The global laser cleaning systems market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for eco-friendly and precision surface treatment solutions across industries such as automotive, aerospace, manufacturing, and cultural heritage restoration. According to Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 350 million in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 12% through 2029. This expansion is attributed to the rising adoption of laser cleaning as a chemical-free alternative to traditional methods, coupled with advancements in fiber laser technology that enhance efficiency and reduce operational costs. As environmental regulations tighten and industries prioritize automation, laser cleaning systems have emerged as a sustainable and scalable solution. This growing demand has spurred innovation and competition, leading to the emergence of key manufacturers worldwide. Here, we highlight the top 9 laser cleaning system manufacturers shaping the future of industrial cleaning through cutting-edge technology, global reach, and strong performance metrics.
Top 9 Laser Cleaning System Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
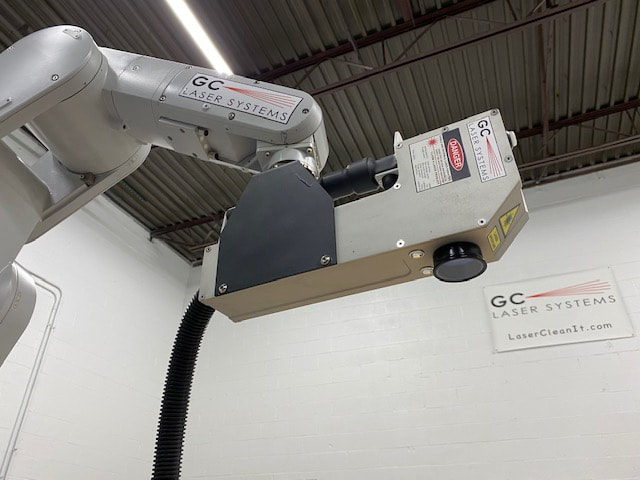
#1 G.C. Laser Systems
Website: gclasers.com
Key Highlights: G.C. Laser Systems Inc. manufactures unique laser cleaning technology that offers unmatched cleaning precision and surface prep. Our laser systems are ……
#2 Laserax
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Laserax works with the world’s leading manufacturers to implement laser cleaning, welding, texturing, and marking solutions….
#3 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: we engineer and manufacture the most advanced—and most powerful—pulsed industrial laser cleaning systems on the market, built for both manual and automated ……
#4 Clean Laser Systems
Website: cleanlaser.de
Key Highlights: IPG | cleanLASER has been developing and producing high-precision laser systems for cleaning and industrial surface treatment for more than 20 years….
#5 SFX Laser
Website: sfxlaser.com
Key Highlights: SFX Laser is a 20+ years professional laser equipment manufacturer including laser cleaning machine, laser welding machine, fiber laser engraver, fiber laser…
#6 SHARK P CL Industrial Laser Cleaning Machines (100
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: SHARK P CL is an industrial pulsed laser cleaning machine series by PULSAR Laser with outputs from 100 W to 1000 W, air-cooled up to 500 W….
#7 Laser Cleaning and Laser Ablation Systems
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Remove rust and surface contaminants with our laser cleaning & laser ablation systems. Experience superior cleaning tech, automation, and eco-friendly ……
#8 Laser Cleaning
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Discover Your Laser Cleaning Solution IPG is a partner for every stage of production from research and development to full-scale manufacturing….
#9 Netalux
Website: netalux.com
Key Highlights: Discover our award-winning Laser Cleaning Solutions for the world’s most demanding industries. Discover our products and global service now….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Cleaning System

H2: Emerging Market Trends in the Laser Cleaning Systems Industry (2026 Outlook)
By 2026, the global laser cleaning system market is poised for significant transformation, driven by technological advancements, environmental imperatives, and expanding industrial applications. Key trends shaping the market landscape include:
1. Accelerated Adoption Driven by Environmental Regulations:
Stringent global regulations targeting chemical waste, abrasive blasting residues, and VOC emissions (e.g., EU Green Deal, EPA guidelines) will propel industries toward eco-friendly alternatives. Laser cleaning’s solvent-free, waste-minimizing operation aligns perfectly, making it a de facto standard in sectors like aerospace, automotive, and cultural heritage restoration. Demand will surge as companies prioritize ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) compliance.
2. Technological Maturation & Cost Reduction:
Advancements in fiber laser efficiency, beam delivery systems, and AI-powered control software will enhance cleaning speed, precision, and automation. Modular designs and economies of scale will drive down system costs, improving ROI and making laser cleaning accessible to SMEs. Integration with robotics and IoT for real-time monitoring will become commonplace, enabling smart, predictive maintenance workflows.
3. Expansion into High-Growth Industrial Sectors:
Beyond traditional uses in mold cleaning and rust removal, adoption will accelerate in:
– Electric Vehicle (EV) Manufacturing: Battery electrode cleaning, motor component degreasing, and weld seam preparation.
– Renewable Energy: Maintenance of solar panels, wind turbine blades, and nuclear decommissioning.
