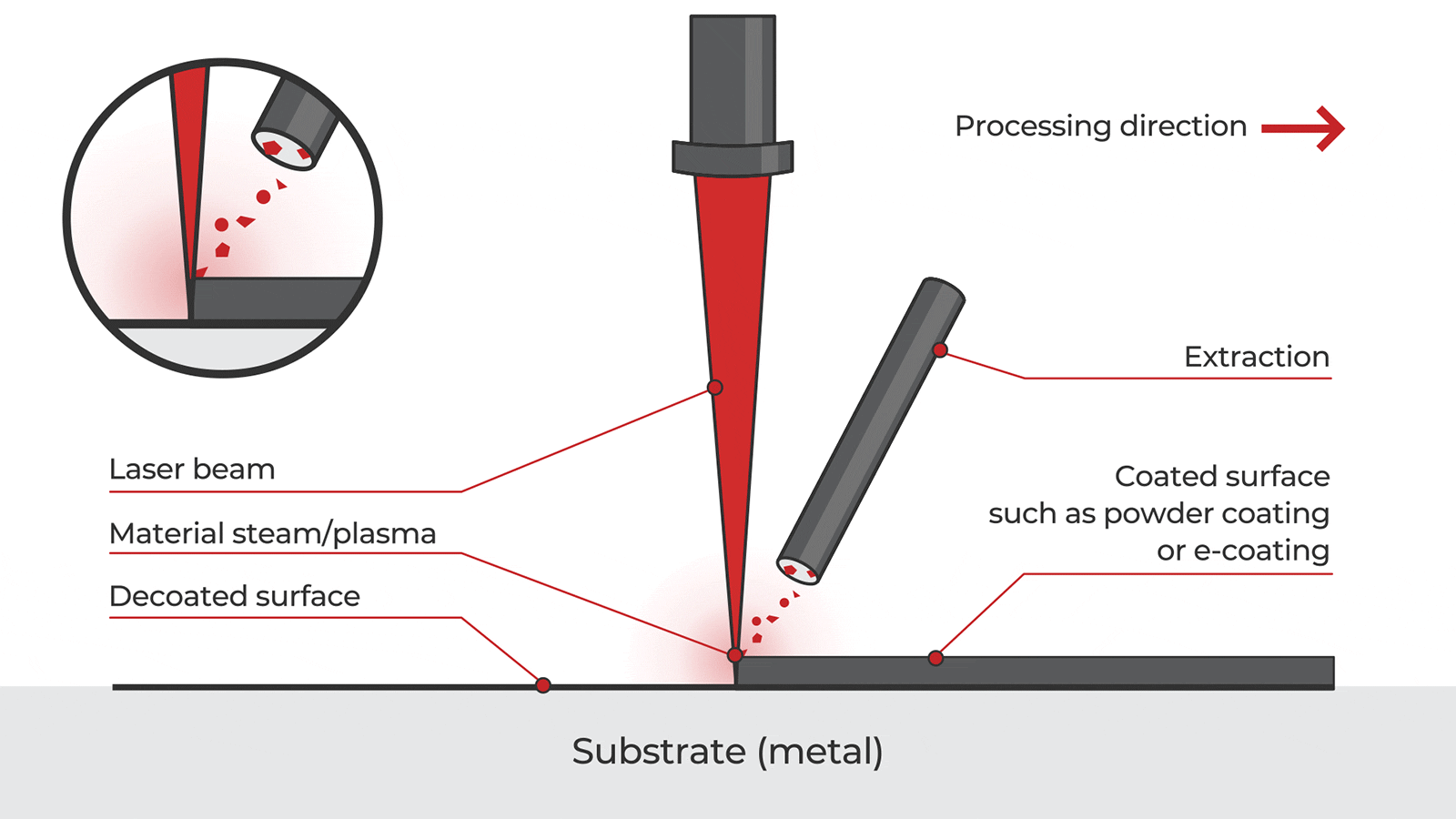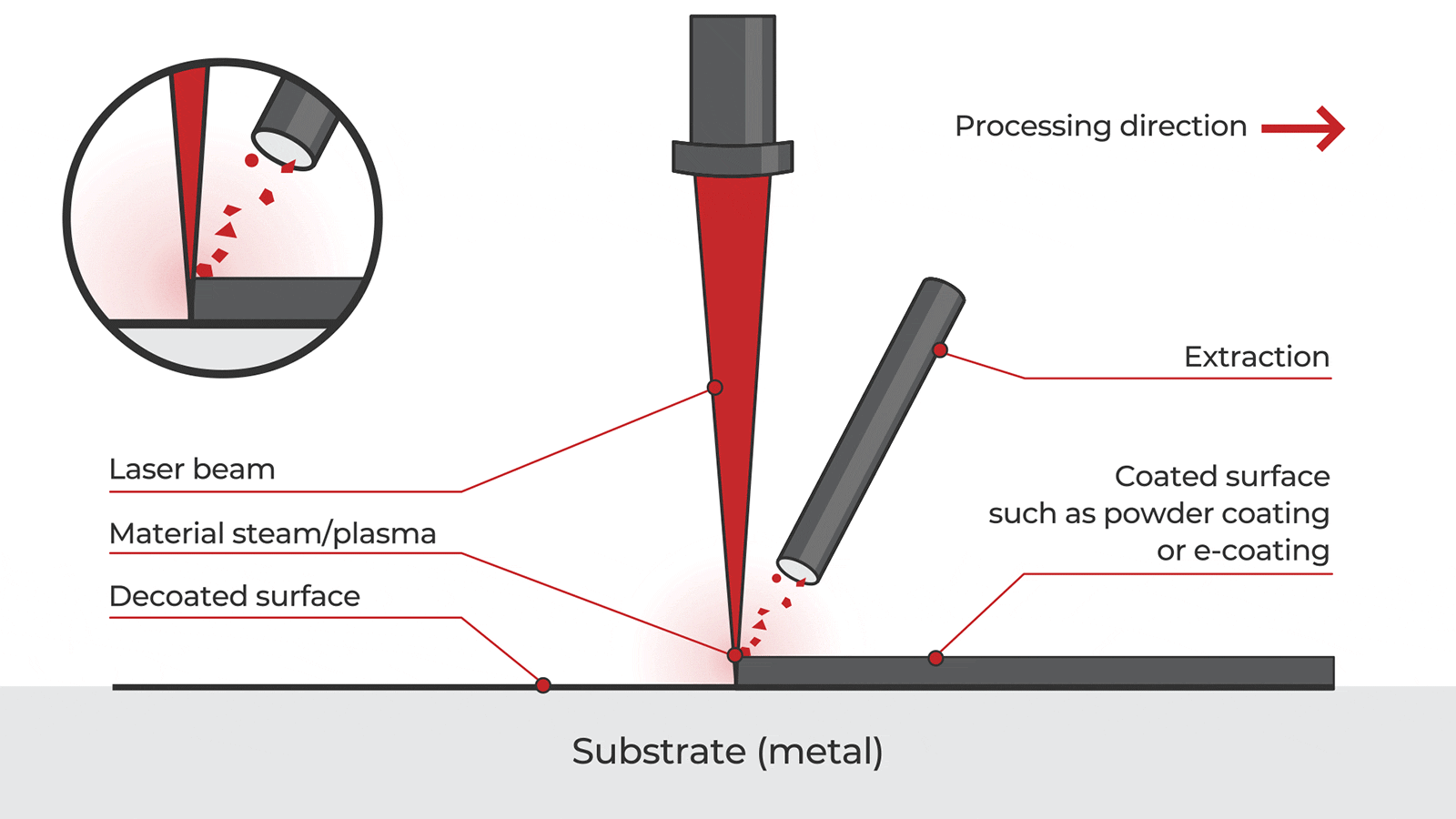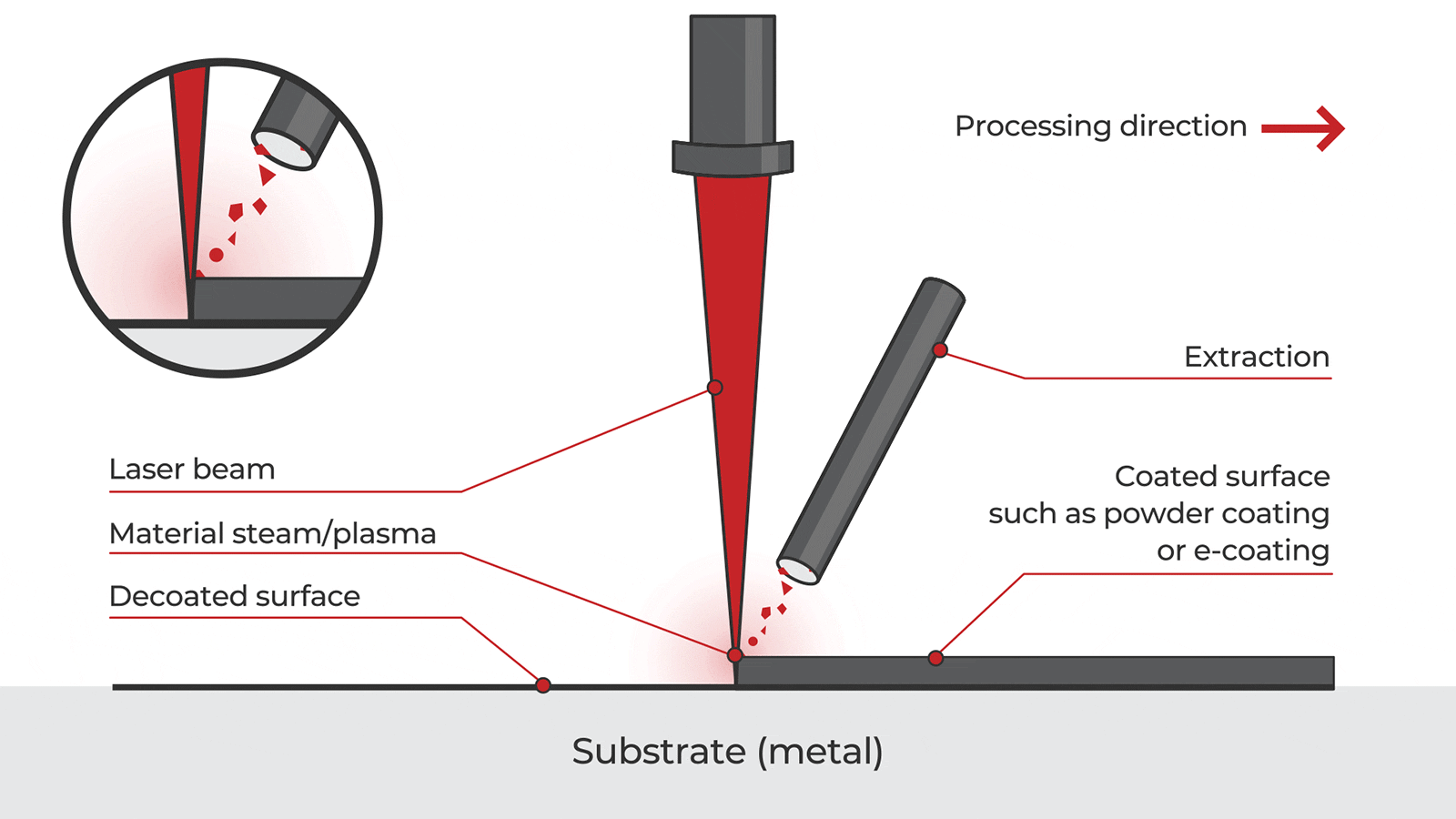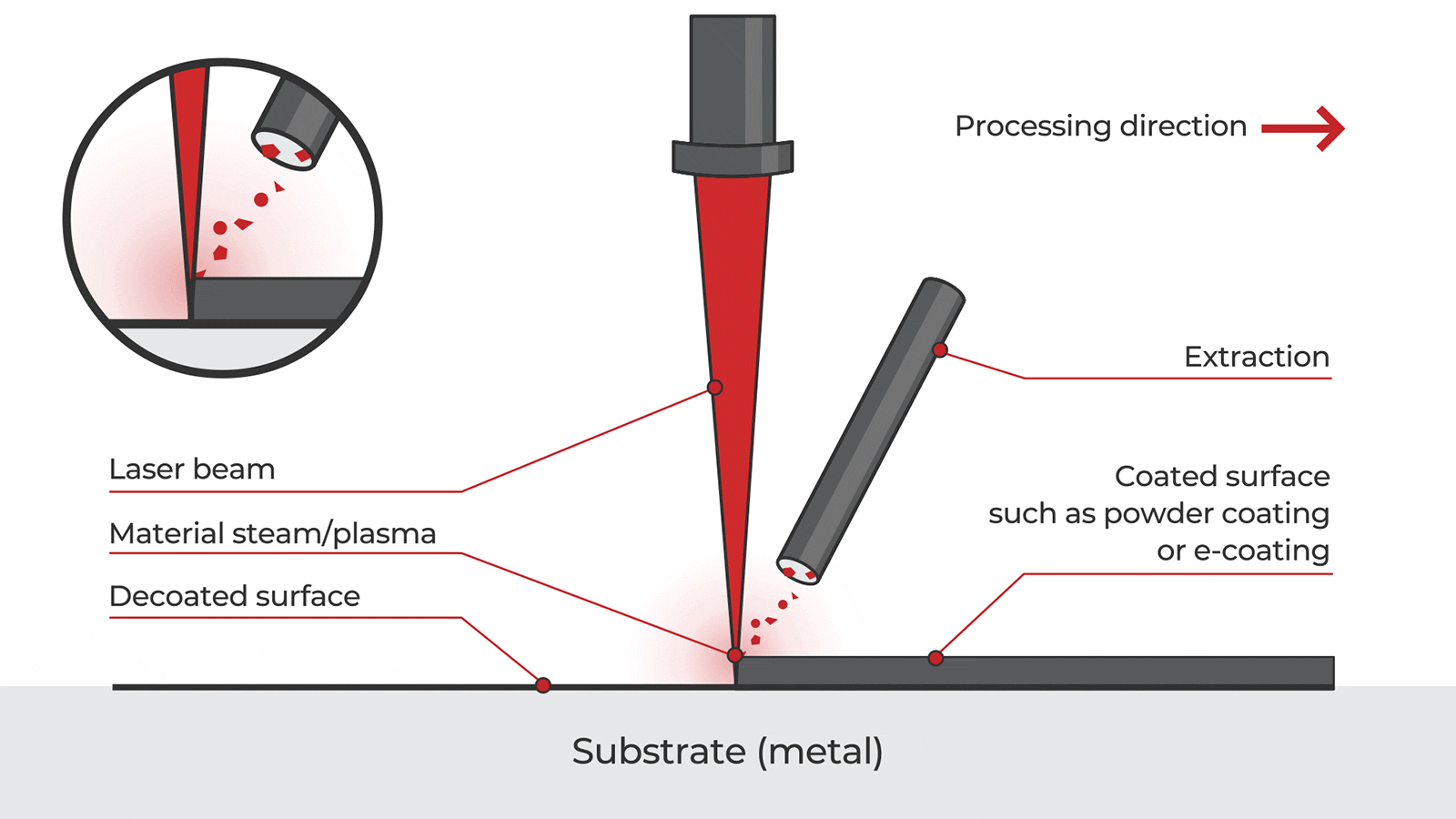
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Paint Rust Remover
Product Overview
The Laser Paint Rust Remover is an industrial cleaning tool that uses high-intensity laser beams to remove paint, rust, and surface contaminants from metal substrates without damaging the underlying material. It is designed for use in manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, and marine industries. Due to its technical nature and potential hazards, strict logistics and regulatory compliance measures are required during storage, transportation, handling, and operation.
Regulatory Classification & Documentation
Hazard Classification
- Product Type: Industrial Laser Equipment (Class 4 Laser Product)
- Laser Safety Class: IEC 60825-1:2014 – Class 4 (Hazardous)
- Electrical Safety: Compliant with IEC 60335-1 (Household and similar electrical appliances) and IEC 61010-1 (Safety requirements for electrical equipment for measurement, control, and laboratory use)
- EMC Compliance: Meets IEC 61326-1 for electromagnetic compatibility in industrial environments
- RoHS & REACH: Compliant with EU directives on hazardous substances and chemical safety
Required Documentation
- CE Declaration of Conformity
- FDA Laser Product Report (for U.S. market)
- IEC 60825-1 Safety Certification
- RoHS and REACH Compliance Certificate
