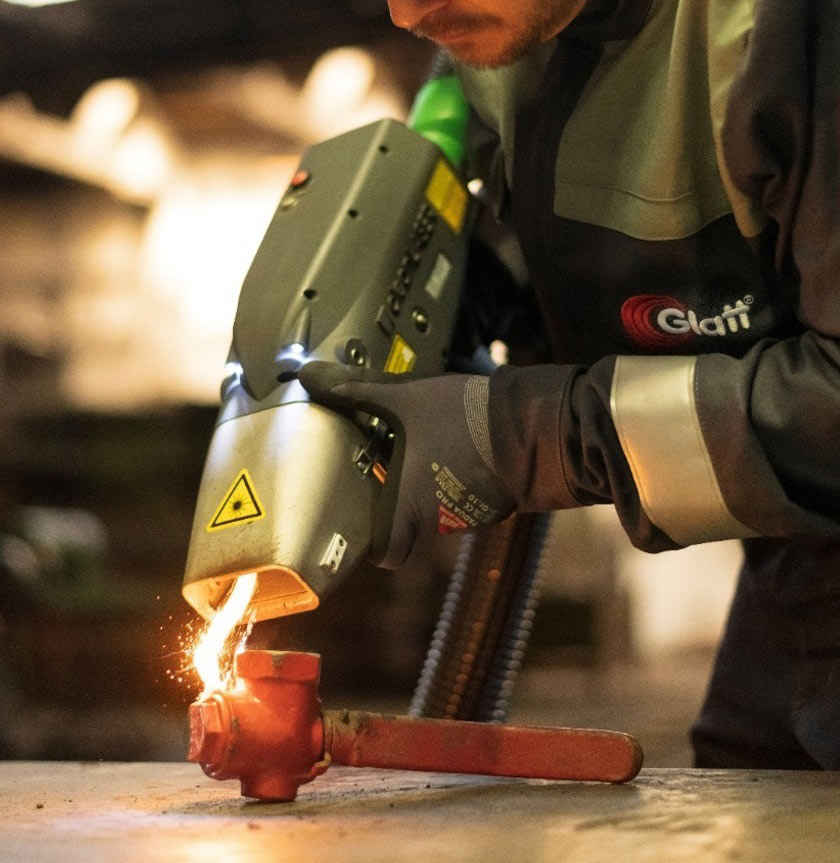
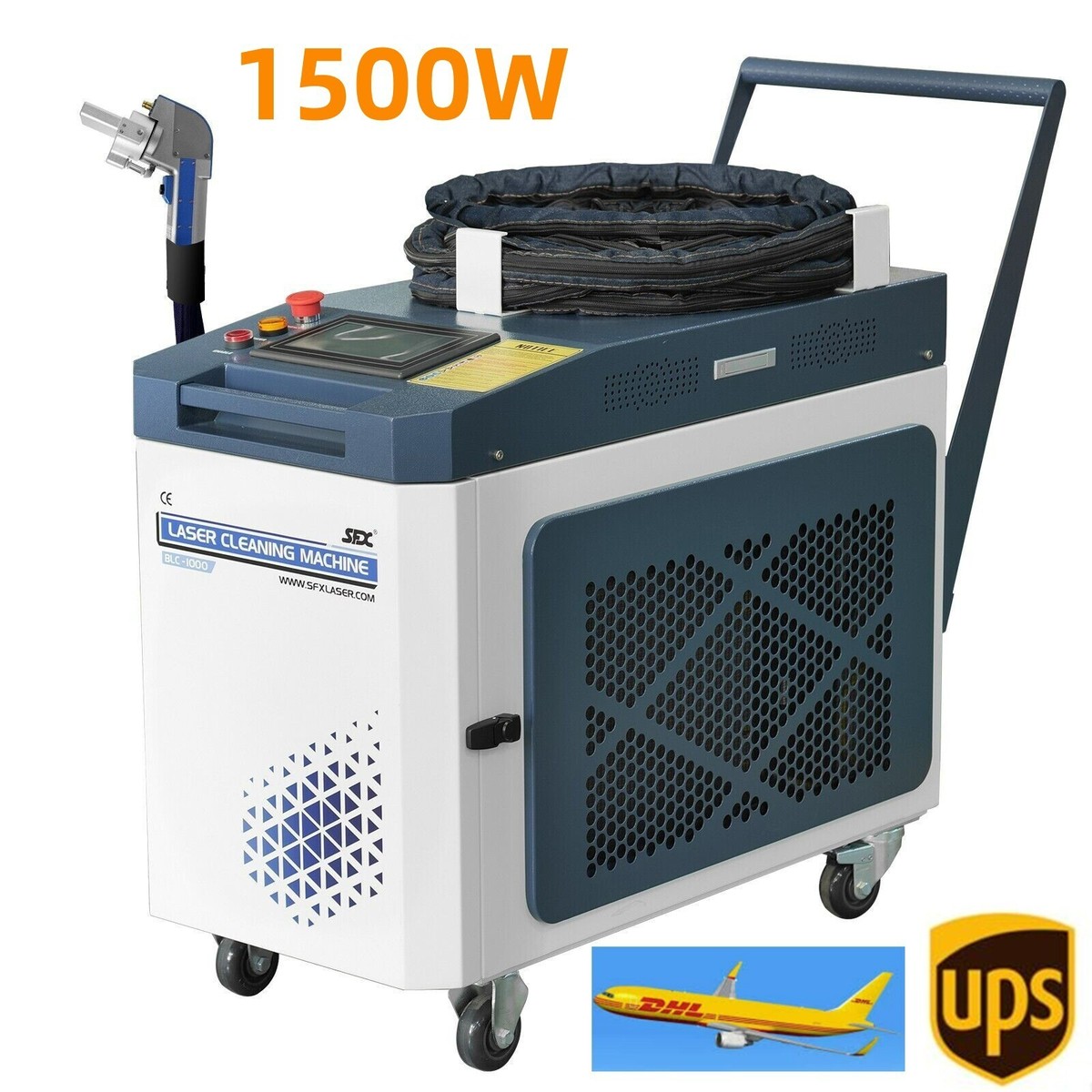
The global laser paint stripping market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for precision surface preparation in aerospace, automotive, and historical restoration applications. According to Grand View Research, the global laser cleaning market—of which paint stripping is a major segment—was valued at USD 1.4 billion in 2023 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 21.6% from 2024 to 2030. This surge is fueled by the shift toward eco-friendly, chemical-free cleaning technologies and the superior accuracy of laser systems compared to traditional sandblasting or solvent-based methods. As industries prioritize safety, efficiency, and sustainability, investment in advanced laser solutions continues to rise. In this evolving landscape, several manufacturers have emerged as leaders, offering high-performance systems tailored for industrial paint removal. Below are the top nine laser manufacturers at the forefront of innovation, reliability, and market presence in the paint stripping sector.
Top 9 Laser For Stripping Paint Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laserax
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Laserax works with the world’s leading manufacturers to implement laser cleaning, welding, texturing, and marking solutions….
#2 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: we engineer and manufacture the most advanced—and most powerful—pulsed industrial laser cleaning systems on the market, built for both manual and automated ……
#3 Laser Photonics
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser Photonics manufactures reliable, safe, and eco-friendly Laser Cleaning, Laser Cutting, Laser Engraving, Laser Marking, and Laser Welding solutions….
#4 Clean Laser Systems
Website: cleanlaser.de
Key Highlights: Our laser systems are primarily in operation with mold and tool cleaning, paint stripping and decoating as well as cleaning and modification of metallic ……
#5 Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: Explore PULSAR Laser P CL laser cleaning machines for industrial rust removal and paint stripping. Compare SHARK P CL, PANDA P CL and FOX P CL….
