The global laser cutting machine market, valued at USD 8.43 billion in 2023, is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.2% through 2030, according to Grand View Research. This growth is driven by increasing demand for precision manufacturing across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics. As laser cutting technology advances, tight tolerance capabilities have become a key differentiator among manufacturers, with ±0.05 mm now considered standard for high-end systems. In this competitive landscape, nine manufacturers have emerged as leaders in delivering exceptional repeatability, micron-level accuracy, and consistent cut quality—setting new benchmarks for performance and reliability. These companies not only dominate in innovation but also reflect the shifting industry focus toward automation, energy efficiency, and integration with Industry 4.0 systems.
Top 9 Laser Cutter Tolerance Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 EAGLE Lasers
Website: eagle-group.eu
Key Highlights: EAGLE is the producer of the fastest and most efficient laser cutters in the world. Discover our innovative fiber laser products and matching software!…
#2 Laser Cutting Tolerances
Website: a-laser.com
Key Highlights: In the laser precision cutting world, tight tolerance is defined as the acceptable amount of variation when a part is being processed….
#3 Tolerances and Manufacturing Capabilities
Website: laserboost.com
Key Highlights: Useful information about the manufacturing tolerances offered by LaserBoost, certified by our team and aligned with our production facility….
#4 Laser and Sheet Cutting Services
Website: xometry.com
Key Highlights: Xometry’s typical part tolerance is +/- 0.010” for laser cutting or waterjet cutting; this includes compensation for kerf. Small holes, thin gaps, and relief ……
#5 What is the tolerance of laser cut parts?
Website: fabworks.com
Key Highlights: Laser cut parts typically have tolerances ranging from +/- 0.002 inches to +/- 0.005 inches, with tighter tolerances for smaller features and slightly wider ……
#6 Laser Cutting Services
Website: techfoundry.ucdavis.edu
Key Highlights: Laser cutting is a precise subtractive manufacturing process that uses a high-powered laser to cut (through or engrave) a variety of sheet- ……
#7 Tolerances and accuracy in laser cutting
Website: teprosa.de
Key Highlights: All cutting parts are manufactured according to the standard DIN ISO 2768-1 m (general tolerances) for the geometric dimension, unless otherwise agreed with ……
#8 Laser tolerances
Website: hypertherm.com
Key Highlights: As a general rule, tighter dimensional tolerances create added cost in your manufacturing operation and product….
#9 What is the precision tolerance of laser cutting?
Website: astmanufacturing.com
Key Highlights: Discover how laser cutting achieves precision within ±0.005 inches. Enhance your projects’ quality and efficiency. Learn more today!…
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Cutter Tolerance

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Laser Cutter Tolerance
As the manufacturing and fabrication industries continue to evolve with advancements in precision engineering and automation, laser cutter tolerance is emerging as a critical performance metric shaping market dynamics in 2026. Tolerance—defined as the permissible limit of variation in the dimensions of a cut—directly influences the quality, repeatability, and efficiency of laser cutting processes. In 2026, several key trends are driving demand for tighter tolerances and more consistent performance across industrial, aerospace, medical, and electronics sectors.
