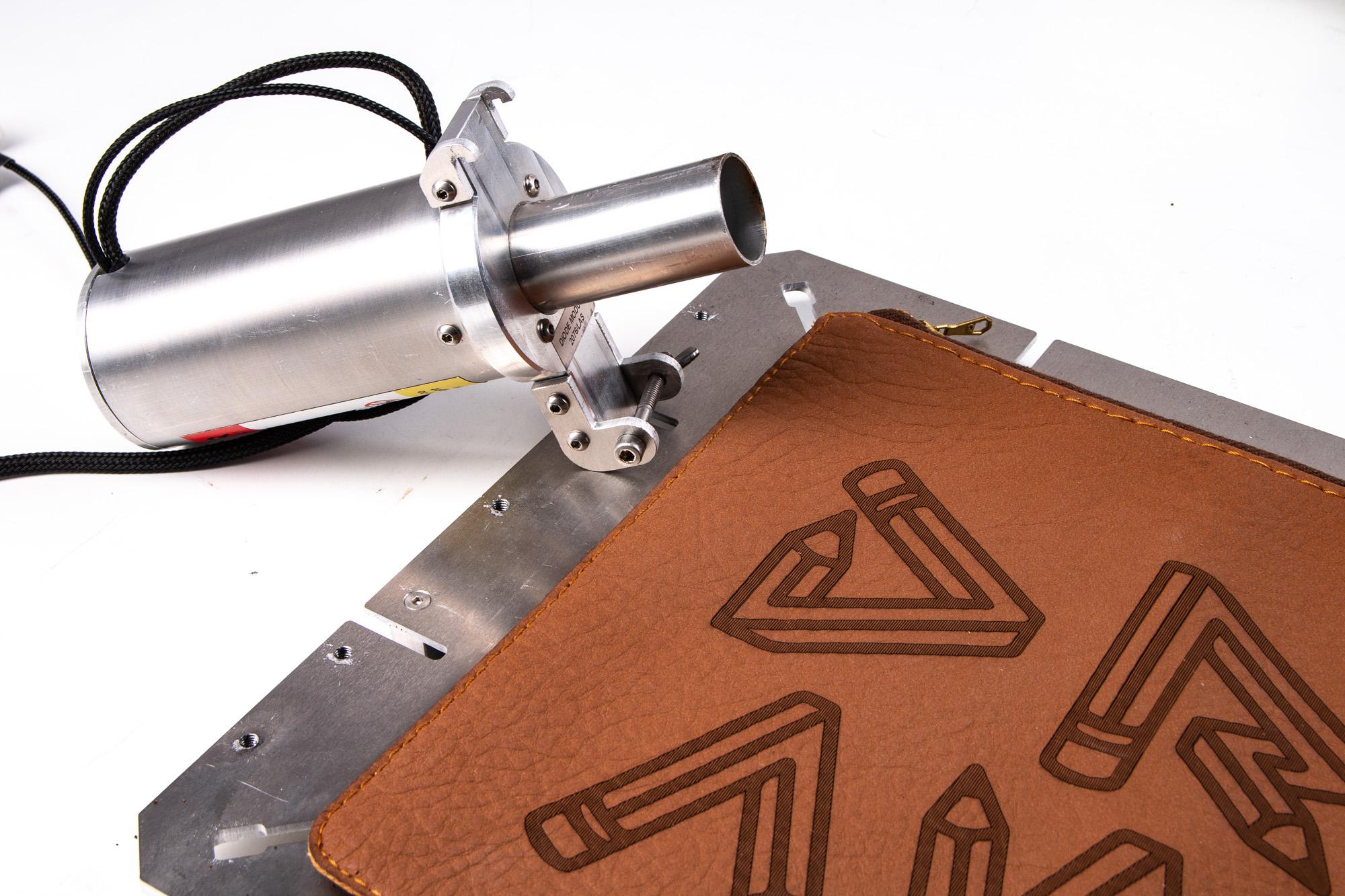
The global laser cutting equipment market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for precision manufacturing across industries such as automotive, textiles, and consumer goods. According to Grand View Research, the global laser cutting machine market size was valued at USD 3.5 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030. A key contributor to this expansion is the rising adoption of laser technology in leather processing, where accuracy, speed, and automation are critical. In particular, the leather goods sector—spanning luxury fashion, footwear, and automotive interiors—has accelerated its shift toward laser-based cutting solutions to reduce material waste and improve design flexibility. As highlighted by Mordor Intelligence, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a dominant player in this space, fueled by industrial modernization and growing manufacturing output in countries like China and India. With such strong market tailwinds, identifying the leading laser leather cutter manufacturers becomes essential for businesses aiming to enhance production efficiency and maintain competitive advantage.
