The global laser engraving market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for precision marking and personalization across industries such as automotive, electronics, healthcare, and consumer goods. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global laser marking and engraving machines market was valued at USD 2.65 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach USD 4.17 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 7.6% during the forecast period. This expansion is fueled by advancements in fiber laser technology, rising automation in manufacturing processes, and growing adoption in emerging economies. As industries prioritize permanent, high-speed, and non-contact marking solutions, the need for reliable and innovative laser engraving equipment has surged. In this competitive landscape, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders, combining technical expertise, product versatility, and global reach to meet evolving market demands. Based on technological capabilities, market presence, customer reviews, and shipment volumes, the following overview highlights the top 10 laser engraving products manufacturers shaping the industry’s future.
Top 10 Laser Engraving Products Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Universal Laser Systems
Domain Est. 1996
Website: ulsinc.com
Key Highlights: Discover our process and products to build your ideal laser system. Learn More. Begin exploring what’s possible with advanced laser technology. Contact us….
#2 Rowmark
Domain Est. 1997
Website: rowmark.com
Key Highlights: With over 30 years experience Rowmark is the premier sign plastic manufacturer in the world. Manufactured with you in mind. Tough. Tested. Trusted….
#3 Trotec Laser
Domain Est. 2002
Website: troteclaser.com
Key Highlights: Trotec is a leading international laser manufacturer and makes the work of laser users easier, faster and more profitable….
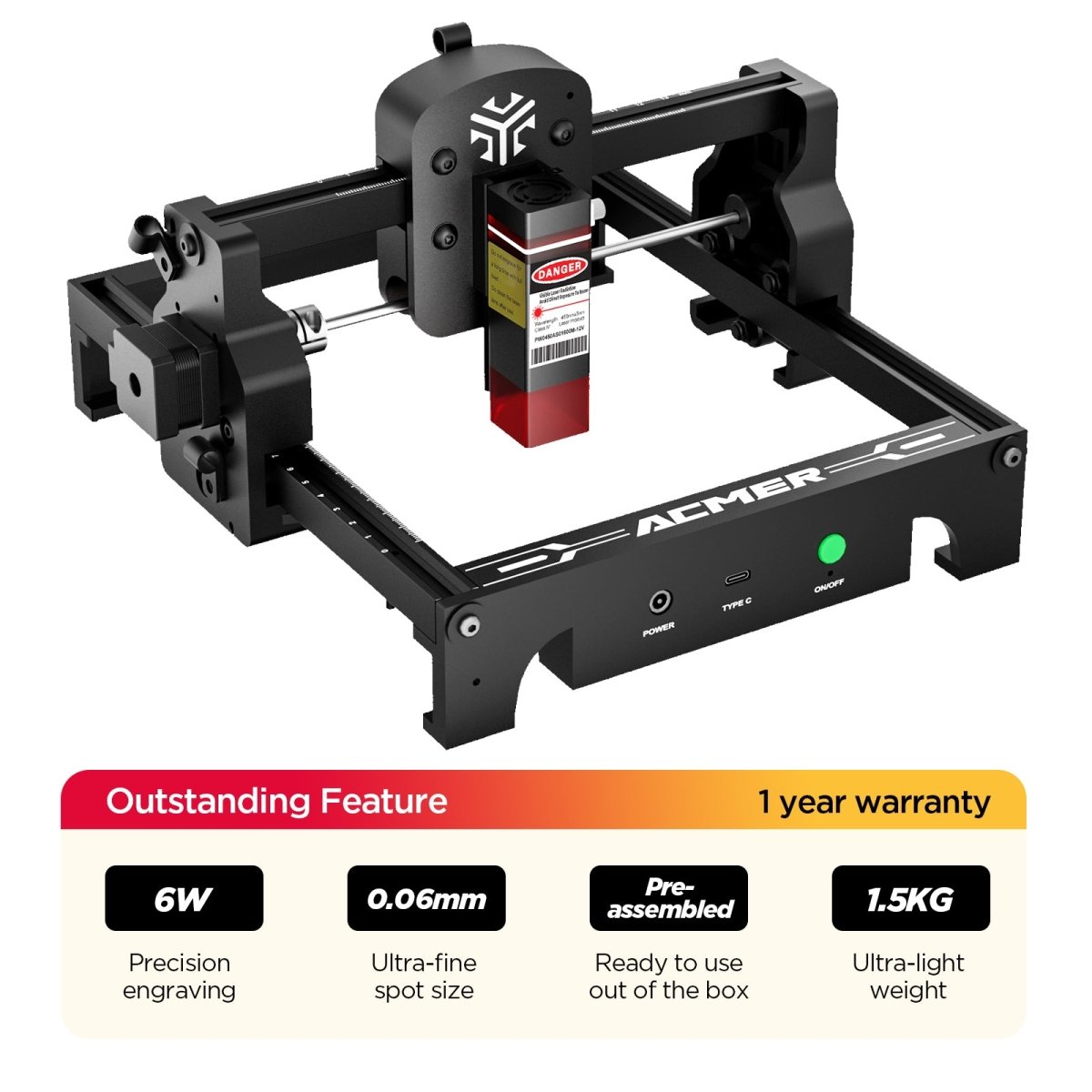
#4 ACMER
Domain Est. 2023
Website: acmerlaser.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery 30-day returnsACMER is committed to top laser technology, it is equipped with the world’s first corexy laser engraving machine and the world’s first Gantry dual laser…
#5 MECCO
Domain Est. 1996
Website: mecco.com
Key Highlights: Our expertise in automated laser engraving and pin marking systems encompasses a comprehensive range of solutions for your industry, materials, and ……
#6 Laser engravers & laser cutters
Domain Est. 2007
Website: gravotech.us
Key Highlights: Our laser tables are designed to engrave, mark and cut on a wide variety of materials (plastic, wood, metal, leather, glass, paper, stone) and shapes….
#7 Full Spectrum Laser
Domain Est. 2010
#8 Laser Engraving, Laser Etching, Laser Marking, Laser Cutting …
Domain Est. 2010
Website: innotech-laser.com
Key Highlights: We offer product decorating, engraving, cutting, annealing, and etching, as well as cylindrical printing and full-color UV-cured prints….
#9 Laser Cutting, Engraving & Marking Machines
Domain Est. 2010
Website: thunderlaser.com
Key Highlights: Thunder Bolt Plus. The best home desktop laser engraving machine. Up to 1500mm/s speed and a design so small that just two people can easily lift it….
