The global laser cutting equipment market is witnessing robust expansion, driven by increasing demand for precision manufacturing across industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and medical devices. According to Grand View Research, the market size was valued at USD 9.32 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.4% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by advancements in fiber laser technology, rising automation in production processes, and the need for tighter tolerances in high-precision components. As manufacturers increasingly prioritize accuracy—often requiring tolerances within ±0.1 mm to ±0.05 mm—the ability to consistently achieve tight laser cut tolerances has become a critical differentiator. In this competitive landscape, a select group of manufacturers stand out for their engineering excellence, advanced machinery, and rigorous quality control processes. The following list highlights the top 9 companies renowned for their capabilities in delivering precise, repeatable laser cutting results that meet the most demanding specifications.
Top 9 Laser Cut Tolerances Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laser Cutting Tolerances
Website: a-laser.com
Key Highlights: In the laser precision cutting world, tight tolerance is defined as the acceptable amount of variation when a part is being processed….
#2 Laser Cutting for Stainless & Nickel Alloys
Website: usa.myjacquet.com
Key Highlights: JACQUET in the US offers precision laser cutting for stainless and nickel alloys. Contact your local branch for fast service and tight tolerances….
#3 Laser and Sheet Cutting Services
Website: xometry.com
Key Highlights: Xometry’s typical part tolerance is +/- 0.010” for laser cutting or waterjet cutting; this includes compensation for kerf. Small holes, thin gaps, and relief ……
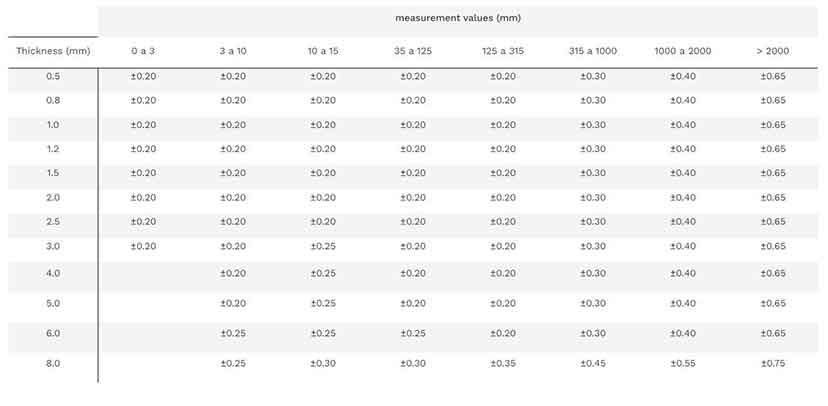
#4 Tolerances and accuracy in laser cutting
Website: teprosa.de
Key Highlights: All cutting parts are manufactured according to the standard DIN ISO 2768-1 m (general tolerances) for the geometric dimension, unless otherwise agreed with ……
#5 Laser Cutting Plastic and Other Non
Website: espemfg.com
Key Highlights: ESPE MANUFACTURING: A (LASER) CUT ABOVE. ESPE Manufacturing Co. brings years of experience in laser cutting to produce high-quality products at affordable ……
#6 What is the tolerance of laser cut parts?
Website: fabworks.com
Key Highlights: The tolerance of laser cut parts typically ranges from +/- 0.002 inches to +/- 0.05 inches, depending on various factors such as part size and feature ……
#7 Metal Profile Cutting Tolerances
Website: protocase.com
Key Highlights: Comprehensive resource of fabrication tolerances and dimensional variation guidelines for sheet metal manufacturing and fabrication….
#8 Laser Cutting Metal Parts Design Guide
Website: laserboost.com
Key Highlights: Prepare your files easily with our Design Guidelines for laser cutting metal parts ➤ From 1 to 10.000 Parts ➤ Instant Quote ➤ 72 h Shipping | LaserBoost….
#9 A Comprehensive Guide to Laser Cutting Machine Tolerances
Website: yazhimachine.com
Key Highlights: Learn practical laser cutting machine tolerance ranges, key influencing factors, and cost-effective design tips….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Cut Tolerances

2026 Market Trends for Laser Cut Tolerances
As industrial manufacturing advances towards greater precision, efficiency, and automation, laser cutting technology continues to evolve—particularly in the realm of dimensional accuracy and tolerance control. By 2026, several key trends are shaping the expectations and capabilities of laser cut tolerances across industries such as automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and electronics.
Advancements in Laser Source and Beam Control Technologies
One of the most significant drivers behind tighter laser cut tolerances in 2026 is the widespread adoption of high-brightness fiber lasers and ultrafast (pico- and femtosecond) laser systems. These advanced laser sources deliver more consistent beam quality and reduced heat-affected zones (HAZ), enabling cut tolerances of ±0.05 mm or better—especially in thin to medium-thickness materials. Integrated beam shaping and real-time adaptive optics allow dynamic focus control, minimizing edge taper and improving part consistency, which directly enhances tolerance repeatability.
