The global laser surface preparation market, a key segment enabling advanced oxide removal in industrial applications, is experiencing robust expansion driven by increasing demand for precision cleaning in aerospace, automotive, and energy sectors. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market is projected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 6.8% from 2023 to 2028, fueled by the shift from chemical and mechanical descaling methods toward eco-friendly, automated laser solutions. This growth is further validated by Grand View Research, which reports a CAGR of 7.1% for the industrial laser cleaning market from 2022 to 2030, citing rising regulatory pressure to reduce hazardous waste and solvent use. As adoption accelerates, a select group of manufacturers has emerged at the forefront of innovation—leveraging high-powered pulsed lasers, AI-driven control systems, and scalable designs to deliver efficient, non-abrasive oxide removal. The following list highlights the top 10 companies leading this transformation, evaluated on technology performance, market reach, customer reviews, and industry partnerships.
Top 10 Laser Oxide Removal Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: we engineer and manufacture the most advanced—and most powerful—pulsed industrial laser cleaning systems on the market, built for both manual and automated ……
#2 Laser Oxide Removal
Website: arku.com
Key Highlights: Improve metal part quality, durability, & corrosion resistance with laser oxide removal techniques. Learn more about our solutions!…
#3 Laser Oxide Removal
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaning is the best solution to remove oxide from aluminum. For example, oxide can be removed before welding to strengthen the welds….
#4 Laser Oxide Removal
Website: adapt-laser.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaning is effective at removing oxides, rust, and other contaminants from metal and some non-metal products. Learn how it works and more here….
#5 Laser Oxide Removal
Website: kvfquad.com
Key Highlights: KVF Quad can mechanically remove the laser oxide and prepare the substrate for paint process all under one roof, eliminating the need for excessive material ……
#6 Laser Oxide Removal for Metal Surface Treatment
Website: chutianlasergroup.com
Key Highlights: Learn how laser oxide removal works, recommended parameter settings, and real cleaning results on steel, aluminum, copper, titanium, and more….
#7 Laser Oxide Removal
Website: gemachinery.co.uk
Key Highlights: Laser Oxide Removal – GE Machinery is a supplier for timesaving machine solutions for radiussing and metal finishing across the UK and Ireland….
#8 Laser Cleaning Applications
Website: nuwavelaser.com
Key Highlights: Removes rust, oxide, paint, coatings · Maintains structural integrity and longevity · Effective in aerospace, automotive, manufacturing, and marine industries….
#9 Laser Oxide Scale Removal
Website: chemicalmethods.com
Key Highlights: Remove 100% of Laser Oxide Scale. You must remove laser oxide scale prior to painting parts in order to produce a quality finished part….
#10 Laser Oxide Removal Machine
Website: alphamanufacturing.co.uk
Key Highlights: Professional pre-powder coating laser oxide edge removal service. Learn more about our laser oxide removal machine….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Oxide Removal

H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for Laser Oxide Removal
As industrial manufacturing and surface treatment technologies evolve, laser oxide removal is poised to become a pivotal solution across multiple sectors by 2026. Driven by advancements in laser precision, environmental regulations, and the demand for sustainable, chemical-free cleaning processes, the global market for laser oxide removal is expected to experience robust growth and technological refinement. Below is an analysis of key market trends projected for 2026:
1. Expansion in Industrial Applications
By 2026, laser oxide removal is expected to see increased adoption in heavy industries such as aerospace, automotive, shipbuilding, and energy. The aerospace sector, in particular, will leverage laser technology for restoring turbine blades and critical components without damaging base materials. The non-abrasive nature of laser cleaning makes it ideal for high-precision and safety-sensitive applications.
2. Growth in Green Manufacturing Initiatives
With global emphasis on sustainability, industries are shifting away from chemical-based or abrasive cleaning methods that produce hazardous waste. Laser oxide removal offers a dry, eco-friendly alternative with minimal environmental impact. Regulatory pressures in regions like the EU (under REACH and Green Deal policies) and North America will drive demand for compliant surface preparation technologies.
3. Technological Advancements in Laser Systems
By 2026, advancements in fiber laser efficiency, automation integration, and AI-driven process control will enhance the speed, accuracy, and scalability of oxide removal systems. Portable and handheld laser units will gain popularity for on-site maintenance in large infrastructure projects, while robotic integration will streamline high-volume production lines.
4. Cost Reduction and ROI Improvement
Although initial investment in laser systems remains high, projected declines in component costs—especially for fiber lasers—and longer equipment lifespans will improve return on investment (ROI). Increased competition among manufacturers will also drive pricing optimization, making the technology more accessible to SMEs.
5. Regional Market Growth
Asia-Pacific, led by China, Japan, and South Korea, is expected to dominate market growth due to rapid industrialization, government support for advanced manufacturing, and rising investments in automation. North America and Europe will follow, driven by aerospace modernization and stringent environmental compliance requirements.
