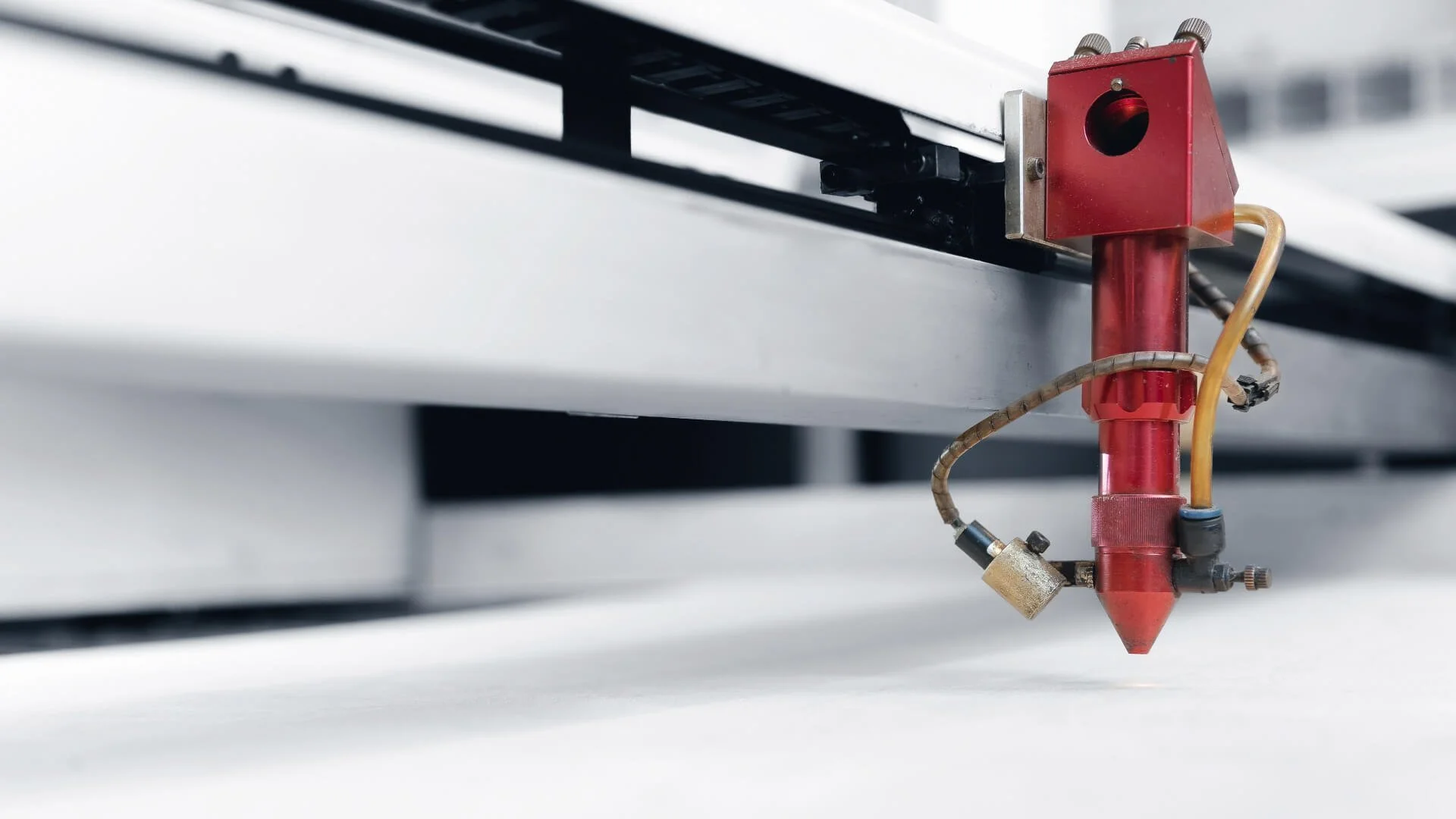
The global laser printing machinery market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by rising demand for precision, speed, and customization across industries such as automotive, electronics, packaging, and healthcare. According to a 2023 report by Grand View Research, the global industrial laser systems market size was valued at USD 13.8 billion and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.2% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by the increasing adoption of laser-based marking and engraving technologies, particularly in emerging economies where manufacturing modernization is accelerating. Furthermore, Mordor Intelligence projects that advancements in fiber laser technology and the integration of automation and Industry 4.0 capabilities are reshaping production floors, making laser printing machines more efficient and accessible. As competition intensifies, a select group of manufacturers are leading innovation, offering scalable, high-precision solutions that meet evolving industry standards. Below, we highlight the top 10 laser machine printing manufacturers at the forefront of this technological transformation.