#6 Industrial 1500W 2000W CW Laser Cleaning Machine Rusty Remove
Website: xinglaser.com
Key Highlights: In stockXING Laser (6am Life LLC, DBA XING Laser) specializes in the development and manufacture of high-performance handheld laser cleaning and rust removal equipment….
#7 Laser Paint Removal
Website: keyence.com
Key Highlights: Laser marking paint removal can quickly and effectively remove layers of paint or plating from plastics, metals, and other surfaces….
#8 Laser Cleaning
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaning is used across a variety of industries to remove unwanted surface materials like coatings, paints, rust, oil, and for surface preparation for ……
#9 Laser Coating Removal Solutions for Industry
Website: surclean.com
Key Highlights: SurClean manufactures laser coating removal and surface preparation equipment that is precise, safe and clean….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser For Stripping Paint
2026 Market Trends for Laser for Stripping Paint
The global market for laser-based paint stripping technologies is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in industrial automation, environmental regulations, and growing demand for precision surface preparation. This analysis explores key trends shaping the Laser for Stripping Paint market through the H2 (second half) of 2026, highlighting technological, economic, and regional developments.
Rising Adoption in Aerospace and Defense
By H2 2026, the aerospace and defense sector is expected to be the dominant adopter of laser paint stripping systems. Stringent maintenance protocols, the need for non-destructive surface treatment, and lifecycle extension of aircraft fleets are accelerating the shift from chemical and abrasive methods to laser ablation. Laser systems offer precise control, minimizing substrate damage—critical for sensitive composites and aluminum alloys used in modern aircraft. Defense contractors are increasingly investing in automated laser stripping cells to enhance efficiency and reduce downtime during maintenance cycles.
Growth Driven by Environmental and Regulatory Pressures
Environmental regulations across North America, Europe, and parts of Asia-Pacific are tightening restrictions on volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and hazardous waste generated by traditional paint removal techniques. By H2 2026, laser paint stripping will gain broader acceptance as a clean, chemical-free alternative. Regulatory bodies such as the U.S. EPA and EU REACH are incentivizing green technologies, pushing manufacturers in automotive, shipbuilding, and infrastructure to adopt laser systems. This regulatory tailwind is expected to boost market penetration, especially in environmentally sensitive regions.
Technological Advancements and Cost Reduction
In H2 2026, laser systems for paint stripping will benefit from innovations in fiber laser technology, improved beam control, and integration with AI-driven robotics. These advancements enhance stripping speed, adaptability to complex geometries, and operational efficiency. Moreover, declining costs of high-power lasers and increased competition among suppliers are making laser systems more accessible to mid-sized enterprises. Portable and handheld laser stripping devices are also gaining traction, enabling field applications in construction and heritage restoration.
Expansion in Automotive and Marine Industries
The automotive and marine sectors are emerging as high-growth markets for laser paint removal. OEMs and refinishers are adopting laser systems for pre-paint surface preparation, corrosion removal, and restoration of vintage vehicles. In marine applications, lasers are being used to strip anti-fouling coatings from ship hulls without damaging protective layers—reducing dry-docking time and environmental impact. By H2 2026, increased awareness and proven ROI are expected to drive wider deployment in these industries.
Regional Market Dynamics
North America and Europe will remain at the forefront of laser paint stripping adoption, supported by strong industrial bases and environmental policies. However, Asia-Pacific—particularly China, Japan, and South Korea—is projected to witness the fastest growth in H2 2026. Expanding aerospace manufacturing, shipbuilding capacity, and government initiatives promoting smart manufacturing are fueling demand. Local manufacturers are also beginning to develop cost-competitive laser systems, reducing reliance on imports.
