The global laser cutting machines market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for high-precision manufacturing across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics. According to Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 6.35 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 9.82 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of approximately 7.5% during the forecast period. This expansion is underpinned by technological advancements in fiber and CO₂ laser systems, which enable tighter tolerances, faster processing speeds, and improved energy efficiency. As industries demand increasingly intricate components with minimal dimensional deviation, the capability to maintain tight laser cutting tolerances—often within ±0.1 mm—has become a critical differentiator among equipment manufacturers. In this competitive landscape, a select group of companies are leading the way in precision engineering, process consistency, and innovation in laser control systems. The following list highlights the top eight manufacturers renowned for their exceptional tolerance performance and technological leadership in laser cutting.
Top 8 Laser Cutting Tolerances Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laser Cutting Plastic and Other Non
Founded: 1948
Website: espemfg.com
Key Highlights: ESPE Manufacturing Co., Inc. Delivering Quality Plastics & Fabricated Parts Since 1948 Call: 800-367-3773 (800-FOR-ESPE) Email: [email protected]….
#2 Laser Cutting Tolerances
Website: a-laser.com
Key Highlights: In the laser precision cutting world, tight tolerance is defined as the acceptable amount of variation when a part is being processed….
#3 Tolerances and Manufacturing Capabilities
Website: laserboost.com
Key Highlights: Useful information about the manufacturing tolerances offered by LaserBoost, certified by our team and aligned with our production facility….
#4 Laser and Sheet Cutting Services
Website: xometry.com
Key Highlights: Xometry’s typical part tolerance is +/- 0.010” for laser cutting or waterjet cutting; this includes compensation for kerf. Small holes, thin gaps, and relief ……
#5 What is the tolerance of laser cut parts?
Website: fabworks.com
Key Highlights: The tolerance of laser cut parts typically ranges from +/- 0.002 inches to +/- 0.05 inches, depending on various factors such as part size and feature ……
#6 Tolerances and accuracy in laser cutting
Website: teprosa.de
Key Highlights: All cutting parts are manufactured according to the standard DIN ISO 2768-1 m (general tolerances) for the geometric dimension, unless otherwise agreed with ……
