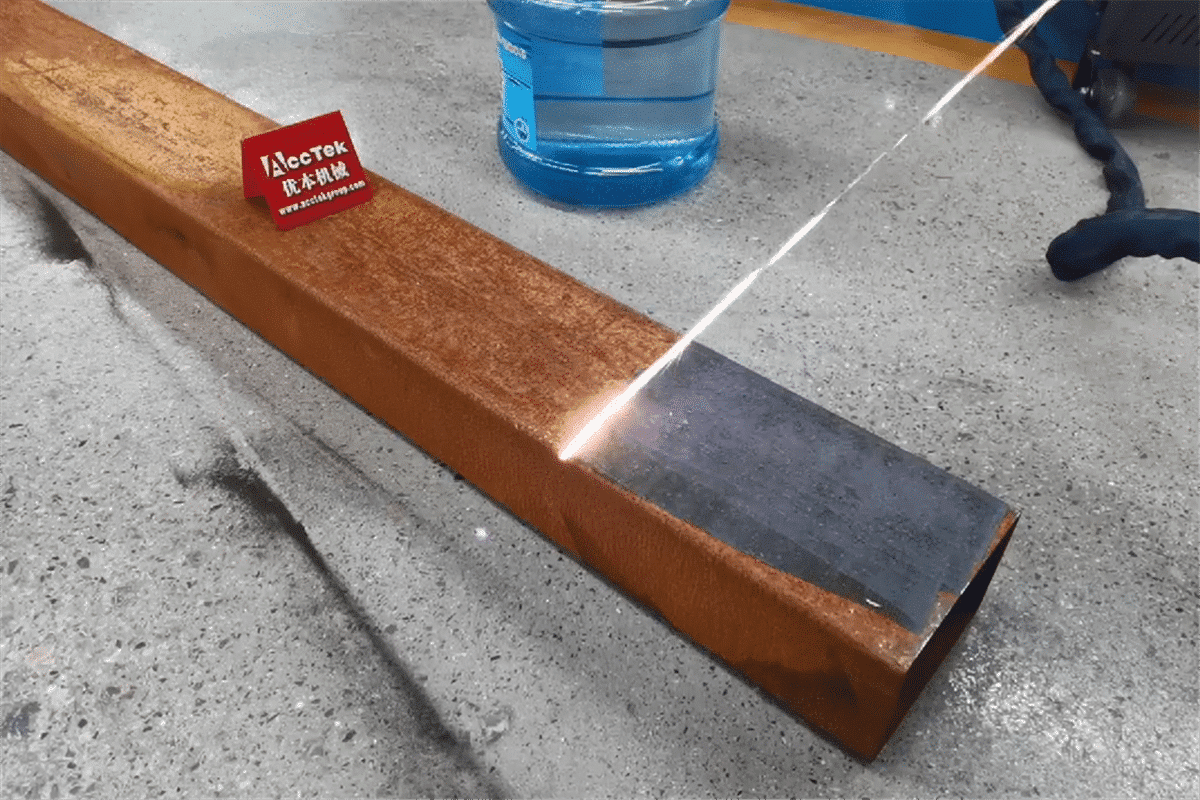
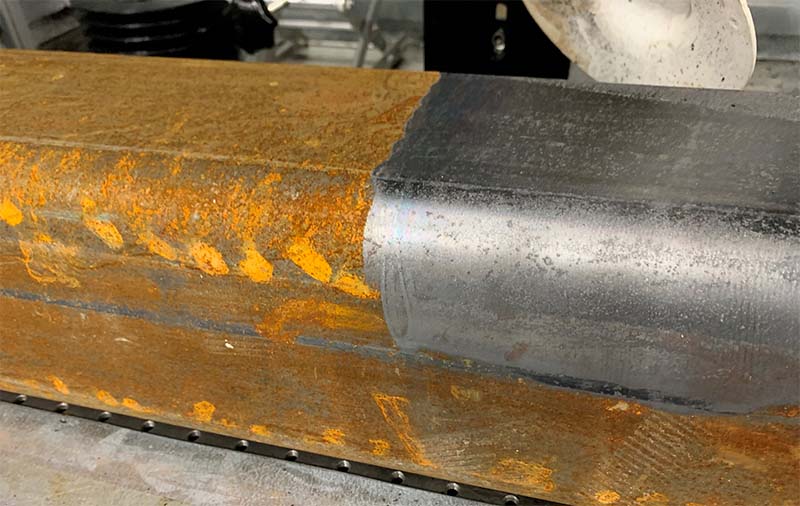
The global laser cleaning market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for eco-friendly and precision surface treatment technologies across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and heavy manufacturing. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 642.8 million in 2022 and is projected to reach USD 1,557.6 million by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 15.8% during the forecast period. A key application fueling this expansion is laser-based rust removal, which offers a non-abrasive, chemical-free alternative to traditional methods. As industries prioritize sustainability and operational efficiency, adoption of laser cleaning systems has surged—Grand View Research noted in 2022 that the industrial cleaning segment accounted for over 40% of total laser cleaning applications, with metal surface preparation leading the demand. With technological advancements reducing equipment costs and improving portability, investment in laser rust removal solutions is accelerating. This growing momentum has led to a competitive landscape of manufacturers innovating in power efficiency, automation integration, and handheld usability. Based on market presence, technological capability, and customer adoption metrics, the following ten companies represent the leading players in laser cleaning for rust removal as of 2024.
Top 10 Laser Cleaning Rust Removal Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laserax
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Our laser cleaning solutions are used to remove a range of contaminants from metal surfaces such as rust, oxide, paint, and electrolyte. … DPSS Lasers – Booth ……
#2 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: Clean smarter with laser light. Fully cleaning rust of machine parts with the help of laser cleaning. WHY LASER CLEANING? Embrace the future of sustainable ……
#3 Clean Laser Systems
Website: cleanlaser.de
Key Highlights: IPG | cleanLASER has been developing and producing high-precision laser systems for cleaning and industrial surface treatment for more than 20 years….