– Additive Manufacturing: Post-processing of 3D-printed metal parts to remove support structures and surface oxides.
4. Shift Toward Automated and Robotic Integration:
The demand for consistent, high-throughput cleaning in automated production lines will fuel growth in robotic laser cleaning cells. Collaborative robots (cobots) equipped with lightweight laser modules will enable flexible, human-safe operation in dynamic environments, particularly in automotive and electronics assembly.
5. Geographic Market Diversification:
While North America and Europe lead in technology adoption due to regulatory pressure, Asia-Pacific (especially China, Japan, and South Korea) will emerge as the fastest-growing region. This growth will be fueled by manufacturing expansion, government support for green tech, and rising labor costs making automation more attractive.
6. Rising Focus on Safety and Standardization:
As deployment increases, standardized safety protocols (laser safety, fume extraction) and industry-specific cleaning validation standards will emerge. Training and certification programs for operators will become critical, addressing skill gaps and ensuring safe, effective implementation.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the laser cleaning systems market will transition from a niche technology to a mainstream industrial solution. Success will favor vendors offering cost-effective, automated, and application-specific systems, while end-users leverage the technology for sustainability, precision, and operational efficiency in an increasingly automated and regulated industrial world.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Laser Cleaning Systems: Quality and Intellectual Property (IP) Concerns
Sourcing a laser cleaning system can significantly enhance industrial cleaning processes, but businesses often encounter critical pitfalls related to quality and intellectual property (IP). Overlooking these factors can lead to subpar performance, safety risks, legal liabilities, and long-term operational setbacks.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Laser Source Quality
One of the most common pitfalls is selecting systems with low-quality or underspecified laser sources. Many suppliers, especially those offering budget systems, use unbranded or reconditioned fiber lasers that lack reliability and consistent output. Poor-quality lasers degrade quickly, resulting in unstable beam parameters, reduced cleaning efficiency, and frequent downtime. Always verify the laser source manufacturer (e.g., IPG, Raycus, nLIGHT) and request performance data such as average power stability, beam quality (M²), and duty cycle.
Compromised Optical Components
Low-cost systems often cut corners on optics like lenses, mirrors, and protective windows. Inferior coatings and materials can lead to rapid degradation under high-intensity laser exposure, causing beam distortion, power loss, and increased maintenance costs. Systems lacking robust beam delivery and focusing optics will underperform, particularly in demanding industrial environments.
Insufficient Safety Features and Compliance
Sourcing from suppliers that do not adhere to international safety standards (e.g., IEC 60825 for laser safety) poses serious risks. Incomplete interlocks, absent emergency stops, or inadequate enclosure designs can endanger operators. Always confirm that the system has proper CE, FDA, or equivalent certifications and includes essential safety features like key switches, warning indicators, and protective housings.
Lack of Real-World Performance Validation
Many suppliers provide idealized lab results that don’t reflect real-world conditions. Without access to third-party testing data or customer references in your specific application (e.g., rust removal from steel, paint stripping from composites), you risk investing in a system that fails in practice. Insist on application-specific trials or on-site demonstrations before finalizing a purchase.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Use of Counterfeit or Cloned Technology
Some manufacturers, particularly in regions with lax IP enforcement, produce systems that clone or reverse-engineer proprietary designs from established brands. These systems may infringe on patents related to beam delivery mechanisms, control software, or cooling systems. Purchasing such equipment exposes your business to potential legal action, especially if deployed in markets with strong IP protections like the EU or U.S.
Proprietary Software and Hidden Limitations
Many laser systems rely on proprietary control software for parameter optimization, diagnostics, and integration. Sourcing from vendors who do not provide software access or API documentation can limit customization, integration with existing production lines, and long-term maintenance. Beware of vendors who lock users into closed ecosystems or charge exorbitant fees for updates and support.
Unclear Warranty and Support Terms
Poor-quality or IP-infringing systems often come with vague or unenforceable warranty terms. If a system fails due to a copied design flaw or substandard components, the supplier may refuse support or disappear altogether. Ensure that warranties cover both hardware and software, and verify the vendor’s track record for after-sales service and spare parts availability.
Supply Chain and Component Traceability Issues
Reputable suppliers provide transparency about component origins and manufacturing processes. When IP is disregarded, component traceability often suffers, making it difficult to assess quality, ensure compliance, or resolve field failures. Always request documentation on key component suppliers and manufacturing standards.
Conclusion
To mitigate these pitfalls, conduct thorough due diligence: evaluate the supplier’s reputation, insist on certifications and test data, verify IP compliance, and prioritize long-term support over initial cost savings. Investing time upfront in assessing quality and IP integrity ensures a reliable, safe, and legally sound laser cleaning solution.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Cleaning Systems
Overview
This guide outlines the key logistics and compliance considerations for the transportation, import/export, installation, and operation of Laser Cleaning Systems. Adherence to these guidelines ensures safety, regulatory alignment, and smooth deployment across international and domestic markets.