6. Integration with Industry 4.0 and Smart Factories
Laser oxide removal systems will increasingly be integrated into smart manufacturing ecosystems. Real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and data analytics will allow for adaptive cleaning protocols, minimizing downtime and improving process consistency—key factors in Industry 4.0 environments.
7. Standardization and Safety Regulations
By 2026, global standards for laser cleaning operations—particularly concerning operator safety, emission controls, and process validation—are expected to be formalized. These standards will boost user confidence and facilitate broader industrial acceptance.
Conclusion
The 2026 market for laser oxide removal will be characterized by technological maturity, environmental alignment, and expanding industrial integration. As industries prioritize precision, sustainability, and automation, laser-based surface cleaning is set to transition from a niche solution to a mainstream industrial standard, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) projected above 15% through 2026.

H2: Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Laser Oxide Removal Systems – Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
When sourcing Laser Oxide Removal (LOR) systems, organizations must navigate several critical challenges, particularly concerning quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can result in substandard performance, legal exposure, and loss of competitive advantage.
1. Quality-Related Pitfalls
-
Inconsistent Laser Performance: Not all LOR systems deliver uniform beam quality, pulse control, or wavelength accuracy. Poorly calibrated or lower-grade lasers may fail to remove oxides effectively, risking substrate damage or incomplete cleaning—especially on sensitive materials like aerospace alloys or electronic components.
-
Lack of Process Validation: Vendors may provide systems without comprehensive validation data (e.g., surface profilometry, adhesion testing, or corrosion resistance post-treatment). Without third-party verification or standardized test protocols, buyers cannot confirm performance claims.
-
Insufficient Integration Support: High-quality LOR systems must integrate seamlessly with existing production lines (e.g., robotics, conveyors, or inspection systems). Sourcing from suppliers with limited integration experience often leads to downtime and costly retrofitting.
-
Inadequate After-Sales Service and Calibration: Maintenance, recalibration, and technician training are essential for sustained performance. Suppliers from regions with weak service infrastructure may be unable to support long-term operations, leading to system degradation.
2. Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
-
Unprotected Custom Configurations: Companies often customize LOR systems for specific applications (e.g., turbine blade refurbishment). If IP rights to these configurations are not clearly defined in contracts, suppliers may reuse or resell the designs, eroding competitive differentiation.
-
Use of Infringing Components: Some suppliers may incorporate third-party laser sources or control software with questionable IP provenance. Buyers risk secondary liability if these components violate patents or copyrights, especially in regulated industries.
-
Weak Contractual Safeguards: Failure to include robust IP clauses—such as ownership of modifications, confidentiality, and non-disclosure agreements (NDAs)—exposes the buyer to reverse engineering or unauthorized replication of proprietary processes.
-
Jurisdictional IP Enforcement Challenges: Sourcing from countries with underdeveloped IP enforcement mechanisms increases the risk of design theft or unauthorized manufacturing. Even with contracts in place, legal recourse may be limited or impractical.
Mitigation Strategies
- Conduct thorough technical due diligence, including on-site demonstrations and material testing under real-world conditions.
- Require detailed documentation of system specifications, compliance certifications (e.g., ISO, CE), and service level agreements (SLAs).
- Engage legal counsel to draft IP agreements that explicitly assign ownership of custom developments to the buyer and restrict supplier reuse.
- Source from reputable vendors with a proven track record in industrial laser applications and strong IP management practices.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls, organizations can ensure reliable performance and protect their innovation when adopting Laser Oxide Removal technology.

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Oxide Removal
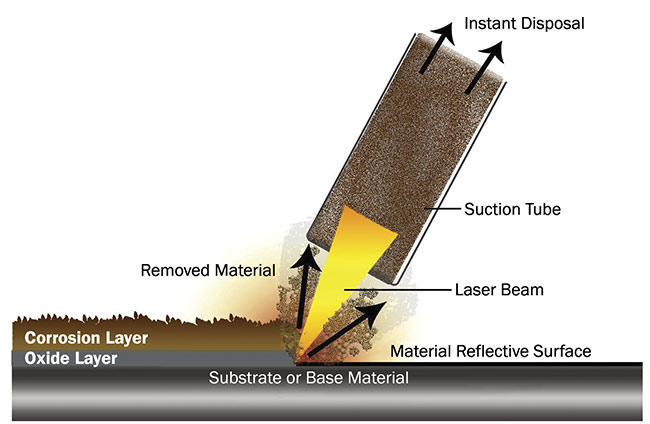
Laser oxide removal is an advanced, non-abrasive cleaning method used to remove rust, oxides, and contaminants from metal surfaces using high-intensity laser beams. While highly effective and environmentally friendly compared to traditional methods, its implementation requires strict adherence to logistics planning and regulatory compliance. This guide outlines key considerations under the H2 classification for safe, efficient, and compliant operations.