Integration of AI and Machine Learning for Process Optimization
Artificial intelligence is increasingly embedded in laser cutting systems to predict and correct deviations before they occur. By 2026, predictive analytics powered by machine learning models use historical cutting data, material properties, and environmental conditions to adjust cutting parameters in real time. This results in reduced variation and tighter achieved tolerances across production batches. Closed-loop feedback systems with in-process monitoring (e.g., vision systems and thermal sensors) further refine cut accuracy, ensuring compliance with tight engineering specifications.
Rising Demand for Micro and Precision Cutting in High-Tech Sectors
Industries such as medical device manufacturing and consumer electronics are pushing the limits of laser cutting capabilities. By 2026, demand for micron-level tolerances (±0.01 mm or less) in components like stents, sensors, and semiconductor housing is driving investments in specialized laser systems. UV and green lasers, known for their cold ablation properties, are becoming more common for achieving these ultra-precise cuts without thermal distortion, setting new benchmarks for tolerance performance.
Standardization and Metrology Advancements
As tolerances tighten, the need for standardized measurement and verification processes grows. In 2026, there is increased alignment with international standards (e.g., ISO 9013 for thermal cutting quality) and the adoption of automated optical inspection (AOI) systems. These systems use high-resolution imaging and coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) integrated directly into production lines, allowing for 100% in-line tolerance verification. This shift supports quality assurance and reduces scrap rates in high-mix, low-volume manufacturing.
Material-Specific Tolerance Optimization
Manufacturers are moving away from one-size-fits-all cutting strategies. In 2026, laser cutting systems employ material-specific databases and adaptive algorithms to optimize tolerances based on alloy type, thickness, and surface condition. For example, cutting high-strength steels or composites requires different parameter sets than aluminum or copper. This tailored approach ensures that even challenging materials meet tight tolerance requirements consistently.
Conclusion
By 2026, laser cut tolerances are becoming increasingly predictable, tighter, and more consistent, driven by technological innovation and market demands for precision. The convergence of advanced lasers, intelligent software, and enhanced metrology is redefining what is achievable in industrial fabrication. As a result, manufacturers who adopt these trends will gain a competitive edge through improved product quality, reduced waste, and faster time-to-market.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Laser Cut Tolerances (Quality, IP)
When sourcing laser cutting services, overlooking critical aspects related to tolerances, quality control, and intellectual property (IP) protection can lead to project delays, increased costs, or compromised designs. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Inadequate Understanding of Achievable Tolerances
Many buyers assume standard laser cutting can achieve extremely tight tolerances without considering material, thickness, or machine capabilities. Reality often differs—typical laser cutting tolerances range from ±0.1 mm to ±0.2 mm for thin materials, but this worsens with thicker stock or reflective metals. Failing to align design expectations with actual process limits results in rejected parts or costly rework.
Overlooking Material and Thickness Variability
Tolerances are highly dependent on material type and thickness. For example, cutting 10 mm steel requires different parameters and yields looser tolerances than 1 mm aluminum. Sourcing without specifying exact material grades and thicknesses leads to inconsistencies. Suppliers may use substitute materials that alter edge quality and dimensional accuracy.
Poor Communication of Quality Requirements
Vague specifications like “high quality” are insufficient. Without clear documentation—such as GD&T (Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing), surface finish requirements, or acceptable dross levels—suppliers may interpret quality differently. This misalignment often surfaces only during inspection, causing delays and disputes.
Ignoring Machine Capability and Maintenance
Not all laser cutters are equal. CO₂ vs. fiber lasers, machine age, optics condition, and calibration frequency directly impact precision and edge quality. Sourcing based solely on price without vetting a supplier’s equipment and maintenance protocols risks receiving parts with burrs, taper, or positional inaccuracies.
Lack of IP Protection in Supplier Agreements
Sharing CAD files or technical drawings without proper non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) or IP clauses exposes sensitive designs. Some suppliers may reuse or even sell your designs, especially in regions with weak IP enforcement. Always formalize IP ownership and confidentiality before releasing design data.
Skipping Prototyping and First Article Inspection (FAI)
Jumping straight to full production without a prototype run or FAI increases the risk of tolerances being out of spec. A first-article inspection validates that the supplier can meet dimensional and quality requirements before scaling up, minimizing costly errors.
