The global aerospace surface treatment market is undergoing a transformative shift as advanced technologies such as laser paint removal gain traction among leading aircraft manufacturers. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the aircraft maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 4.8% from 2023 to 2028, driven by increasing fleet sizes, aging aircraft undergoing frequent servicing, and a growing emphasis on environmentally sustainable maintenance practices. A key contributor to this shift is the adoption of laser ablation technology for paint stripping, which offers precision, reduced material damage, and eliminates the need for chemical solvents—aligning with tightening environmental regulations across Europe and North America.
Grand View Research further underscores this trend, noting in its 2022 analysis that the global laser cleaning equipment market size was valued at USD 752.6 million and is expected to expand at a CAGR of 19.3% from 2023 to 2030. Within aerospace applications, laser-based systems are increasingly being integrated into maintenance workflows by OEMs and MRO providers seeking efficiency and compliance. As sustainability and operational cost savings become strategic priorities, aircraft manufacturers are investing in or partnering with laser technology providers to modernize their surface preparation processes.
This convergence of regulatory, environmental, and economic factors has prompted leading aerospace companies to pioneer the integration of laser paint removal systems. The following list highlights the top 10 aircraft manufacturers at the forefront of adopting and implementing this innovative technology, setting new benchmarks for efficiency and sustainability in aircraft maintenance.
Top 10 Laser Paint Removal Aircraft Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laser Photonics
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser Photonics manufactures reliable, safe, and eco-friendly Laser Cleaning, Laser Cutting, Laser Engraving, Laser Marking, and Laser Welding solutions….
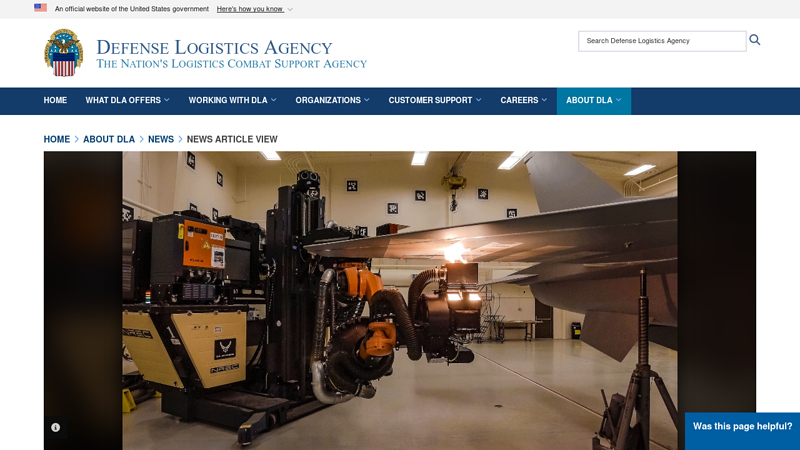
#2 AFRL helps enable laser paint removal technology
Website: dla.mil
Key Highlights: The Robotics Laser Coating Removal System has recently been approved for production F-16s and transitioned to the Ogden Air Logistics Complex ……
#3 Trusted Laser Cleaning Service For Aerospace Industry
Website: adapt-laser.com
Key Highlights: For aerospace, coatings removal, tool or mold cleaning and bonding preparation are perfect uses for our laser cleaning solutions for all the above reasons….