#7 Metal Profile Cutting Tolerances
Website: protocase.com
Key Highlights: Profile cutting tolerance is the slight positional variance that occurs when sheet metal is cut. This happens in the position of features, diameter of holes….
#8 A Comprehensive Guide to Laser Cutting Machine Tolerances
Website: yazhimachine.com
Key Highlights: Learn practical laser cutting machine tolerance ranges, key influencing factors, and cost-effective design tips….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Cutting Tolerances
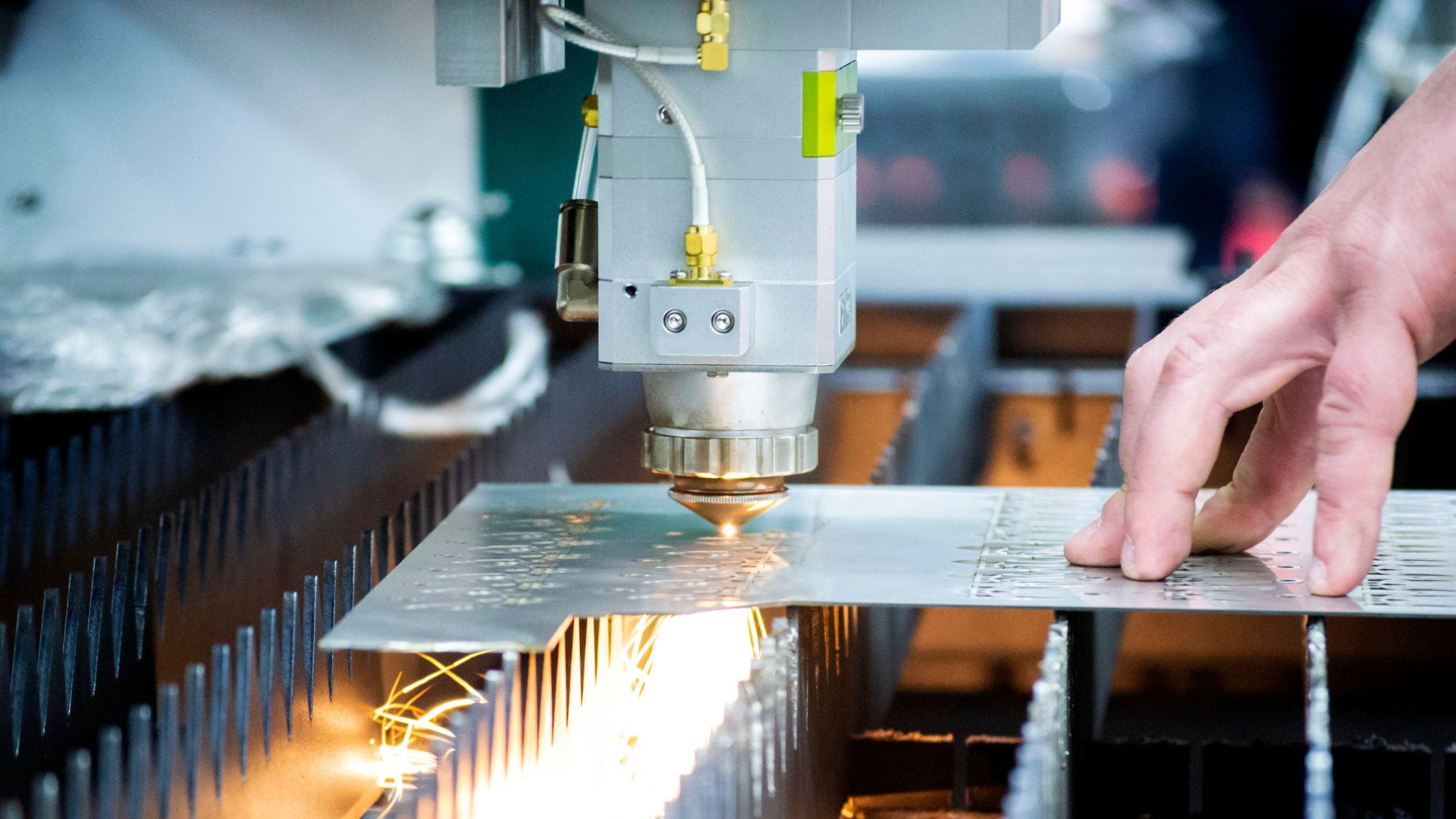

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Laser Cutting Tolerances
In 2026, the market for laser cutting tolerances is witnessing significant transformation driven by advancements in laser technology, rising demand for precision across industries, and the integration of automation and artificial intelligence (AI). As manufacturing sectors—particularly aerospace, automotive, medical devices, and electronics—push the boundaries of miniaturization and performance, tighter and more consistent cutting tolerances have become critical.
One of the most prominent trends in 2026 is the widespread adoption of high-precision fiber laser systems capable of achieving tolerances within ±0.05 mm to ±0.1 mm. These systems outperform traditional CO2 lasers in both accuracy and repeatability, especially when processing thin to medium-thickness materials. The refinement of beam quality, coupled with improved motion control systems and real-time monitoring, enables manufacturers to maintain tighter tolerances across high-volume production runs.
Additionally, the integration of AI-driven process optimization and predictive maintenance is enhancing tolerance consistency. In 2026, smart laser cutting machines utilize machine learning algorithms to adjust cutting parameters dynamically based on material variations, thermal distortions, and tool wear. This real-time feedback loop minimizes deviation and reduces scrap rates, directly impacting production efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Another key trend is the growing emphasis on standardization and certification of laser cutting tolerances. Industry bodies and end users are demanding traceable, repeatable results, pushing suppliers to adopt ISO and ASME standards more rigorously. This shift is particularly evident in regulated industries such as medical device manufacturing, where tolerance compliance is directly tied to product safety and regulatory approval.
