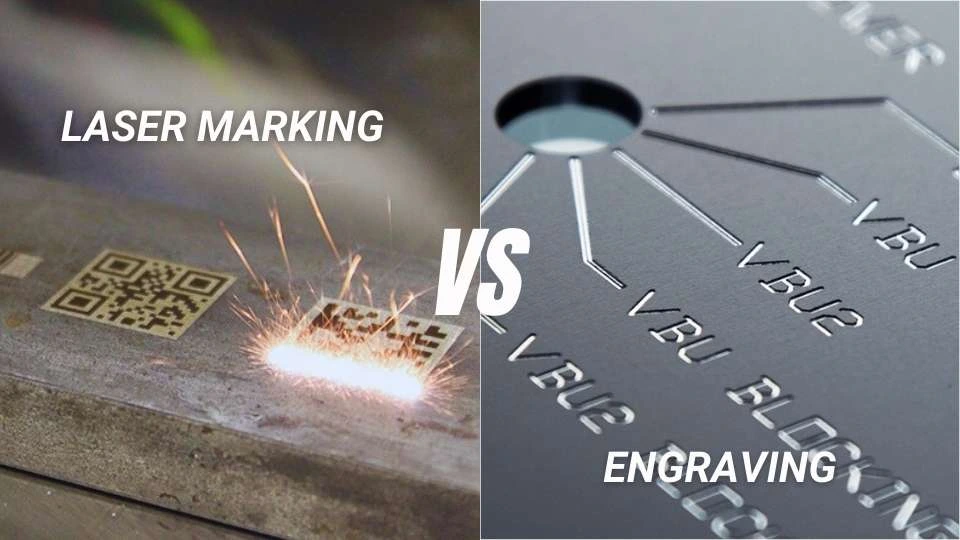
The global laser marking and laser engraving market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for permanent, high-precision product identification across industries such as automotive, electronics, medical devices, and consumer goods. According to Grand View Research, the global laser marking machine market size was valued at USD 1.24 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.3% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by the rising adoption of laser systems in industrial manufacturing for traceability, branding, and regulatory compliance. As the technological distinction between laser marking and laser engraving becomes more nuanced—particularly in terms of depth, speed, and material compatibility—manufacturers are differentiating themselves through innovation in fiber, CO₂, and UV laser technologies. In this competitive landscape, nine key players have emerged as leaders, setting benchmarks in precision, durability, and automation. The following analysis compares these top manufacturers based on market presence, technological capabilities, application versatility, and customer adoption trends.
Top 9 Laser Marking Vs Laser Engraving Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laser marking vs. laser engraving: what’s the difference?
Website: gravotech.us
Key Highlights: Laser marking and laser engraving are two techniques commonly used to personalize objects, create signage, or mark industrial parts. Discover the world of laser ……
#2 Laser Marking for All Industries
Website: lasermarktech.com
Key Highlights: Discover innovative laser marking solutions tailored for various industries. Explore our cutting-edge technology as leaders in laser marking and engraving….
#3 Laser Etching vs Laser Engraving vs Laser Marking
Website: keyence.com
Key Highlights: Laser engraving is much more durable than printing, resisting scratches, chemicals, and weather that would quickly damage ink. Unlike printed labels that fade ……
#4 Differences Between Laser Marking, Laser Engraving and Laser …
Website: permanentmarking.com
Key Highlights: Laser marking discolors the surface of the material, while laser etching and engraving actually removes a portion of the surface area as it marks….
#5 The Differences Between Laser Engraving and Marking
Website: elettrolaser.com
Key Highlights: Engraving and marking are two different types of work, although both can be successfully used to imprint indelible signs on metal surfaces….
#6 Laser Engraving vs. Laser Etching
Website: xometry.com
Key Highlights: Markings made by laser engraving are more durable than those formed by laser etching. Laser engraving produces more long-lasting markings ……
#7 What is Laser Marking?
