The global laser cutting market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for precision manufacturing across aerospace, automotive, and electronics industries. According to Grand View Research, the market size was valued at USD 7.98 billion in 2023 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.2% from 2024 to 2030. This growth is fueled by advancements in fiber laser technology, rising adoption of automation, and the growing need for tighter tolerances in high-precision components. As manufacturers increasingly prioritize accuracy—often requiring tolerances within ±0.1 mm—the ability to consistently achieve tight dimensional control has become a key competitive differentiator. In this evolving landscape, the following nine manufacturers have emerged as leaders in delivering laser-cut parts with exceptional tolerance capabilities, supported by advanced machinery, rigorous quality control systems, and industry-specific expertise.
Top 9 Laser Cut Tolerance Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laser Cutting Plastic and Other Non
Website: espemfg.com
Key Highlights: Using hybrid laser cutting systems, manufacturers can achieve consistent beam delivery while reducing the amount of power used for cutting. Laser Cutting with ……
#2 EAGLE Lasers
Website: eagle-group.eu
Key Highlights: EAGLE is the producer of the fastest and most efficient laser cutters in the world. Discover our innovative fiber laser products and matching software!…
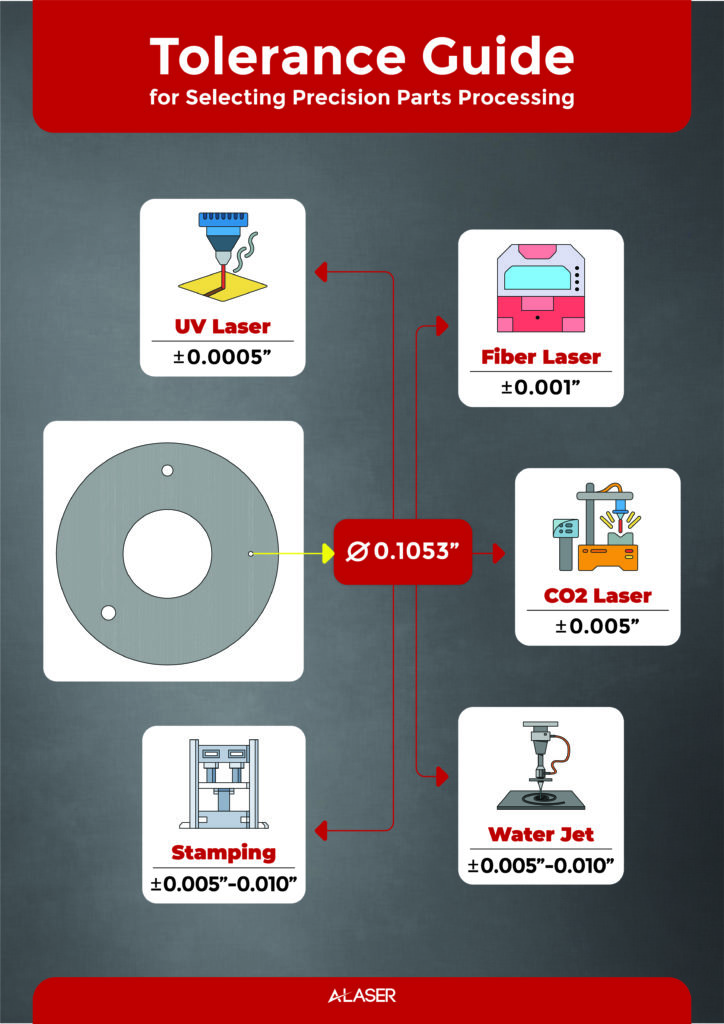
#3 Standard Tolerances
Website: a-laser.com
Key Highlights: Generally, laser cutting tolerances can range from ±0.005 inches to ±0.010 inches for metals and ±0.001 inches to ±0.005 inches for non-metals….
#4 Laser and Sheet Cutting Services
Website: xometry.com
Key Highlights: Instant quotes for laser cutting or waterjet cut parts. No minimums. Get parts in days. Free standard shipping on US and international orders….
#5 What is the tolerance of laser cut parts?