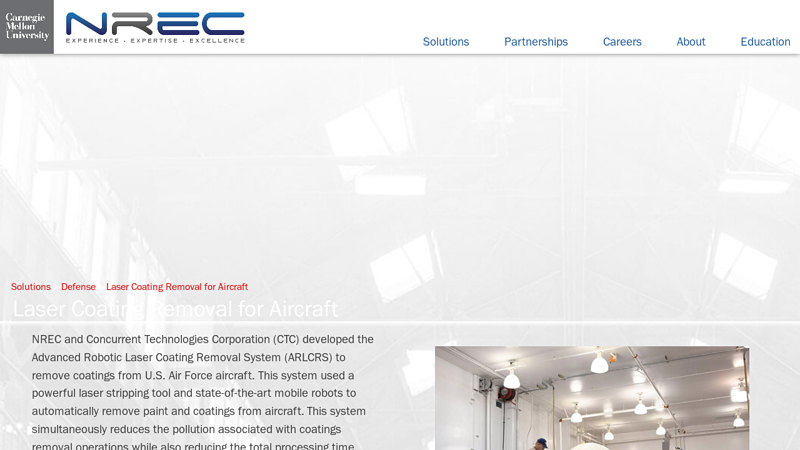
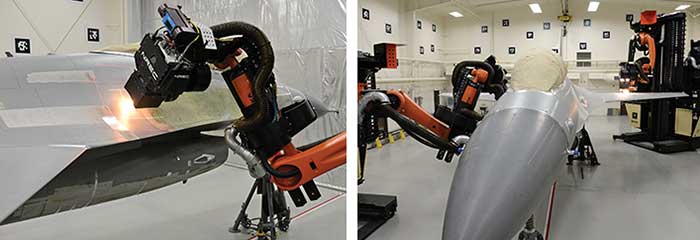
#4 Laser Coating Removal for Aircraft
Website: nrec.ri.cmu.edu
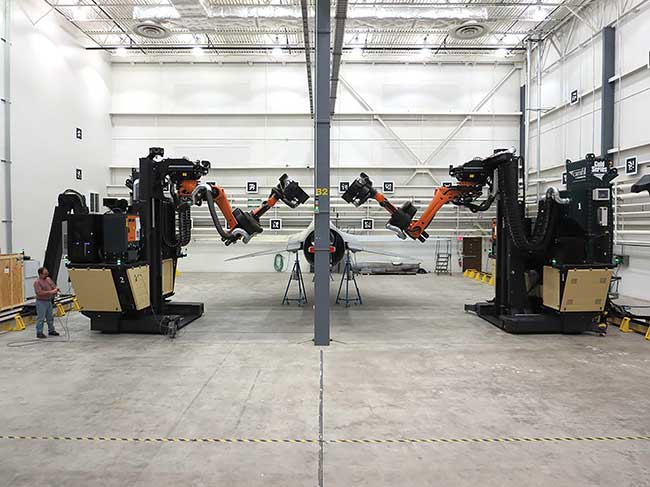
Key Highlights: This system used a powerful laser stripping tool and state-of-the-art mobile robots to automatically remove paint and coatings from aircraft. This system ……
#5 Aviation Laser Services
Website: aviationlaser.com
Key Highlights: Efficiently remove paints and coatings from aircraft components with micrometer precision. No damage to underlying material. Enhance productivity in ……
#6 Laser Ablation of Aircraft Paint: Strengthens Aluminum Skins
Website: vytek.com
Key Highlights: Laser paint removal presents a scientifically validated, non-destructive approach for the restoration and enhancement of aluminum aircraft skins ……
#7 Aerospace and Aviation
Website: cleanlaser.de
Key Highlights: The laser light removes the lacquer without damage up to the sensitive base material without negatively changing the flexural fatigue strength of the substrate….
#8 Aerospace
Website: 4jet.de
Key Highlights: Our solutions for laser-based cleaning and paint stripping enable the preparation of coatings and painting processes as well as the gentle laser ablation….
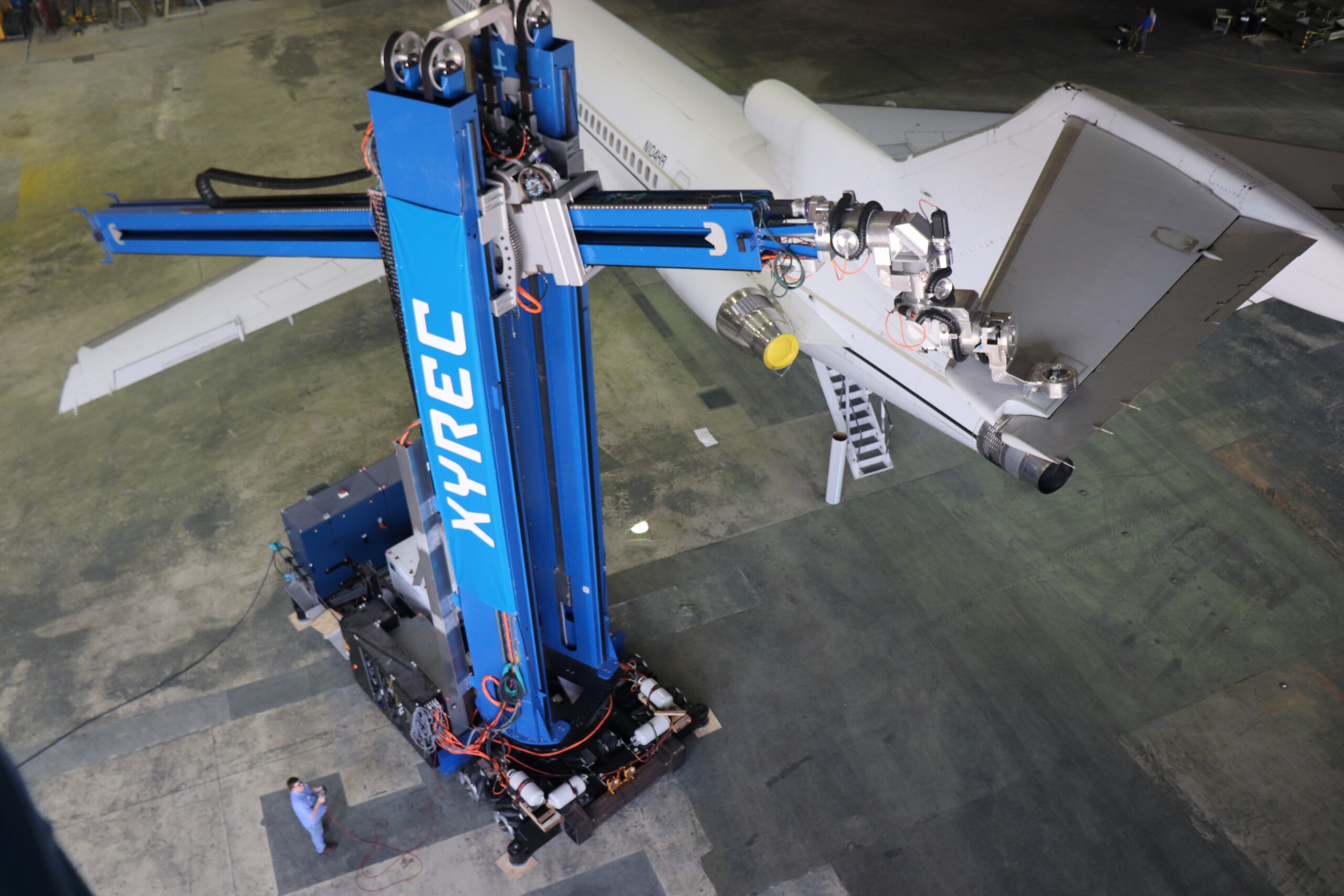
#9 Laser Coating Removal Robot (LCR)
Website: xyrec.com
Key Highlights: The Laser Coating Removal Robot (LCR) is a state-of-the-art, sustainable, high performance paint stripping solution for all types of commercial and military ……
#10 Laser Paint Removal from Metals with Laser Cleaning
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: High-power Laser Cleaning Systems Laserax manufactures high-power fiber laser systems specifically designed to remove coatings from metal surfaces….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Paint Removal Aircraft