Challenges and Outlook
Despite positive momentum, challenges persist, including high initial investment, skilled labor requirements, and safety concerns related to laser operation. However, by H2 2026, improved training programs, modular system designs, and leasing models are helping to lower entry barriers. Overall, the global laser for stripping paint market is expected to grow at a CAGR of over 10% leading into 2026, with H2 marking a pivotal phase of mainstream industrial integration and technological maturation.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Lasers for Stripping Paint: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
When sourcing laser systems for paint stripping applications—commonly used in aerospace, automotive restoration, and heritage conservation—organizations often encounter critical pitfalls related to equipment quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these factors can result in operational inefficiencies, safety hazards, legal complications, and financial loss.
Poor Quality and Performance Issues
One of the most prevalent challenges is acquiring low-quality laser equipment that fails to deliver consistent or safe performance. Key quality-related pitfalls include:
- Substandard Components: Some suppliers use inferior optical components, cooling systems, or power supplies to cut costs. This can lead to frequent breakdowns, reduced efficiency, and inconsistent paint removal, especially on sensitive substrates like aircraft aluminum or historic woodwork.
- Inadequate Safety Features: High-powered lasers used in paint stripping pose serious safety risks. Low-quality systems may lack essential safety interlocks, proper beam shielding, or compliance with international laser safety standards (e.g., IEC 60825).
- Lack of Calibration and Testing Data: Reputable suppliers provide detailed calibration reports and performance validation. Without this, users cannot verify the laser’s power output, beam quality (M² factor), or pulse stability—critical for effective and safe paint removal.
- Insufficient Technical Support and Training: Poor after-sales service and inadequate operator training increase the risk of improper use, which can damage substrates or create safety incidents.
Intellectual Property (IP) and Legal Risks
Sourcing lasers from unverified or offshore suppliers introduces significant intellectual property and legal concerns:
- Counterfeit or Unlicensed Technology: Some manufacturers may incorporate patented technologies (e.g., specific laser diodes, control algorithms, or beam delivery systems) without proper licensing. Purchasing such systems may expose the buyer to infringement liabilities, especially in regulated industries.
- Ambiguous IP Ownership in Custom Solutions: When commissioning customized laser systems, failure to define IP ownership in contracts can result in disputes. For example, process improvements developed during integration may not be legally owned by the buyer.
- Export Control and Compliance Gaps: Laser systems, particularly those with high power or specific wavelengths, may be subject to export control regulations (e.g., ITAR in the U.S. or dual-use controls in the EU). Sourcing from non-compliant suppliers can lead to customs delays, fines, or legal action.
- Lack of Documentation and Traceability: Reputable suppliers provide full technical documentation, software source code (if applicable), and component traceability. Absence of such documentation can hinder regulatory audits and invalidate warranties, especially in aerospace or defense sectors.
To mitigate these risks, organizations should conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers—verifying certifications (e.g., ISO 9001), requesting third-party test reports, and engaging legal counsel to review IP and compliance clauses in procurement contracts. Ensuring quality and protecting IP from the outset safeguards both operational success and long-term liability.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser for Stripping Paint
Overview of Laser Paint Stripping Technology
Laser paint stripping is a non-abrasive, environmentally friendly method for removing coatings from surfaces such as metal, composites, and concrete. It uses high-intensity laser beams to ablate paint without damaging the underlying substrate. Due to its precision and reduced waste, it is increasingly used in aerospace, automotive, and maritime industries. However, its deployment involves specific logistics and regulatory compliance considerations.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Laser systems used for paint stripping are subject to multiple regulatory frameworks depending on the country and application. Key compliance areas include:
- Laser Safety (IEC 60825 / FDA 21 CFR): Lasers must meet international safety standards for classification, labeling, and operational controls. Users must implement engineering controls (e.g., interlocks, beam enclosures) and administrative controls (e.g., training, access restriction).
- Occupational Health & Safety (OSHA, EU-OSHA): Employers must conduct risk assessments for laser radiation, fumes, and noise. Personal protective equipment (PPE), including laser safety goggles and respiratory protection, is mandatory.