Website: fabworks.com
Key Highlights: Laser cut parts typically have tolerances ranging from +/- 0.002 inches to +/- 0.005 inches, with tighter tolerances for smaller features and slightly wider ……
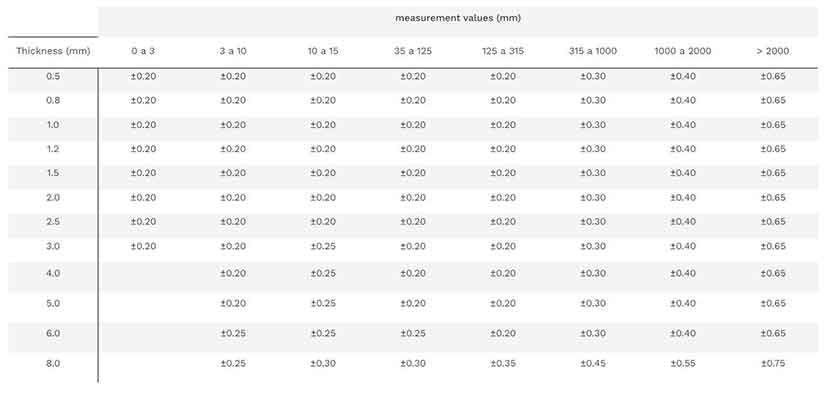
#6 Tolerances and accuracy in laser cutting
Website: teprosa.de
Key Highlights: Through the four possible tolerance classes fine (f), medium (m), coarse (g) and very coarse (sg), the respective accuracy in manufacturing is defined and ……
#7 Precision Laser Cutting
Website: greatlakeseng.com
Key Highlights: Depend on Great Lakes Engineering for precision laser cutting services and parts, delivering exceptional accuracy for your most delicate components….
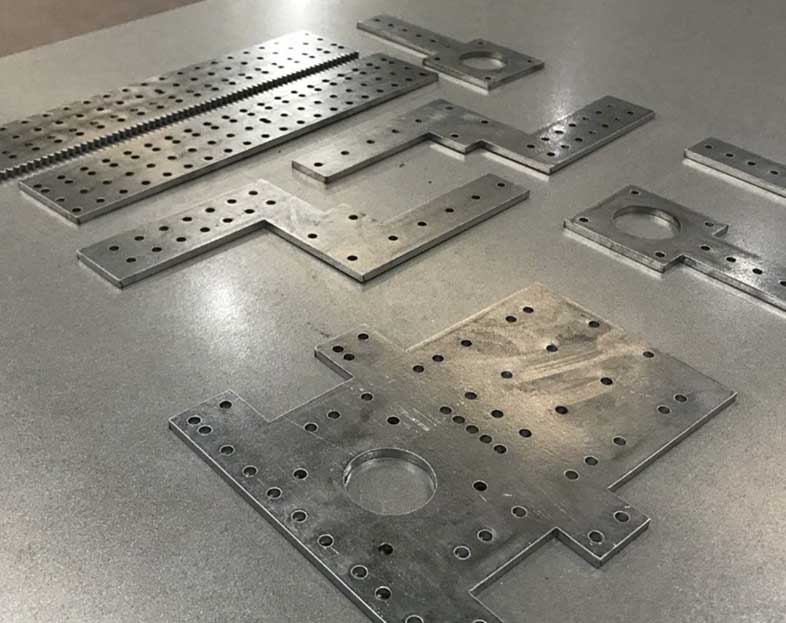
#8 Metal Profile Cutting Tolerances
Website: protocase.com
Key Highlights: Profile cutting tolerance is the slight positional variance that occurs when sheet metal is cut. This happens in the position of features, diameter of holes….
#9 Laser Cutting Metal Parts Design Guide
Website: laserboost.com
Key Highlights: Prepare your files easily with our Design Guidelines for laser cutting metal parts ➤ From 1 to 10.000 Parts ➤ Instant Quote ➤ 72 h Shipping | LaserBoost….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Cut Tolerance

H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for Laser Cut Tolerance
The laser cutting industry is poised for significant advancements by 2026, with precision—specifically laser cut tolerance—emerging as a central competitive differentiator and market driver. Driven by demand from high-tech sectors, technological innovation, and evolving manufacturing standards, the following key trends are expected to define the landscape:
1. Tighter Tolerance Standards Become Mainstream:
By 2026, the baseline expectation for laser cut tolerance is projected to tighten significantly. While ±0.1 mm (±0.004″) remains standard for many applications today, high-precision fiber laser systems will increasingly deliver tolerances of ±0.05 mm (±0.002″) or better as standard capability, especially in industrialized markets. This shift will be fueled by industries like aerospace, medical devices, and electric vehicles (EVs), where micro-level precision directly impacts performance, safety, and regulatory compliance.
2. Rise of Adaptive and AI-Driven Process Control:
A dominant trend will be the integration of real-time adaptive control systems powered by artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). These systems will continuously monitor cut quality through sensors (e.g., vision systems, acoustic emission, plasma monitoring) and automatically adjust laser parameters (power, speed, focus, gas pressure) to maintain tight tolerances despite material variations, thermal distortion, or machine wear. This minimizes human intervention and ensures consistent, high-accuracy output across batches.