#4 Laser Cleaning
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaning is used across a variety of industries to remove unwanted surface materials like coatings, paints, rust, oil, and for surface preparation for ……
#5 Laser Cleaning and Laser Ablation Systems
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Remove rust and surface contaminants with our laser cleaning & laser ablation systems. Experience superior cleaning tech, automation, and eco-friendly ……
#6 Laser Rust Removal
Website: keyence.com
Key Highlights: The laser rust removal machine uses a focused laser beam with high peak power and short pulse to heat the external surface (the rust) to its evaporation point….
#7 Laser cleaning
Website: p-laserusa.com
Key Highlights: Our laser machines are mainly used to remove the following contaminants: Rust – Paint – Coatings – Release Agents – Grease, Oils – Soot – Rubber- Organic ……
#8 Laser Rust Removal
Website: powerlase-limited.com
Key Highlights: Achieve super fast rust removal rates with out lasers. Watch this super fast rust removal from carbon steel panel with the new ultra-lightweight Vulcan handheld ……
#9 Laser Cleaning Rust Removal
Website: nuwavelaser.com
Key Highlights: Our equipment uses pulsating lasers to blast away any contaminants from metal surfaces. This process is eco-friendly, as you won’t need any ……
#10 Laser Rust Removal Guide
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: A practical guide for professionals and entrepreneurs using PULSAR Laser systems to remove rust safely, efficiently and without abrasives….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Cleaning Rust Removal

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Laser Cleaning Rust Removal
The global market for laser cleaning, particularly in rust removal applications, is poised for significant transformation by 2026. Driven by technological advancements, increasing environmental regulations, and rising demand for precision industrial cleaning, laser-based rust removal is emerging as a preferred alternative to traditional methods such as sandblasting, chemical treatments, and mechanical scraping.
