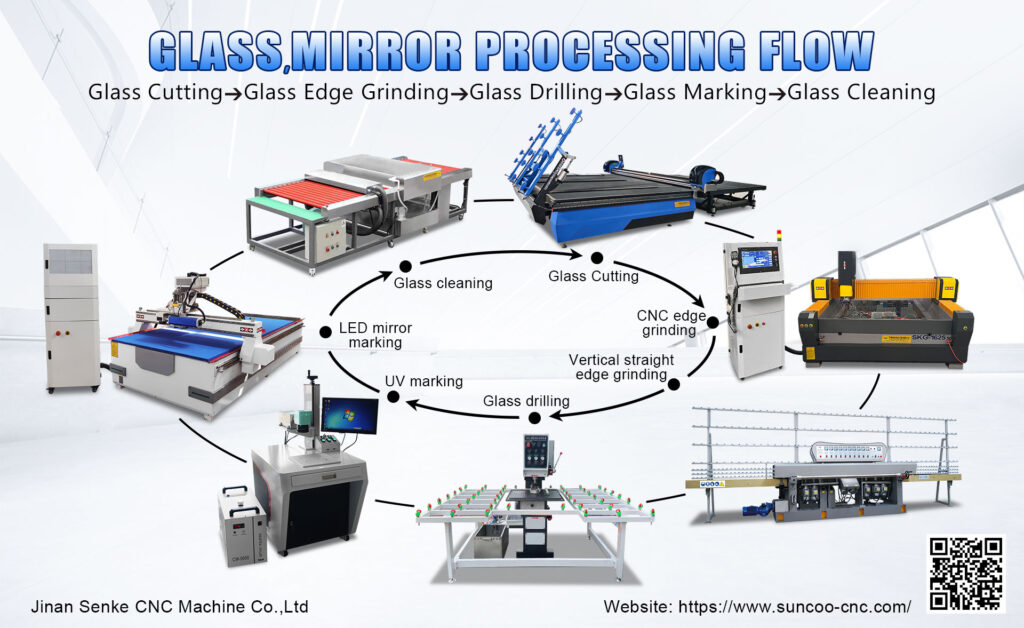
The global laser mirror market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand in industrial manufacturing, healthcare, telecommunications, and defense sectors. According to Mordor Intelligence, the Laser Market size was valued at USD 13.7 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.2% from 2024 to 2029, reaching an estimated USD 20.8 billion by the end of the forecast period. As critical components in laser systems—ensuring precise beam delivery and optimal efficiency—laser mirrors are witnessing increased technological advancements and production scalability. Grand View Research further supports this trajectory, noting that expanding applications in laser cutting, welding, and additive manufacturing are propelling component-level demand, particularly for high-reflectivity, durable optics. With Asia-Pacific emerging as a key growth region due to rapid industrialization and investments in photonics infrastructure, the competitive landscape among laser mirror manufacturers is intensifying. Below, we profile the top nine companies leading innovation, quality, and market reach in this evolving sector.
Top 9 Laser Mirror Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Edmund Optics: Optics Manufacturer & Supplier
Domain Est. 1999
Website: edmundoptics.com
Key Highlights: Edmund Optics has been a leading producer of optics, imaging, and laser optics for 80 years. Discover the latest optical and imaging technology….
#2 ULO Optics
Domain Est. 2005
Website: ulooptics.com
Key Highlights: We are a specialist manufacturer of metal mirrors for industrial and scientific application · We provide a unique range of standard and custom-designed laser ……
#3 Custom Laser Optics
Domain Est. 1996
Website: cascadelaser.com
Key Highlights: We have provided thousands of custom optical components for universities, industrial laser companies, OEM’s, and more….
#4 // ARO Laser Research Optics, Precision Optics Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1996
Website: arocorp.com
Key Highlights: High precision optics manufacturer Alpine Research Optics (ARO) company offers thin-film polarizers, laser mirrors, optical lences……
#5 Laseroptik GmbH
Domain Est. 2000
Website: laseroptik.com
Key Highlights: LASEROPTIK is a manufacturer of high LIDT laser optics and coatings from VUV to IR and employs more than 40 coating machines with 6 different coating methods….
#6 Lenses & Mirrors
Domain Est. 1994
Website: coherent.com
Key Highlights: Enhance laser performance with lenses, mirrors, and high-power optics, and improve laser gain with non-linear and magneto-optic crystals from Coherent….