Assuming Automation Guarantees Consistency
While laser cutting is automated, human input in setup, nesting, and maintenance affects outcomes. Assuming consistency across batches without agreed-upon process controls or SPC (Statistical Process Control) monitoring can lead to variance in part dimensions or edge quality over time.
Failing to Define Acceptance Criteria
Without mutually agreed-upon acceptance criteria—such as maximum kerf width, edge squareness, or allowable heat-affected zone (HAZ)—disputes arise during delivery. Clearly define and document inspection methods and pass/fail thresholds in the procurement contract.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires thorough vetting of suppliers, precise technical documentation, robust IP safeguards, and proactive quality validation. Investing time upfront ensures reliable, repeatable results and protects your product integrity.
Laser Cut Tolerances: Logistics & Compliance Guide
Understanding and managing laser cut tolerances is critical for ensuring part functionality, assembly accuracy, and supply chain efficiency. This guide outlines key considerations for logistics and compliance when working with laser-cut components.
Understanding Laser Cut Tolerances
Laser cutting offers high precision, but tolerances vary based on material type, thickness, laser type (CO₂ or fiber), machine calibration, and cutting parameters. Standard tolerances typically range from ±0.1 mm to ±0.2 mm for thin sheet metal, but may widen with thicker materials or complex geometries. It is essential to specify required tolerances clearly in design and purchase documentation to avoid production delays and non-conformance.
Design for Manufacturability (DFM)
To support compliance and streamline logistics, designs should adhere to DFM principles. Avoid excessively tight tolerances unless functionally necessary, as they increase production time, cost, and rejection rates. Maintain consistent material thickness, minimize sharp internal corners, and consider kerf width (typically 0.1–0.3 mm) during design. Providing a Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T) framework ensures clarity and compliance with international standards such as ISO 1101.
Material Selection and Certification
Material choice directly affects achievable tolerances and compliance outcomes. Common materials include mild steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and acrylic—each with unique thermal properties influencing cut precision. Ensure all materials are certified to relevant standards (e.g., ASTM, EN, or ISO) and accompanied by Mill Test Certificates (MTCs) when required. For regulated industries (e.g., aerospace or medical), material traceability is mandatory and must be documented throughout the supply chain.
Quality Control and Inspection Protocols
Establish robust inspection procedures to verify conformance to specified tolerances. Use calibrated coordinate measuring machines (CMM), optical comparators, or laser scanners for accurate measurement. Acceptance criteria should align with defined tolerances and be documented in quality inspection reports. First-article inspections (FAIs) and statistical process control (SPC) help ensure consistency across production batches and support regulatory audits.
Documentation and Compliance Standards
Maintain comprehensive documentation to support logistics and regulatory compliance. Required documents include:
– Engineering drawings with clear tolerance callouts
– Approved supplier list (ASL) and sub-tier traceability
– Quality inspection reports and non-conformance records
– Compliance with ISO 9001 (Quality Management) and ISO 3834 (Welding Quality) where applicable
– Adherence to regional regulations such as REACH, RoHS for material safety
Logistics and Supply Chain Coordination
Clear communication of tolerance requirements between procurement, manufacturing, and logistics teams minimizes delays. Ensure shipping and handling procedures prevent deformation of precision-cut parts—use protective packaging and controlled environments where necessary. Implement barcode or RFID tracking for high-precision components to maintain traceability from production to delivery.
Continuous Improvement and Supplier Audits
Regularly audit suppliers for tolerance capability, equipment calibration records, and quality processes. Encourage feedback loops between design, production, and logistics to refine tolerance specifications and reduce waste. Employ corrective and preventive actions (CAPA) for recurring tolerance-related issues to enhance supply chain reliability.
By aligning laser cut tolerance specifications with logistical and compliance requirements, organizations can achieve repeatable quality, reduce lead times, and ensure adherence to industry standards.
Conclusion on Sourcing Laser Cut Tolerances:
When sourcing laser cutting services, understanding and specifying appropriate tolerances is critical to achieving the desired fit, function, and quality of the final product. Standard laser cutting typically offers tolerances within ±0.1 mm to ±0.2 mm, though actual results depend on material type, thickness, machine calibration, and processing conditions. High-precision systems can achieve tighter tolerances of ±0.05 mm or better, especially with thin materials and optimal setup.
It is essential to collaborate closely with fabricators early in the design phase, communicate tolerance requirements clearly, and consider the cost-effectiveness of tighter tolerances. Over-specifying tolerances can increase production time and cost unnecessarily, while under-specifying may lead to part incompatibility. Therefore, a balanced approach—based on functional requirements, material behavior, and process capabilities—ensures reliable, repeatable results. Ultimately, successful sourcing of laser cut components hinges on aligning design intent with the practical realities of the laser cutting process.