-
Market Growth and Expansion
The laser cleaning market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 20% between 2021 and 2026, with rust removal representing a key application segment. Industries such as automotive, aerospace, maritime, and heavy manufacturing are increasingly adopting laser systems to improve efficiency and reduce downtime. The global market value for laser cleaning is expected to surpass USD 1.5 billion by 2026, with rust removal accounting for approximately 35–40% of total demand. -
Technological Advancements
By 2026, fiber laser systems will dominate the rust removal segment due to their higher efficiency, durability, and lower maintenance requirements. Innovations such as handheld laser cleaners, automated robotic integration, and AI-driven control systems will enhance precision and usability, making laser cleaning accessible to small and medium enterprises (SMEs). Pulsed laser technologies will continue to improve, allowing for selective rust ablation without damaging underlying substrates like steel or aluminum. -
Environmental and Regulatory Drivers
Stringent environmental regulations across North America, Europe, and parts of Asia-Pacific are pushing industries to adopt eco-friendly cleaning methods. Laser cleaning produces no secondary waste, eliminates the need for chemical solvents, and reduces hazardous particulate emissions—key advantages over abrasive blasting. Compliance with standards such as ISO 14001 and REACH is accelerating the shift toward laser-based rust removal. -
Industry Adoption and Demand
The maritime and offshore sectors are expected to be major adopters by 2026, where rust is a persistent challenge due to saltwater exposure. In the automotive industry, laser cleaning is being integrated into pre-welding and surface preparation processes to ensure high-quality joins and coatings. Aerospace manufacturers are utilizing laser systems for delicate rust removal on aircraft components without compromising structural integrity. -
Regional Trends
Europe leads in early adoption, supported by strong environmental policies and advanced manufacturing infrastructure. North America is experiencing rapid growth, fueled by investments in defense and infrastructure renewal. Meanwhile, Asia-Pacific—especially China, Japan, and South Korea—is emerging as a high-growth region due to expanding industrialization and increased R&D in laser technologies. -
Challenges and Outlook
Despite strong momentum, high initial equipment costs and the need for skilled operators remain barriers to widespread adoption. However, as production scales and technological maturity increases, prices are expected to decline, improving ROI. By 2026, laser cleaning for rust removal is anticipated to become a standard practice in critical industries, supported by ongoing innovation, regulatory tailwinds, and growing awareness of sustainability benefits.

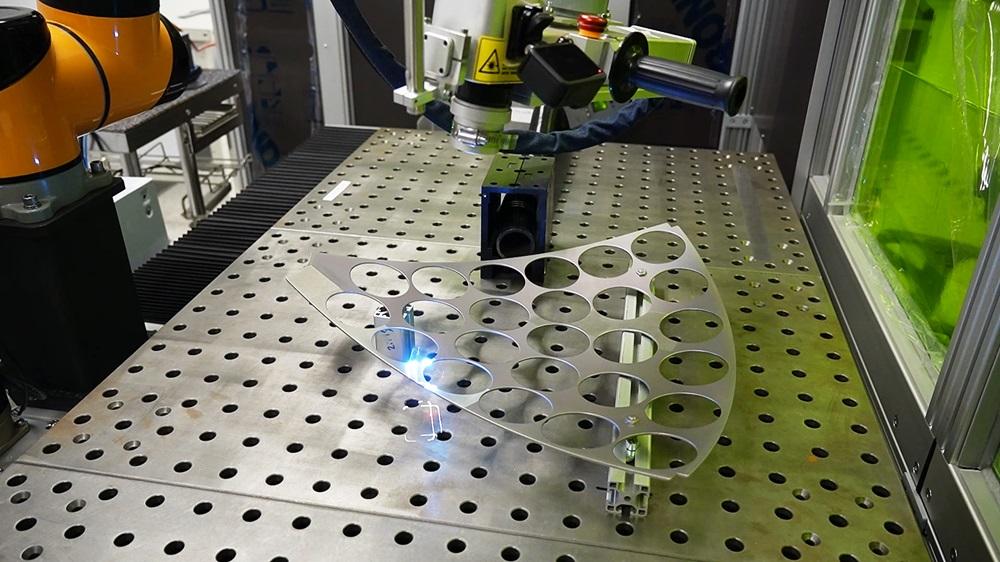
Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Laser Cleaning Equipment for Rust Removal
When sourcing laser cleaning systems specifically for rust removal, businesses often encounter significant challenges related to quality and intellectual property (IP). Overlooking these pitfalls can lead to poor performance, legal risks, and long-term cost inefficiencies.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Power and Pulse Specifications
Many suppliers advertise high-power lasers without disclosing critical pulse parameters such as pulse energy, frequency, and beam quality. A system may claim 1000W output, but if the pulse structure isn’t optimized for rust ablation, it may fail to remove corrosion effectively or damage the underlying substrate. Buyers must verify pulse duration (typically nanosecond or picosecond for rust), beam spot size, and scanning speed capabilities.