Furthermore, the rise of hybrid manufacturing—combining laser cutting with additive manufacturing and CNC machining—is creating new requirements for tolerance interoperability across processes. In 2026, laser cutting is increasingly viewed not as a standalone process but as a component of a fully integrated digital production chain, where tolerance data is shared seamlessly across systems via digital twins and cloud-based platforms.
In summary, the 2026 market for laser cutting tolerances is defined by tighter accuracy demands, intelligent process control, standardization, and integration within advanced manufacturing ecosystems. As competition intensifies and customer expectations rise, manufacturers investing in precision-enabling technologies are positioned to lead in quality, efficiency, and innovation.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Laser Cutting: Tolerances, Quality, and Intellectual Property
Sourcing laser cutting services involves more than just selecting a machine and material. Overlooking key aspects related to tolerances, quality assurance, and intellectual property (IP) can lead to costly delays, rework, or legal issues. Being aware of these common pitfalls helps ensure a successful outsourcing experience.
Unclear or Unrealistic Tolerance Specifications
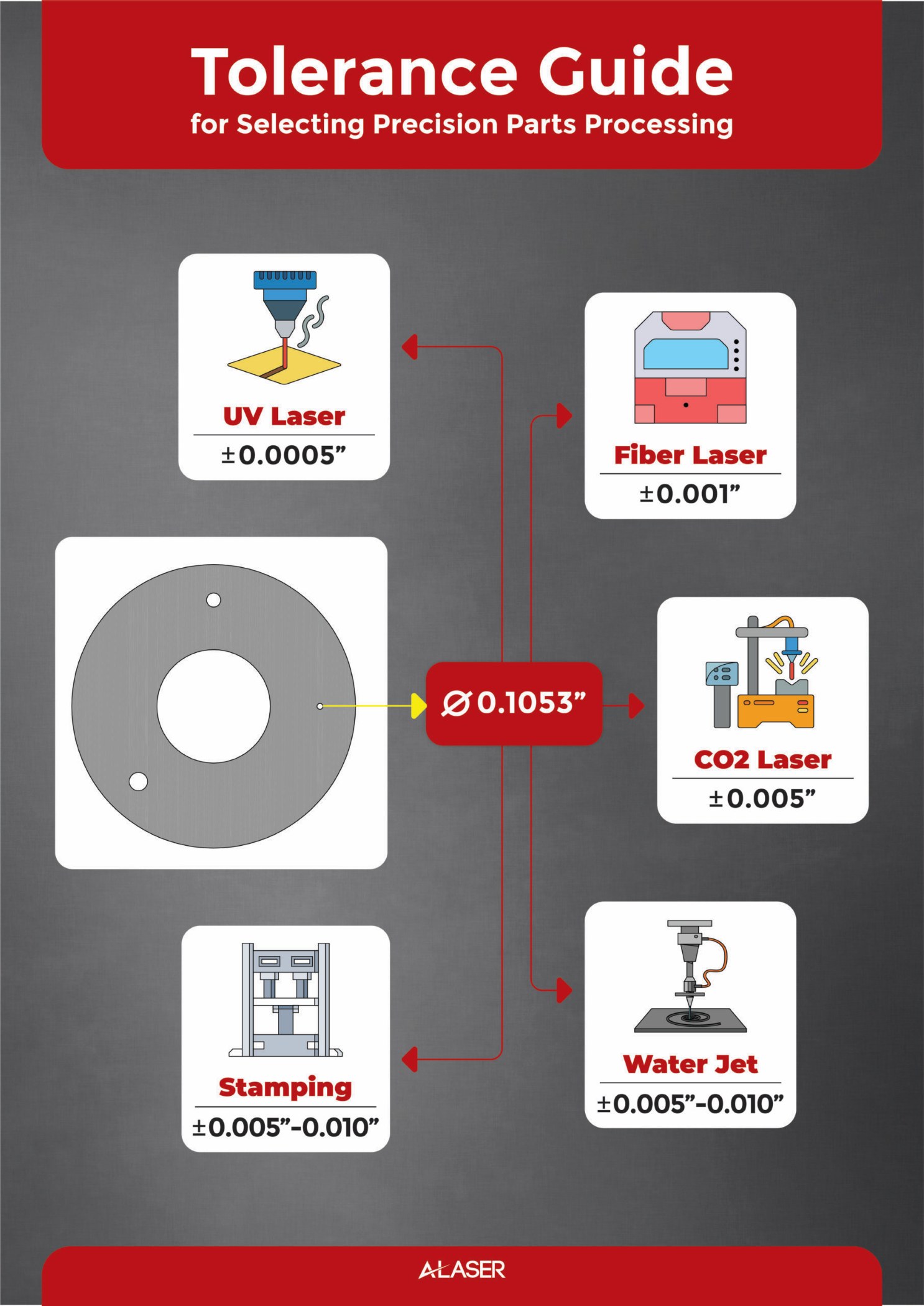
One of the most frequent issues is providing ambiguous or technically unachievable tolerance requirements. Clients may specify tight tolerances (e.g., ±0.05 mm) without considering material behavior, part geometry, or the capabilities of different laser types (CO2 vs. fiber). This can lead to increased costs, production delays, or rejected parts. Always confirm with the supplier what tolerances are realistically maintainable for your material and design.
Overlooking Material-Specific Variability
Different materials respond uniquely to laser cutting—metals like stainless steel, aluminum, and mild steel have varying thermal conductivity and melting points, affecting edge quality and dimensional accuracy. Non-metals such as acrylic or wood may exhibit charring or warping. Failing to account for material behavior can result in inconsistent quality. Ensure your supplier understands the material’s properties and adjusts parameters accordingly.
