The global laser cleaning equipment market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by increasing demand for eco-friendly, precision-based industrial cleaning solutions. According to Grand View Research, the market was valued at USD 568.3 million in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 22.4% from 2023 to 2030. This surge is fueled by the rising adoption of laser cleaning in automotive, aerospace, and heritage conservation sectors, where non-abrasive and chemical-free surface treatment is critical. As industries prioritize automation and sustainability, laser cleaning technology has emerged as a preferred alternative to traditional methods. With this accelerating demand, several manufacturers have distinguished themselves through innovation, reliability, and technological advancement. Here are the top 7 laser cleaning system manufacturers shaping the future of industrial cleaning.
Top 7 Laser Czyszczący Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laserax
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Laserax works with the world’s leading manufacturers to implement laser cleaning, welding, texturing, and marking solutions….
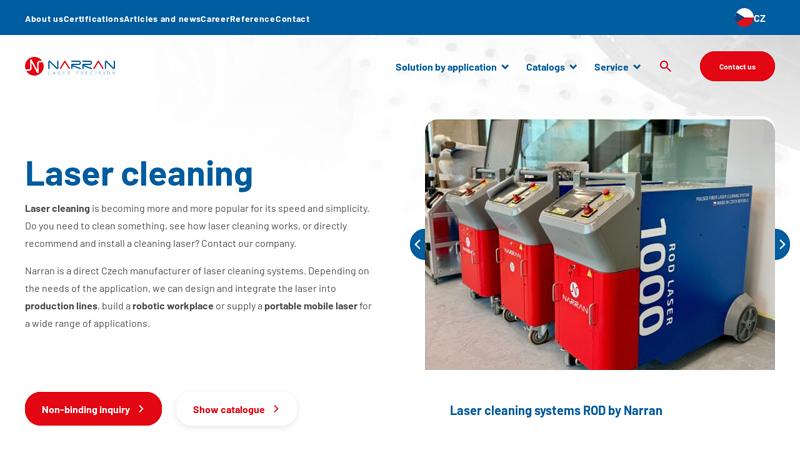
#2 Laser cleaning
Website: narran.cz
Key Highlights: We can design and integrate a laser cleaning system into production, build a robotic workstation or supply a mobile laser for a wide range of applications….
#3 Industrial laser cleaning
Website: emtechiph.pl
Key Highlights: EMTECH IPH GROUP is the official distributor of P-Laser. We offer both laser products and laser cleaning services. We operate in Poland and the Czech Republic….
#4 Laser machine world for cleaning, engraving, marking and welding …
Website: lasermachineworld.com
Key Highlights: Laser Machine World is offering affordable laser cleaning machine, marking machine and welding machine. Top class manufacturer of reliable laser equipments, ……
#5 Cleaning, cutting and engraving lasers. CNC marking and …
Website: grawostar.com
Key Highlights: We provide a complete range of laser cleaning, cutting, welding, and marking equipment. We also have a set of machines of our design such as laser welders, ……
#6 Fanuci & Falcon
Website: fanuci-falcon.com
Key Highlights: We offer, among others, laser welders, cleaning lasers, laser cutters for pipes, profiles, and sheet metal, nitrogen generators, and 3D laser printers for ……
#7 We will bring your laser system back into operation
Website: olafltd.pl
Key Highlights: The OLAF LTD company provides services in the field of parts distribution and service of machines and devices….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Czyszczący
H2: Prognozowane trendy rynkowe dla Laserów Czyszczących w 2026 roku
Do 2026 roku rynek laserów czyszczących doświadczy znaczącego wzrostu i ewolucji, napędzanej postępami technologicznymi, rosnącym zapotrzebowaniem na ekologiczne rozwiązania oraz poszerzającym się zastosowaniem w kluczowych sektorach. Poniżej przedstawiono kluczowe trendy:
1. Dynamiczny Wzrost Rynku i Ekspansja Zastosowań
Rynek laserów czyszczących (ang. laser cleaning systems) będzie nadal rosnąć szybciej niż wiele tradycyjnych metod czyszczenia, z prognozowanym rocznym tempem wzrostu (CAGR) powyżej 15–20% w latach 2023–2026. Głównymi sektorami napędzającymi popyt będą:
– Motoryzacja i przemysł lotniczy: do precyzyjnego usuwania rdzy, farb i warstw ochronnych z elementów silników, nadwozi i struktur aluminiowych.
– Energia i energetyka jądrowa: bezkontaktowe czyszczenie rur, reaktorów i infrastruktury, minimalizujące ryzyko zanieczyszczeń radioaktywnych.
– Konserwacja zabytków i dziedzictwa kulturowego: delikatne usuwanie zanieczyszczeń z kamienia, metalu czy ceramiki bez uszkadzania oryginalnej powierzchni.
– Elektronika i mikroprodukcja: czyszczenie płytek drukowanych (PCB), połączeń i mikroskopijnych elementów.
