The global laser marking machines market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for permanent, high-precision marking solutions across industries such as automotive, electronics, medical devices, and aerospace. According to Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 2.65 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.8% from 2024 to 2029. Grand View Research further supports this trajectory, reporting that the market size reached USD 2.78 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a CAGR of 7.2% through 2030. This growth is fueled by the rising adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies, stringent regulatory requirements for product traceability, and advancements in fiber and ultrafast laser systems. As demand for reliable, efficient, and scalable marking solutions increases, a select group of manufacturers are leading innovation and market share. Here, we present a data-driven overview of the top 10 laser marking machine manufacturers shaping the future of industrial identification and traceability.
Top 10 Laser Marking Types Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Industrial Laser Markers
Website: telesis.com
Key Highlights: Laser marking systems are ideal for manufacturers looking to mark serial numbers, codes, logos and more on their products. Learn more today!…
#2 Laserax
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Laserax works with the world’s leading manufacturers to implement laser cleaning, welding, texturing, and marking solutions….
#3 Universal Laser Systems
Website: ulsinc.com
Key Highlights: ULS helps companies evaluate the feasibility of laser technology. Discover our process and products to build your ideal laser system. Universal Laser Systems, ……
#4 8 Types of Common Lasers
Website: keyence.com
Key Highlights: Learn about the most common industrial lasers – fiber, UV, and CO₂—and get expert tips on choosing the best laser type for your specific application needs….
#5 Technomark North America
Website: technomark-inc.com
Key Highlights: Technomark provides advanced laser marking industrial laser marking systems provide permanent, high-contrast marks on metal, plastic, and composites….
#6 Industrial Laser Marking Machines by Domino North America
Website: domino-printing.com
Key Highlights: Domino has been a leader in industrial laser for over 40 years. Our CO2, Fiber and UV Lasers have been installed in factories all over the world. Reach out!…
#7 IPG Photonics
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: IPG Photonics manufactures high-performance fiber lasers, amplifiers, and laser systems for diverse applications and industries. Discover your solution….
#8 Laser marking
Website: trumpf.com
Key Highlights: Laser marking is a collective term for several marking procedures: ablation, engraving, annealing, black marking, colour change and foaming….
#9 Laser Marking Solutions for Industries
Website: lasermarktech.com
Key Highlights: Discover cutting-edge laser marking solutions tailored for various industries. From premium machines to custom options, we meet all your marking needs….
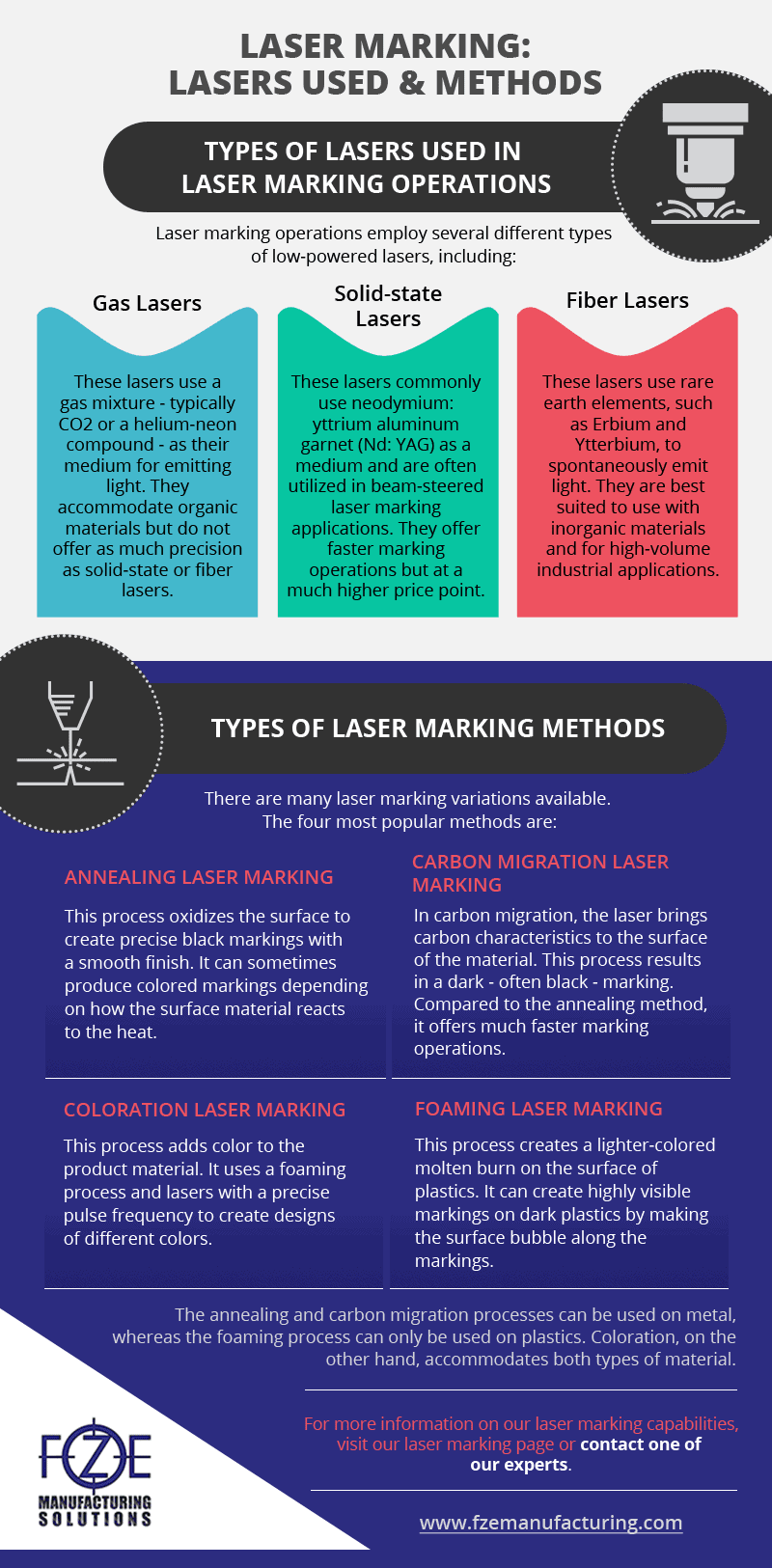