Top 10 Laser Machine Printing Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Focus on laser
Founded: 1996
Website: hanslaser.net
Key Highlights: Han’s Laser Technology Industry Group Co., Ltd, a public company which was established in 1996, has now become the flagship of Chinese national laser ……
#2 Universal Laser Systems
Website: ulsinc.com
Key Highlights: Solve Material Processing Challenges. Overcome your most demanding and complex applications. ULS helps companies evaluate the feasibility of laser technology….
#3 Laser Photonics
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser Photonics manufactures reliable, safe, and eco-friendly Laser Cleaning, Laser Cutting, Laser Engraving, Laser Marking, and Laser Welding solutions….
#4 Industrial Printers, Laser Marking, Continuous Inkjet, Label …
Website: videojet.com
Key Highlights: Videojet Technologies is a world-leader in the product identification market, providing industrial printers for in-line printing, coding, and marking ……
#5 Laserax
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Laserax works with the world’s leading manufacturers to implement laser cleaning, welding, texturing, and marking solutions….
#6 Full Spectrum Laser
#7 Laser engravers & laser cutters
Website: gravotech.us
Key Highlights: Our laser tables are designed to engrave, mark and cut on a wide variety of materials (plastic, wood, metal, leather, glass, paper, stone) and shapes….
#8 Laser Cutting, Engraving & Marking Machines
Website: thunderlaser.com
Key Highlights: Thunder Laser offers high-quality, reliable laser machines to meet the needs of a variety of industries. ThunderLaser has become a well-recognized icon in ……
#9 ACMER
#10 Laser Equipment Supplier
Website: radianlaser.com
Key Highlights: Radian Laser Systems is a laser equipment supplier specializing in high-speed, customizable laser machinery, including fiber, CO2, and galvo lasers….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Machine Printing

2026 Market Trends for Laser Machine Printing
The global laser machine printing market is poised for dynamic evolution by 2026, driven by technological advancements, shifting industrial demands, and expanding applications across diverse sectors. Here are the key trends shaping the landscape:
Accelerated Adoption in Industrial Manufacturing
Laser printing technologies, particularly laser marking, engraving, and direct part marking (DPM), are becoming indispensable in industrial automation. By 2026, manufacturers across automotive, aerospace, and electronics will increasingly integrate laser systems for high-speed, permanent, and tamper-proof identification of components. This trend aligns with growing regulatory requirements for traceability (e.g., UDI in medical devices, VIN in automotive) and Industry 4.0 initiatives demanding smart factory integration, where laser printers serve as critical data carriers via QR codes and Data Matrix codes.
Rising Demand for Fiber and Ultrafast Lasers
Fiber lasers will dominate the industrial segment due to their superior efficiency, reliability, and low maintenance compared to CO2 and lamp-pumped lasers. Concurrently, ultrafast lasers (picosecond and femtosecond) will gain traction in high-precision applications such as medical device manufacturing, solar cell scribing, and microelectronics. These lasers enable cold ablation processes that minimize heat-affected zones, preserving material integrity—making them ideal for delicate substrates and advanced materials.
Expansion into Consumer Goods and Personalization
The consumer market will drive demand for laser printing in product customization and branding. From personalized electronics and luxury goods to customized packaging and promotional items, businesses will leverage laser engraving for unique, high-quality finishes. Advances in compact and user-friendly desktop laser systems will empower small enterprises and makerspaces, further democratizing access to laser personalization technologies.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Processes
Environmental considerations will influence laser printing adoption. As a non-contact, ink-free process, laser marking eliminates consumables like inks and solvents, reducing waste and VOC emissions. By 2026, sustainability will be a key differentiator, with industries seeking greener production methods. Laser printing’s alignment with circular economy principles—through durable, non-fading markings that support recycling and lifecycle tracking—will enhance its appeal.
Integration with AI and Smart Manufacturing
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning will enhance laser printing systems by enabling predictive maintenance, real-time quality control, and adaptive beam control. In smart factories, laser printers will communicate with MES and ERP systems, allowing dynamic content changes and full traceability. This integration will boost productivity, reduce downtime, and ensure consistent output quality across high-volume production lines.