3. Convergence of Laser Cutting with Advanced Metrology:
The line between fabrication and inspection will blur. In-line and near-line metrology integration will become standard in high-end laser cutting cells. Systems will feature integrated coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) or non-contact optical scanners that measure critical dimensions immediately after cutting. Feedback loops will allow for automatic compensation in subsequent cuts or real-time alerts, ensuring adherence to tight tolerance specifications and reducing scrap rates.
4. Growth in Demand for Micro and Ultra-Precision Laser Cutting:
Applications requiring micron-level precision (< ±0.01 mm / ±0.0004″)—such as stents, microfluidics, semiconductor components, and photonics—will expand rapidly. This will drive adoption of ultrafast (picosecond and femtosecond) lasers and specialized beam delivery systems. While currently niche, the market for these ultra-precision capabilities will see double-digit growth by 2026, pushing the boundaries of what is achievable with laser cutting.
5. Material-Specific Tolerance Optimization Platforms:
Laser cutting service providers and OEMs will increasingly offer digital platforms and software suites that provide validated, material-specific cutting recipes optimized for maximum tolerance consistency. These platforms, often cloud-based and updated with real-world performance data, will reduce setup times, minimize trial-and-error, and ensure that first-part accuracy meets stringent tolerance requirements across diverse materials (e.g., advanced alloys, composites, thin foils).
6. Sustainability and Precision Efficiency Synergy:
Tighter tolerances will be increasingly linked to sustainability goals. Minimizing kerf width and optimizing cut paths not only improve precision but also reduce material waste and energy consumption per part. By 2026, eco-efficiency metrics tied to precision output (e.g., material utilization ratio at ±0.05mm tolerance) will influence purchasing decisions, especially in cost-sensitive and environmentally regulated industries.
7. Regional Diversification and Standardization Pressures:
While North America, Europe, and East Asia will lead in adopting tight-tolerance laser cutting, emerging markets will see accelerated adoption due to global supply chain integration. This will increase demand for harmonized international standards governing laser cut tolerance measurement, reporting, and verification, reducing ambiguity and enhancing cross-border manufacturing reliability.
Conclusion:
By 2026, laser cut tolerance will transcend a technical specification to become a strategic enabler of innovation and quality. The market will be characterized by smarter, more responsive laser systems, deeper integration of AI and metrology, and a relentless push toward micron-level accuracy. Companies that invest in precision-enabling technologies and processes today will be best positioned to capture value in the high-growth, high-precision manufacturing sectors of tomorrow.
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Laser Cut Tolerance (Quality, IP)
When sourcing laser cutting services, paying close attention to tolerance specifications is critical to ensure part functionality, fit, and overall quality. Overlooking tolerance requirements or mismanaging intellectual property (IP) can lead to significant production issues, cost overruns, and legal risks. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Inadequate Tolerance Specifications
Suppliers may quote standard tolerances (e.g., ±0.1 mm) that don’t meet your design needs. Assuming default tolerances are sufficient without verifying against engineering requirements can result in parts that don’t assemble correctly or fail under stress.
Lack of Process Documentation
Failing to require process documentation (e.g., laser type, power settings, assist gas, speed) undermines quality consistency. Without this, reproducing precise tolerances across batches or suppliers becomes unreliable.
Ignoring Material Variability
Different materials (steel, aluminum, acrylic) react uniquely to laser cutting. Not accounting for thermal expansion, warping, or edge quality based on material type can compromise tolerance accuracy and surface finish.
Overlooking Geometric Complexity
Tight tolerances on complex geometries (e.g., sharp internal corners, narrow slots) may exceed the capabilities of standard laser systems. Designing without consulting the supplier’s equipment limits leads to unachievable specs and rework.
Poor Communication of Tolerances
Providing ambiguous or incomplete tolerance callouts on drawings (e.g., missing GD&T symbols) leads to misinterpretation. This increases the risk of non-conforming parts and delays.
No Prototyping or First Article Inspection (FAI)
Skipping physical prototyping or FAI to validate tolerances before full production can result in mass-producing out-of-spec parts. This is both costly and time-consuming to correct.
IP Exposure Without Protection
Sharing detailed CAD files and tolerance requirements with unvetted suppliers risks unauthorized use or replication of proprietary designs. Always use Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) and limit access to essential geometry.
Assuming All Lasers Are Equal
Not all laser cutting systems (CO2 vs. fiber) or machines (entry-level vs. high-precision) deliver the same accuracy. Sourcing based on price alone without evaluating machine capability can compromise tolerance performance.
Failure to Audit Supplier Quality Systems
Neglecting to audit a supplier’s quality management system (e.g., ISO 9001 certification) or review their calibration and maintenance records may result in inconsistent tolerance control over time.
Not Defining Acceptance Criteria
Failing to formally define how tolerance compliance will be measured (e.g., CMM, optical comparator) and accepted (sampling plan, AQL levels) leads to disputes over part quality and rejection risks.