#7 RMI Optics
Domain Est. 1997
Website: rmico.com
Key Highlights: Rocky Mountain Instrument Co. offers cutting edge optical technologies for a changing world. Call us at (303) 664-5000 to discuss your next project….
#8 Nd:YAG Laser Mirrors
Domain Est. 2008
#9 Mirrors
Domain Est. 2020
Website: idexot.com
Key Highlights: We have mirrors for every typical laser application, including partial and high reflectivity mirrors coated on flat and curved substrates for use at single, ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Mirror

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Laser Mirrors
The global laser mirror market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in laser technology, increasing demand across industrial, medical, and defense sectors, and the rising adoption of high-precision optical systems. As a critical component in laser systems—responsible for directing and controlling laser beams—laser mirrors are witnessing evolving performance requirements and manufacturing innovations. Below are the key market trends expected to shape the laser mirror industry in 2026:
1. Rising Demand from Industrial Laser Applications
The expansion of industrial laser applications—particularly in cutting, welding, engraving, and additive manufacturing (3D printing)—is a major driver. As manufacturers adopt high-power fiber and CO₂ lasers for improved efficiency and precision, the need for durable, high-reflectivity laser mirrors capable of withstanding intense thermal loads increases. By 2026, the industrial segment is projected to dominate laser mirror consumption, especially in automotive and aerospace manufacturing.
2. Growth in Medical and Aesthetic Laser Procedures
The medical sector, including dermatology, ophthalmology, and surgical applications, continues to adopt laser-based treatments. These applications require highly specialized mirrors with precise wavelength selectivity and low absorption rates. The trend toward minimally invasive procedures and cosmetic treatments is expected to boost demand for customized laser optics, including dielectric-coated mirrors tailored for specific medical laser wavelengths (e.g., Er:YAG, CO₂, and diode lasers).
3. Advancements in Coating Technologies
Dielectric and metallic coating innovations are enhancing mirror performance. By 2026, anti-reflective (AR), high-reflective (HR), and ultra-low absorption coatings will be standard in high-end laser systems. The adoption of ion-beam sputtering (IBS) and advanced plasma-assisted deposition techniques ensures superior coating durability and thermal stability, particularly under high-power laser conditions.
4. Miniaturization and Integration in Photonic Systems
The trend toward smaller, integrated photonic devices—especially in telecommunications and consumer electronics—is influencing laser mirror design. Micro-electromechanical systems (MEMS) mirrors and ultra-compact reflective optics are gaining traction in LiDAR, AR/VR, and sensing applications. This shift demands precision-engineered, lightweight mirrors with high surface accuracy and fast response times.
5. Defense and Aerospace Applications Driving High-Performance Demand
Directed energy weapons, laser rangefinders, and communication systems in defense and aerospace are pushing the need for rugged, high-efficiency mirrors capable of operating in extreme environments. By 2026, defense spending on laser technologies—especially in the U.S., China, and Europe—is expected to fuel demand for radiation-hardened and temperature-stable laser mirrors.
6. Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific, led by China, Japan, and South Korea, is anticipated to be the fastest-growing region due to robust manufacturing infrastructure and investment in laser-based automation. North America and Europe remain key markets, driven by innovation in healthcare, defense, and research. Localized production and supply chain resilience will become strategic priorities.
7. Sustainability and Cost Optimization
Manufacturers are focusing on sustainable production methods and longer-lasting mirror solutions to reduce waste and operational costs. Recycling of rare coating materials (e.g., gold, silver, and dielectric oxides) and improved substrate polishing techniques contribute to greener manufacturing practices.
8. Increased R&D in Ultrafast and High-Power Lasers
With the growing use of ultrafast (femtosecond/picosecond) lasers in micromachining and scientific research, mirrors must handle high peak powers without damage. By 2026, there will be increased demand for dispersion-controlled and chirped mirrors that maintain beam quality in ultrafast systems.
Conclusion
By 2026, the laser mirror market will be shaped by technological innovation, diversification of applications, and the need for higher performance under extreme conditions. Companies investing in advanced coating technologies, precision manufacturing, and application-specific designs will be best positioned to capitalize on these evolving trends. The convergence of industrial automation, healthcare advancements, and defense modernization will ensure sustained growth and innovation in the laser mirror sector.