Growth in Emerging Applications
Beyond traditional uses, laser printing will expand into new domains such as bioprinting, flexible electronics, and additive manufacturing. Research into laser-induced forward transfer (LIFT) and selective laser sintering (SLS) for printing conductive inks or biological materials will create niche but high-growth opportunities. Additionally, the rise of wearable technology and IoT devices will spur demand for precise, miniaturized laser patterning.
Regional Market Shifts
Asia-Pacific, particularly China and India, will remain the fastest-growing region due to rapid industrialization, government support for advanced manufacturing, and a booming electronics sector. North America and Europe will focus on high-end applications in aerospace, medical, and automotive, with strong emphasis on innovation and compliance. Cross-border collaborations and localized production will influence supply chain strategies for laser equipment manufacturers.
In conclusion, by 2026, the laser machine printing market will be characterized by smarter, faster, and more sustainable solutions tailored to evolving industrial and consumer needs. Companies that invest in innovation, software integration, and application-specific development will be best positioned to capitalize on these transformative trends.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Laser Machine Printing (Quality, IP)
Sourcing laser printing machines—especially for industrial, medical, or high-precision applications—can present significant challenges related to both product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Being aware of these pitfalls helps avoid costly mistakes and ensures long-term reliability and compliance.
Poor Quality Control and Inconsistent Output
Many suppliers, particularly in highly competitive or low-cost markets, may deliver laser machines that lack rigorous quality assurance. This can result in inconsistent engraving depth, misalignment, or variable marking precision. Buyers often discover these issues only after deployment, leading to production delays, rework, or customer complaints. Always verify the supplier’s manufacturing standards, request sample outputs, and inspect certifications such as ISO 9001.
Use of Substandard or Counterfeit Components
Some sourced machines incorporate low-grade optics, lasers, or control systems to reduce costs. These components degrade faster, deliver lower performance, and increase maintenance needs. In extreme cases, counterfeit laser diodes or controllers may pose safety risks. Conduct component-level audits and insist on transparency about part specifications and origins.
Lack of Calibration and Standardization
Laser machines require precise factory calibration to ensure accuracy and repeatability. Poorly calibrated units may produce non-compliant marks, especially in regulated industries like aerospace or medical devices. Confirm that each unit undergoes full calibration and comes with a traceable certificate of conformance.
Inadequate After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Suppliers in distant markets may offer attractive upfront pricing but provide limited technical support, training, or spare parts. This can lead to prolonged downtime when maintenance is needed. Evaluate the supplier’s support infrastructure, response times, and availability of localized service centers before procurement.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Sourcing from regions with weak IP enforcement raises the risk of purchasing machines that incorporate stolen or reverse-engineered technology. Using such equipment may expose your company to legal liability, especially if the original IP holder takes action. Conduct due diligence on the supplier’s R&D practices and request documentation proving legitimate design ownership.
Hidden Software Limitations and Licensing Traps
Many laser machines rely on proprietary software for design and operation. Some suppliers impose restrictive licensing terms, limit functionality, or embed backdoors that compromise data security. Additionally, software updates may cease unexpectedly. Review software licensing agreements carefully and ensure compatibility with your existing systems.
Non-Compliance with Regional Safety and Regulatory Standards
Laser machines must comply with local regulations such as FDA (U.S.), CE (Europe), or GB (China) standards for laser safety, emissions, and electrical safety. Machines sourced from non-compliant suppliers may fail inspections or be barred from operation. Confirm that the equipment meets all required certifications for your target market.
Insufficient Documentation and Training Materials
Poorly documented systems—lacking user manuals, maintenance guides, or technical schematics—make onboarding and troubleshooting difficult. Language barriers can compound this issue. Require comprehensive, multilingual documentation and hands-on training as part of the sourcing agreement.
Failure to Protect Your Own IP During Integration
When customizing laser systems for proprietary applications, sharing sensitive designs or processes with suppliers increases the risk of IP leakage. Always use non-disclosure agreements (NDAs), limit data sharing, and consider modular integration that keeps core IP separate from the machine’s control system.