Website: telesis.com
Key Highlights: Laser engraving and laser marking are popular methods for creating permanent marks on various materials. You can use them on everything from metals and wood to ……
#8 Laser Marking, Laser Etching, and Engraving
Website: waferworld.com
Key Highlights: In this blog post, a Silicon Wafer Supplier will discuss the differences between laser marking, laser etching, and laser engraving and the ……
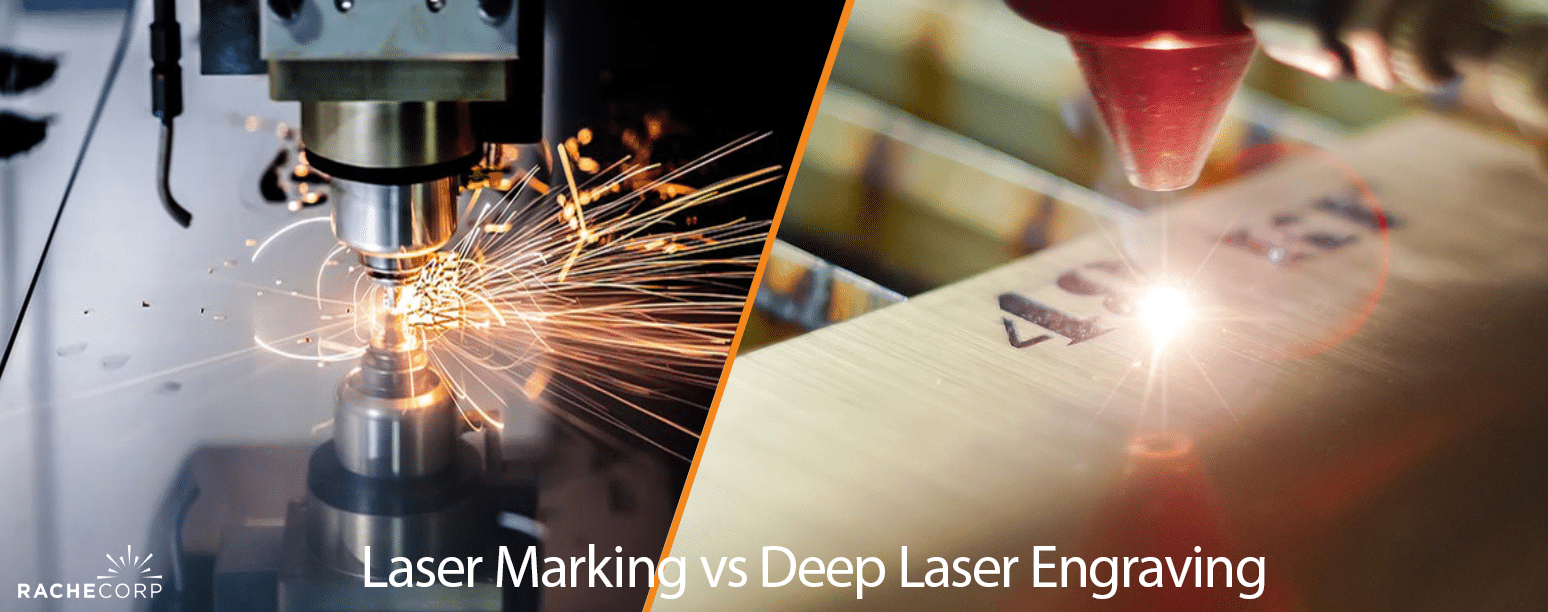
#9 Laser Marking vs Deep Laser Engraving
Website: rache.com
Key Highlights: Laser marking works best for consumer products, electronics, and branding. Deep engraving is essential for aerospace, defense, medical devices, and tools where ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Marking Vs Laser Engraving

2026 Market Trends: Laser Marking vs. Laser Engraving
As industrial manufacturing, product traceability, and customization demands evolve, laser-based technologies continue to play a pivotal role in material processing. By 2026, the distinction between laser marking and laser engraving is becoming increasingly nuanced—not just in technical application but in market dynamics, technological advancement, and end-user preferences. This analysis explores key market trends shaping the laser marking and laser engraving sectors, highlighting growth drivers, industry adoption, and competitive positioning.
Market Growth and Industry Adoption
The global laser marking and engraving market is projected to exceed $8.5 billion by 2026, according to industry forecasts. Laser marking is expected to capture a larger market share—estimated at around 60%—driven by increasing demand for non-destructive, high-speed, and permanent identification in regulated industries such as medical devices, automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
Laser marking, which includes techniques like annealing, foaming, and coloration, is favored for applications requiring high legibility without compromising material integrity. In contrast, laser engraving—where material is physically ablated to create deeper, tactile marks—remains dominant in signage, tooling, and decorative applications.
Key drivers for laser marking growth include:
– Strict regulatory compliance (e.g., FDA UDI requirements, EU MDR).
– Demand for high-speed serialization and anti-counterfeiting measures.
– Expansion of Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing, where traceability is essential.
Laser engraving maintains strong growth, particularly in niche markets such as personalized consumer goods, luxury items, and industrial tool identification. However, its market expansion is slightly more constrained due to slower processing speeds and material limitations.