Top 10 Laser Leather Cutter Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 International Laser Marking Machine Manufacturer & Supplier …
Domain Est. 2015
Website: hunstlaser.com
Key Highlights: Hunst Laser. Co., Ltd is a well- recognized laser technology leader in China laser marking machine industry. Our focus is on top-notch laser cutting machine, ……
#2 Custom Leather Laser Cutter Manufacturer Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2016
Website: kasulaser.com
Key Highlights: Kasu is a professional custom leather laser cutting machine manufacturer for more than 12 years. Our machines are widely recognized for delivering various ……
#3 Fiber Laser Cutting Machine and CO2 Laser Cutter Manufacturer …
Domain Est. 2016
Website: gwklaser.com
Key Highlights: Leading manufacturer of laser cutting machine, CO2 laser cutter, laser welding machine, laser bending machine and laser cleaning machine, etc….
#4 Leather Cutting Machine Manufactures and Suppliers
Domain Est. 2017
Website: cklasermachine.com
Key Highlights: CKLASER is one of the leading manufacturers and suppliers of leather cutting machine. Top quality, great selection and expert advice are our main ……
#5 Laser Engraving & Cutting Leather
Domain Est. 1997
Website: epiloglaser.com
Key Highlights: Laser machines for engraving and cutting leather. Epilog Laser machines save you time and expand your creative options when working with ……
#6 Laser engraving and cutting leather
Domain Est. 2002
Website: troteclaser.com
Key Highlights: Laser engraver and cutter for fine engravings and delicate cuts on natural leather, buckskin or suede. Get more information now!…
#7 Laser engravers & laser cutters
Domain Est. 2007
Website: gravotech.us
Key Highlights: Our laser tables are designed to engrave, mark and cut on a wide variety of materials (plastic, wood, metal, leather, glass, paper, stone) and shapes….
#8 Leather Laser Engraving
Domain Est. 2010
Website: thunderlaser.com
Key Highlights: Unleash your creativity with the Thunder Laser machine for leather laser engraving. Achieve precision and intricate designs on laser leather….
#9 Leather Laser Cutter
Domain Est. 2011
Website: brmlasers.com
Key Highlights: Laser cutting and engraving of leather – Suitable for all leathers ✓ Fast processing ✓ Great for engravings | BRM Lasers….
#10 Best Laser Cutting and Engraving Machine, Metal …
Domain Est. 2014
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Leather Cutter

2026 Market Trends for Laser Leather Cutters
Rising Demand in Customization and Personalization
By 2026, the global market for laser leather cutters is expected to be significantly driven by increasing consumer demand for customized and personalized leather goods. From monogrammed handbags and bespoke footwear to personalized wallets and accessories, laser cutting enables high-precision engraving and intricate designs at scale. The integration of digital design platforms with laser systems allows small and medium enterprises (SMEs) and individual artisans to offer made-to-order products, supporting the growing trend of mass customization in fashion and luxury markets.
Expansion in the Fashion and Luxury Sectors
The fashion and luxury leather goods industries are adopting laser cutting technology to achieve complex patterns, textures, and detailing that traditional cutting methods cannot replicate. By 2026, major fashion houses and emerging designers are expected to rely heavily on laser systems for prototyping and production, reducing material waste and increasing design flexibility. This adoption is further accelerated by sustainability goals, as laser cutting minimizes excess material usage and improves production efficiency.
Advancements in Automation and Smart Manufacturing
Automation is a key trend shaping the 2026 landscape for laser leather cutters. Integration with Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software enables seamless workflow from concept to production. Additionally, AI-powered optimization algorithms are enhancing cutting paths and nesting efficiency, reducing cycle times and energy consumption. Smart laser systems with IoT connectivity allow for remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and real-time quality control, improving uptime and reducing operational costs for manufacturers.
