The global laser paint removal market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for precision surface restoration in industrial and heritage conservation applications. According to Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 482.3 million in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.8% through 2029. A key segment within this expansion is the adoption of laser ablation technology for wood restoration, particularly in high-value sectors such as furniture manufacturing, restoration of historic timber structures, and aerospace wood components. This surge is attributed to the technology’s non-abrasive, eco-friendly nature, which preserves the integrity of delicate wooden surfaces while effectively removing coatings. As manufacturers seek sustainable and efficient alternatives to chemical or mechanical stripping methods, several industry leaders have emerged in integrating laser paint removal systems into wood processing workflows. Below are the top 8 manufacturers pioneering this shift with innovative, data-backed advancements in laser-based wood surface treatment.
Top 8 Laser Paint Removal Wood Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: we engineer and manufacture the most advanced—and most powerful—pulsed industrial laser cleaning systems on the market, built for both manual and automated ……
#2 Argento Lux
Website: argentolux.com
Key Highlights: Our Laser Ablation is the most cost-effective, efficient, and safest method of industrial cleaning, rust removal, paint removal, and surface preparation….
#3 Laser cleaning
Website: narran.cz
Key Highlights: We can design and integrate a laser cleaning system into production, build a robotic workstation or supply a mobile laser for a wide range of applications….
#4 Laser cleaning wood
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: A laser cleaner is a device that uses high-intensity light to remove dirt, grime and stains from wood surfaces. It is a non-abrasive method of cleaning….
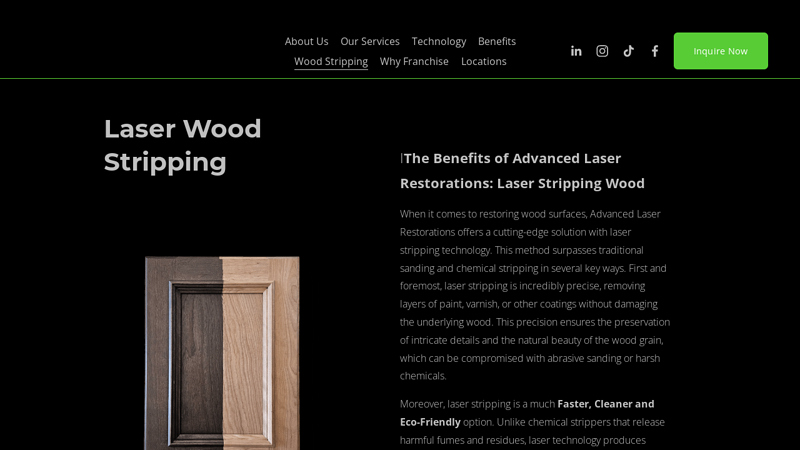
#5 Laser Wood Cleaning & Restoration
Website: advancedlaserrestoration.com
Key Highlights: Laser stripping is incredibly precise, removing layers of paint, varnish, or other coatings without damaging the underlying wood….
#6 Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: lmelaser.com
Key Highlights: The pulse laser cleaning machine have 100w, 200w, 300w, 500w, 1000w, Mainly used to rust, thin paint layer, wood, oil removal, It will no impact on the surface….
#7 Laser Cleaning and Laser Ablation Systems
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Remove rust and surface contaminants with our laser cleaning & laser ablation systems. Experience superior cleaning tech, automation, and eco-friendly ……
#8 Does the Laser Wood Stripping Machine Really Work?
Website: hantencnc.com
Key Highlights: So the laser wood stripping machine is an ideal tool for stripping paint from wooden, They offer precise and eco-friendly cleaning without damaging the base ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Paint Removal Wood

2026 Market Trends for Laser Paint Removal on Wood
As industries continue to prioritize precision, sustainability, and non-destructive restoration methods, laser paint removal is emerging as a transformative technology—especially in wood restoration and preservation. By 2026, the market for laser-based paint removal systems tailored for wood substrates is poised for significant growth, driven by technological advancements, regulatory shifts, and increasing demand in heritage conservation, furniture manufacturing, and construction.