Inadequate Quality Control Processes
Assuming that all laser cutting providers follow rigorous quality assurance protocols is risky. Some vendors may lack formal inspection processes, such as first-article inspection (FAI), statistical process control (SPC), or post-process metrology (e.g., CMM or optical measurement). Without documented QC steps, consistency across production runs cannot be guaranteed. Always request details of their quality control procedures and certifications (e.g., ISO 9001).
Ignoring the Impact of Part Geometry and Size
Complex geometries, intricate internal features, or large sheet utilization can influence cutting accuracy and edge quality. Small features may distort due to heat-affected zones (HAZ), while large parts may experience bowing or positional deviation. Not communicating design constraints or nesting strategies with the supplier can compromise tolerance adherence. Provide detailed drawings and discuss design for manufacturability (DFM) early.
Failure to Define Surface Finish and Edge Quality Standards
“Good quality” is subjective. Without clear specifications for edge dross, burr levels, or surface roughness, the final product may not meet your expectations. Use industry standards (e.g., ISO 9013 for thermal cutting quality classes) or provide physical samples to define acceptable finish. Misalignment here often leads to disputes during inspection.
Neglecting Intellectual Property Protection
Sharing detailed CAD files and technical drawings with third-party suppliers exposes your IP to potential misuse or unauthorized replication. Many companies fail to establish legal safeguards such as non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) or clear IP ownership clauses in contracts. Always ensure that your supplier signs an NDA and that your agreement explicitly states that all design rights remain with you.
Assuming All Laser Cutters Are Equal
Not all laser cutting equipment delivers the same precision. Differences in laser power, beam quality, motion control systems, and maintenance schedules affect output consistency. Sourcing from a vendor without auditing their equipment or process capabilities can result in variable quality. Request machine specifications, maintenance logs, and sample cut pieces before committing.