-
Demand for Higher Precision in Advanced Manufacturing
Industries such as aerospace, medical devices, and electric vehicles (EVs) require micron-level accuracy in component fabrication. In 2026, laser cutters with tolerances within ±0.05 mm or better are becoming standard in high-end applications. This shift is fueled by the need for lightweight, complex geometries and miniaturized parts, where even minor deviations can compromise performance or safety. -
Adoption of Fiber and Ultrafast Lasers
Fiber lasers continue to dominate the market due to their superior beam quality, energy efficiency, and ability to achieve tighter tolerances compared to CO₂ lasers. In 2026, ultrafast (picosecond and femtosecond) lasers are gaining traction in niche high-precision applications such as medical stents and semiconductor components, offering sub-micron tolerances with minimal heat-affected zones (HAZ). -
Integration of AI and Real-Time Monitoring
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are being embedded into laser cutting systems to dynamically adjust parameters (e.g., power, speed, focus) based on real-time feedback. These smart systems enhance tolerance consistency by compensating for material variations, thermal drift, and mechanical wear. Predictive maintenance and closed-loop control systems are reducing scrap rates and improving dimensional accuracy. -
Material Diversification and Challenges
As manufacturers work with advanced materials—including composites, high-strength alloys, and ceramics—maintaining tight tolerance becomes more complex. In 2026, laser cutter manufacturers are focusing on adaptive optics and multi-axis control systems to preserve precision across diverse material types and thicknesses. -
Standardization and Industry Compliance
Regulatory demands in sectors like medical devices (ISO 13485) and aerospace (AS9100) are pushing for stricter documentation and traceability of cutting tolerances. Laser cutting equipment suppliers are responding by offering calibrated systems with certified performance metrics, ensuring compliance and consistency in production. -
Growth in Automated and Integrated Workflows
Factory automation and Industry 4.0 integration are accelerating the use of robotic loading/unloading and in-line metrology. In 2026, laser cutting cells are increasingly paired with automated inspection systems (e.g., laser scanners or vision systems) that validate tolerances immediately post-cut, enabling rapid adjustments and reducing rework. -
Regional Market Developments
Asia-Pacific, particularly China, South Korea, and Japan, is leading in the adoption of high-tolerance laser systems due to strong electronics and automotive manufacturing bases. Meanwhile, North America and Europe are investing heavily in R&D for next-generation laser technologies, supported by government initiatives in advanced manufacturing.
In conclusion, the 2026 market for laser cutter tolerance is defined by a relentless push toward higher precision, driven by technological innovation, material complexity, and stringent industry standards. Manufacturers that invest in advanced laser sources, intelligent control systems, and process validation are best positioned to meet the growing demand for micron-level accuracy across high-value industries.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Laser Cutter Tolerance (Quality, IP)
When sourcing laser cutters, especially for precision applications, overlooking tolerance specifications can lead to significant quality and intellectual property (IP) risks. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Inadequate Understanding of Specified vs. Actual Tolerance
Suppliers often advertise ideal tolerance ranges under perfect laboratory conditions. However, real-world performance can vary due to material type, thickness, machine calibration, and environmental factors. Relying solely on datasheet values without verifying real-world test cuts can result in parts that fail to meet functional requirements, leading to rework or product failure.
Lack of Standardized Testing and Documentation
Many suppliers do not provide comprehensive tolerance validation reports or standardized testing protocols. Without documented evidence—such as first-article inspection reports or statistical process control (SPC) data—it becomes difficult to assess consistency. This absence of traceability raises quality concerns and complicates supplier qualification.
Overlooking Machine Calibration and Maintenance Practices
Laser cutters drift over time due to thermal expansion, optical misalignment, or wear. Sourcing from vendors that do not enforce strict calibration schedules or preventive maintenance can compromise long-term tolerance stability. Failing to audit these processes may result in inconsistent output, especially during high-volume production.
Insufficient Verification of IP Protection Measures
When sharing design files to validate tolerance capabilities, sensitive IP is at risk. Some suppliers lack secure data handling policies, non-disclosure agreements (NDAs), or encrypted file transfer systems. Entrusting designs to such vendors could lead to unauthorized replication, reverse engineering, or loss of competitive advantage.
Misalignment Between Material Capability and Tolerance Claims
A laser cutter may achieve tight tolerances on thin steel but struggle with thicker or non-metallic materials like acrylic or composites. Vendors may generalize tolerance specs across all materials, leading to unexpected deviations. Always confirm tolerance performance on the exact material and thickness intended for production.