Technological Innovation Driving Adoption
One of the most influential trends shaping the 2026 landscape is the advancement in pulsed fiber laser systems. These lasers offer improved wavelength selectivity and pulse control, allowing effective paint and coating ablation without damaging delicate wood fibers. Innovations in real-time monitoring and AI-integrated feedback systems enable operators to optimize energy settings dynamically, reducing the risk of charring or surface degradation. Portable and handheld laser units are also becoming more compact and user-friendly, expanding their accessibility beyond industrial workshops to field restoration applications.
Regulatory and Environmental Pressures
Stringent environmental regulations regarding chemical strippers and abrasive blasting methods are accelerating the shift toward eco-friendly alternatives. Traditional methods such as methylene chloride-based removers are facing bans or restrictions in many regions, including the European Union and parts of North America. Laser paint removal produces no chemical waste, minimal particulate matter (especially when paired with HEPA filtration), and eliminates the need for hazardous disposal—making it a sustainable option aligned with green building standards and ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals.
Growth in Heritage and Restoration Sectors
The preservation of historical wooden structures, from colonial buildings to antique furniture, is a key driver for laser adoption. By 2026, cultural heritage institutions and conservation agencies are increasingly investing in laser systems due to their precision and non-contact nature. Laser technology allows for selective layer removal, preserving original finishes and intricate carvings that sandblasting or chemical methods might damage. Government grants and heritage funding in Europe and North America are further supporting this trend.
Expansion in Commercial and Industrial Applications
Beyond restoration, the laser paint removal market for wood is gaining traction in commercial sectors such as yacht building, luxury furniture manufacturing, and architectural millwork. High-end clients demand flawless surface preparation prior to refinishing, and lasers offer a repeatable, contamination-free process. Automation integration—such as robotic arms equipped with laser heads—is expected to scale up in production environments, improving throughput and consistency.
Regional Market Dynamics
Europe leads in laser paint removal adoption for wood, particularly in countries with rich historical architecture like Italy, France, and Germany. However, North America is projected to experience the fastest growth by 2026, fueled by aging infrastructure and rising investment in building renovation. Meanwhile, Asia-Pacific markets, especially Japan and South Korea, are beginning to adopt the technology in fine woodworking and restoration, though cost barriers remain a challenge.
Cost and Accessibility Challenges
Despite its advantages, the high initial investment in laser systems remains a barrier for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). However, by 2026, declining costs of laser components, increased competition among manufacturers, and the availability of rental and service-based models are expected to improve market penetration. Training programs and certification courses for laser technicians are also emerging, addressing the skills gap and promoting safer, standardized operations.
Conclusion
By 2026, the laser paint removal market for wood will be shaped by a convergence of technological progress, sustainability mandates, and growing demand across restoration and manufacturing sectors. As systems become more efficient, affordable, and widely supported, laser ablation is set to transition from a niche solution to a mainstream method for safe, precise, and environmentally responsible wood surface preparation.