#10 Glowforge: Your At
Domain Est. 2014
Website: glowforge.com
Key Highlights: Glowforge’s lasers use a beam of light the width of a human hair to precisely cut, engrave, and score hundreds of materials up to ½” thick….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Engraving Products

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Laser Engraving Products
The global laser engraving products market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, expanding industrial applications, and growing demand across diverse sectors. Key trends shaping the market include increased automation, miniaturization of laser systems, rising adoption in small and medium enterprises (SMEs), and a shift toward eco-friendly manufacturing processes.
-
Technological Advancements and Smart Integration
By 2026, laser engraving systems are expected to integrate more deeply with Industry 4.0 technologies. Features such as IoT-enabled monitoring, AI-driven design optimization, and cloud-based software platforms will enhance precision, reduce downtime, and streamline production workflows. Fiber and UV laser technologies will dominate due to their high efficiency, maintenance-free operation, and suitability for a wide range of materials including metals, plastics, and ceramics. -
Expansion into Consumer and Personalization Markets
The demand for personalized products—ranging from custom jewelry and electronics to promotional items and home décor—will continue to drive adoption of desktop and compact laser engravers. E-commerce platforms and on-demand manufacturing models will fuel this trend, with consumer-grade lasers becoming more affordable and user-friendly. -
Growth in Industrial and Automotive Applications
Industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics will increasingly rely on laser engraving for permanent part marking (PPM), traceability, and compliance with regulatory standards like UDI (Unique Device Identification) in medical devices. High-speed, high-precision laser systems will be critical for mass production environments. -
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Environmental concerns will push manufacturers to adopt energy-efficient laser systems with lower carbon footprints. Solid-state lasers, particularly fiber lasers, will gain preference over traditional CO2 lasers due to their higher energy efficiency and reduced need for consumables. -
Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific, especially China and India, will remain a key growth region due to rapid industrialization, government support for advanced manufacturing, and a booming electronics sector. Meanwhile, North America and Europe will focus on high-value applications in medical devices, luxury goods, and precision engineering. -
Competitive Landscape and Innovation
Market competition will intensify, with established players like TRUMPF, IPG Photonics, and Trotec Laser innovating to maintain market share. At the same time, new entrants offering cost-effective, open-source laser platforms will expand access to emerging markets and hobbyist communities.