Failure to Define Tolerance in Contractual Agreements
Verbal assurances or vague marketing claims are insufficient. Tolerance requirements must be explicitly defined in purchase agreements and service level agreements (SLAs), including acceptable deviation limits, measurement methods (e.g., CMM, optical comparator), and recourse for non-compliance. Without contractual enforcement, quality disputes become difficult to resolve.
Ignoring Post-Processing Impact on Final Tolerance
Laser cutting can induce thermal distortion, burring, or edge hardening, affecting final dimensional accuracy. If post-processing steps like grinding, polishing, or bending are required, their impact on net tolerance must be evaluated. Sourcing decisions based solely on as-cut performance may overlook downstream quality issues.
Conclusion
To mitigate these pitfalls, conduct thorough due diligence: request sample parts made from your materials, audit the supplier’s quality management system (e.g., ISO 9001), validate IP protection protocols, and ensure tolerance commitments are contractually binding. A proactive approach ensures both quality integrity and IP security in your laser cutting supply chain.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Cutter Tolerance
This guide outlines key logistics considerations and compliance requirements related to maintaining and verifying laser cutter tolerance in manufacturing and fabrication environments. Ensuring precise tolerances is critical for product quality, regulatory adherence, and operational efficiency.
Understanding Laser Cutter Tolerance Specifications
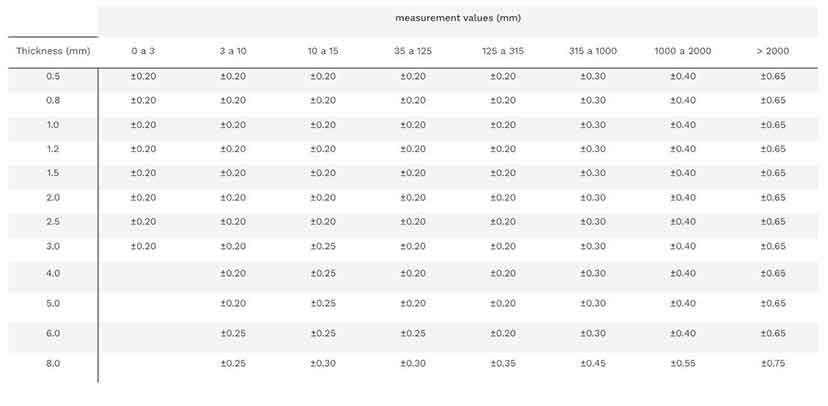
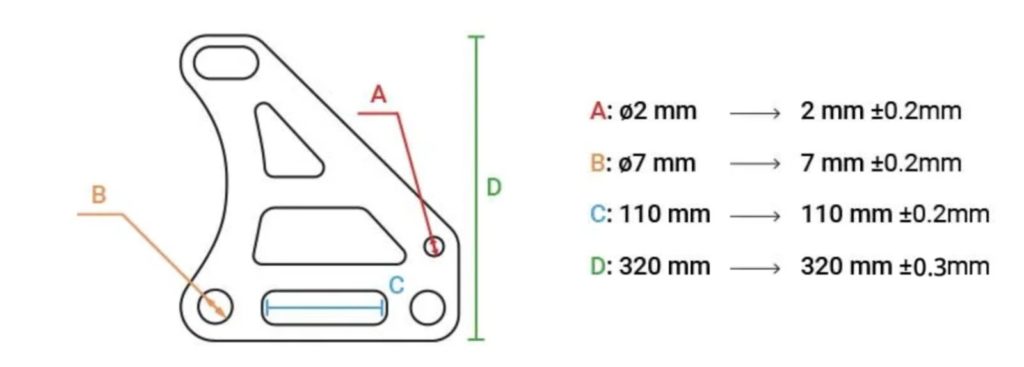
Laser cutter tolerance refers to the allowable deviation between the intended design dimensions and the actual cut outcome. Typical tolerance ranges vary by material, thickness, laser type (CO2, fiber, etc.), and machine calibration but commonly fall between ±0.1 mm to ±0.5 mm. Accurate documentation of these tolerances is essential for quality assurance and compliance with industry standards such as ISO 9001 and AS9100.
