The global laser marking machine market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for permanent marking solutions across industries such as automotive, electronics, medical devices, and consumer goods. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 2.78 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.8% from 2023 to 2028. This expansion is fueled by advancements in fiber laser technology, rising automation trends, and stringent regulatory requirements for product traceability and serialization. Grand View Research also highlights similar momentum, noting the growing adoption of non-contact marking processes that ensure high precision and durability. As competition intensifies, a select group of manufacturers are leading innovation with scalable, high-performance systems. Here are the top 9 laser marking machine manufacturers shaping the industry’s future through technological excellence and global reach.
Top 9 Laser Marking Machine Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laserax
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Laserax works with the world’s leading manufacturers to implement laser cleaning, welding, texturing, and marking solutions….
#2 Industrial Laser Marking & Dot Peen Marking Solutions
Website: telesis.com
Key Highlights: At Telesis Technologies, we’re dedicated to creating the perfect laser marking system for you, with integrated software solutions and custom machines….
#3 Laser Marking for All Industries
Website: lasermarktech.com
Key Highlights: Discover innovative laser marking solutions tailored for various industries. Explore our cutting-edge technology as leaders in laser marking and engraving….
#4 Marking Machinery Manufacturers
Website: markingmachinery.com
Key Highlights: Epilog Laser specializes in laser marking systems, CO2 lasers, diode lasers, laser cutting machines & systems for laser engraving like tabletop engravers, mid- ……
#5 Automator Marking Systems
Founded: 1940
Website: automator.com
Key Highlights: Since 1940, Automator Marking Systems has been a world leader in industrial marking solutions, with an unwavering commitment to customer-centric innovation….
#6 Gravotech
Website: gravotech.us
Key Highlights: Gravotech designs, manufactures, and distributes innovative engraving, marking, and cutting solutions….
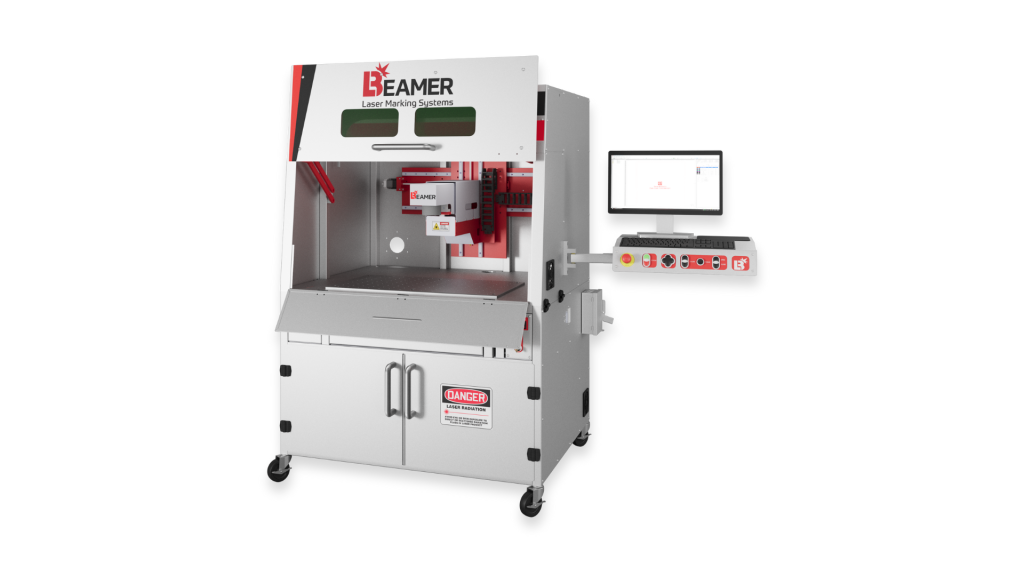
#7 Beamer Laser Marking Systems
Website: beamerlasermarking.com
Key Highlights: We offer a wide range of powerful standard, engineered, and inline 1064nm IR laser marking solutions with unmatched 100,000+ hour lifespan….
#8 Full Spectrum Laser
#9 Laser Cutting, Engraving & Marking Machines
Website: thunderlaser.com
Key Highlights: Thunder Laser offers high-quality, reliable laser machines to meet the needs of a variety of industries. ThunderLaser has become a well-recognized icon in ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Marking Machine

2026 Market Trends for Laser Marking Machines
The global laser marking machine market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, evolving industry demands, and the accelerating adoption of automation across key sectors. As industries prioritize precision, traceability, and efficiency, laser marking technology is becoming increasingly indispensable. Key trends shaping the market landscape include the rise of ultrafast lasers, integration with Industry 4.0 systems, expansion into emerging applications, and a growing emphasis on sustainability and customization.