#10 The 6 Most Common Types of Laser Marking
Website: permanentmarking.com
Key Highlights: Foaming laser marking; Coloration laser marking; Ablation laser marking; Frosting laser marking. In this post, we will examine each of these ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Marking Types

2026 Market Trends for Laser Marking Types
The global laser marking market is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by advancements in laser technology, increasing industrial automation, and stringent traceability requirements across key sectors. Different laser marking types are experiencing distinct trajectories, shaped by their unique capabilities and application demands.
Fiber Lasers: Dominance and Expansion in Industrial Applications
Fiber laser marking is expected to maintain its dominant market position by 2026, capturing the largest share due to its reliability, low maintenance, and high efficiency. These lasers excel in marking metals and engineered plastics, making them ideal for automotive, aerospace, and electronics manufacturing. Trends indicate a shift toward higher-power fiber lasers for faster processing speeds and deeper engraving, particularly in heavy-duty industrial environments. Integration with Industry 4.0 systems—enabling real-time monitoring, remote diagnostics, and seamless data traceability—is becoming standard, enhancing productivity and quality control. Additionally, compact and portable fiber marking systems are gaining traction for field service and maintenance applications.
CO2 Lasers: Steady Demand in Packaging and Organic Materials
CO2 lasers will continue to hold a strong niche, particularly in industries requiring high-contrast marking on non-metallic substrates. By 2026, demand will remain robust in food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods packaging, where CO2 lasers provide clean, permanent marks on plastics, glass, paper, and wood. The trend toward sustainable packaging solutions is prompting innovations in CO2 laser systems that minimize material waste and energy consumption. Moreover, advancements in RF-excited CO2 lasers are improving beam quality and longevity, supporting higher throughput in high-speed production lines. Integration with vision systems for precise positioning on variable packaging formats will further solidify their relevance.
UV Lasers: Growth in High-Precision and Sensitive Applications
UV (ultraviolet) laser marking is projected to witness the fastest growth rate through 2026, driven by demand for cold marking processes in sensitive and high-value applications. UV lasers produce minimal heat-affected zones, making them ideal for marking medical devices, microelectronics, and heat-sensitive polymers without damaging the substrate. The proliferation of miniaturized electronic components and the need for permanent, tamper-proof UDI (Unique Device Identification) in healthcare are key growth drivers. Technological improvements in diode-pumped solid-state (DPSS) UV lasers are reducing costs and improving reliability, broadening their adoption beyond high-end niches. Expect increased use in semiconductor packaging and biocompatible materials.