Equipment Calibration and Maintenance
Regular calibration of laser cutting equipment is mandatory to maintain specified tolerances. A documented maintenance schedule should include:
– Daily inspection of lens cleanliness and alignment
– Monthly verification of gantry alignment and beam focus
– Quarterly performance testing using standardized test cuts
– Annual certification by an accredited technician
Calibration records must be retained for audit purposes and should be accessible to quality control and compliance personnel.
Material Handling and Storage Protocols
Consistent laser cutting tolerance depends heavily on material quality and condition. Implement the following logistics procedures:
– Store sheet materials in a climate-controlled environment to prevent warping or moisture absorption
– Label all materials with lot numbers, thickness, and material grade
– Implement first-in, first-out (FIFO) inventory rotation
– Inspect incoming materials for surface defects or inconsistencies prior to processing
Deviation in material properties can directly impact cut accuracy and must be recorded and reported.
Quality Control and Inspection Procedures
To ensure compliance with tolerance requirements:
– Conduct first-article inspections on new designs or material batches
– Perform in-process measurements using calibrated micrometers, calipers, or coordinate measuring machines (CMM)
– Maintain traceability through digital logs linking job numbers, machine settings, operator IDs, and inspection results
– Implement corrective actions for any tolerance deviation exceeding acceptable limits
All inspection data should be stored securely and made available for internal audits or customer reviews.
Regulatory and Industry Compliance
Adherence to relevant standards is required for legal and commercial operations:
– Follow OSHA safety regulations for laser operation (29 CFR 1910.97)
– Comply with ANSI Z136.1 for laser safety
– Meet ISO 2768 for general geometric tolerances if no specific tolerances are defined
– For aerospace or medical applications, conform to stricter standards such as ASTM F2792 or ISO 13485
Documentation must demonstrate ongoing compliance during regulatory audits.
Training and Operator Certification
Only trained and certified personnel should operate laser cutting equipment. Training must cover:
– Machine-specific tolerance capabilities
– Proper setup and nesting techniques
– Interpretation of engineering drawings and GD&T (Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing)
– Emergency procedures and PPE requirements
Maintain training records and conduct annual refresher courses to ensure continued compliance.
Documentation and Traceability Requirements
Robust documentation supports logistics and compliance efforts:
– Maintain machine logs with uptime, maintenance, and calibration history
– Archive digital design files with revision control
– Store inspection reports and non-conformance records for a minimum of 7 years (or as required by industry)
– Ensure cloud or on-site backups of all critical data
Traceability enables rapid root-cause analysis in case of tolerance-related defects.
Conclusion
Maintaining laser cutter tolerance is a multidisciplinary effort involving logistics, quality control, and regulatory compliance. By implementing standardized procedures for calibration, material handling, inspection, and documentation, organizations can ensure consistent product quality and meet stringent compliance requirements across industries.
Conclusion on Sourcing Laser Cutter Tolerance:
When sourcing a laser cutter, understanding and defining the required tolerance is critical to achieving the desired precision and quality in manufactured parts. Laser cutting offers high accuracy, typically within ±0.1 mm to ±0.2 mm for most industrial systems, but actual tolerance depends on several factors including laser type (CO2, fiber, or Nd:YAG), material properties (type, thickness, and consistency), cutting speed, beam focus, and machine calibration.
To ensure optimal results, it is essential to match the laser cutter’s capabilities with the application’s tolerance requirements. Tighter tolerances may necessitate higher-end machines, advanced control systems, or post-processing steps. Therefore, when sourcing laser cutting services or equipment, clear communication of dimensional tolerances, material specifications, and intended use is crucial. Collaborating with experienced suppliers who can provide process validation and sample testing further ensures that the final output meets design and functional expectations. Ultimately, selecting the right laser cutter with appropriate tolerance capabilities balances precision, cost, and production efficiency for the project at hand.