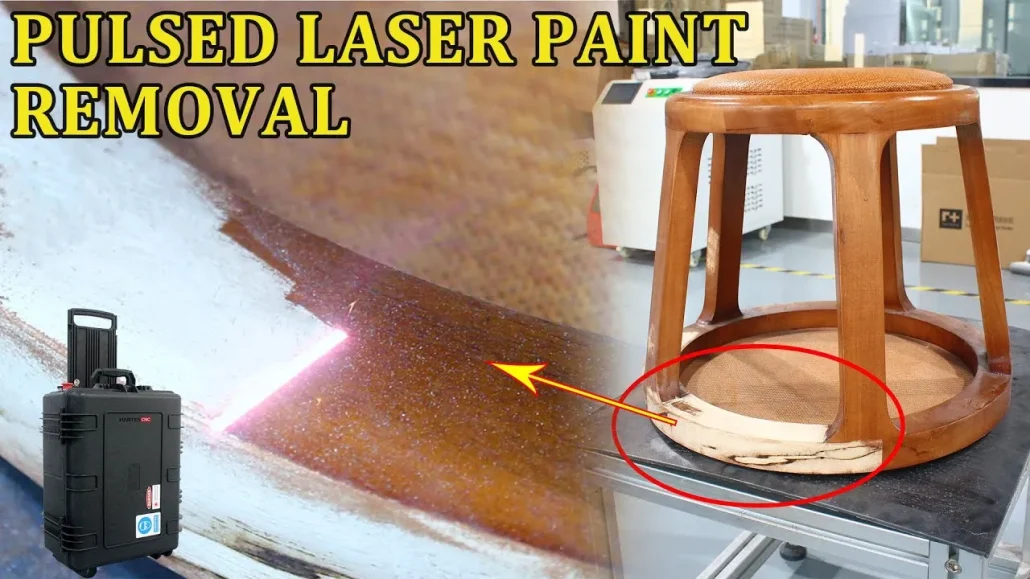

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Laser Paint Removal Wood (Quality, IP)
When sourcing wood intended for laser paint removal applications—commonly used in restoration, art, or industrial processes—two critical areas often present challenges: material quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these can lead to project delays, compromised results, or legal risks.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
- Inconsistent Wood Grain and Density: Variations in grain pattern or density affect how laser energy interacts with the surface, leading to uneven paint removal or unintended wood charring. Sourcing from unreliable suppliers increases the risk of inconsistent material quality.
- Presence of Residual Moisture or Treatments: Wood with high moisture content or chemical preservatives (e.g., pressure-treated lumber) can produce unpredictable reactions under laser exposure, including warping, smoke, or hazardous fumes.
- Surface Imperfections and Defects: Knots, cracks, or prior damage may interfere with laser precision and result in incomplete paint removal or aesthetic flaws in the final product.
- Incorrect Wood Species Selection: Not all woods respond well to laser ablation. Softer woods like pine may degrade too easily, while dense hardwoods may require excessive energy. Choosing the wrong species impacts efficiency and outcome quality.
Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
- Unauthorized Use of Protected Designs: If the wood piece features engraved or painted designs (e.g., logos, artwork, or branded patterns), using laser removal to alter or replicate them may infringe on copyrights, trademarks, or design patents—especially if done without proper licensing.
- Reverse Engineering Concerns: Removing paint to reveal underlying layers or hidden details for replication or analysis may breach trade secret protections or non-disclosure agreements, particularly in industrial or restoration contexts.
- Lack of Documentation and Provenance: When sourcing reclaimed or antique wood with existing finishes, unclear origin or ownership history can expose buyers to IP disputes, especially if the item contains proprietary or culturally sensitive designs.
- Vendor IP Compliance Gaps: Suppliers may not verify the legal status of pre-finished wood items, inadvertently providing materials tied to protected IP, leaving the end user liable.
To mitigate these risks, ensure rigorous vetting of suppliers, confirm wood specifications (species, treatment, moisture content), and conduct IP due diligence—especially when handling branded or artistic materials. Legal consultation may be necessary when the intent involves modification or commercial use of identifiable designs.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Paint Removal on Wood
Overview of Laser Paint Removal on Wood
Laser paint removal is a non-abrasive, eco-friendly method for stripping paint, coatings, and surface contaminants from wooden substrates. It utilizes focused laser beams to vaporize coatings without damaging the underlying wood. This method is increasingly adopted in restoration, aerospace, marine, and heritage conservation due to its precision and minimal waste generation. However, successful implementation requires careful planning around logistics and regulatory compliance.
Equipment Handling and Transportation
Laser removal systems—comprising the laser unit, power supply, cooling system, fume extraction, and robotic or handheld applicator—must be transported securely. Use shock-absorbent packaging and climate-controlled vehicles if necessary. Ensure equipment is de-energized and components are properly secured before transit. Verify compliance with carrier-specific dangerous goods regulations, particularly for high-voltage components and batteries. Upon delivery, inspect for damage and perform calibration checks before deployment.