Green and Blue Lasers: Emerging Roles in Advanced Materials
Green (532 nm) and blue (450 nm) lasers, while currently smaller segments, are emerging as critical tools for marking challenging materials like copper, gold, and certain transparent or highly reflective plastics. By 2026, advancements in direct diode green and blue lasers are expected to lower system costs and improve efficiency, enabling wider adoption in electronics, photovoltaics, and electric vehicle (EV) battery manufacturing. These wavelengths offer superior absorption in non-ferrous metals, allowing for high-contrast, durable marks essential for traceability in high-reliability industries. As EV and renewable energy markets expand, so too will the demand for these specialized laser types.
Hybrid and Smart Systems: The Rise of Adaptive Marking Solutions
A cross-cutting trend by 2026 is the integration of multiple laser types within hybrid platforms and the adoption of AI-driven control systems. Smart laser markers equipped with machine learning algorithms can automatically select optimal parameters based on material detection, ensuring consistent quality across mixed production lines. These adaptive systems reduce operator dependency and minimize errors, particularly in complex manufacturing environments. Cloud connectivity and predictive maintenance features will further enhance operational efficiency, positioning laser marking not just as a labeling tool, but as a core component of digital manufacturing ecosystems.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Laser Marking Systems (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing laser marking systems involves more than just comparing prices and technical specs. Overlooking key quality and intellectual property (IP) concerns can lead to performance issues, legal risks, and long-term costs. Here are common pitfalls to avoid:
Overlooking Build Quality and Component Reliability
Many suppliers offer budget-friendly laser markers, but cheaper systems often use substandard optical components, unstable laser sources, or poor mechanical construction. This results in inconsistent marking, frequent downtime, and shorter system life. Always verify the quality of core components like the laser resonator, galvanometer scanners, and f-theta lenses—preferably from reputable manufacturers.
Ignoring Certification and Compliance Standards
Low-cost systems, especially from regions with lax regulations, may lack necessary certifications (e.g., CE, FDA, RoHS). This can prevent deployment in regulated industries like medical devices or aerospace. Ensure the system complies with regional safety, electrical, and laser emission standards to avoid legal and operational issues.
Falling for Inflated Laser Specifications
Some suppliers exaggerate laser power, beam quality (M²), or marking speed. For example, a claimed 50W fiber laser might actually deliver significantly less effective power due to poor thermal management or low-quality diodes. Request third-party test reports or conduct on-site validation before purchasing.
Underestimating After-Sales Support and Service Access
Even high-quality systems require maintenance and repairs. Sourcing from vendors without local service centers or technical support can result in long downtimes. Verify the availability of spare parts, firmware updates, and responsive technical assistance—especially if the supplier is overseas.
Overlooking Software Limitations and Licensing
The marking software is critical for integration and functionality. Some systems use proprietary software with restrictive licensing, high upgrade fees, or limited compatibility with factory automation systems (e.g., PLCs, MES). Ensure the software supports necessary file formats, barcode generation, and network connectivity without hidden costs.
Assuming All Marking Types Are Interchangeable
Different lasers (fiber, CO₂, UV, green) are suited for specific materials and applications. Sourcing a fiber laser for delicate plastic marking, for example, may cause melting or poor contrast. Misalignment between laser type and application leads to subpar results and wasted investment. Confirm the laser wavelength and pulse characteristics match your material requirements.
Neglecting Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Using a laser system that incorporates patented technology (e.g., in beam delivery, marking algorithms, or software) without proper licensing can expose your company to IP infringement claims. This is especially risky with OEM systems from lesser-known manufacturers who may have copied protected designs. Perform due diligence on the supplier’s IP ownership or licensing agreements.
Relying on Counterfeit or Refurbished Components
Some low-cost suppliers use counterfeit or recycled laser modules and optics sourced from dubious channels. These components may fail prematurely or underperform. Ask for component traceability and avoid suppliers unwilling to disclose their supply chain.
Skipping Factory Acceptance Testing (FAT)
Failing to conduct a thorough FAT—where the system is tested under real-world conditions—can lead to discovering defects only after installation. Always insist on witnessing key performance tests, including marking consistency, uptime, and integration with existing systems, before final acceptance.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence, technical validation, and clear contractual terms. Prioritize long-term reliability and legal safety over upfront cost savings when sourcing laser marking systems.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Marking Types
Understanding the logistics and compliance considerations for different laser marking types is essential for ensuring product traceability, regulatory adherence, and operational efficiency across industries such as automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and electronics. This guide outlines key logistical requirements and compliance standards associated with common laser marking technologies.
Fiber Laser Marking
Fiber laser marking is widely used for permanent marking on metals and some plastics. It offers high precision, speed, and durability—ideal for part serialization, barcodes, and data matrix codes.
