The global market for laser paint and rust removal technology is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for precision cleaning solutions in industries such as automotive, aerospace, maritime, and heritage conservation. According to Mordor Intelligence, the industrial cleaning equipment market—which includes advanced technologies like laser ablation—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.8% between 2024 and 2029. Moreover, the rising emphasis on eco-friendly, non-abrasive cleaning methods is accelerating the adoption of laser-based systems, with Grand View Research valuing the global laser cleaning equipment market at USD 1.2 billion in 2023 and forecasting a CAGR of 18.4% from 2024 to 2030. This surge reflects a broader industry shift toward automation, sustainability, and reduced operational downtime. As demand intensifies, a select group of manufacturers has emerged as leaders, pioneering innovation in power efficiency, portability, and user safety. Below are the top 10 laser paint and rust removal machine manufacturers shaping the future of industrial surface preparation.
Top 10 Laser Paint And Rust Removal Machine Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 FOX P CL – laser for removing rust
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: An innovative laser cleaner that revolutionizes the maintenance and restoration of large vehicles and industrial equipment….
#2 Laserax
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Laserax works with the world’s leading manufacturers to implement laser cleaning, welding, texturing, and marking solutions….
#3 Laser Photonics
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser Photonics manufactures reliable, safe, and eco-friendly Laser Cleaning, Laser Cutting, Laser Engraving, Laser Marking, and Laser Welding solutions….
#4 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: we engineer and manufacture the most advanced—and most powerful—pulsed industrial laser cleaning systems on the market, built for both manual and automated ……
#5 Clean Laser Systems
Website: cleanlaser.de
Key Highlights: IPG | cleanLASER has been developing and producing high-precision laser systems for cleaning and industrial surface treatment for more than 20 years….
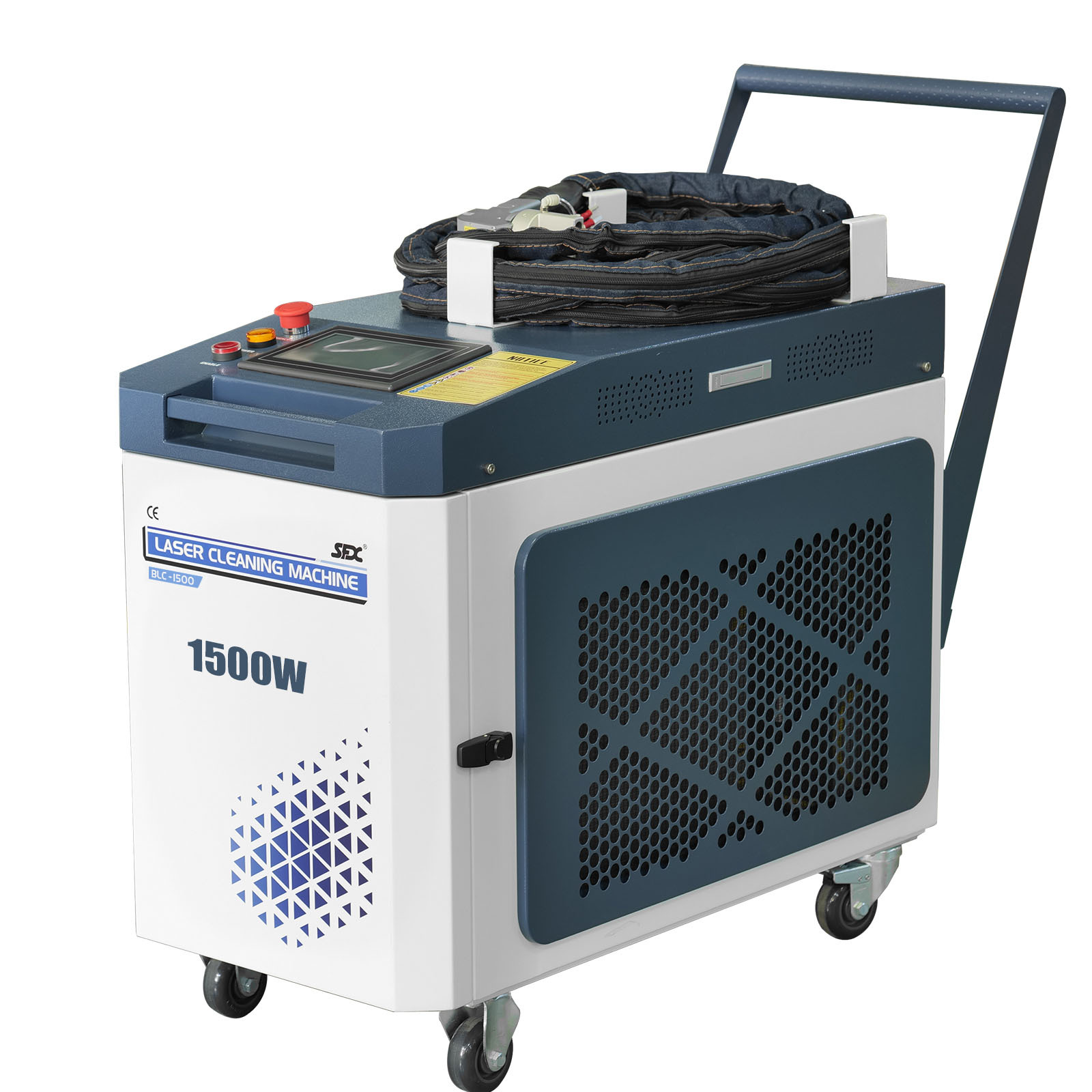
#6 SFX Laser
Website: sfxlaser.com
Key Highlights: SFX Laser is a 20+ years professional laser equipment manufacturer including laser cleaning machine, laser welding machine, fiber laser engraver, ……
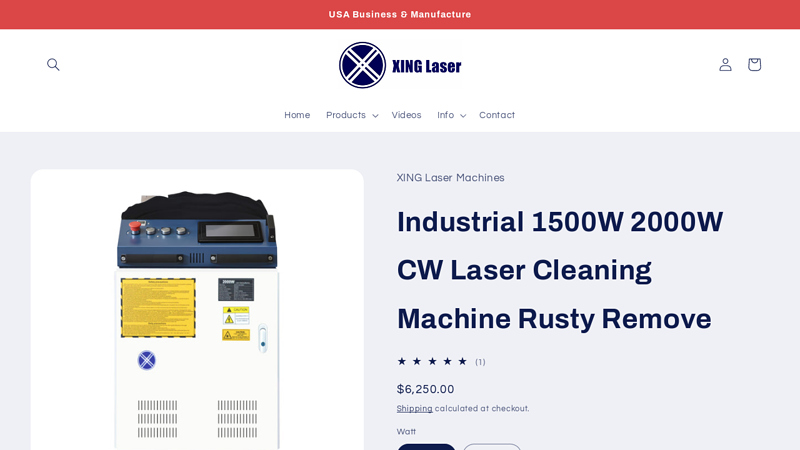
#7 Industrial 1500W 2000W CW Laser Cleaning Machine Rusty Remove
Website: xinglaser.com
Key Highlights: XING Laser (6am Life LLC, DBA XING Laser) specializes in the development and manufacture of high-performance handheld laser cleaning and rust removal equipment….