- User Manual with Safety Instructions
- Technical Datasheet
- Warranty and Service Information
Packaging & Handling Requirements
Packaging Standards
- Secure, impact-resistant wooden or heavy-duty composite crate with internal foam or custom molded inserts
- Waterproof lining to protect against moisture during transit
- Clearly labeled with:
- “Fragile – Handle with Care”
- “This Side Up”
- “Protect from Moisture”
- “Class 4 Laser – Avoid Direct Exposure”
- Internal labeling of components and sub-assemblies
Handling Instructions
- Use mechanical lifting equipment (e.g., forklift, pallet jack) for units >25 kg
- Avoid tilting beyond 30 degrees unless specified in manual
- Do not open or service during transit
- Store in upright position when not in use
Transportation Guidelines
Domestic & International Shipping
- Mode of Transport: Suitable for air, sea, and ground freight
- Air Freight (IATA):
- Battery components (if applicable) must comply with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations (e.g., UN3481 for lithium-ion batteries)
- Laser components are not classified as hazardous under IATA but require proper labeling
- Sea Freight (IMDG): Not classified as dangerous goods; standard industrial equipment protocols apply
- Ground Transport (ADR/RID): Non-hazardous classification; standard secure loading procedures required
Labeling Requirements
- CE Mark
- Laser Radiation Warning Symbol (IEC 60825-1)
- Manufacturer and model information
- Weight and dimensions