H2: Market Trends for Laser Paint Removal in the Aircraft Industry (2026 Outlook)
As the aerospace sector continues to prioritize sustainability, efficiency, and precision in maintenance operations, laser paint removal (LPR) is emerging as a transformative technology by 2026. The market for laser-based aircraft paint stripping is experiencing strong growth, driven by regulatory pressures, technological advancements, and increasing demand for cost-effective, environmentally responsible maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) solutions.
1. Rising Demand for Eco-Friendly MRO Solutions
By 2026, environmental regulations—such as those set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the European Union’s REACH and RoHS directives—are increasingly restricting the use of chemical paint strippers containing hazardous substances like methylene chloride. This regulatory shift is accelerating the adoption of laser paint removal systems, which eliminate chemical waste, reduce water usage, and minimize hazardous emissions. Airlines and MRO providers are investing in LPR to comply with sustainability goals and avoid penalties.
2. Technological Advancements in Laser Systems
Advances in fiber and pulsed laser technologies have significantly improved the precision, speed, and safety of paint removal processes. By 2026, next-generation systems feature adaptive optics, real-time monitoring, and AI-driven control algorithms that optimize laser parameters based on paint thickness and substrate type. These innovations reduce the risk of substrate damage to sensitive composite materials (e.g., carbon fiber-reinforced polymers) commonly used in modern aircraft such as the Boeing 787 and Airbus A350.