In conclusion, by 2026, the laser engraving products market will be characterized by smarter, more accessible, and sustainable solutions, catering to both industrial scalability and personalized consumer needs. Companies that invest in innovation, digital integration, and green manufacturing will be best positioned to lead in this evolving landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Laser Engraving Products (Quality, IP)
Poor Build Quality and Component Selection
Many budget laser engravers use substandard materials such as thin or warped metal frames, low-grade belts, and undersized stepper motors. These components lead to misalignment, reduced precision, and premature mechanical failure. Inadequate cooling systems and unreliable power supplies further compromise longevity and performance, resulting in frequent downtime and higher total cost of ownership.
Inaccurate or Inconsistent Engraving Results
Low-cost machines often lack proper calibration and feature poor motion control systems, leading to inconsistent engraving depth, misaligned patterns, or distorted designs. Issues such as backlash in the drive system or flexible gantries reduce repeatability, making it difficult to produce professional-quality results—especially for intricate or high-volume work.
Misleading Laser Power Ratings
Suppliers sometimes exaggerate laser power (e.g., advertising a “10W” diode that actually delivers only 5–6W of optical output). This deceptive labeling affects cutting and engraving efficiency, particularly on harder materials. Always verify actual output power through independent reviews or testing, and request test samples before bulk purchasing.
Software Limitations and Compatibility Issues
Proprietary or outdated software bundled with laser engravers can restrict design flexibility, lack essential features (e.g., grayscale engraving, vector support), or fail to integrate with common design tools (e.g., Adobe Illustrator, Inkscape). Closed ecosystems may also prevent firmware updates or limit third-party control options like LightBurn, reducing usability and versatility.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks from Copycat Designs
Many low-cost laser engravers are direct clones of popular open-source or patented designs (e.g., derivatives of the K40 or open-core machines). Sourcing such products may expose buyers to legal liability, especially in regions with strict IP enforcement. Brands may also rebrand identical machines under multiple names, making it difficult to verify authenticity and support reliability.
Inadequate After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
OEMs from certain regions may offer limited technical support, slow response times, or no local service centers. Spare parts (e.g., laser tubes, lenses, control boards) might be difficult to source or incompatible with standard replacements, leading to extended downtime and increased operational costs.
Lack of Safety Certifications and Standards Compliance
Many imported laser engravers lack essential safety certifications (e.g., CE, FDA, FCC), indicating potential hazards such as insufficient laser shielding, poor electrical insulation, or inadequate emergency shutdown mechanisms. Using non-compliant equipment can violate workplace safety regulations and expose businesses to liability.
Hidden Costs from Frequent Maintenance and Repairs
While initial purchase prices may seem attractive, the total cost of ownership can escalate due to frequent replacements of consumables (lenses, mirrors, belts), repairs, and lost productivity. Poorly engineered systems require more user intervention and maintenance, undermining the value proposition of low upfront cost.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Engraving Products
Product Classification and HS Codes
Accurately classifying laser engraving machines and related products is crucial for international trade compliance. These products typically fall under Harmonized System (HS) codes related to industrial machinery and electronics. Common classifications include:
– 8456.11 or 8456.12: For laser engraving, cutting, or marking machines, depending on the type of laser (e.g., CO₂, fiber) and application.
– 8543.70: For certain laser diodes and optical components used in engraving systems.
– 9013.80: For laser pointers or non-industrial laser modules, if applicable.
Always verify the correct HS code based on the machine’s specifications and intended use, as misclassification can lead to customs delays, fines, or denied shipments.