- Electrical specifications (voltage, frequency)
- “Do Not Block Ventilation”
Storage Conditions
Environmental Requirements
- Temperature: 5°C to 40°C (41°F to 104°F)
- Humidity: Max 80% relative humidity, non-condensing
- Location: Dry, dust-free, well-ventilated indoor area
- Position: Store upright on a level surface
- Security: Access restricted to trained personnel; lockable storage recommended
Long-Term Storage
- Power down and disconnect all cables
- Cover with anti-static protective cover
- Perform visual inspection and functional check every 6 months
Import/Export Compliance
Key Regulatory Bodies
- United States: FDA (CDRH – Center for Devices and Radiological Health), FCC (for EMC), CBP (Customs and Border Protection)
- European Union: Notified Body certification, CE marking, customs declaration (EORI)
- Canada: Health Canada (Radiation Emitting Devices Act), ISED (Interference-Causing Equipment Standard)
- China: CCC Certification (if applicable), MIIT approval for electromagnetic compatibility
Export Controls
- EAR (U.S. Export Administration Regulations): Review for potential dual-use concerns (laser power and precision may trigger scrutiny)
- Wassenaar Arrangement: Laser equipment above certain power thresholds may require export authorization
- Licenses Required: Confirm if a license is needed based on destination country and end-use
On-Site Safety & Compliance
Installation Requirements
- Operate only in designated, controlled areas with restricted access
- Install interlocks and emergency stop systems