#8 Laser cleaning
Website: p-laserusa.com
Key Highlights: Our laser machines are mainly used to remove the following contaminants: Rust – Paint – Coatings – Release Agents – Grease, Oils – Soot – Rubber- Organic ……
#9 Nuwave Laser: Laser Cleaning Experts
Website: nuwavelaser.com
Key Highlights: Nuwave Laser uses high-powered lasers to remove contaminants from surfaces without chemicals. Call our laser cleaning experts today!…
#10 Laser Cleaning
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaning is used across a variety of industries to remove unwanted surface materials like coatings, paints, rust, oil, and for surface preparation for ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Paint And Rust Removal Machine

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Laser Paint and Rust Removal Machines
The global market for laser paint and rust removal machines is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, growing environmental regulations, and rising demand across key industries such as automotive, aerospace, marine, and industrial manufacturing. Here’s an analysis of the key trends expected to shape the market in 2026:
1. Increased Adoption of Eco-Friendly Surface Preparation Technologies
Environmental regulations are becoming stricter worldwide, particularly regarding the use of chemical-based stripping methods and abrasive blasting, which generate hazardous waste and airborne pollutants. Laser ablation technology offers a clean, chemical-free, and residue-free alternative. By 2026, regulatory pressures in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia-Pacific are expected to accelerate the shift toward laser-based systems, making them a preferred choice for sustainable surface treatment.
2. Advancements in Fiber Laser Technology
Ongoing improvements in fiber laser efficiency, power output, and portability are making laser rust and paint removal machines more accessible and cost-effective. By 2026, next-generation systems are expected to feature enhanced beam control, real-time monitoring, and AI-driven optimization, improving precision and reducing operational costs. These innovations will expand usability from large industrial applications to smaller workshops and field maintenance operations.
3. Growth in Aerospace and Defense Applications
The aerospace and defense sectors are major adopters of laser cleaning due to the need for non-destructive, precision surface treatment on sensitive components such as turbine blades, fuselage panels, and landing gear. With increased aircraft production and maintenance cycles anticipated by 2026, demand for automated laser systems integrated into maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) processes will rise significantly.
4. Expansion in Automotive Refinishing and Restoration
The automotive industry is increasingly utilizing laser technology for paint stripping and rust removal in vehicle restoration, OEM manufacturing, and collision repair. By 2026, mid-sized and luxury automakers are expected to invest in laser systems to improve quality control, reduce rework, and support sustainability goals. The vintage and classic car restoration market will also drive demand for handheld and mobile laser units.
5. Rise of Robotics and Automation Integration
The integration of laser cleaning systems with robotic arms and automated production lines is a key trend. By 2026, smart factories will increasingly deploy automated laser stations for continuous surface preparation in high-volume manufacturing environments. This trend is especially prominent in electric vehicle (EV) battery production, where cleanliness and material integrity are critical.
6. Regional Market Growth and Investment
Asia-Pacific, particularly China, Japan, and South Korea, is expected to lead market growth due to heavy investments in industrial automation and manufacturing modernization. Europe will maintain strong growth due to stringent environmental directives (e.g., REACH, RoHS), while North America will see increased adoption in defense and infrastructure rehabilitation projects.
7. Cost Reduction and Improved ROI
Although initial investment costs remain higher than traditional methods, the total cost of ownership for laser systems is improving due to longer lifespans, lower maintenance, and reduced waste disposal costs. By 2026, declining component prices and economies of scale are expected to make laser machines more affordable, improving return on investment (ROI) and broadening their appeal across small and medium enterprises (SMEs).
8. Focus on Safety and Operator Training
As laser systems become more widespread, there will be a growing emphasis on safety protocols, protective equipment, and operator certification. By 2026, industry standards and training programs will likely be more standardized, supporting wider adoption and reducing workplace risks associated with high-power laser use.
In conclusion, the 2026 market for laser paint and rust removal machines will be characterized by technological maturity, regulatory support, and expanding application scope. Companies that invest in innovation, automation, and sustainability will be best positioned to capitalize on this high-growth sector.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Laser Paint and Rust Removal Machine: Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns
Sourcing a Laser Paint and Rust Removal Machine offers significant advantages in precision and efficiency, but buyers often encounter critical pitfalls related to quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Being aware of these issues can help avoid costly mistakes and ensure long-term operational success.