Import/Export Regulations
Laser engraving products are subject to various import and export controls due to their use of laser technology and electronic components:
– Export Controls (e.g., EAR in the U.S.): Some laser systems may be classified under Export Administration Regulations (EAR), especially if they meet performance thresholds (e.g., power output, beam quality). Check if a license is required for destination countries.
– Import Duties and Taxes: Duties vary by country. Some nations impose additional tariffs on high-tech manufacturing equipment. Use the correct HS code to determine applicable rates.
– Restricted Destinations: Certain countries may restrict or prohibit the import of industrial laser equipment due to security or trade sanctions.
Ensure compliance with local regulations in both origin and destination countries by consulting with customs brokers or legal experts.
Safety and Technical Standards
Laser engraving machines must meet stringent safety and electromagnetic compatibility standards:
– Laser Safety (IEC 60825-1): Products must be classified according to laser class (typically Class 1 or 4), with appropriate labeling, interlocks, and protective housings.
– Electrical Safety (e.g., UL/CSA in North America, CE in Europe): Compliance with standards such as UL 61010-1 or EN 61010-1 ensures safe operation and reduces fire or shock risks.
– EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility): Machines must comply with FCC Part 15 (U.S.) or CE EMC Directive (EU) to prevent interference with other electronic devices.
Obtain necessary certifications before shipping and provide documentation (test reports, certificates) to customs and customers.
Packaging and Shipping Requirements
Proper packaging is essential to protect sensitive components during transit:
– Use anti-static materials and moisture barriers to safeguard electronic controls and laser sources.
– Securely fasten internal components to prevent movement during transport.
– Clearly label packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Laser Product” warnings.
– Include compliance labels (e.g., CE, FCC) on the product and packaging.
Choose freight carriers experienced in handling high-value technical equipment and consider insurance for full replacement value.
Documentation and Labeling
Accurate documentation ensures smooth customs clearance and regulatory compliance:
– Commercial Invoice with detailed product description, value, HS code, and country of origin.
– Packing List specifying contents, weights, and dimensions.
– Certificate of Origin, if required by trade agreements.
– Safety and Compliance Certificates (CE, FCC, RoHS, etc.).
– User manuals with safety instructions in the destination country’s language.
Label all units with required regulatory marks, laser classification, and technical specifications.
Environmental and Chemical Compliance
Laser engraving processes may generate fumes and waste requiring special handling:
– RoHS Compliance: Ensure all electronic components are free of restricted substances (e.g., lead, cadmium).
– REACH (EU): Declare substances of very high concern (SVHCs) if applicable.
– WEEE Directive: Provide take-back or recycling information for end-of-life equipment in Europe.
– Fume Extraction: Machines should include or be compatible with filtration systems compliant with local air quality regulations.
Communicate environmental compliance obligations to customers and distributors.
Warranty, Service, and After-Sales Compliance
Support international customers while meeting regional legal requirements:
– Clearly define warranty terms, including duration, coverage, and service procedures.
– Comply with local consumer protection laws (e.g., EU Consumer Rights Directive).
– Offer technical support in local languages and time zones.
– Maintain service parts inventory or partner with local technicians for repairs.
Ensure service personnel are trained on safety protocols, especially when handling Class 3B or Class 4 lasers.
Recordkeeping and Audits
Maintain comprehensive records for regulatory audits and traceability:
– Keep copies of export licenses, certificates, and shipping documents for at least 5 years (or as required by jurisdiction).
– Track product serial numbers and destinations for recalls or compliance investigations.
– Conduct periodic internal audits to verify adherence to logistics and compliance procedures.
Implement a document management system to streamline access and reporting.
In conclusion, sourcing laser engraving products requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, customization capabilities, and supplier reliability. It is essential to evaluate suppliers based on their technical expertise, production capacity, material compatibility, and adherence to industry standards. Whether sourcing for promotional items, industrial components, or personalized goods, partnering with experienced manufacturers—whether domestic or overseas—can significantly impact product consistency and customer satisfaction. Additionally, considering factors such as minimum order quantities, lead times, and post-sale support ensures a smoother supply chain process. By conducting thorough due diligence and maintaining clear communication with suppliers, businesses can effectively integrate high-quality laser-engraved products into their offerings, enhancing branding, functionality, and overall value.