Site Preparation and Workspace Requirements
Designate a controlled work zone with restricted access, adequate ventilation, and fire-resistant surroundings. The workspace must accommodate the laser system, extraction units, and operator safety zones. Ensure stable electrical supply (typically 208–480 V, three-phase) and sufficient cooling capacity. Install physical barriers and laser safety signage (e.g., ANSI Z136-compliant) to prevent accidental exposure. For field operations, temporary enclosures may be needed to contain fumes and debris.
Regulatory Compliance: Environmental Standards
Laser ablation produces particulate matter and potentially hazardous fumes from decomposed paint (e.g., lead, chromium, VOCs). Operations must comply with EPA regulations under the Clean Air Act and NESHAP (National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants). Use HEPA-filtered fume extraction systems to capture airborne particles. Dispose of collected residue as hazardous waste if lead or toxic metals exceed thresholds (e.g., TCLP testing per 40 CFR Part 261). Maintain records of waste manifests and disposal certifications.
Occupational Health and Safety Compliance
Adhere to OSHA standards for respiratory protection (29 CFR 1910.134), eye and face protection (29 CFR 1910.133), and hazard communication (29 CFR 1910.1200). Operators must wear laser-safe goggles with appropriate optical density (OD) ratings and respiratory protection if engineering controls are insufficient. Conduct initial and periodic air monitoring for airborne contaminants. Implement a Laser Safety Program per ANSI Z136.1, including training, controlled access, and emergency procedures.
Lead-Based Paint Abatement Regulations
When removing paint from pre-1978 wood structures, assume lead-based paint is present unless tested otherwise. Comply with EPA’s Renovation, Repair, and Painting (RRP) Rule (40 CFR Part 745) if working in residential or child-occupied facilities. Certified renovators must follow containment, waste handling, and cleaning verification procedures. Laser removal may reduce lead dust compared to sanding, but clearance testing is still required post-abatement.
International and Industry-Specific Requirements
For cross-border operations, verify compliance with local regulations such as EU REACH, RoHS, and the ATEX Directive for equipment in potentially explosive atmospheres. In aerospace and marine sectors, follow OEM specifications (e.g., Boeing D6-17487, Airbus AIMS) for surface preparation and material integrity. Heritage projects may require approval from preservation authorities (e.g., UNESCO, National Trust), mandating non-damaging methods and documentation.
Waste Management and Disposal
Classify removed paint residue through laboratory analysis. Non-hazardous waste can be disposed of in approved landfills; hazardous waste requires licensed transporters and treatment facilities. Maintain a waste tracking system and retain disposal records for at least three years. Minimize waste volume through efficient laser parameters and on-site filtration.
Training and Certification
Personnel must be trained in laser operation, emergency shutdown, hazard recognition, and PPE use. Certification under ANSI Z136 or equivalent is recommended. Document all training and maintain competency records. Refresher training should occur annually or after procedural changes.
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Keep detailed logs of:
– Equipment maintenance and calibration
– Air quality and exposure monitoring results
– Waste generation, testing, and disposal
– Operator training and certifications
– Compliance with permits and regulatory notifications
These records support audits and demonstrate due diligence in regulatory compliance.
Emergency Preparedness and Incident Response
Develop a site-specific emergency plan addressing laser malfunctions, fire, fume release, or exposure incidents. Equip the workspace with fire extinguishers (Class C for electrical), eyewash stations, and spill kits. Establish evacuation routes and communication protocols. Report incidents to relevant authorities as required by OSHA, EPA, or local regulations.
In conclusion, sourcing laser paint removal for wood surfaces presents a highly effective, precise, and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional paint stripping methods. This advanced technology offers superior control, minimizes substrate damage, and eliminates the need for harsh chemicals, making it ideal for preserving the integrity of delicate or historic wooden structures. While the initial investment in laser equipment or professional services may be higher, the long-term benefits—such as reduced labor costs, improved safety, and compliance with environmental regulations—make it a worthwhile solution for restoration, conservation, and precision woodworking projects. When sourcing laser paint removal, it is essential to choose experienced providers with appropriate technology tailored to wood applications to ensure optimal results, efficiency, and preservation of the underlying material.