1. Compromised Machine Quality Due to Inadequate Specifications
Many suppliers, particularly in competitive or less-regulated markets, offer machines that claim high performance but fail to meet technical standards. Buyers may receive units with substandard laser diodes, unstable cooling systems, or inadequate safety features. Poor beam focus or inconsistent power output can lead to inefficient rust removal and increased operational downtime. Always verify technical specifications with third-party testing or on-site demonstrations before purchase.
2. Lack of Certification and Compliance Documentation
A frequent quality red flag is the absence of internationally recognized certifications such as CE, FDA, or IEC 60825 (laser safety standards). Without these, machines may not comply with safety or environmental regulations in your country, leading to legal risks or import restrictions. Ensure suppliers provide valid, traceable compliance documentation.
3. Misrepresentation of Laser Power and Performance
Some suppliers exaggerate laser output (e.g., advertising 1000W when actual usable power is much lower). This misleads buyers into believing they’re getting industrial-grade equipment when the machine may only be suitable for light-duty use. Request independent performance reports or conduct live testing under real-world conditions.
4. Inadequate After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Low-cost machines from unfamiliar manufacturers often come with poor technical support, delayed spare parts delivery, or no local service centers. This can result in extended downtime and higher total cost of ownership. Prioritize suppliers with established service networks and clear maintenance agreements.
5. Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement Risks
Many laser cleaning machines on the market—especially from certain regions—may incorporate patented technologies without proper licensing. Purchasing such equipment can expose your business to legal liability, customs seizures, or injunctions if IP holders pursue enforcement. Always vet suppliers for IP compliance and request documentation showing legitimate technology licensing.
6. Copycat Designs and Reverse-Engineered Systems
Some manufacturers replicate leading brands’ designs without innovation, leading to machines with poor durability and performance. These clones may lack proper R&D investment and fail under continuous industrial use. Choose suppliers with verifiable R&D capabilities and original product designs.
7. Weak Software and Control System Integration
Quality isn’t only about hardware—software plays a crucial role in precision and usability. Inferior machines often use outdated or unlicensed software with limited control features, poor user interfaces, or no update support. This can hinder integration into automated systems and reduce process repeatability.
8. Insufficient Warranty and Ambiguous Service Terms
Beware of warranties that exclude key components (like laser sources) or impose unrealistic conditions for claims. Some suppliers offer “1-year warranty” but require return shipping at the buyer’s expense or refuse remote diagnostics. Clarify all service terms in writing before finalizing the purchase.
To mitigate these pitfalls, conduct thorough due diligence: request customer references, inspect manufacturing facilities if possible, involve technical experts in evaluations, and consult legal advisors when assessing IP risks. Sourcing the right laser cleaning machine requires balancing cost with long-term reliability, safety, and legal security.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Paint and Rust Removal Machine
This guide outlines essential logistics considerations and compliance requirements for the safe, legal, and efficient transportation, import/export, and operation of a Laser Paint and Rust Removal Machine.
Regulatory Compliance
Ensure adherence to all relevant international, national, and local regulations governing laser equipment and industrial machinery.
- Laser Safety Standards: Comply with the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) 60825-1 standard for laser product safety classification and labeling. The machine must meet Class 1, 1M, 2, 2M, 3R, 3B, or 4 requirements based on its output. Provide appropriate warning labels and safety interlocks.
- Electrical Safety: Confirm compliance with electrical safety standards such as IEC 61010-1 (Safety requirements for electrical equipment for measurement, control, and laboratory use) and regional equivalents (e.g., UL/CSA in North America, CE in Europe).
- EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility): Meet applicable EMC directives (e.g., EU EMC Directive 2014/30/EU, FCC Part 15 in the US) to prevent interference with other electronic devices.
- CE Marking (Europe): For sale or use within the European Economic Area, apply CE marking demonstrating conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards, including the Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC), Low Voltage Directive (2014/35/EU), and EMC Directive.