Growth in E-Commerce and On-Demand Production
The booming e-commerce sector, especially in niche leather goods, is fueling demand for agile, on-demand manufacturing. Laser leather cutters are central to this shift, enabling rapid turnaround of small batches and unique designs without extensive tooling. By 2026, more online retailers and direct-to-consumer (DTC) brands are anticipated to invest in in-house laser cutting capabilities or partner with digital manufacturing hubs to offer faster delivery and greater product variety.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Material Trends
As environmental consciousness grows, the leather industry is shifting toward sustainable and alternative materials such as bio-based leathers, recycled leather, and lab-grown options. Laser cutters are proving highly effective in processing these delicate and often non-uniform materials with minimal fraying or damage. By 2026, manufacturers are expected to prioritize laser systems that support eco-friendly production, aligning with circular economy principles and regulatory requirements in key markets like the EU and North America.
Regional Market Expansion and Emerging Economies
While North America and Western Europe remain strong markets, Asia-Pacific—particularly countries like India, Vietnam, and Indonesia—is expected to see rapid growth in laser leather cutter adoption by 2026. This is driven by expanding leather goods manufacturing, rising disposable incomes, and government support for technological modernization in the textile and accessories sectors. Additionally, increased access to affordable mid-range laser systems is empowering local artisans and startups to enter the global market.
Technological Innovation: Faster, Smaller, and Smarter Machines
By 2026, laser cutter technology will continue to evolve with higher power efficiency, improved beam quality (especially fiber and CO₂ hybrid systems), and compact desktop models suitable for small workshops. Innovations such as real-time vision systems and material recognition software will allow automatic adjustment of cutting parameters, enhancing precision and reducing operator dependency. These advancements will lower entry barriers and broaden the user base beyond industrial manufacturers to include hobbyists and educational institutions.
Conclusion
The 2026 market for laser leather cutters is poised for robust growth, driven by customization trends, digital manufacturing, sustainability initiatives, and global market expansion. As technology becomes more accessible and intelligent, laser cutting will remain a cornerstone of innovation in the leather and fashion industries, enabling faster, cleaner, and more creative production methods worldwide.
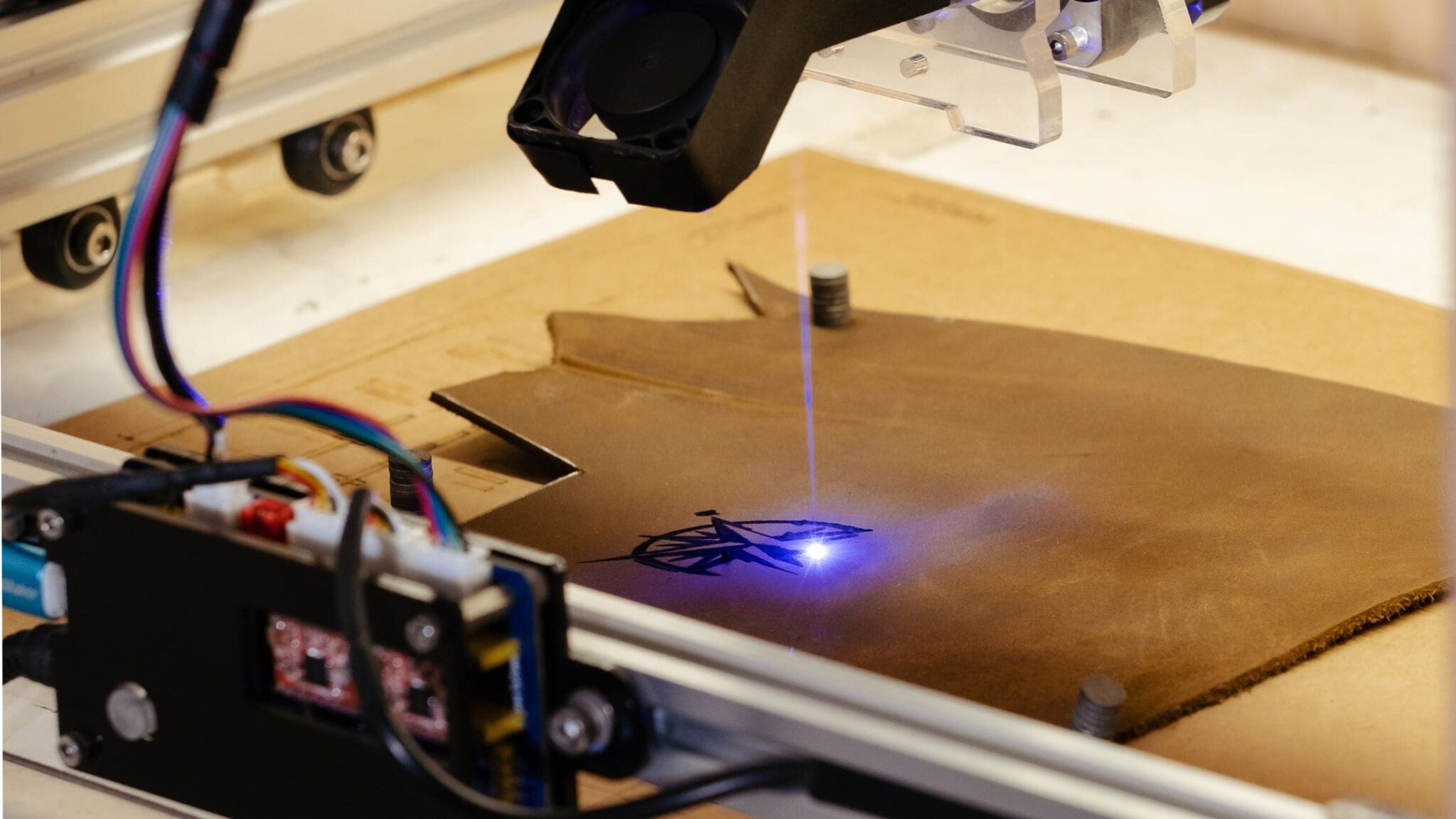
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Laser Leather Cutter (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing a laser leather cutter, especially from international suppliers, involves navigating several critical risks related to both product quality and intellectual property protection. Being aware of these pitfalls can help avoid costly mistakes and legal complications.