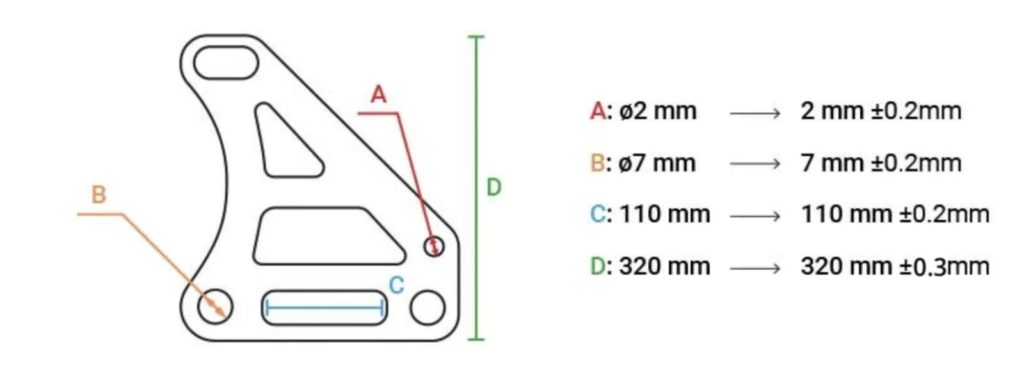
Poor Communication of Critical Features
Failing to highlight which dimensions are critical (e.g., with GD&T callouts) can cause the supplier to apply uniform tolerances across all features—potentially over-manufacturing non-critical areas or under-delivering on key fits. Clearly mark functional surfaces, mating dimensions, and tolerance zones on drawings to guide the manufacturer’s focus.
Skipping Prototype or First Article Validation
Jumping straight into full production without a prototype or first-article inspection (FAI) increases the risk of systemic errors. Early validation catches tolerance drift, material issues, and programming mistakes. Always perform a pre-production review with measurable data to confirm alignment with your requirements.
Lack of Traceability and Documentation
For regulated industries (e.g., medical, aerospace), traceability of materials, processes, and inspections is essential. If your supplier does not provide material certifications, cutting logs, or inspection reports, you may face compliance challenges. Specify documentation requirements upfront and verify the supplier’s ability to deliver them.
By addressing these pitfalls proactively—through clear specifications, robust contracts, and open communication—you can significantly improve the reliability and success of your laser cutting sourcing efforts.

Laser Cutting Tolerances: Logistics & Compliance Guide
Understanding and managing laser cutting tolerances is essential for ensuring product quality, regulatory compliance, and efficient logistics throughout the manufacturing and supply chain process. This guide outlines key considerations for maintaining precision, meeting standards, and streamlining operations.
Understanding Laser Cutting Tolerances
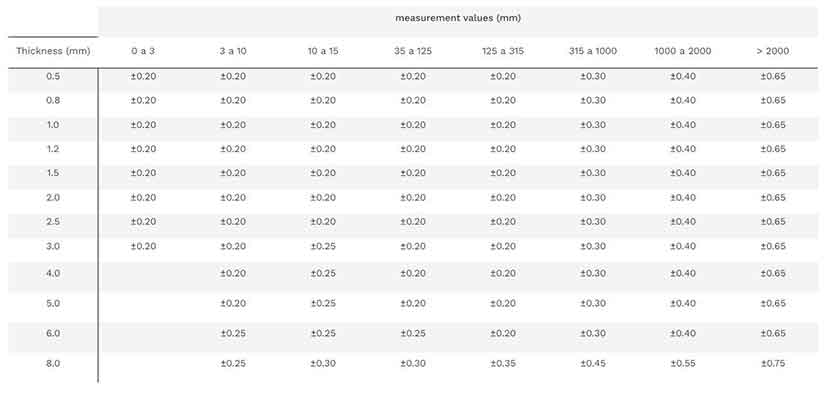
Laser cutting tolerances refer to the acceptable deviation between the intended design dimensions and the actual cut part. These tolerances are influenced by material type, thickness, laser power, cutting speed, and machine calibration. Standard industrial tolerances typically range from ±0.1 mm to ±0.2 mm for thin materials (up to 6 mm), with wider tolerances for thicker or more complex materials.