H2.1 Equipment Transportation and Handling
- Secure Packaging: Laser systems must be transported in shock-absorbent, climate-controlled packaging to prevent damage to sensitive optical and electronic components.
- Crate Labeling: Clearly label crates with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Laser Equipment – Handle with Care” indicators.
- Climate Control: Maintain storage and transport conditions within manufacturer-specified temperature and humidity ranges (typically 5°C–40°C, <80% RH).
- Forklift/Handling Protocols: Use appropriate lifting equipment; never tilt or drop laser units. Follow OEM guidelines for handling rails and base plates.
H2.2 Site Preparation and Installation Logistics
- Power Requirements: Verify site power supply matches laser system specifications (e.g., 208–480V, 3-phase, 50/60 Hz). Include surge protection and uninterruptible power supply (UPS) if required.
- Ventilation and Fume Extraction: Install high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filtration or fume extraction systems to capture laser-generated particulates. Ensure exhaust meets local air quality standards.
- Laser Safety Zone: Designate a controlled access area with appropriate warning signs (e.g., “Laser in Use – Do Not Enter”). Install interlocks and emergency stop buttons.
- Floor Load Capacity: Confirm the installation site can support the weight of the laser system and associated equipment (typically 500–2000 kg).
H2.3 Regulatory Compliance
- Laser Safety (IEC 60825-1 / ANSI Z136.1):
- Classify the laser system (typically Class 4 for industrial oxide removal).
- Appoint a Laser Safety Officer (LSO) to oversee operations.
- Conduct hazard analysis and implement engineering/administrative controls.
-
Provide laser safety training for all personnel.
-
OSHA and Workplace Safety (US):
- Comply with 29 CFR 1910 Subpart K (Electrical) and Subpart Q (Welding, Cutting, and Brazing).
- Implement Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) requirements: laser safety goggles (wavelength-specific), flame-resistant clothing, and face shields.
-
Conduct regular equipment inspections and maintain logs.
-
Environmental Regulations (EPA, EU Directives):
- Address particulate emissions via certified filtration systems.
- Classify and dispose of collected oxide residue per hazardous waste regulations (e.g., RCRA in the US, Waste Framework Directive in EU).
-
Perform air quality monitoring if operating above threshold limits.
-
REACH and RoHS (EU):
- Ensure all components in the laser system comply with REACH (chemical safety) and RoHS (hazardous substance restrictions).
H2.4 Operational Documentation and Recordkeeping
- Maintain a Laser Safety Program document including:
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
- Risk assessments
- Maintenance logs
- Training records
-
Incident reports
-
Keep Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS/SDS) for any auxiliary materials (e.g., cleaning agents, coolants).
-
Retain calibration and service records for laser optics, cooling units, and safety systems.
H2.5 International Shipping and Import Compliance
- Export Controls: Verify if the laser system falls under export control regulations (e.g., U.S. Commerce Control List – ECCN 6A003.b.4). Obtain necessary licenses if exporting.
- Customs Documentation: Provide commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin. Declare laser class and power output.
- CE Marking (EU): Ensure equipment bears CE marking and is accompanied by a Declaration of Conformity (DoC) meeting applicable EU directives (e.g., Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC, EMC Directive 2014/30/EU).
H2.6 End-of-Life and Decommissioning
- Follow WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) Directive for proper disposal or recycling of laser units in the EU.
- Degas and safely dispose of laser cooling fluids in accordance with local environmental regulations.
- De-label and disable laser components to prevent unauthorized reuse.
Conclusion
Proper logistics and compliance management for laser oxide removal systems ensure operational safety, regulatory adherence, and environmental responsibility. By following the H2 guidelines above, organizations can mitigate risks, avoid penalties, and maintain efficient, sustainable operations. Always consult local regulations and equipment manufacturers for site-specific requirements.
Conclusion for Sourcing Laser Oxide Removal:
Sourcing laser oxide removal technology presents a strategic opportunity to enhance precision, efficiency, and sustainability in surface preparation and cleaning processes. Compared to traditional mechanical or chemical methods, laser cleaning offers superior control, minimal substrate damage, and reduced environmental impact due to the absence of consumables and hazardous waste. When sourcing this technology, it is critical to evaluate supplier expertise, system scalability, safety compliance, and total cost of ownership. Investing in reliable, high-performance laser systems from reputable providers ensures long-term operational benefits, including lower maintenance costs, improved product quality, and alignment with green manufacturing initiatives. As industries continue to adopt advanced automation and clean production standards, laser oxide removal emerges as a future-ready solution, making informed sourcing a key driver of competitive advantage and process innovation.