Logistical Considerations:
– Requires integration into production lines with minimal downtime.
– Suitable for high-volume manufacturing due to fast marking speeds.
– Maintenance includes periodic inspection of fiber optics and cooling systems.
Compliance Requirements:
– Meets FDA 21 CFR Part 11 for traceability in medical device manufacturing.
– Complies with UDI (Unique Device Identification) regulations when marking medical instruments.
– Supports REACH and RoHS compliance by avoiding chemical inks or additives.
– Adheres to ISO 13485 and AS9100 standards in regulated industries.
CO2 Laser Marking
CO2 lasers are effective for marking organic materials, glass, and certain plastics. They are commonly used in packaging, electronics, and consumer goods.
Logistical Considerations:
– Requires proper ventilation due to potential emission of fumes during marking.
– Slower than fiber lasers for metal marking; best suited for non-metallic substrates.
– Consumables include laser tubes, which have a limited lifespan and require periodic replacement.
Compliance Requirements:
– Complies with FDA food-safe labeling guidelines when used on food packaging (e.g., expiration dates).
– Supports EU Packaging and Packaging Waste Directive through non-contact, chemical-free marking.
– Meets UL/CSA safety standards for electrical equipment labeling.
– Must comply with OSHA and IEC 60825 laser safety regulations for operator protection.
UV Laser Marking
UV lasers use cold marking technology, making them ideal for heat-sensitive materials such as foils, films, and certain engineered plastics.
Logistical Considerations:
– Lower thermal impact reduces material degradation, beneficial for delicate components.
– Compact systems allow integration into cleanroom environments.
– Higher initial investment but low operational waste.
Compliance Requirements:
– Complies with pharmaceutical serialization requirements under EU Falsified Medicines Directive (FMD).
– Supports 2D data matrix marking for DSCSA (Drug Supply Chain Security Act) compliance in the U.S.
– Meets non-toxic marking standards under ISO 10993 for medical packaging.
– Environmentally compliant with WEEE directives due to absence of solvents.
Green Laser Marking
Green lasers are used for marking highly reflective materials such as copper, gold, and silicon wafers, where standard infrared lasers may reflect or damage the surface.
Logistical Considerations:
– Requires stable power supply and temperature control to maintain beam quality.
– Used in semiconductor and microelectronics manufacturing with stringent cleanroom protocols.
– Limited to specialized applications, which may affect equipment availability.
Compliance Requirements:
– Supports JEDEC and IPC standards for electronic component traceability.
– Complies with ITAR/EAR regulations when used in defense-related manufacturing.
– Meets ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) safety requirements in sensitive electronic environments.
General Compliance & Safety Standards
Regardless of laser type, the following regulatory and safety standards apply across all applications:
- Laser Safety (IEC 60825 / ANSI Z136.1): All laser systems must be classified and equipped with appropriate safety interlocks, warning labels, and protective enclosures.
- CE Marking: Required for equipment sold in the European Economic Area, indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- Machine Safety (ISO 13849): Ensures safe integration into automated systems with risk assessments and emergency stops.
- Environmental Compliance: Laser marking avoids hazardous chemicals, aligning with REACH, RoHS, and ELV Directive requirements.
Conclusion
Selecting the appropriate laser marking technology involves balancing material compatibility, production speed, and regulatory demands. Effective logistics planning—such as maintenance scheduling, operator training, and system integration—ensures continuous compliance and traceability. Always consult industry-specific regulations and conduct regular audits to maintain adherence to evolving standards.
Conclusion on Sourcing Laser Marking Types
When sourcing laser marking systems, selecting the appropriate type—such as fiber, CO₂, UV, or green lasers—depends on several key factors including material compatibility, desired mark quality, production speed, and budget. Fiber lasers are ideal for marking metals and hard plastics, offering durability and low maintenance, making them a popular choice in industrial manufacturing. CO₂ lasers excel in marking organic materials like wood, paper, glass, and certain plastics, providing high-contrast results. UV and green lasers offer precision for sensitive or heat-sensitive materials, such as medical devices or electronics, enabling high-resolution, clean markings without damage.
Ultimately, a thorough evaluation of application requirements—material type, mark permanence, throughput, and environmental conditions—is essential to determine the most suitable laser marking technology. Partnering with reliable suppliers who offer technical support, service, and customization options ensures long-term operational efficiency and return on investment. By aligning laser type with application needs, businesses can achieve consistent, high-quality marking that enhances traceability, branding, and compliance across industries.