- FDA Registration (USA): In the United States, laser products must be registered with the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH) under 21 CFR Subchapter J.
- RoHS & REACH Compliance: Ensure the machine complies with Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) and Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulations in applicable markets.
- Local Workplace Safety Regulations: Adhere to occupational safety standards (e.g., OSHA in the US, HSE in the UK) regarding laser operation, fume extraction, and personal protective equipment (PPE).
Export & Import Documentation
Prepare accurate and complete documentation to facilitate customs clearance and ensure legal shipment across borders.
- Commercial Invoice: Include detailed product description, Harmonized System (HS) code, value, buyer/seller information, and terms of sale (e.g., Incoterms® 2020 such as FOB, CIF).
- Packing List: Specify packaging type, dimensions, weight (gross and net), and item count.
- Certificate of Origin: Required by many countries to determine tariff rates; may need chamber of commerce certification.
- Bill of Lading (BOL) or Air Waybill (AWB): Contract of carriage issued by the carrier; choose appropriately based on transport mode.
- Laser Product Report (US FDA): Required for US imports; typically includes product classification, performance specifications, and safety features.
- Export License (if applicable): Some countries require export licenses for high-powered lasers or dual-use technologies. Verify EAR (Export Administration Regulations) or other national control lists.
- Import Permits: Check destination country requirements for permits related to lasers, electrical equipment, or industrial machinery.
Packaging & Handling
Use robust packaging and proper handling procedures to prevent damage during transit.
- Protective Packaging: Secure the machine in a custom-engineered wooden crate or heavy-duty pallet with shock-absorbing materials (e.g., foam, corner boards) to protect sensitive components such as optics and electronics.
- Environmental Protection: Include desiccants to prevent moisture damage and ensure seals protect against dust and humidity.
- Handling Labels: Clearly mark the package with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” “Do Not Stack,” and “Protect from Moisture” labels.
- Weight & Dimensions: Accurately record and communicate shipping weight and dimensions for freight calculations and handling planning.
- Internal Fixtures: Secure all movable parts (e.g., robotic arms, scanners) using transit locks or braces provided by the manufacturer.
Transportation Requirements
Select appropriate transport modes and carriers experienced with high-value industrial equipment.
- Mode of Transport: Choose based on urgency, cost, and destination:
- Air Freight: Fastest, suitable for urgent or high-value shipments; higher cost.
- Ocean Freight: Cost-effective for heavy or large machines; longer lead times.
- Ground Freight: Ideal for regional or domestic delivery.
- Carrier Selection: Use freight forwarders or carriers with experience handling sensitive industrial and laser equipment. Ensure they provide real-time tracking and insurance.
- Insurance: Obtain comprehensive cargo insurance covering damage, loss, or theft during transit (e.g., All-Risk coverage).
- Temperature & Humidity Control: For sensitive components, consider climate-controlled transport, especially for long ocean voyages or extreme climates.
- Security: Implement anti-theft measures, including tamper-evident seals and GPS tracking for high-value shipments.
Site Preparation & Installation
Prepare the destination site to ensure safe and efficient machine setup and operation.
- Access & Space: Verify adequate space for the machine, fume extraction system, power supply, and operator access. Confirm doorways, elevators, and hallways accommodate machine dimensions.
- Power Supply: Ensure availability of correct voltage, phase, frequency, and sufficient amperage. Provide dedicated circuits if required. Include grounding specifications.
- Ventilation & Fume Extraction: Install appropriate local exhaust ventilation (LEV) systems to capture and filter laser-generated particulates and fumes, complying with air quality regulations.
- Floor Requirements: Confirm floor load capacity, levelness, and static discharge (ESD) protection if needed.
- Environmental Conditions: Maintain recommended operating temperature, humidity, and cleanliness levels (e.g., avoid dust, corrosive atmospheres).