Material Selection and Certification
To ensure compliance and consistency, use materials with certified mechanical and dimensional properties. Suppliers should provide mill test certificates (e.g., EN 10204 3.1 or 3.2) confirming material composition and adherence to international standards (e.g., ASTM, ISO). Consistent material properties reduce variation in cut quality and help maintain tolerance control.
Design for Manufacturability (DFM)
Collaborate with design and engineering teams to implement DFM principles. This includes specifying appropriate tolerance levels based on functional requirements, avoiding unnecessarily tight tolerances that increase cost and lead time, and incorporating kerf allowances (typically 0.1–0.3 mm) into CAD models. Use standardized hole sizes and feature spacing to minimize setup changes and improve throughput.
Machine Calibration and Maintenance
Ensure laser cutting machines undergo regular calibration and preventive maintenance. Misaligned optics, worn nozzles, or degraded lenses can cause dimensional inaccuracies and non-compliance. Maintain a documented maintenance log and follow OEM guidelines. Implement in-process inspection using calibrated tools (e.g., micrometers, CMMs) to verify cut accuracy and alignment with specified tolerances.
Quality Assurance and Inspection Protocols
Establish a quality control plan that includes first-article inspection (FAI) and periodic in-line checks. Use statistical process control (SPC) to monitor dimensional consistency across production runs. Document inspection results and non-conformance reports (NCRs) to support traceability and continuous improvement. Align inspection procedures with ISO 9001 or AS9100 standards where applicable.
Regulatory and Industry Compliance
Adhere to relevant industry standards such as ISO 2768 (general tolerances), ISO 9013 (thermal cutting tolerances), or customer-specific requirements (e.g., aerospace, medical devices). Maintain compliance documentation for audits, including calibration records, material certifications, and inspection reports. For export shipments, ensure parts meet destination market regulations (e.g., CE marking, RoHS compliance).
Packaging and Logistics Considerations
Protect precision-cut parts during handling and shipping to prevent deformation or damage that could affect dimensional integrity. Use custom fixtures, anti-corrosion packaging, and cushioned containers as needed. Clearly label packages with part numbers, revision levels, and tolerance specifications to support traceability and reduce handling errors in logistics.
Supplier and Subcontractor Management
When outsourcing laser cutting, vet suppliers for technical capability, quality certifications, and compliance history. Define tolerance requirements clearly in purchase orders and technical specifications. Conduct supplier audits and request process capability (Cp/Cpk) data to ensure consistent output. Establish corrective action procedures for out-of-tolerance deliveries.
Continuous Improvement and Documentation
Regularly review tolerance performance data to identify trends and opportunities for improvement. Update process documentation, work instructions, and training materials to reflect best practices. Foster cross-functional collaboration between design, production, quality, and logistics teams to optimize the end-to-end workflow and ensure compliance with both internal and external standards.
Conclusion on Sourcing Laser Cutting Tolerances
When sourcing laser cutting services, understanding and specifying appropriate tolerances is critical to ensuring the quality, functionality, and interchangeability of fabricated parts. Laser cutting offers high precision, typically achieving tolerances within ±0.1 mm to ±0.2 mm for standard operations, though tighter tolerances may be attainable with advanced equipment and process control.
Key factors influencing achievable tolerances include material type and thickness, laser technology (CO₂, fiber, or Nd:YAG), machine calibration, cutting speed, and edge quality requirements. It is essential to communicate clearly with suppliers about design specifications, critical dimensions, and tolerance expectations early in the sourcing process.
In practice, balancing precision with cost-efficiency is crucial—over-specifying tight tolerances can increase production time and costs unnecessarily. Therefore, designers and engineers should apply geometric dimensioning and tolerancing (GD&T) principles to specify only what is functionally required.
Ultimately, successful sourcing of laser cutting services depends on selecting a capable and experienced provider, providing detailed technical drawings, and establishing mutual understanding around tolerances and quality standards. Collaboration and clear communication ensure that parts meet performance requirements while remaining cost-effective and manufacturable at scale.