Increased Adoption of Ultrafast and Fiber Lasers
By 2026, ultrafast lasers—particularly picosecond and femtosecond systems—are expected to gain substantial market share due to their ability to mark heat-sensitive and high-reflectivity materials without thermal damage. These lasers are increasingly used in medical devices, electronics, and aerospace applications where precision and material integrity are critical. Concurrently, fiber lasers will continue to dominate in industrial environments due to their reliability, low maintenance, and cost-effectiveness, especially for marking metals and plastics in high-volume production lines.
Integration with Smart Manufacturing and Industry 4.0
Laser marking systems are becoming integral components of smart factories. By 2026, seamless integration with MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems), ERP platforms, and IoT-enabled devices will be standard. Real-time data exchange, remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and automated job scheduling will enhance productivity and traceability. The ability to generate dynamic, variable data marks (such as QR codes, Data Matrix codes, and serialization) supports compliance with regulatory standards in pharmaceuticals, automotive, and aerospace sectors.
Growth in High-Precision and Micro-Marking Applications
Demand for miniaturization in electronics and medical devices is fueling the need for micro-marking capabilities. Laser systems capable of marking features below 10 microns will see increased deployment. This trend is particularly evident in semiconductor packaging, wearable tech, and implantable medical devices, where permanent, high-contrast, and non-invasive marking is essential for product identification and patient safety.
Expansion into Renewable Energy and EV Manufacturing
The booming electric vehicle (EV) and renewable energy sectors are emerging as major growth drivers. Battery manufacturers require permanent, tamper-proof marking on cells and battery packs for traceability and safety. Similarly, solar panel producers use laser marking for serializing components and ensuring long-term durability under harsh environmental conditions. By 2026, specialized laser systems designed for these applications will constitute a rapidly growing segment.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Marking Solutions
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals are pushing manufacturers toward greener production methods. Laser marking, being a non-contact, chemical-free process, aligns well with these objectives. Compared to ink-based marking, it eliminates solvent waste and reduces consumable usage. This environmental advantage is expected to further accelerate adoption across eco-conscious industries.
Rise of Compact, Portable, and Customized Systems
Market demand is shifting toward smaller, modular, and portable laser marking units that can be easily integrated into existing production lines or used in field applications. Customization is also on the rise, with OEMs offering tailored software interfaces, ergonomic designs, and application-specific configurations to meet diverse customer needs across industries such as jewelry, tools, and consumer goods.