Poor Build Quality and Component Selection
Many low-cost laser cutters, particularly those from less reputable manufacturers, use substandard materials and components. This includes flimsy frames prone to misalignment, underpowered or unstable laser sources, and low-grade optics that degrade quickly. Such issues lead to inconsistent cutting performance, frequent breakdowns, and shortened machine lifespan, ultimately increasing total cost of ownership.
Inaccurate or Overstated Specifications
Suppliers may exaggerate key performance metrics such as laser power, cutting speed, or maximum work area. For example, a machine advertised as a “100W CO2 laser” might actually deliver significantly less effective power due to inefficient drivers or cooling. This misrepresentation can result in the machine failing to handle intended leather thicknesses or production volumes, undermining operational efficiency.
Lack of Safety and Compliance Certifications
Reputable laser systems should meet international safety standards such as CE, FDA, or IEC 60825. However, some suppliers provide counterfeit or self-issued certifications. Machines without proper safety interlocks, ventilation integration, or laser shielding pose serious risks to operators and may be illegal to operate in regulated markets.
Insufficient After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Many overseas suppliers offer limited technical support, delayed response times, or no local service network. When a critical component fails, obtaining replacements can take weeks or months, leading to costly production downtime. Additionally, some manufacturers use proprietary parts that are difficult or expensive to source independently.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Purchasing a laser cutter that incorporates copied designs, software, or patented technologies exposes buyers to legal liability. Some suppliers reverse-engineer leading brands’ systems and sell them at lower prices. Using such equipment could result in cease-and-desist orders, fines, or reputational damage, especially if your business operates in IP-sensitive regions like the EU or North America.
Hidden Software Limitations and Licensing Issues
The control software bundled with budget machines may include restrictive licensing, limited functionality, or embedded malware. Some systems lock users into proprietary software platforms or require recurring subscription fees. Others may use unlicensed copies of popular software like LightBurn, creating compliance risks for the end user.
Inadequate Documentation and Language Barriers
Poorly translated manuals, missing technical documentation, or lack of English-language support hinder setup, maintenance, and troubleshooting. This increases reliance on the supplier for basic operations and can lead to improper use, reducing machine performance and safety.