- Provide local exhaust ventilation if fumes are generated
- Ensure proper grounding and stable power supply (per manual specifications)
Operator Training & PPE
- Mandatory training on laser safety (ANSI Z136.1 or IEC 60825)
- Required PPE:
- Laser safety goggles (wavelength-specific)
- Flame-resistant clothing
- Face shield
- Hearing protection (if auxiliary equipment is noisy)
- Maintain training records and equipment logs
Regulatory Inspections & Audits
- Keep all compliance documents on-site
- Conduct annual laser safety audits
- Register equipment with local occupational safety authority if required (e.g., OSHA in the U.S.)
Disposal & End-of-Life
Recycling & Disposal
- Follow WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directives in the EU
- Disassemble and recycle components (metals, plastics, electronics) through certified e-waste handlers
- Laser diodes and optics may contain hazardous materials – dispose per local regulations
- Remove batteries (if present) and recycle separately under battery disposal laws
Documentation
- Maintain a disposal log with date, method, and certified recycler information
- Provide certificate of destruction upon request
Support & Compliance Assistance
For assistance with customs documentation, import permits, or safety certification:
– Contact your regional compliance officer
– Reach out to technical support at [email protected]
– Visit our compliance portal: www.laserremovaltech.com/compliance
Ensure all users and handlers are trained and documentation is current to maintain full regulatory compliance.
Conclusion:
Sourcing a laser paint and rust remover represents a forward-thinking investment in precision, efficiency, and sustainability within industrial surface treatment processes. Unlike traditional methods such as sandblasting or chemical stripping, laser cleaning offers a non-abrasive, eco-friendly solution that minimizes material waste, reduces operational downtime, and eliminates the need for hazardous chemicals. While the initial equipment cost may be higher, the long-term benefits—such as reduced maintenance, improved safety, and superior cleaning accuracy—justify the investment for many manufacturers, heritage restorers, and maintenance operations.
When sourcing laser cleaning systems, it is essential to evaluate key factors including laser power, wavelength, portability, ease of integration, after-sales support, and compliance with safety standards. Partnering with reputable suppliers offering scalable solutions and technical expertise ensures optimal system performance and adaptability to evolving operational needs.
In conclusion, laser paint and rust removers are transforming surface preparation across industries, and sourcing the right system requires a strategic balance of performance, cost, and support. As technology advances and costs continue to decrease, laser cleaning is poised to become the standard for high-precision, environmentally responsible surface restoration.