Poor Beam Delivery and Scanning Systems
Low-quality galvanometer scanners or poorly designed optical paths result in inconsistent cleaning, especially on curved or complex surfaces. Substandard focusing mechanisms reduce cleaning precision and increase processing time. Always request live demonstrations on rusted metal samples relevant to your application.
Insufficient Cooling and Duty Cycle
Some budget systems overstate continuous operation capacity. Inadequate cooling leads to thermal lensing and premature component failure, especially during extended rust removal tasks. Verify the system’s duty cycle and cooling mechanism (air vs. water) to ensure reliability in industrial environments.
Lack of Safety Features and Compliance
Non-compliant systems may lack proper laser safety certifications (e.g., FDA, CE Class 4 requirements), interlocks, or fume extraction integration. This poses serious workplace safety risks and may prevent deployment in regulated industries.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Use of Counterfeit or Cloned Components
Some suppliers, particularly in less-regulated markets, use copied control boards, software, or laser sources that infringe on original manufacturers’ IP. These clones often lack reliability, firmware updates, and technical support, increasing downtime and maintenance costs.
Proprietary Software Limitations
Hidden IP pitfalls include restricted software access, lack of API for integration, or region-locked updates. Ensure the supplier provides full operational control, parameter customization, and compatibility with your automation systems. Avoid vendors that lock users into proprietary ecosystems without transparency.
Unclear Ownership of Customizations
If you request custom configurations (e.g., robotic arm integration or specific cleaning patterns), clarify IP ownership upfront. Some suppliers retain rights to modifications, limiting your ability to replicate or upgrade the system without ongoing fees.
Risk of Legal Exposure
Purchasing equipment that incorporates stolen or unlicensed IP can expose your company to third-party litigation, import bans, or confiscation—especially when sourcing from jurisdictions with weak IP enforcement.