In conclusion, the laser marking machine market in 2026 will be characterized by smarter, faster, and more versatile systems, deeply embedded in digital manufacturing ecosystems. As innovation continues to lower costs and expand capabilities, laser marking will transition from a niche industrial tool to a cornerstone of modern production, ensuring product authenticity, compliance, and operational efficiency across global supply chains.
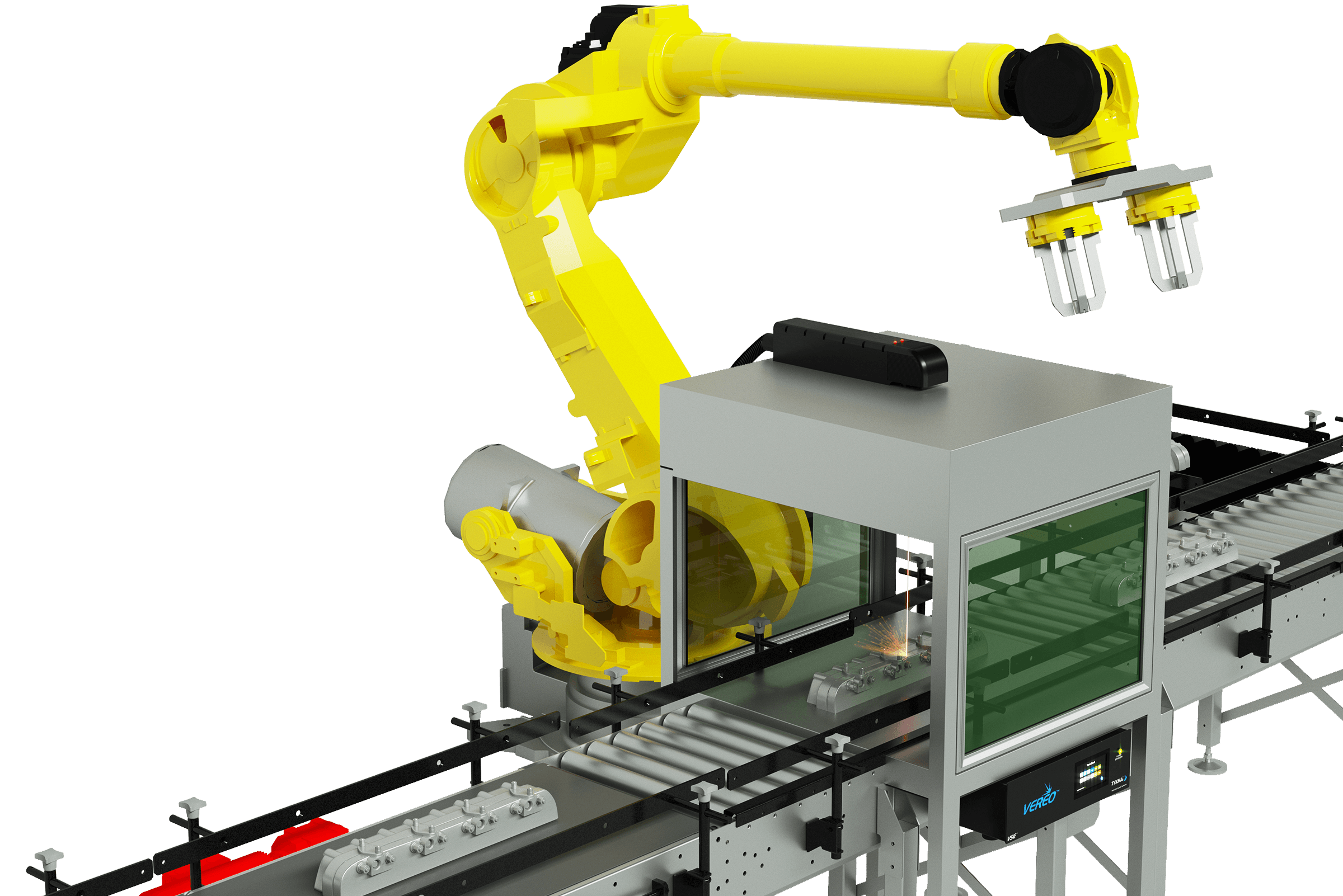
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Laser Marking Machine (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing a laser marking machine involves significant investment and technical considerations. Overlooking key aspects related to quality and intellectual property (IP) can lead to operational disruptions, legal risks, and financial losses. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Build Quality and Component Selection
Many suppliers, especially low-cost manufacturers, use substandard materials and components to cut costs. This includes low-grade optics, unreliable laser sources (e.g., diode or fiber lasers with short lifespans), and poorly designed cooling systems. Machines built with inferior parts often suffer from inconsistent marking results, frequent breakdowns, and high maintenance costs. Always verify the specifications and origin of critical components like the laser resonator, galvanometer scanners, and control electronics.
Inadequate or Misrepresented Laser Performance
Some suppliers exaggerate laser power, marking speed, or depth capabilities. For example, a machine advertised as a “50W fiber laser” might deliver significantly less actual output due to inefficient design or power regulation. This can result in poor mark quality or inability to process certain materials. Request third-party test reports or conduct on-site demonstrations with your actual materials to validate performance claims.
Lack of Quality Certifications and Compliance
Reputable laser machines should comply with international safety and quality standards such as CE, FDA (for U.S. markets), and ISO 9001. Suppliers without these certifications may not adhere to rigorous manufacturing or safety protocols, increasing the risk of equipment failure or regulatory non-compliance. Always verify documentation and ensure the machine meets local regulatory requirements.
Opaque Supply Chain and Component Origins
Some suppliers source critical components—like laser sources or control boards—from unknown or unauthorized manufacturers. This not only affects reliability but also raises IP concerns. Be cautious of machines using well-known brand components (e.g., IPG or Trumpf lasers) at suspiciously low prices, as they may be counterfeit or grey-market goods.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Low-cost machines, particularly from certain regions, may incorporate cloned firmware, copied software interfaces, or reverse-engineered designs that violate intellectual property rights. Using such equipment could expose your business to legal liability, especially in regions with strict IP enforcement. Ensure the supplier can provide licensing documentation for all software and firmware used.