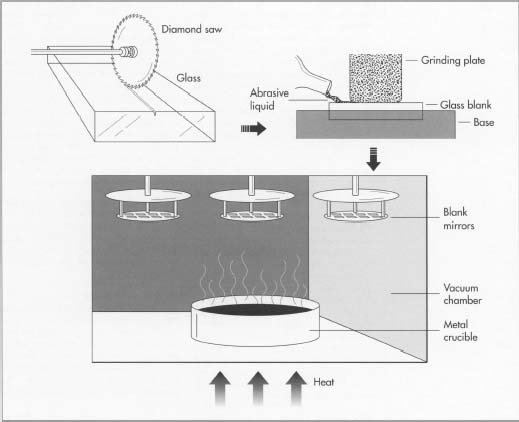
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Laser Mirrors: Quality and Intellectual Property
Sourcing laser mirrors—critical components in laser systems for applications ranging from medical devices to industrial cutting—requires careful attention to both performance specifications and legal considerations. Overlooking key aspects can lead to system failure, safety risks, or legal disputes. Below are common pitfalls related to quality and intellectual property (IP) that procurement teams and engineers should avoid.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inadequate Surface Accuracy and Flatness
Laser mirrors must maintain precise surface flatness (often specified in fractions of a wavelength, e.g., λ/10) to avoid beam distortion. Sourcing from suppliers without proper metrology equipment can result in mirrors that degrade beam quality or reduce system efficiency. Always verify surface specifications with certified test reports.
2. Poor Coating Durability and Laser-Induced Damage Threshold (LIDT)
The mirror’s coating must withstand high-intensity laser exposure without degradation. Low-cost suppliers may use coatings with insufficient LIDT, leading to premature failure, especially in high-power applications. Ensure LIDT values are tested and documented under conditions matching your use case.
3. Substandard Substrate Material and Homogeneity
Mirror substrates (e.g., fused silica, silicon, molybdenum) must be free of internal stresses and inclusions. Poor material quality causes thermal distortion or cracking during operation. Confirm substrate specifications and request material certifications.
4. Inconsistent Manufacturing Tolerances
Tolerances for dimensions, surface finish, and coating uniformity must be tightly controlled. Suppliers with inconsistent quality control may deliver parts that do not fit or perform as expected. Require first-article inspections and batch testing.
5. Lack of Environmental and Longevity Testing
Mirrors used in demanding environments (e.g., vacuum, high humidity, thermal cycling) must be tested for stability. Suppliers may overlook real-world conditions, leading to failures in the field. Request environmental test data and accelerated aging reports.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
1. Infringement of Patented Designs or Coating Formulations
Some high-performance mirror designs, multilayer coating stacks, or manufacturing processes are protected by patents. Sourcing from suppliers who replicate patented technology without licensing exposes your company to infringement claims. Conduct due diligence on the supplier’s IP rights or freedom-to-operate.
2. Unclear Ownership of Custom Designs
When commissioning custom mirrors, failure to define IP ownership in contracts can lead to disputes. Suppliers may claim rights to design improvements or reuse your specifications for other clients. Always include clear IP assignment clauses in sourcing agreements.
3. Use of Counterfeit or Reverse-Engineered Components
Low-cost suppliers may offer mirrors that mimic branded products but are reverse-engineered or counterfeit. These components often lack certification and may breach IP laws. Source from reputable, audited manufacturers and verify component traceability.
4. Insufficient Documentation for Compliance and Traceability
Regulated industries (e.g., aerospace, healthcare) require full documentation of materials, processes, and design origins. Missing or falsified documentation can result in non-compliance and liability. Demand complete technical dossiers, including coating recipes (where permissible) and material traceability.
By addressing these quality and IP pitfalls proactively, organizations can ensure reliable laser system performance while minimizing legal and operational risks. Always prioritize suppliers with strong technical credentials, transparent processes, and clear IP policies.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Mirrors
Laser mirrors are precision optical components used in various industrial, medical, and scientific applications. Due to their sensitivity and regulated nature, proper logistics and compliance management is essential to ensure safe transport, customs clearance, and adherence to international standards.
Handling and Packaging
Laser mirrors are fragile and susceptible to contamination, scratches, and environmental damage. Proper handling and packaging are critical:
- Use cleanroom-compatible gloves when handling mirrors to prevent oil and particulate transfer.