2. Miniaturyzacja i Mobilność Rozwiązań
Oczekuje się zwiększonego popytu na przenośne i ręczne urządzenia do czyszczenia laserowego. Producentowie będą inwestować w technologie pozwalające na tworzenie lżejszych, bardziej kompaktowych i ergonomicznych systemów, co umożliwi ich wykorzystanie na placach budów, w terenie czy w małych warsztatach. Integracja z robotami mobilnymi lub kamerami AI będzie stanowić kluczowy krok w kierunku automatyzacji.
3. Postęp Technologiczny: Moc, Precyzja i Inteligencja
– Lepsza efektywność energetyczna: urządzenia będą zużywać mniej energii przy jednocześnie wyższej wydajności usuwania zanieczyszczeń.
– Integracja z sztuczną inteligencją i IoT: systemy będą wyposażone w czujniki monitorujące jakość powierzchni, automatycznie dostosowujące parametry (długość fali, częstotliwość impulsów, prędkość skanowania) do rodzaju zanieczyszczenia i podłoża.
– Rozwój laserów o różnych długościach fal: rosnąca dostępność laserów UV, zielonych i podczerwonych pozwoli na lepsze dopasowanie do specyficznych zastosowań (np. czyszczenie polimerów, kolorowych metali).
4. Silny Kierunek Ekologiczny i Kompatybilność z ESG
Laserowe czyszczenie stanie się kluczowym narzędziem w strategiach zrównoważonego rozwoju firm. W 2026 roku jego zalety – brak środków chemicznych, minimalne odpady (same odparowane zanieczyszczenia), brak zużywanych ścierni – będą głównym argumentem marketingowym. Coraz więcej firm będzie wymagać laserowych rozwiązań, aby spełnić normy ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) i redukować ślad węglowy.
5. Spadek Kosztów i Zwiększona Dostępność
Choć nadal droższe od tradycyjnych metod, ceny urządzeń laserowych będą systematycznie spadać dzięki masowej produkcji, konkurencji i innowacjom. W 2026 roku dostępność systemów w niższych i średnich klasach cenowych umożliwi ich adopcję przez MŚP, co z kolei przyspieszy wzrost rynku.
6. Wzrost Regulacji i Standardów Branżowych
Oczekuje się wprowadzenia bardziej szczegółowych norm bezpieczeństwa (np. dotyczące ochrony wzroku, wentylacji pyłów) oraz standardów jakości procesu czyszczenia laserowego. To zwiększy zaufanie klientów i ułatwi wdrożenie technologii w wrażliwych sektorach, takich jak medycyna czy lotnictwo.
Podsumowanie
Do 2026 roku laserowe czyszczenie stanie się technologią mainstreamową w wielu branżach przemysłowych i usługowych. Kluczowe znaczenie będą miały innowacje w zakresie inteligencji systemów, mobilności i ekologiczności. Firmy, które wczesnie zaadoptują te rozwiązania, zyskają przewagę konkurencyjną pod względem efektywności, jakości i zgodności z rosnącymi wymogami środowiskowymi.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Laser Czyszczący (Quality, IP)
Sourcing a laser cleaning machine (“Laser Czyszczący” in Polish) requires careful attention to avoid significant risks related to product quality, performance, and intellectual property (IP). Overlooking these factors can lead to equipment failure, safety hazards, legal disputes, and financial losses.
Poor Build Quality and Component Selection
Many low-cost suppliers, especially from certain regions, use substandard materials and components to cut costs. This includes inferior laser diodes, unstable power supplies, and poorly calibrated optics. Such machines often suffer from inconsistent cleaning performance, frequent breakdowns, shorter lifespans, and unreliable cooling systems, leading to premature failure. Always request third-party test reports and inspect sample units before committing to large orders.
Inaccurate or Inflated Specifications
Suppliers may exaggerate key performance metrics such as laser power (e.g., claiming 1000W when actual output is 600W), pulse frequency, or cleaning speed. These misleading specs can result in a machine that fails to meet your operational requirements. Demand verifiable data from independent labs or conduct on-site performance tests to validate claims before purchase.
Lack of Safety Certifications and Compliance
Laser cleaning devices are high-power tools that must comply with international safety standards (e.g., IEC 60825 for laser safety, CE, FDA, or RoHS). Machines without proper certifications pose serious risks to operators and your facility. Non-compliant units may be blocked at customs or banned from use in regulated environments. Always verify compliance documentation and ensure the supplier provides full certification packages.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement Risks
Some manufacturers clone designs or use patented technologies without authorization. Sourcing such equipment exposes your business to legal liability, including customs seizures, lawsuits, or reputational damage. Conduct due diligence on the supplier’s R&D capabilities, request proof of IP ownership or licensing agreements, and consider legal consultation to avoid purchasing counterfeit or infringing products.
Inadequate After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Even high-quality machines require maintenance and occasional repairs. Suppliers located overseas may offer limited technical support, long response times, or fail to stock essential spare parts. This can lead to extended downtime and increased operating costs. Prioritize suppliers with a local service network, clear SLAs, and long-term parts availability commitments.