Regulatory Classification & Documentation
Laser cleaning systems are subject to multiple regulatory frameworks based on their component technologies. Proper classification and documentation are essential for compliance.
- HS Code (Harmonized System Code): Typically classified under 8543.70 (“Electro-thermic appliances with laser or optical radiation”) or 8479.89 (“Machines of a kind used in industrial processes, not elsewhere specified”). Confirm with local customs authorities.
- Export Control Classification Number (ECCN): In the U.S., laser systems may fall under 6A003.b.4 (lasers exceeding specific power or pulse criteria). Conduct an ECCN review to determine if export licenses are required.
- Documentation Required: Commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading/air waybill, certificate of origin, technical specifications, and compliance certifications (e.g., CE, FDA, IEC).
Safety & Laser Classification
Laser cleaning systems are categorized based on laser output and potential hazard.
- Laser Class: Most industrial laser cleaners are Class 4 lasers (high-power, capable of causing skin and eye injuries, fire hazards).
- Compliance Standards:
- IEC 60825-1: Safety of laser products
- ANSI Z136.1: Safe Use of Lasers (U.S.)
- EN 60825-1 (European equivalent)
- Required Safeguards: Interlocks, emergency stop buttons, warning labels, beam enclosures, and interlocked access doors.
- User Training: Mandatory for operators; include laser safety, PPE use, and emergency procedures.
Transportation & Packaging
Secure handling and packaging are critical due to the system’s sensitivity and hazard level.
- Packaging Requirements:
- Use shock-absorbent, moisture-resistant materials.
- Secure optical and electronic components with anti-vibration mounts.
- Clearly label packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Laser Radiation” warnings.
- Transport Regulations:
- For air freight: Comply with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations (Class 9 – Miscellaneous).
- For ground/sea: Follow ADR/RID (Europe) or IMDG Code (maritime) as applicable.
- Include safety data sheets (SDS) for any accompanying chemicals (e.g., cooling agents).
- Battery Handling: If system includes lithium batteries, follow UN 38.3 testing and packaging standards.
Import & Customs Clearance
Proper preparation streamlines customs entry and avoids delays.
- Country-Specific Requirements:
- EU: CE marking with Declaration of Conformity (DoC), notified body involvement if needed.
- USA: FDA registration (CDRH – Center for Devices and Radiological Health) for laser products.
- Canada: Compliance with Health Canada’s Radiation Emitting Devices Act (REDA).
- China: CCC certification may be required; verify with local agent.
- Duties & Taxes: Research applicable tariffs and VAT/GST rates. Use Incoterms (e.g., DDP, DAP) to clarify responsibility.
Installation & Site Compliance
Ensure the operational environment meets regulatory and safety standards.
- Electrical Requirements:
- Match local voltage (e.g., 230V/50Hz in EU, 120V/60Hz in US).
- Ensure proper grounding and surge protection.
- Ventilation & Fume Extraction:
- Laser cleaning produces fumes and particulates; install certified filtration/extraction systems compliant with OSHA (U.S.) or REACH/CLP (EU).
- Workplace Safety:
- Establish laser-controlled areas with warning signs and access restrictions.
- Provide appropriate PPE (laser safety goggles, respirators, protective clothing).
- Environmental Compliance:
- Dispose of contaminated waste (e.g., ablated materials) per local hazardous waste regulations.
- Monitor noise levels; ensure compliance with limits (e.g., EU Directive 2003/10/EC).
Maintenance & Documentation
Maintain compliance throughout the product lifecycle.
- Calibration & Servicing: Follow manufacturer’s schedule; use authorized technicians.
- Record Keeping: Retain logs of maintenance, safety inspections, operator training, and incident reports.
- Software Updates: Ensure firmware complies with electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) and safety standards (e.g., IEC 61326).
Conclusion
Compliance with logistics and regulatory requirements is essential for the safe and legal deployment of laser cleaning systems. Proactive planning, accurate documentation, and adherence to international and local standards minimize risks and ensure operational continuity. Consult with legal, customs, and safety experts in each target market to verify requirements.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Laser Cleaning System
After thorough evaluation of available technologies, suppliers, and operational requirements, sourcing a laser cleaning system represents a strategic investment in advancing efficiency, sustainability, and precision in surface treatment processes. Laser cleaning offers significant advantages over traditional methods—including reduced environmental impact, minimal substrate damage, elimination of consumables, and improved worker safety.
By selecting a reliable supplier with proven technical expertise, strong after-sales support, and scalable solutions, organizations can ensure optimal integration of the system into existing workflows. Key considerations such as power requirements, automation compatibility, maintenance needs, and total cost of ownership have been assessed to align the chosen system with long-term operational goals.
In conclusion, adopting a laser cleaning system supports a transition toward smarter, cleaner manufacturing and maintenance practices. It enhances process reliability, reduces downtime, and positions the organization at the forefront of innovative, eco-friendly technology—making it a justified and forward-thinking procurement decision.