- Safety Perimeter: Define and mark a controlled access area with appropriate laser warning signs and interlocks.
Training & Documentation
Provide comprehensive training and operational documentation to ensure safe and compliant use.
- Operator Training: Conduct hands-on training covering machine operation, safety protocols, emergency shutdown procedures, and maintenance routines.
- Safety Manual: Supply a detailed safety manual including laser hazard warnings, PPE requirements (e.g., laser safety goggles with correct OD rating), and interlock procedures.
- User Manual: Provide full technical documentation, including installation instructions, operating procedures, troubleshooting guides, and maintenance schedules.
- Compliance Certificates: Supply copies of all relevant compliance certificates (CE, FDA, IEC, etc.) and test reports.
- Warranty & Service Information: Include warranty terms and contact details for technical support and service.
Maintenance & Servicing Logistics
Establish a plan for ongoing maintenance and spare parts support.
- Preventive Maintenance (PM) Schedule: Follow manufacturer-recommended PM intervals to ensure performance and safety.
- Spare Parts Inventory: Maintain critical spare parts (e.g., lenses, nozzles, filters) on-site or ensure rapid access through a distributor network.
- Service Contracts: Consider service agreements with qualified technicians for calibration, repairs, and compliance checks.
- Calibration Records: Keep logs of laser power calibration and safety system checks for audit purposes.
- Waste Disposal: Follow local regulations for disposing of collected particulate waste, which may be classified as hazardous depending on the substrate material.
Emergency & Incident Response
Prepare procedures for handling potential malfunctions or safety incidents.
- Emergency Shutdown: Clearly mark and train personnel on the location and use of emergency stop buttons.
- Fire Response: Have Class C (electrical) fire extinguishers accessible. Laser operations may generate ignition sources.
- Exposure Protocol: Establish procedures for accidental laser exposure (skin or eye), including first aid and medical follow-up.
- Fume Leak Response: Define actions if fume extraction fails, including halting operations and evacuating the area if necessary.
- Incident Reporting: Maintain a log of all incidents, near misses, and corrective actions taken.
Record Keeping
Maintain accurate records to demonstrate compliance and support operations.
- Shipping Documentation: Retain copies of all export/import paperwork for at least the required statutory period (e.g., 5 years).
- Compliance Certificates: Archive current versions of safety and regulatory certifications.
- Maintenance Logs: Document all maintenance, repairs, calibrations, and parts replacements.
- Training Records: Keep records of personnel who have been trained and certified to operate the machine.
- Incident Reports: Store all safety incident and investigation reports securely.
By following this guide, stakeholders can ensure the Laser Paint and Rust Removal Machine is transported, installed, and operated in full compliance with applicable laws and safety standards.
Conclusion: Sourcing a Laser Paint and Rust Removal Machine
In conclusion, sourcing a laser paint and rust removal machine represents a forward-thinking investment in innovative, efficient, and environmentally sustainable surface preparation technology. Unlike traditional methods such as sandblasting or chemical stripping, laser cleaning offers precision, minimal substrate damage, reduced waste, and improved operator safety by eliminating hazardous chemicals and particulates.
When selecting a supplier or system, key factors to consider include laser power output, pulse frequency, portability, ease of integration into existing workflows, after-sales support, and overall cost-effectiveness. It is essential to evaluate multiple vendors, review real-world performance data, and, if possible, conduct on-site demonstrations to ensure the machine meets specific operational requirements.
While the initial investment may be higher than conventional tools, the long-term benefits—such as lower maintenance costs, compliance with environmental regulations, and increased productivity—justify the expense across industrial, automotive, aerospace, and heritage restoration applications.
Ultimately, sourcing the right laser cleaning machine requires a balance of technical capability, reliability, and vendor support. With the technology rapidly advancing and becoming more accessible, adopting laser-based paint and rust removal positions organizations at the forefront of clean, smart, and sustainable manufacturing practices.