By proactively addressing these common pitfalls, businesses can mitigate risks and ensure that their investment in laser machine printing delivers reliable performance and legal peace of mind.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Machine Printing
Overview and Purpose
This guide outlines essential logistics considerations and regulatory compliance requirements for businesses involved in the manufacturing, distribution, operation, and maintenance of laser machine printing systems. Adherence to these guidelines ensures safety, legal conformity, and efficient supply chain operations.
Applicable Regulations and Standards
Laser printing machines are subject to multiple international and national regulations. Key standards include:
– IEC 60825-1: Safety of laser products – Equipment classification and requirements.
– FDA 21 CFR Part 1040.10 and 1040.11: U.S. regulations for laser radiation safety.
– CE Marking (EU): Compliance with the Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC) and Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive.
– RoHS and REACH (EU): Restrictions on hazardous substances in electrical equipment.
– OSHA 29 CFR 1910.97: Occupational safety for non-ionizing radiation (U.S.).
Ensure all laser printing equipment meets local and destination country requirements before shipment.
Laser Classification and Safety Labeling
Laser machines are classified from Class 1 to Class 4 based on power output and potential hazard:
– Class 1: Safe under normal operating conditions.
– Class 2/2M: Low-power visible lasers; eye protection through blink reflex.
– Class 3R/3B: Moderate risk; requires safety controls.
– Class 4: High-power lasers; can cause fires and severe injury. Requires strict controls.
All devices must display appropriate warning labels, including laser class, wavelength, maximum output, and manufacturer information. Documentation must include safety instructions and emergency procedures.
Packaging and Shipping Requirements
Proper packaging is critical to prevent damage and ensure safe transport:
– Use shock-absorbent, anti-static packaging materials.
– Secure optical components and laser heads to prevent movement.
– Clearly label packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Laser Radiation” warning symbols.
– Include compliance documentation (e.g., Declaration of Conformity, safety data sheets).
For international shipments, comply with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations if applicable (e.g., Class 4 lasers may require special handling).
Import and Export Compliance
Cross-border logistics must adhere to export control and customs regulations:
– Export Controls: Verify if laser equipment falls under export control lists (e.g., U.S. Commerce Control List – ECCN 6A003).
– Customs Documentation: Provide accurate HS codes (e.g., 8443.32 for laser printers), commercial invoices, and certificates of origin.
– Restricted Destinations: Check for trade sanctions or embargoes affecting shipment destinations.
Engage certified freight forwarders experienced in handling high-tech and regulated equipment.
Installation and Operational Compliance
Upon delivery, ensure compliance during setup and daily use:
– Install in controlled environments with proper ventilation and fire suppression.
– Use interlocks, beam enclosures, and emergency stop mechanisms.
– Train operators on laser safety (ANSI Z136.1 recommended in the U.S.).
– Conduct regular maintenance and safety audits.
Maintain logs of inspections, repairs, and personnel training.
Waste Disposal and End-of-Life Management
Dispose of laser machines and components in compliance with environmental regulations:
– Separate and recycle electronic parts per WEEE (EU) or state e-waste laws (e.g., California).
– Handle laser diodes and optical components as electronic waste; avoid landfill disposal.
– Partner with certified e-waste recyclers who follow R2 or e-Stewards standards.
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Maintain comprehensive records for at least five years, including:
– Product compliance certificates (CE, FDA, RoHS).
– Safety data sheets (SDS) for consumables.
– Shipping manifests and export licenses.
– Maintenance logs and incident reports.
Digital records should be securely stored and regularly backed up.
Conclusion
Compliance in laser machine printing logistics ensures operational safety, legal adherence, and smooth global distribution. Regular review of evolving regulations and internal audits is recommended to maintain standards and minimize liability.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Laser Machine for Printing:
After thorough evaluation of requirements, capabilities, and vendor options, sourcing a laser printing machine represents a strategic investment in enhancing production efficiency, print quality, and operational versatility. Laser machines offer precision, speed, and durability, making them ideal for applications ranging from product marking and labeling to custom engraving and industrial serialization.
Key considerations such as laser type (fiber, CO2, or UV), power requirements, software compatibility, maintenance support, and total cost of ownership have been assessed to ensure alignment with business needs. Selecting a reputable supplier with strong technical support and warranty options further ensures long-term reliability and minimal downtime.
Ultimately, the integration of a laser printing machine will streamline operations, support scalability, and improve product traceability and branding—delivering a strong return on investment and positioning the organization for future growth and competitiveness in the market.