3. Integration with Industry 4.0 and Automation
The integration of laser paint removal systems with robotics and digital twin technology is a key trend in 2026. Automated robotic arms equipped with laser heads enable consistent, high-speed stripping of large fuselage areas with minimal human intervention. Digital twins allow operators to simulate paint removal processes beforehand, enhancing planning accuracy and reducing downtime. This level of automation supports faster turnaround times in MRO facilities, increasing aircraft availability and reducing operational costs.
4. Cost Efficiency Over Lifecycle
While the initial investment in laser paint removal systems remains high, lifecycle cost analysis shows significant savings by 2026. Reduced labor requirements, lower waste disposal costs, and decreased rework due to improved surface integrity contribute to a favorable return on investment. Airlines and MRO providers are increasingly viewing LPR as a long-term strategic asset rather than a short-term expense.
5. Expansion of OEM and MRO Adoption
Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) such as Airbus and Boeing are incorporating LPR into their production and maintenance workflows. In 2026, several major MRO hubs—including those in North America, Europe, and the Asia-Pacific region—have installed dedicated laser paint removal cells. Partnerships between laser technology providers (e.g., Laser Photonics, BAE Systems, and 4Sight) and aerospace firms are expanding, signaling strong market confidence.
6. Regional Growth and Market Drivers
The Asia-Pacific region is expected to see the fastest growth in LPR adoption due to the expanding airline fleet, rising passenger traffic, and government initiatives promoting green aviation technologies. Meanwhile, North America leads in technological innovation and early adoption, supported by a mature MRO infrastructure and strong defense aviation sector.
Conclusion
By 2026, laser paint removal is transitioning from a niche technology to a mainstream solution in aircraft maintenance. Driven by environmental regulations, digital integration, and compelling economic benefits, the global market for laser-based aircraft paint stripping is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 12% from 2023 to 2026. As the technology matures and becomes more accessible, it is poised to redefine aerospace surface preparation standards, offering a cleaner, safer, and more efficient alternative to traditional methods.
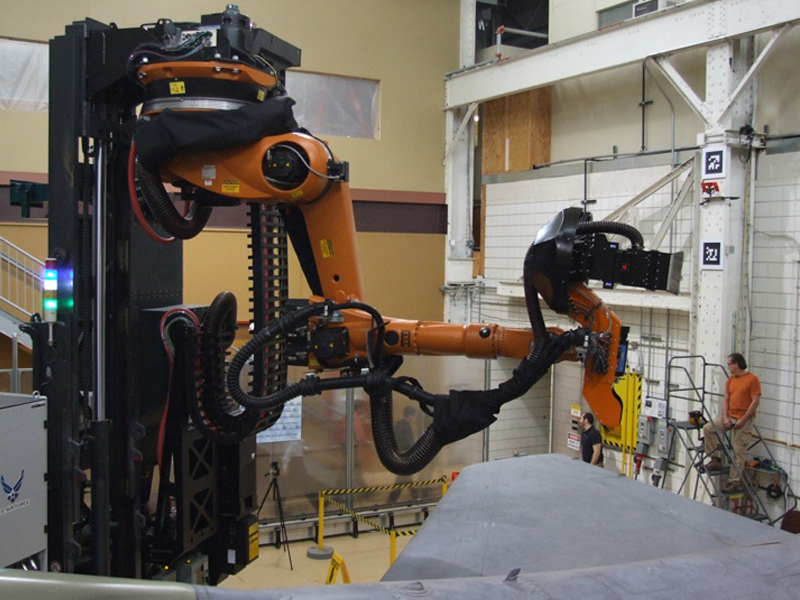
Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Laser Paint Removal Systems for Aircraft
When sourcing laser paint removal systems for aircraft maintenance, organizations must navigate several critical challenges related to quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Failure to address these can result in operational inefficiencies, safety risks, legal liabilities, and financial losses.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate System Performance Validation
A common mistake is assuming that laboratory or small-scale demonstrations equate to consistent real-world performance. Sourcing teams may overlook the need for full-scale testing on actual aircraft surfaces under operational conditions. This can lead to procuring systems that fail to meet throughput, precision, or safety standards required in aviation maintenance environments.
Lack of Aerospace-Specific Certification and Compliance
Not all laser systems are built to meet stringent aerospace regulatory requirements. A major pitfall is selecting equipment without proper certification (e.g., compliance with FAA, EASA, or OEM specifications). Systems lacking NADCAP accreditation or documented validation for material compatibility—especially with sensitive composites and underlying structures—can compromise airframe integrity.