- Store and ship mirrors in protective cases with foam or custom inserts to prevent movement and physical shock.
- Include desiccants in packaging to control humidity and prevent fogging or coating degradation.
- Seal packaging in anti-static, moisture-resistant materials to protect against electrostatic discharge and environmental exposure.
- Clearly label packages as “Fragile,” “Optical Components – Handle with Care,” and “Do Not Stack.”
Shipping and Transportation
Choose reliable carriers experienced in handling high-value, sensitive optical equipment:
- Use temperature-controlled transport when possible, especially for mirrors with sensitive coatings.
- Avoid standard parcel sorting systems; opt for direct handling or white-glove delivery services.
- Maintain a chain of custody documentation for high-value shipments.
- Consider shipping with insurance that covers full replacement value.
Export Controls and Regulatory Compliance
Laser mirrors may be subject to export control regulations due to their use in laser systems, which can have military or dual-use applications.
ITAR and EAR Compliance
- Determine if the laser mirror falls under the International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) or the Export Administration Regulations (EAR).
- ITAR: Applies if the mirror is designed or modified for use in defense articles listed on the U.S. Munitions List (USML).
- EAR: Most commercial laser mirrors fall under the Commerce Control List (CCL), typically under ECCN 6A003 or 6A005, which cover optical components for lasers.
- Verify the ECCN (Export Control Classification Number) based on mirror specifications (e.g., reflectivity, wavelength range, substrate material, coating type).
- Obtain required export licenses or use license exceptions (e.g., LVS, TMP, BAG) as applicable.
Country-Specific Restrictions
- Check end-user and end-use restrictions for the destination country.
- Screen all parties (end-user, consignee, freight forwarder) against denied persons lists (e.g., U.S. Department of Commerce’s Denied Persons List, OFAC Specially Designated Nationals).
- Be aware of heightened scrutiny for shipments to certain regions (e.g., China, Russia, Iran) due to national security concerns.
Documentation Requirements
Ensure all shipments are accompanied by accurate and complete documentation:
- Commercial Invoice: Include detailed technical description, value, country of origin, ECCN, and license information.
- Packing List: Specify quantity, weight, dimensions, and contents per package.
- Export License or License Exception Authorization: Attach if required.
- Certificate of Origin: May be required by customs authorities.
- Technical Data Export: If shipping design files or specifications, ensure compliance with data export rules (e.g., encryption, deemed exports).
Import Compliance
Understand the importing country’s requirements:
- Research local optical component regulations, import tariffs, and certification needs.
- Some countries require conformity assessment, labeling, or registration (e.g., CE marking in the EU, CCC in China).
- Provide necessary documentation to customs brokers to avoid delays.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
- Laser mirrors are generally not hazardous materials but may contain materials regulated under REACH (EU) or RoHS.
- Ensure compliance with environmental regulations regarding substance use (e.g., lead, cadmium in coatings).
- Follow proper disposal procedures for damaged or obsolete mirrors, especially those with hazardous coatings.
Recordkeeping
Maintain comprehensive records for at least five years (or as required by jurisdiction):
- Export licenses and authorizations
- Technical specifications and ECCN determinations
- Shipping documents and tracking information
- Denied party screening results
- Internal compliance audits
By adhering to this logistics and compliance guide, organizations can ensure the secure, legal, and efficient transport of laser mirrors across international borders while minimizing risk and maintaining regulatory compliance.
Conclusion on Sourcing Laser Mirrors
In conclusion, sourcing high-quality laser mirrors is a critical factor in ensuring the optimal performance, efficiency, and longevity of laser systems. The selection process must consider several key parameters, including substrate material (e.g., molybdenum, silicon, copper), coating type (dielectric, metallic, or protected), wavelength compatibility, surface flatness, damage threshold, and environmental durability.
Sourcing from reputable suppliers with proven expertise in optical manufacturing and stringent quality control processes is essential to achieve consistent performance and reliability. Additionally, customization capabilities, lead times, and cost-effectiveness should be evaluated to meet specific application requirements—whether for industrial cutting, medical lasers, or research and development.
By prioritizing technical specifications, supplier credibility, and total cost of ownership, organizations can secure laser mirrors that enhance system accuracy, reduce maintenance needs, and support long-term operational success. Ultimately, a strategic and informed approach to sourcing laser mirrors contributes significantly to the advancement and stability of laser-based technologies.