Insufficient Training and Documentation
Effective use of laser cleaning systems requires proper training and comprehensive manuals (preferably in your language). Poor documentation or lack of operator training increases the risk of misuse, accidents, and suboptimal performance. Ensure the supplier provides on-site or remote training and detailed user guides before finalizing the purchase.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls, businesses can source reliable, safe, and legally compliant Laser Czyszczący systems that deliver long-term value.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Czyszczący
Product Overview
Laser Czyszczący refers to laser cleaning devices used for removing contaminants, oxides, or coatings from surfaces without abrasive materials. These systems are widely used in industrial, automotive, and restoration applications. Ensuring proper logistics and regulatory compliance is essential for safe distribution and legal operation.
Classification & Harmonized System (HS) Code
Laser cleaning equipment typically falls under the following HS Code:
8515.10 – Electrical welding and cutting machines, including those using laser or other light/photonic sources.
Note: Confirm with local customs authorities, as classification may vary by country and specific technical specifications.
Shipping & Packaging Requirements
- Secure Packaging: Use shock-absorbent materials and rigid outer casings to protect sensitive optical and electronic components.
- Climate Control: Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures and humidity during transit.
- Labeling: Clearly mark packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Protect from Moisture.” Include handling instructions for laser equipment.
- Battery Handling (if applicable): If the unit contains lithium-ion batteries, comply with IATA/IMDG regulations for dangerous goods (UN 3480 or 3481).
Export Controls & Licensing
- Dual-Use Regulations: Laser systems may be subject to dual-use export controls under the Wassenaar Arrangement due to potential military applications.
- Export Licenses: Check if your device exceeds power thresholds (e.g., lasers > 500W may require authorization).
- Destination Restrictions: Verify if the destination country is under trade sanctions or requires import permits. Use tools like the EU’s Dual-Use Regulation or U.S. Commerce Control List (CCL) for classification.
Safety & Regulatory Compliance
- Laser Safety (IEC 60825-1): Ensure compliance with IEC 60825-1 for laser product safety. Classify the laser (typically Class 4 for industrial cleaners) and provide appropriate warning labels.
- CE Marking (EU): Required for sale in the European Economic Area. Must meet directives including:
- Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC)
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive (2014/30/EU)
- Low Voltage Directive (2014/35/EU)
- Radio Equipment Directive (if wireless functions apply)
- FDA Registration (USA): Report laser products to the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH) under 21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11.
- RoHS & REACH (EU): Confirm that materials used in the device comply with restrictions on hazardous substances (RoHS) and chemical registration (REACH).
Import Requirements by Region
- European Union: Provide a Declaration of Conformity, technical documentation, and ensure CE marking. Notify national authorities if required.
- United States: Partner with a U.S. agent for FDA compliance. No general import license required, but customs may inspect for safety standards.
- Canada: Comply with Health Canada’s radiation-emitting devices regulations. Registration with the Radiation Emitting Devices Act (REDA) may be required.
- Asia-Pacific (e.g., China, Japan): Check local certifications (e.g., CCC in China, PSE in Japan). High-power lasers may face additional scrutiny.
Documentation Checklist
Ensure the following documents accompany each shipment:
– Commercial Invoice
– Packing List
– Bill of Lading / Air Waybill
– Certificate of Origin
– CE Declaration of Conformity (or equivalent)
– FDA Product Report (for U.S.)
– Export License (if applicable)
– Safety Data Sheet (for batteries or consumables)
– Technical User Manual with safety warnings in local language
Training & End-User Compliance
- Provide end-users with operational and safety training.
- Include multilingual manuals covering laser safety, emergency shutdown, and PPE requirements.
- Advise users to conduct risk assessments per local OSHA or equivalent regulations.
Environmental & Disposal Considerations
- Follow WEEE Directive (EU) for proper end-of-life recycling of electronic components.
- Inform customers about safe disposal of optical parts and batteries.
Summary
Proper logistics and compliance for Laser Czyszczący involve accurate classification, adherence to international safety standards, and thorough documentation. Always consult local regulatory bodies and consider working with a customs broker or compliance specialist to ensure smooth cross-border operations.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Laser Cleaning Machine
After evaluating various suppliers, technologies, and market options, sourcing a laser cleaning machine presents a strategic opportunity to enhance precision, efficiency, and sustainability in industrial cleaning processes. Laser cleaning offers significant advantages over traditional methods—such as reduced environmental impact, minimal substrate damage, no consumables, and improved operator safety.
Key considerations in the sourcing process include machine power, wavelength, portability, automation compatibility, and after-sales support. Leading suppliers from Europe, the United States, and Asia offer competitive solutions, with increasing adoption in automotive, aerospace, heritage restoration, and mold maintenance industries.
It is recommended to select a supplier that provides scalable technology, comprehensive training, and service support, ensuring long-term reliability and integration into existing workflows. Investing in a high-quality laser cleaning system not only improves operational performance but also aligns with sustainability goals by eliminating chemical usage and reducing waste.
In conclusion, sourcing a laser cleaning machine is a forward-looking decision that supports innovation, cost savings, and environmental responsibility, positioning organizations at the forefront of advanced manufacturing and maintenance practices.