Insufficient Training and Support Infrastructure
High-quality laser removal systems require specialized operator training and ongoing technical support. Sourcing from vendors who do not provide comprehensive training programs or maintenance support can result in improper use, equipment damage, and inconsistent paint removal outcomes, undermining the investment.
Overlooking Safety and Environmental Standards
Aircraft maintenance facilities must adhere to strict health, safety, and environmental regulations. Sourcing systems without integrated fume extraction, laser shielding, or fail-safe mechanisms can lead to workplace hazards and non-compliance with OSHA or local environmental codes.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
Unverified IP Ownership and Licensing
One significant risk is sourcing laser systems where the vendor does not hold clear ownership or proper licensing of core technologies. This can expose the buyer to third-party IP litigation, especially if the system incorporates patented laser control algorithms, scanning mechanisms, or software. Always require proof of IP ownership or valid licensing agreements before procurement.
Proprietary Software and Data Access Limitations
Many advanced laser systems rely on proprietary software for process control, data logging, and quality assurance. A common pitfall is failing to negotiate rights to access, modify, or export operational data. Vendors may restrict software access, limiting integration with existing MRO (Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul) systems or impeding compliance with audit requirements.
Inadequate Protection of Operational Know-How
When customizing a laser system for specific aircraft types or paint formulations, the buyer may contribute proprietary process knowledge. Without robust contractual safeguards (e.g., non-disclosure agreements and clear IP assignment clauses), this know-how could be exploited by the vendor for competitive advantage or shared with other clients.
Export Control and ITAR Compliance Risks
Laser technologies used in defense or commercial aviation may be subject to export control regulations such as ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations). Sourcing from international vendors without verifying compliance can result in legal penalties and shipment delays. Ensure that both hardware and software components meet applicable regulatory frameworks.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP-related pitfalls, organizations can ensure they procure reliable, compliant, and legally secure laser paint removal solutions that support safe and efficient aircraft maintenance operations.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Paint Removal Aircraft
This guide outlines the essential logistics considerations and regulatory compliance requirements for deploying and operating laser paint removal systems on aircraft. Proper planning and adherence to standards are critical for safety, efficiency, and legal operation.
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Standards
Laser paint removal on aircraft must comply with a range of national and international regulations. Key compliance areas include:
- FAA & EASA Regulations: Adhere to aircraft maintenance standards under FAA Part 145 (U.S.) or EASA Part-145 (Europe). Any process affecting aircraft structure or surface must be approved through Supplemental Type Certificates (STCs) or Service Bulletins.
- Laser Safety Standards (ANSI Z136.1 / IEC 60825): Ensure laser systems are classified and operated in accordance with laser safety standards. Implement controlled access zones, protective eyewear, and laser safety officer (LSO) oversight.
- Occupational Health & Safety (OSHA, EU-OSHA): Comply with workplace safety regulations, including hazard communication, ventilation, and personal protective equipment (PPE) requirements.
- Environmental Regulations (EPA, REACH, RoHS): Manage hazardous materials generated during paint ablation, such as airborne particulates and metal oxides. Use HEPA filtration and follow waste disposal protocols for hazardous byproducts.
- ITAR/EAR Compliance: If the laser system or related technology is export-controlled, ensure proper licensing and handling under International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) or Export Administration Regulations (EAR).
Facility and Infrastructure Requirements
Successful laser paint removal operations require specialized infrastructure:
- Controlled Environment Hangar: Operations should occur in an enclosed hangar with climate control to prevent contamination and ensure process consistency.
- Ventilation & Fume Extraction: Install high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filtration systems to capture fine particulates and hazardous fumes generated during ablation.
- Fire Safety Systems: Equip the workspace with fire detection and suppression systems, especially since laser operations involve high energy and may ignite flammable residues.
- Electrical & Power Supply: Ensure adequate and stable power supply for high-energy laser systems, potentially requiring dedicated circuits or backup generators.
- Lighting and Access: Provide optimal lighting and scaffolding or robotic positioning systems to access all aircraft surfaces safely and efficiently.
Equipment Handling and Transportation
Laser systems and associated components must be transported and handled with care:
- Crate and Secure Packaging: Transport lasers, optical components, and control systems in shock-resistant, climate-controlled containers to prevent damage.
- Calibration and Alignment: Perform system recalibration and alignment checks after transport to maintain beam accuracy and safety.