Laser Cut Tolerance: Logistics & Compliance Guide
Understanding and managing laser cut tolerances is essential for ensuring that parts meet design specifications, function correctly in assembly, and comply with relevant industry standards. This guide outlines key considerations related to logistics and regulatory compliance when working with laser cutting processes.
Understanding Laser Cut Tolerances
Laser cut tolerances refer to the allowable deviation from a specified dimension in a manufactured part. Standard laser cutting typically achieves tolerances of ±0.1 mm to ±0.2 mm, though tighter tolerances (±0.05 mm) are possible with high-precision systems and controlled conditions. Tolerances can be affected by material type, thickness, laser type (CO₂, fiber), machine calibration, and cutting speed.
Material and Thickness Considerations
Different materials—such as mild steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and acrylic—respond uniquely to laser cutting, affecting edge quality and dimensional accuracy. Thicker materials generally result in wider kerf widths and increased taper, impacting tolerance consistency. Ensure material certifications (e.g., mill test reports) are available and maintained for traceability, especially in regulated industries like aerospace or medical devices.
Geometric and Design Constraints
Design features such as internal corners, narrow slots, and intricate contours can challenge tolerance maintenance. Minimum feature sizes and recommended bend radii should align with machine capabilities. Design for manufacturability (DFM) reviews help identify potential tolerance risks early. Use standardized tolerance callouts (e.g., ISO 2768 or ASME Y14.5) on technical drawings to ensure clarity across supply chain partners.
Machine Calibration and Process Control
Regular calibration of laser cutting equipment is vital for maintaining tolerance consistency. Implement preventive maintenance schedules and perform routine inspections of optics, nozzles, and alignment systems. Utilize statistical process control (SPC) methods to monitor cutting performance and detect drift before non-conforming parts are produced.
Quality Assurance and Inspection Protocols
Establish inspection procedures using calibrated tools such as coordinate measuring machines (CMM), optical comparators, or micrometers. First article inspections (FAI) and production part approval processes (PPAP) may be required for compliance in automotive (IATF 16949) or aerospace (AS9100) sectors. Maintain documented evidence of inspections for audit readiness.
Regulatory and Industry Compliance
Adhere to relevant standards based on application:
– ISO 9001: Quality management systems for consistent product conformity.
– ASME Y14.5: Dimensioning and tolerancing standards.
– ISO 2768: General tolerances for linear and angular dimensions without individual tolerance indications.
– Industry-specific regulations (e.g., FDA for medical devices, FAA for aerospace) may impose additional traceability and documentation requirements.
Supply Chain and Logistics Coordination
Communicate tolerance requirements clearly with suppliers and subcontractors. Include tolerance specifications in purchase orders and technical data packages. Ensure that packaging and handling methods prevent part deformation during shipping, which could affect dimensional integrity. Track lot numbers and production batches for full traceability.
Documentation and Record Keeping
Maintain comprehensive records including:
– Approved drawings with tolerance specifications
– Material certifications
– Machine calibration logs
– Inspection reports and non-conformance records
– Corrective action reports (CARs)
These documents support compliance audits and facilitate root cause analysis in case of quality issues.
Continuous Improvement and Supplier Audits
Regularly evaluate supplier performance through on-site audits and quality metrics. Encourage feedback loops to refine tolerancing practices and reduce variability. Invest in training for design, production, and quality teams to stay current with laser cutting advancements and compliance requirements.
By integrating precise tolerance management with robust compliance protocols, organizations can ensure reliable, high-quality laser-cut components while meeting logistical and regulatory demands.
Conclusion for Sourcing Laser Cut Tolerance:
When sourcing laser cutting services, understanding and specifying the appropriate cut tolerance is critical to ensuring part accuracy, functionality, and compatibility with assemblies. Laser cutting generally offers tight tolerances—typically within ±0.1 mm to ±0.2 mm for most materials and thicknesses—though actual precision depends on factors such as material type, thickness, machine quality, and laser type (CO₂, fiber, etc.). Variability can also arise from heat-affected zones, kerf width, and edge quality.
To achieve consistent and reliable results, it is essential to:
- Clearly communicate tolerance requirements in technical drawings.
- Collaborate closely with suppliers to understand their machine capabilities and limitations.
- Consider post-processing needs if tighter tolerances or smoother edges are required.
- Perform prototyping or sampling before full-scale production to validate dimensional accuracy.
Ultimately, selecting a reputable laser cutting provider with proven precision, process control, and material experience ensures that tolerance specifications are met, minimizing rework, fit issues, and project delays. Proper tolerance management balances design intent with manufacturing feasibility, leading to successful, cost-effective outcomes.