Failure to Verify IP Ownership and Design Originality
Buyers often neglect to investigate whether the supplier holds legitimate rights to the technology they’re selling. Without due diligence—such as checking patents, requesting IP declarations, or verifying trademarks—companies risk acquiring equipment that infringes on third-party rights, potentially leading to supply chain disruptions or litigation.
By carefully evaluating suppliers, requesting third-party certifications, conducting factory audits, and consulting legal experts on IP matters, businesses can mitigate these risks and source a reliable, compliant laser leather cutting solution.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Leather Cutter
Product Classification & Identification
Determine the correct Harmonized System (HS) Code for the laser leather cutter based on technical specifications such as laser power, dimensions, and intended use. Typical classifications fall under HS Code 8456 (machines for working metal, stone, ceramics, etc., using laser or other thermal processes). Accurate classification ensures proper duty assessment and regulatory compliance during international shipping.
Import/Export Regulations
Verify export controls applicable to laser equipment, particularly under dual-use regulations such as the Wassenaar Arrangement. High-powered lasers may require export licenses depending on destination country. Check U.S. Department of Commerce (BIS) or equivalent national authority requirements. Import regulations, including conformity assessments and labeling, must be met in the destination country.
Safety & Technical Standards Compliance
Ensure the laser leather cutter complies with international safety standards such as:
– IEC 60825-1: Safety of laser products (laser radiation)
– IEC 61010-1: Safety requirements for electrical equipment for measurement, control, and laboratory use
– CE Marking (for EU market) indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards
– FDA/CDRH compliance (U.S.) for laser radiation safety, including reporting and product certification
Packaging & Shipping Requirements
Package the laser cutter securely using shock-absorbing materials and a rigid outer crate. Include moisture barriers if shipping through humid environments. Clearly label packages with:
– “Fragile”
– “This Side Up”
– Laser warning symbols
– Handling instructions per IATA/IMDG regulations if batteries (e.g., for control systems) are included
Transportation & Freight Documentation
Prepare comprehensive shipping documentation, including:
– Commercial Invoice (detailing value, quantity, and HS code)
– Packing List
– Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
– Certificate of Conformity (if required)
– Export License (if applicable)
– Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for any hazardous components (e.g., laser gases or coatings)
Customs Clearance Procedures
Submit all required documents to customs authorities in both origin and destination countries. Provide technical specifications to support HS code classification. Be prepared for customs inspections, especially for high-value or regulated equipment. Use a licensed customs broker if unfamiliar with local requirements.
Environmental & Disposal Compliance
Adhere to environmental regulations related to electronic waste (WEEE Directive in EU) and hazardous materials. Provide customers with end-of-life disposal instructions. Ensure all components comply with RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) directives regarding lead, mercury, cadmium, and other restricted substances.
Warranty & After-Sales Support Logistics
Establish a clear process for handling warranty claims, spare parts distribution, and technical support. Maintain an inventory of critical components in key regional hubs to reduce downtime. Document compliance with local consumer protection laws regarding warranty periods and service availability.
Training & User Documentation
Supply comprehensive user manuals in the local language of the destination market, including:
– Safety instructions
– Laser operation and maintenance
– Emergency shutdown procedures
– Compliance statements (CE, FCC, etc.)
Ensure documentation meets regulatory requirements for technical equipment in the target market.
Risk Management & Insurance
Insure shipments against damage, loss, or delay during transit. Assess liability risks associated with laser operation and ensure product liability insurance covers international sales. Maintain records of compliance audits, safety certifications, and shipping logs for traceability and regulatory inspections.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Laser Leather Cutter
After thorough evaluation of technical specifications, supplier reliability, cost-efficiency, and long-term operational needs, sourcing a laser leather cutter represents a strategic investment in precision, productivity, and product quality. The selected machine offers advanced cutting accuracy, consistent performance on various leather types, and integration capabilities with existing design software, enhancing overall manufacturing efficiency.
By choosing a reputable supplier with strong after-sales support, warranty coverage, and training services, the risks associated with downtime and maintenance are minimized. Additionally, energy efficiency and scalability options ensure the machine aligns with both current production demands and future growth.
In conclusion, procuring a high-quality laser leather cutter not only improves manufacturing capabilities but also strengthens competitive advantage by enabling intricate designs, reducing material waste, and accelerating production timelines. This acquisition supports innovation and excellence in leather product development, positioning the business for sustained success in a dynamic market.