Technological Advancements and Equipment Innovation
By 2026, fiber lasers continue to dominate both markets, but advancements are tailoring systems to each application. Laser marking systems are increasingly integrating with automated production lines, featuring real-time data input and vision-guided marking for dynamic content like QR codes and Data Matrix barcodes.
In contrast, hybrid laser systems that combine marking and engraving capabilities in a single platform are gaining traction, particularly in job shops and small-to-medium enterprises (SMEs). These systems offer flexibility, reducing capital expenditure and floor space.
Ultrafast (picosecond and femtosecond) lasers are also influencing both sectors. In laser marking, they enable cold ablation for sensitive materials like polymers and thin films without thermal damage. In engraving, they allow micron-level precision for micro-texturing and functional surface engineering—especially in medical and semiconductor applications.
Material Compatibility and Sustainability Trends
Laser marking is increasingly preferred for its minimal material waste and non-contact processing, aligning with sustainability goals. It requires no inks or chemicals, supporting green manufacturing initiatives. In plastics, metals, and coated materials, laser marking provides durable, environmentally safe solutions.
Laser engraving, while more material-intensive, is evolving with closed-loop fume extraction and recyclable material integration. However, environmental regulations are pushing industries toward less invasive marking methods, giving laser marking a competitive edge in eco-conscious markets.
Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific, particularly China, India, and South Korea, leads in market growth for both technologies, driven by electronics manufacturing and automotive production. China’s push for domestic innovation in laser technology is accelerating local production of high-power fiber lasers, reducing reliance on imported systems.
In North America and Europe, adoption is centered on high-value applications. Medical device manufacturers in these regions are adopting laser marking for compliance and traceability, while the luxury goods sector sustains demand for precision engraving.
Competitive Landscape and Future Outlook
Major players like TRUMPF, IPG Photonics, Han’s Laser, and Trotec are investing heavily in smart, software-driven laser systems with IoT connectivity. By 2026, AI-powered process optimization is expected to enhance marking accuracy and reduce downtime, particularly in high-volume laser marking environments.
While laser engraving retains importance in artistic and industrial durability applications, the overall market momentum favors laser marking due to its scalability, compliance advantages, and integration with digital manufacturing ecosystems.
In conclusion, by 2026, laser marking is poised to outpace laser engraving in market growth and technological innovation, especially in regulated and high-throughput industries. However, laser engraving will maintain relevance in specialized sectors requiring depth and tactile feedback. The convergence of both technologies into flexible, intelligent platforms may ultimately blur the lines—but for now, their distinct value propositions ensure parallel, evolving market trajectories.
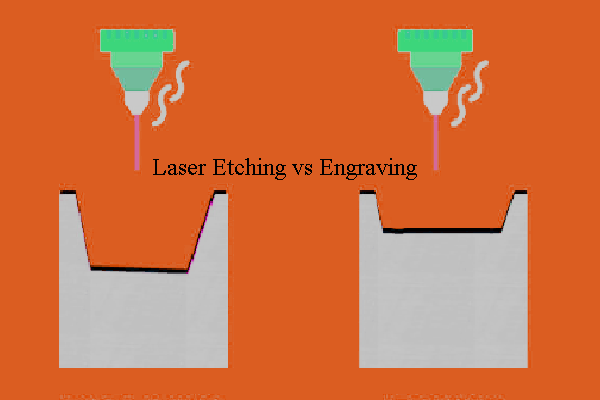
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Laser Marking vs. Laser Engraving (Quality & IP)
When sourcing laser marking or laser engraving services or equipment, businesses often overlook critical differences between the two processes. Misunderstanding these distinctions can lead to quality issues, intellectual property (IP) risks, and supply chain inefficiencies. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Confusing Surface Marking with Deep Engraving
One of the most common mistakes is assuming laser marking and laser engraving are interchangeable. Laser marking typically alters the surface layer (e.g., color change, annealing, or foaming) without significant material removal, while laser engraving involves physically removing material to create deeper, tactile marks. Sourcing engraving capabilities for a marking application can lead to excessive material waste and higher costs, while using marking for applications requiring durability (e.g., tooling or aerospace parts) may result in marks that wear off prematurely.
Overlooking Material Compatibility and Quality Consistency
Different lasers (fiber, CO₂, green, UV) and settings are optimal for various materials (metals, plastics, ceramics). Sourcing from a provider without verifying their expertise in your specific material can result in inconsistent mark quality—such as fading, charring, or insufficient contrast. For example, UV lasers are often required for high-precision marking on sensitive plastics, while fiber lasers dominate metal engraving. Failing to match the correct technology to the application risks batch rejections and production delays.