- On-Site Installation Protocol: Follow manufacturer guidelines for setup, including grounding, cooling systems, and network connectivity for control software.
- Spare Parts and Support Equipment: Maintain an inventory of critical spares (e.g., lenses, filters, cooling units) and diagnostic tools to minimize downtime.
Personnel Training and Certification
Only qualified personnel should operate laser paint removal systems:
- Laser Safety Officer (LSO): Appoint a certified LSO responsible for hazard evaluation, safety program implementation, and compliance audits.
- Operator Certification: Ensure technicians complete manufacturer-specific training and are certified in laser system operation, emergency procedures, and aircraft surface handling.
- Aircraft Maintenance Training: Personnel must understand aircraft materials, paint systems, and structural tolerances to avoid substrate damage.
- Refresher and Recurrent Training: Conduct regular training updates to reinforce safety protocols and introduce new procedures or equipment.
Documentation and Record Keeping
Thorough documentation supports compliance and traceability:
- Work Orders and Job Logs: Record details of each removal job, including aircraft ID, areas treated, laser settings, and operator information.
- Compliance Certificates: Maintain records of laser safety certifications, equipment maintenance logs, and environmental compliance permits.
- Non-Conformance Reports (NCRs): Document any deviations from procedures, including surface damage or system malfunctions, with corrective actions taken.
- Audit Readiness: Organize all records for internal audits and regulatory inspections by aviation authorities or environmental agencies.
Environmental and Waste Management
Laser ablation produces waste that must be managed responsibly:
- Particulate Collection: Use integrated vacuum and filtration systems to capture debris. Regularly inspect and replace HEPA filters.
- Hazardous Waste Classification: Test ablated material for heavy metals (e.g., chromium, lead) and classify waste accordingly. Follow local disposal regulations.
- Spill and Leak Response: Have spill kits and emergency procedures in place for coolant or chemical leaks from laser systems.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Explore recycling options for collected particulates and implement energy-efficient practices to reduce operational footprint.
Operational Workflow Integration
Integrate laser paint removal into existing MRO (Maintenance, Repair, Overhaul) processes:
- Pre-Removal Inspection: Assess paint condition, substrate integrity, and identify sensitive areas (e.g., antennas, sensors) requiring masking.
- Process Validation: Conduct test patches to optimize laser parameters (wavelength, pulse duration, fluence) for specific paint types and substrates.
- Post-Removal Verification: Inspect surfaces for cleanliness, adhesion readiness, and absence of thermal damage using non-destructive testing (NDT) methods.
- Handover to Painting Team: Provide documented surface condition reports to ensure smooth transition to repainting operations.
Emergency Procedures and Risk Mitigation
Prepare for potential incidents to ensure rapid response:
- Laser Interlock Systems: Install emergency stop buttons and beam shutters to deactivate the system instantly.
- Eye Injury Protocol: Establish immediate response procedures for suspected laser exposure, including medical evaluation and incident reporting.
- Fire Response Plan: Train staff in using fire extinguishers and evacuating the hangar if ignition occurs.
- System Failure Contingency: Define backup plans for equipment failure, including alternative removal methods or rescheduling protocols.
By adhering to this logistics and compliance framework, organizations can safely and efficiently implement laser paint removal technology in aircraft maintenance while meeting all regulatory and operational standards.
Conclusion: Sourcing Laser Paint Removal Systems for Aircraft
The sourcing of laser paint removal systems for aircraft represents a strategic advancement in maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) operations. As the aviation industry continues to prioritize efficiency, environmental compliance, and aircraft longevity, laser ablation emerges as a superior alternative to traditional methods such as chemical stripping and abrasive blasting. Laser technology offers precise, non-contact paint removal that minimizes substrate damage, reduces hazardous waste, and supports sustainability goals by eliminating the need for toxic chemicals.
When sourcing laser paint removal systems, key considerations include system power and wavelength compatibility with aircraft materials, automation and robotics integration for complex geometries, scalability for fleet operations, safety protocols, and total cost of ownership. Leading suppliers should demonstrate proven aerospace applications, regulatory compliance (e.g., FAA/EASA standards), and robust technical support.
In conclusion, investing in laser paint removal technology not only enhances operational efficiency and safety but also aligns with the aviation industry’s commitment to innovation and environmental responsibility. Organizations that proactively source and implement these advanced systems will gain a competitive advantage through reduced downtime, improved aircraft integrity, and compliance with increasingly stringent environmental regulations.