Incomplete or Missing Documentation and Source Code
Some suppliers withhold technical documentation, software source code, or API access, limiting your ability to integrate the machine into automated systems or perform in-house troubleshooting. This dependence on the supplier for support can be costly and time-consuming. Confirm in writing that you will receive full technical documentation and necessary software development kits (SDKs).
Weak After-Sales Support and Warranty Enforcement
Even if a machine meets initial quality standards, poor after-sales service can undermine its long-term value. Some suppliers offer warranties that are difficult to enforce due to unclear terms or lack of local service centers. Ensure the warranty covers both parts and labor, and verify the availability of technical support and spare parts in your region.
Hidden Costs from Non-Standard Interfaces
Machines with proprietary software or communication protocols can create integration challenges and increase total cost of ownership. Avoid systems that do not support standard industrial communication protocols (e.g., Ethernet/IP, Modbus, or OPC UA), as they may require expensive custom solutions to connect with existing production lines.
By thoroughly vetting suppliers, demanding transparency on component origins, verifying performance claims, and ensuring IP compliance, businesses can avoid these common pitfalls and secure a reliable, legally sound laser marking solution.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Marking Machine
Shipping and Transportation
Ensure the laser marking machine is securely packaged in a robust, shock-resistant crate with adequate internal cushioning to prevent movement during transit. Use moisture-resistant materials to protect against humidity, especially for international shipments. Clearly label the package with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Do Not Stack” indicators. Follow all carrier-specific guidelines for heavy or sensitive equipment, and consider using a freight forwarder experienced in handling industrial machinery.
Import/Export Regulations
Verify compliance with export control regulations such as the Export Administration Regulations (EAR) in the U.S. or equivalent regulations in your country. Classify the machine using the appropriate Harmonized System (HS) code—commonly 8456.10 or 8456.30 depending on configuration. Determine if the machine or its components (e.g., high-powered lasers) require export licenses due to technology controls. For imports, check destination country requirements including customs duties, import permits, and local certifications.
Laser Safety Compliance
Ensure the laser marking machine meets the safety standards of the destination market. Key standards include:
– IEC 60825-1: Safety of laser products – Equipment classification and requirements.
– FDA 21 CFR Part 1040.10 (U.S.): Federal laser product performance standard.
– EN 60825-1 (EU): European standard for laser safety.
Provide required documentation such as a Laser Safety Certification, User Manual with safety warnings, and a Declaration of Conformity (DoC) for CE-marked equipment. Include safety interlocks, protective enclosures, and appropriate warning labels on the machine.
Electrical and EMC Standards
Confirm that the machine’s electrical specifications (voltage, frequency) match those of the destination region. The equipment must comply with electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) regulations such as:
– FCC Part 15 (U.S.)
– EMC Directive 2014/30/EU (EU)
Provide test reports or certifications (e.g., FCC ID, CE-EMC) to demonstrate compliance. Include power adapters or transformers if required for voltage conversion.
Installation and On-Site Compliance
Prior to installation, verify that the operating environment meets required conditions (e.g., stable power supply, adequate ventilation, temperature range). Conduct a site safety assessment to ensure compliance with local occupational health and safety regulations. Train operators on proper use, safety procedures, and emergency shutdown protocols. Maintain logs of maintenance and safety checks as required by local labor and safety authorities.
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Maintain complete technical files including:
– User and service manuals
– Safety data sheets (if applicable)
– Certificates of Compliance (CE, FCC, etc.)
– Warranty and service information
– Export control documentation (e.g., ECCN, license numbers)
Retain these records for a minimum of five years or as required by local regulations to support audits or inspections.
Environmental and Disposal Regulations
Dispose of or recycle the machine at end-of-life in accordance with local environmental regulations such as WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) in the EU. Ensure proper handling of laser components, batteries, and electronic circuitry. Provide customers with take-back or recycling instructions as required by law.
In conclusion, sourcing a reliable laser marking machine manufacturer requires careful evaluation of several key factors, including technical expertise, product quality, customization capabilities, after-sales support, and cost-effectiveness. It is essential to partner with manufacturers who have a proven track record, relevant industry certifications, and positive customer feedback. Conducting thorough research, requesting product demonstrations, and comparing multiple suppliers will help ensure the selection of a manufacturer that meets both current needs and future scalability requirements. Ultimately, choosing the right laser marking machine supplier contributes significantly to enhancing production efficiency, maintaining product traceability, and achieving long-term operational success.