Underestimating Traceability and Regulatory Compliance Needs
In industries like medical devices, automotive, or aerospace, laser marks often serve as permanent traceability identifiers (e.g., UDI, serial numbers). Sourcing providers without validated processes for consistent mark readability (e.g., ISO/IEC 15415 for 2D codes) can lead to non-compliance. Poorly marked parts may fail automated scanning systems, disrupting logistics and recalls. Ensure your supplier validates mark permanence, legibility, and resistance to environmental factors like heat, chemicals, or abrasion.
Neglecting Intellectual Property Protection
When outsourcing laser marking or engraving, especially with proprietary designs, logos, or data matrix codes containing sensitive information, IP exposure is a major risk. Pitfalls include:
– Sharing CAD files or marking templates with unvetted suppliers lacking NDAs or secure data handling practices.
– Failing to audit subcontractors in the supply chain who may replicate or misuse marked designs.
– Not retaining ownership rights to custom-created marking programs or fixtures.
Always use legal agreements to define IP ownership and require cybersecurity measures for digital files.
Assuming All Laser Systems Deliver Equal Precision
High-resolution marking (e.g., micro-text or intricate logos) requires specialized equipment with fine beam control and stable platforms. Sourcing based on cost alone may lead to partnering with providers using outdated or repurposed systems incapable of meeting tight tolerances. This results in blurry, distorted, or incomplete marks—especially problematic for branding or authentication applications.
Ignoring Long-Term Maintenance and Support
Laser systems require calibration, lens cleaning, and periodic maintenance. Sourcing equipment or services from vendors without reliable technical support or spare parts availability can lead to unplanned downtime. Ensure service level agreements (SLAs) and maintenance plans are in place, especially for mission-critical marking operations.
Conclusion
To avoid these pitfalls, clearly define whether your application requires marking or engraving, verify supplier expertise with your materials and compliance needs, protect intellectual property through contracts, and prioritize long-term reliability over initial cost savings. Due diligence in sourcing ensures high-quality, durable marks while safeguarding your brand and IP.
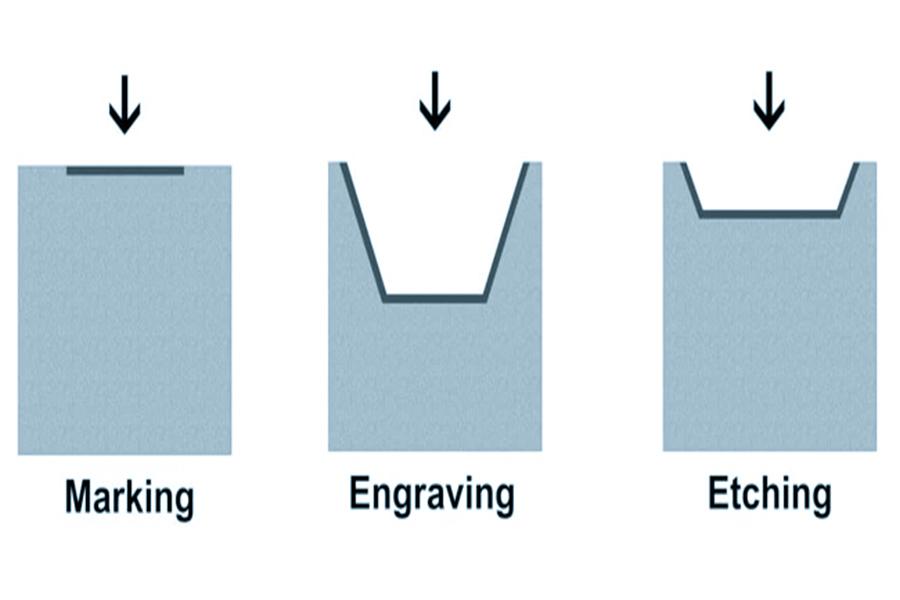
Logistics & Compliance Guide: Laser Marking vs. Laser Engraving
Understanding the differences between laser marking and laser engraving is essential for making informed decisions regarding equipment selection, supply chain logistics, and regulatory compliance. This guide outlines key logistical and compliance considerations for both processes.
Equipment and Operational Logistics
Laser Marking:
– Typically uses fiber or CO₂ lasers optimized for surface modification rather than deep material removal.