- Hazardous Waste Management (EPA, RCRA, EU Waste Framework Directive): Although laser stripping generates less waste than sandblasting, the removed paint particles may contain hazardous materials (e.g., lead, chromates). These residues must be classified, collected, and disposed of according to hazardous waste regulations.
- Air Emissions (EPA NESHAP, EU Industrial Emissions Directive): Fumes and particulates generated during laser ablation require capture and filtration via HEPA and/or activated carbon systems. Emission levels must comply with local air quality standards.
- Equipment Certification: Mobile or industrial laser units may require CE marking (EU), FCC compliance (USA), or other regional certifications.
Transportation and Logistics
Proper handling, packaging, and transport are critical due to the sensitive nature of laser systems:
- Packaging: Lasers and associated components must be shipped in shock-resistant, moisture-proof containers with protective cushioning. Optics and cooling systems require special handling.
- Transport Mode: Ground transport is typical for domestic shipments; air freight may be used internationally but requires compliance with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations (e.g., for lithium batteries in portable units).
- Import/Export Controls: High-power lasers may be subject to export controls under ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations) or EAR (Export Administration Regulations) if used in defense applications. Export licenses may be required.
- Customs Documentation: Accurate HS codes (e.g., 8543.70 for laser systems), commercial invoices, and technical specifications are required. Declare any restricted components (e.g., high-energy lasers).
On-Site Handling and Installation
- Site Assessment: Verify electrical supply (voltage, grounding), ventilation, space clearance, and structural stability. Ensure fire suppression systems are in place.
- Installation Team: Use certified technicians for setup. Align laser components and test safety systems before operation.
- Permitting: Check local requirements for industrial laser use, especially in urban or environmentally sensitive zones. Permits may be needed for emissions or noise.
Operational Compliance and Monitoring
- Training and Certification: Operators must be trained in laser safety (e.g., ANSI Z136.1 compliance) and emergency procedures. Maintain training records.
- Fume Extraction: Monitor filtration system performance regularly. Replace filters as needed and log maintenance.
- Waste Tracking: Label and store waste in sealed, compliant containers. Maintain manifests for disposal and ensure use of licensed waste handlers.
- Inspections and Audits: Conduct routine safety audits and document compliance with internal and external standards.
Decommissioning and End-of-Life Management
At end-of-life, laser systems must be decommissioned responsibly:
– Data Wiping: Remove any operational or calibration data from control units.
– Hazardous Components: Separate batteries, coolants, and electronic boards for proper recycling (e.g., WEEE Directive in the EU).
– Recycling and Disposal: Partner with certified e-waste recyclers. Document disposal to meet environmental reporting requirements.
Summary
Effective logistics and compliance for laser paint stripping systems require a proactive approach across the equipment lifecycle—from import and transport to operation and disposal. Adherence to safety, environmental, and regulatory standards ensures operational legality, protects personnel, and minimizes environmental impact. Always consult local regulations and involve compliance officers early in deployment planning.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Laser for Paint Stripping:
After evaluating various options, laser technology emerges as a highly efficient, precise, and environmentally friendly solution for paint stripping compared to traditional methods such as sandblasting, chemical removers, or media blasting. Lasers offer non-contact surface cleaning, minimal substrate damage, reduced waste generation, and improved operator safety, making them ideal for sensitive materials and regulated industries such as aerospace, automotive restoration, and cultural heritage conservation.
When sourcing a laser system for paint stripping, key considerations include laser type (typically fiber or pulsed lasers), power output, portability, automation capabilities, and compliance with safety standards. While the initial investment is higher than conventional methods, the long-term benefits—such as lower operational costs, reduced downtime, and elimination of hazardous chemicals—justify the cost for high-value or repetitive applications.
Ultimately, sourcing a laser for paint stripping should be guided by specific application requirements, material compatibility, and return on investment. Partnering with reputable suppliers offering technical support, training, and service maintenance further ensures optimal performance and integration into existing workflows. With the right system in place, laser paint stripping represents a sustainable, scalable, and future-ready solution for modern surface preparation needs.