– Requires lower power settings, resulting in reduced energy consumption and lower operating costs.
– Faster processing speeds due to minimal material ablation; ideal for high-volume production lines.
– Equipment is often compact, enabling integration into existing manufacturing cells with minimal footprint.
– Minimal waste generation (no significant particulate or debris), reducing need for extensive filtration or disposal systems.
Laser Engraving:
– Generally demands higher-powered lasers (CO₂, fiber, or UV) capable of vaporizing material layers.
– Higher energy consumption and longer processing times, impacting throughput and operational efficiency.
– Generates particulate matter and fumes, requiring robust exhaust, filtration, or fume extraction systems.
– Equipment may be larger and more complex, necessitating additional floor space and safety enclosures.
– Increased maintenance due to debris accumulation on optics and laser components.
Material Compatibility and Supply Chain Integration
Laser Marking:
– Suitable for a wide range of materials including metals, plastics, and ceramics.
– Ideal for direct part marking (DPM) in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and medical devices.
– Minimal impact on material integrity; preserves mechanical strength and surface finish.
– Facilitates serialization and traceability (e.g., Data Matrix codes), supporting supply chain transparency and inventory management.
Laser Engraving:
– Best suited for materials that can withstand deeper material removal (e.g., wood, acrylic, anodized aluminum).
– Can compromise material strength or seal integrity if engraving depth is excessive—critical in safety-sensitive applications.
– May require material-specific consumables or pre/post-treatment processes, adding complexity to supply chains.
– Preferred for decorative or branding applications where visual depth is desired.
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
Laser Marking:
– Complies with industry standards for permanent identification, including ISO 13485 (medical devices), AS9100 (aerospace), and IATF 16949 (automotive).
– Meets U.S. FDA UDI (Unique Device Identification) requirements for medical instruments.
– Generates little to no hazardous waste, aligning with environmental regulations such as RoHS and REACH.
– Lower laser classification (typically Class 1 or 4 with interlocks), reducing safety compliance burden.
Laser Engraving:
– Must comply with laser safety standards (e.g., IEC 60825, FDA 21 CFR 1040.10) due to higher power and potential exposure risks.
– Requires proper ventilation and air quality controls to meet OSHA and EPA regulations regarding airborne particulates.
– Material-specific regulations apply—e.g., engraving certain plastics may release toxic fumes (e.g., PVC), violating chemical safety laws.
– May require hazardous waste disposal procedures for collected debris, increasing regulatory documentation and costs.
Traceability and Data Management
Laser Marking:
– Enables high-precision, machine-readable codes (barcodes, QR codes, Data Matrix) for automated tracking.
– Supports Industry 4.0 initiatives with seamless integration into MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems) and ERP platforms.
– Permanent marks resist wear, chemicals, and heat, ensuring long-term traceability.
Laser Engraving:
– Also supports traceability but may be less reliable in harsh environments if engraving fills with contaminants.
– Depth can enhance readability under low-light conditions but may trap debris affecting scanner performance.
– Requires calibration to ensure consistent depth and legibility across production batches.
Summary: Choosing the Right Process
Select laser marking for high-speed, compliant, and cost-effective identification in regulated industries. Choose laser engraving when deeper, visually prominent marks are required and when material and environmental factors are properly managed. Evaluate both processes against your logistical capabilities, safety protocols, and compliance obligations to ensure long-term operational success.
Conclusion: Sourcing Laser Marking vs. Laser Engraving
When deciding between sourcing laser marking and laser engraving, the choice ultimately depends on the specific application, material requirements, durability needs, and production efficiency.
Laser marking is ideal for applications requiring high-speed, non-destructive, and permanent surface marking with minimal material removal. It is well-suited for industries such as electronics, medical devices, and automotive, where traceability (e.g., barcodes, serial numbers, or data matrix codes) is critical without compromising material integrity. Marking produces clean, high-contrast results on metals, plastics, and coated materials with little to no surface disruption.
Laser engraving, on the other hand, involves the physical removal of material to create deeper, tactile marks. It is best for decorative applications, branding, signage, or when deeper markings are required for longevity under wear and harsh environments. While slower and more material-intensive than marking, engraving provides greater depth and visual contrast, making it suitable for applications like tool identification, awards, and nameplates.
In summary, source laser marking for fast, precise, and surface-level identification needs, especially in regulated or high-volume manufacturing. Choose laser engraving when deeper, more durable, or decorative markings are essential. Evaluating your material type, required mark depth, production speed, and end-use environment will ensure the optimal laser solution for your business needs.