Mitigating these pitfalls requires thorough due diligence: demand technical documentation, conduct on-site testing, verify component origins, and consult legal experts when necessary. Prioritize suppliers with transparent engineering practices, proven field performance, and clear IP licensing terms.
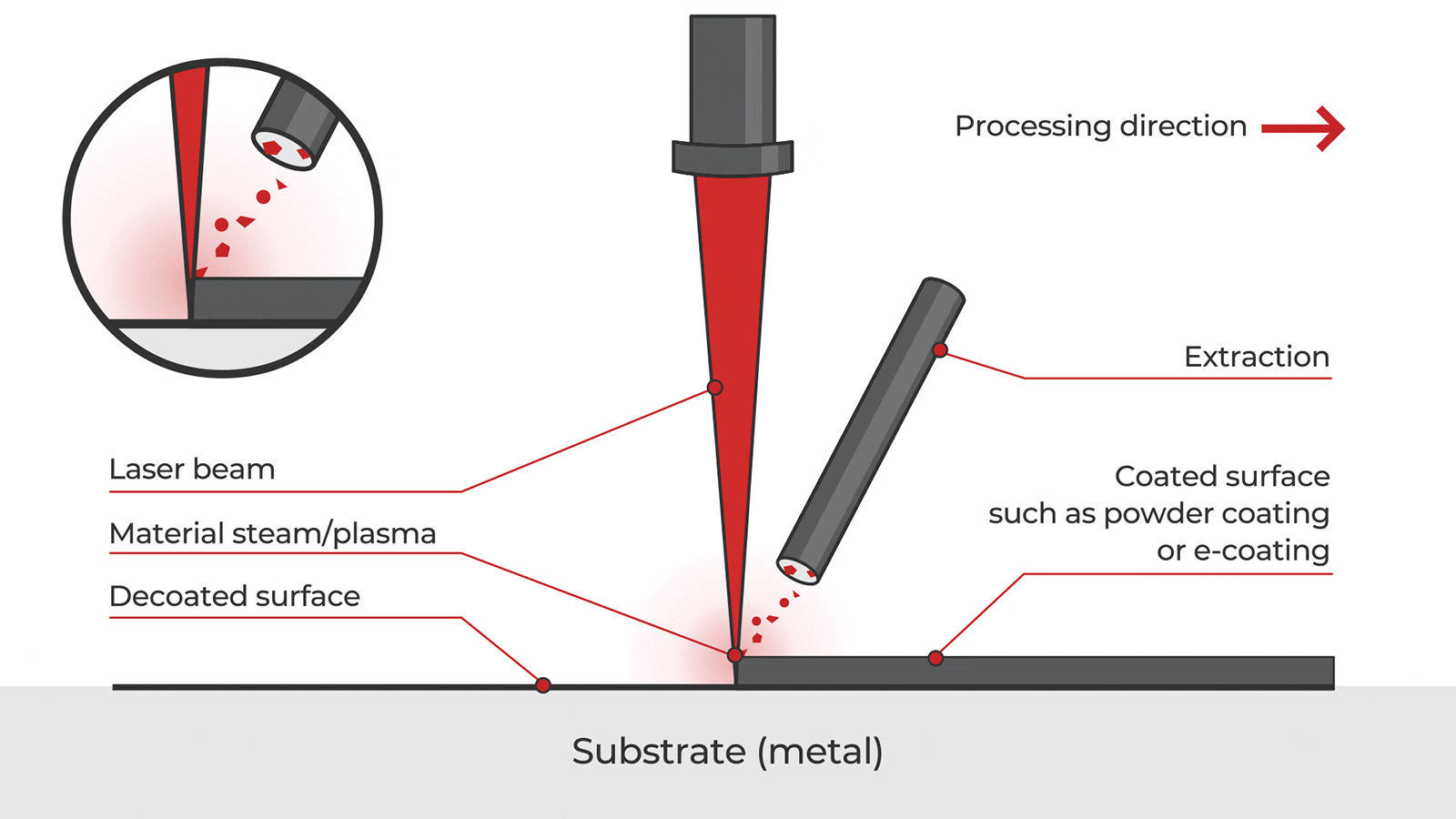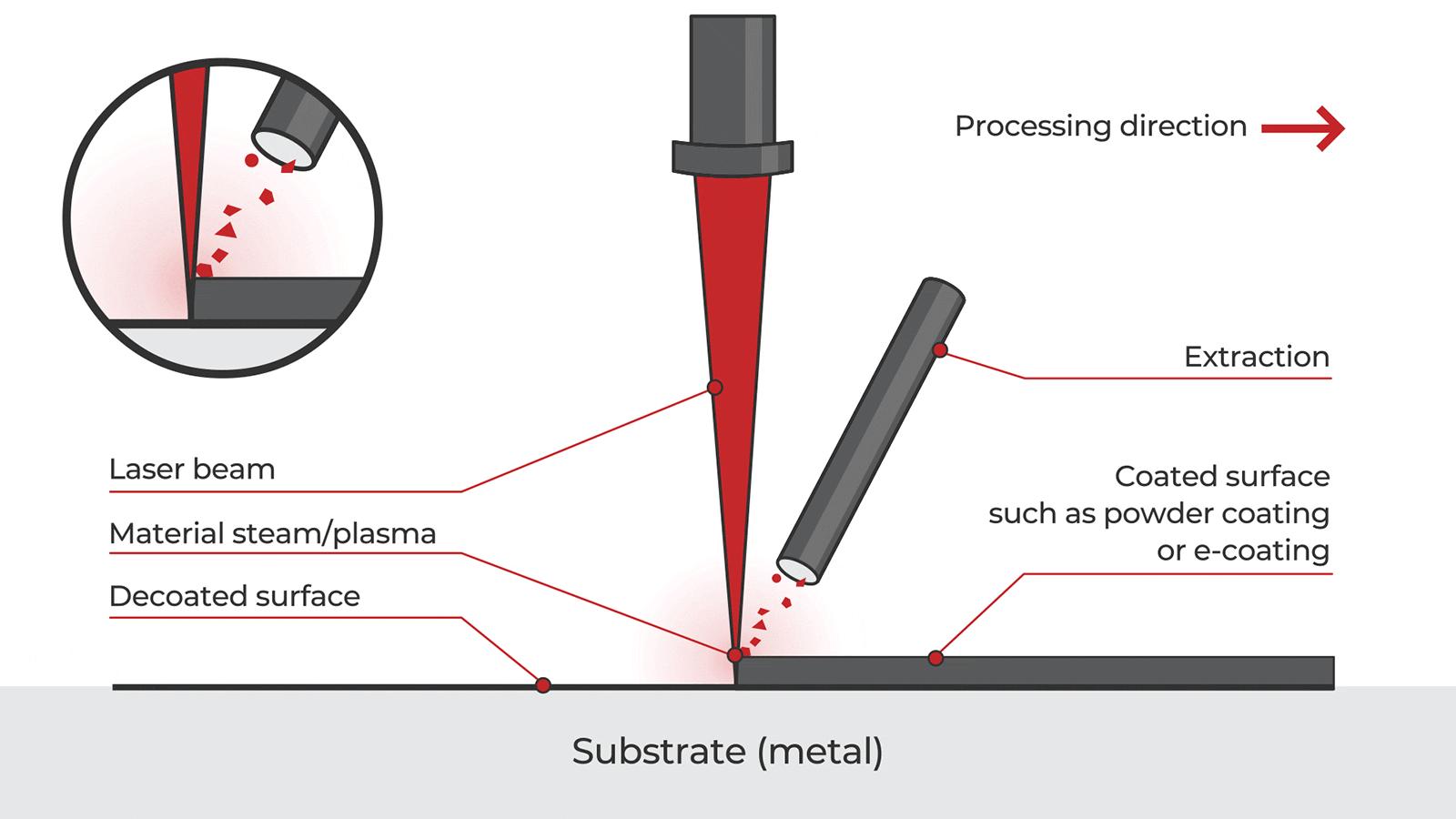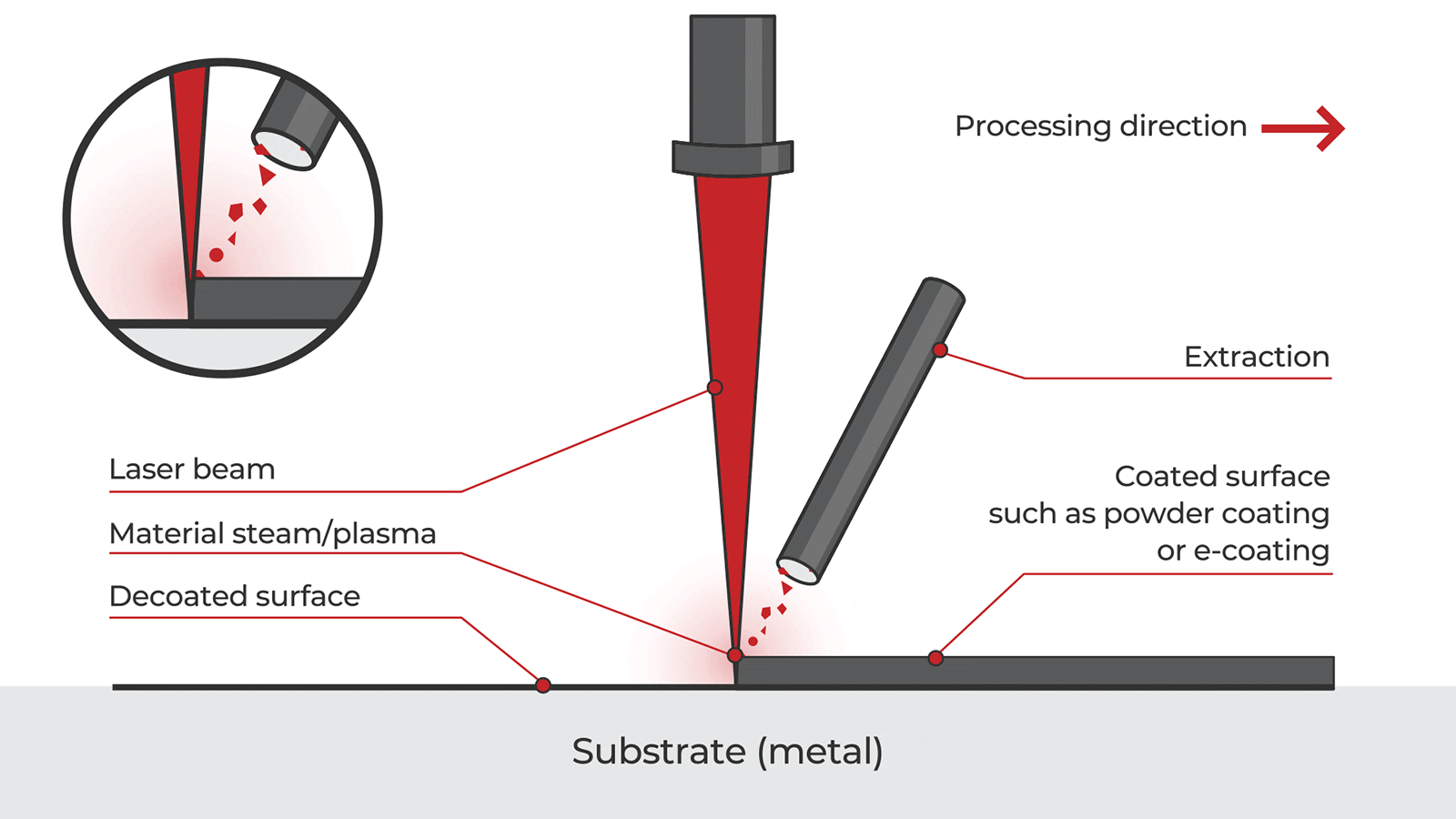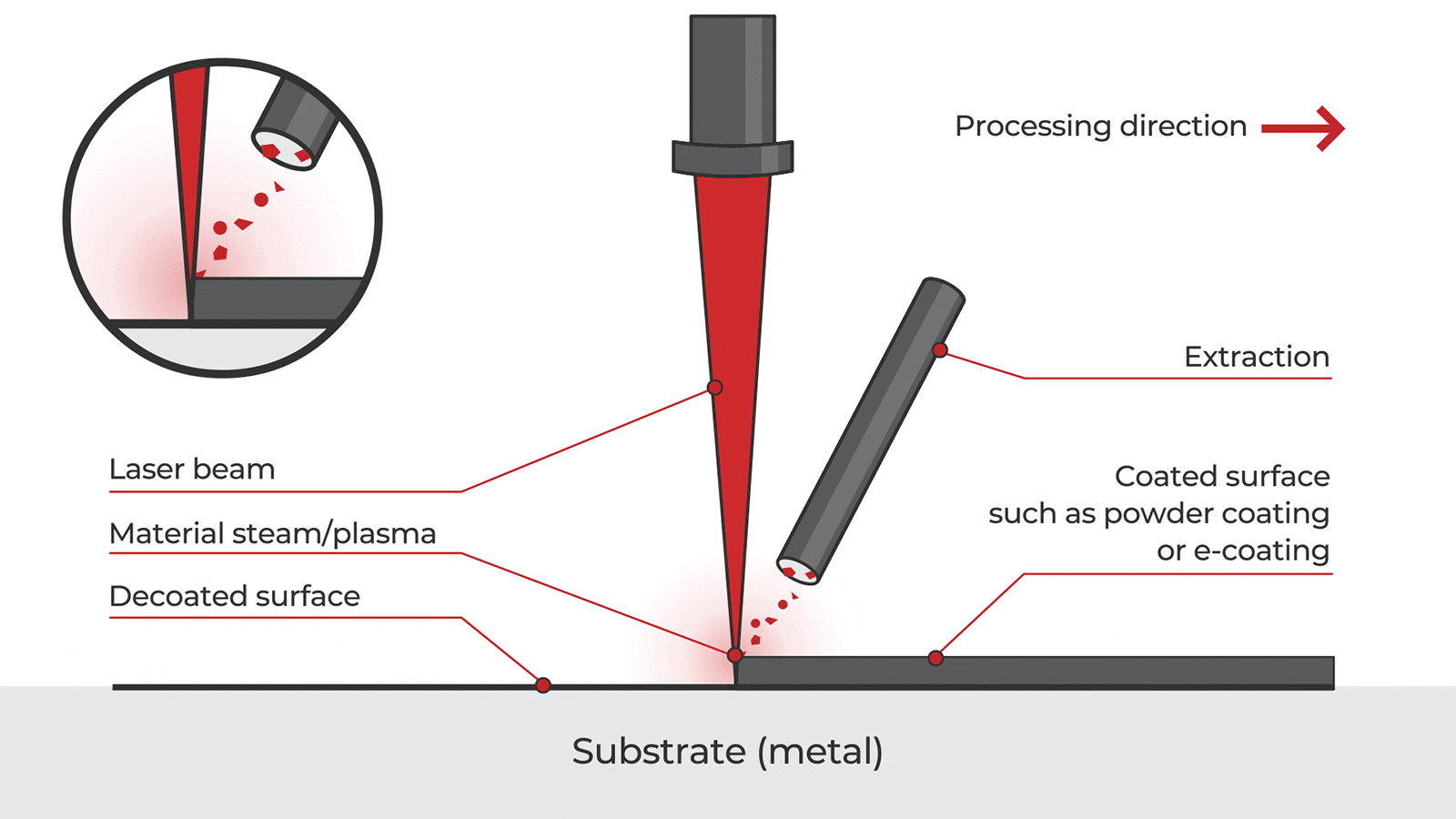
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Cleaning Rust Removal
Understanding Laser Cleaning for Rust Removal
Laser cleaning is an advanced, non-abrasive method for removing rust, oxides, coatings, and contaminants from metal surfaces using high-intensity laser beams. This process vaporizes or ablates unwanted material without damaging the underlying substrate. Due to its precision, environmental benefits, and minimal waste, laser rust removal is increasingly used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, marine, and heritage restoration. However, its deployment requires strict adherence to logistical planning and regulatory compliance.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Laser Safety Standards (IEC 60825 & ANSI Z136)
Laser cleaning systems must comply with international laser safety standards:
– IEC 60825: International Electrotechnical Commission standard governing laser product safety.
– ANSI Z136.1: American National Standard for Safe Use of Lasers.
Ensure all equipment is classified (typically Class 4), and operators are trained in:
– Beam hazard awareness (eye and skin protection)
– Proper use of safety interlocks and emergency stops
– Controlled access to laser operation zones
Occupational Health and Safety (OSHA & Local Regulations)
In the U.S., OSHA mandates safe working conditions under the General Duty Clause and specific standards:
– Ventilation and Fume Extraction: Laser cleaning produces airborne particulates and fumes (e.g., metal oxides). Use local exhaust ventilation (LEV) systems compliant with OSHA 29 CFR 1910.134 (Respiratory Protection).
– Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Operators must wear laser safety goggles (wavelength-specific), flame-resistant clothing, gloves, and respiratory protection when necessary.
– Hazard Communication (HazCom): Provide Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for materials being cleaned and train staff on chemical hazards.
Environmental Compliance (EPA & REACH)
- Air Emissions: Laser ablation may release hazardous particulates. Facilities must comply with EPA National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants (NESHAP) if applicable. Use HEPA-filtered extraction systems.
- Waste Handling: Collected debris is often classified as hazardous waste if it contains heavy metals (e.g., lead, chromium). Follow RCRA guidelines for storage, labeling, and disposal.
- REACH & RoHS (EU): Ensure no restricted substances are generated or released during cleaning that violate EU chemical regulations.
Transport and Logistics of Laser Cleaning Equipment
Equipment Handling and Storage
- Fragility: Laser systems contain sensitive optical components. Transport in manufacturer-approved packaging with shock and moisture protection.
- Climate Control: Store in dry, temperature-controlled environments (typically 5°C–40°C) to prevent condensation and component damage.
- Power Requirements: Verify voltage, phase, and grounding compatibility at the destination. Industrial lasers often require 208V/480V three-phase power.
International Shipping Considerations
- Export Controls: High-powered lasers may be subject to export regulations (e.g., U.S. Commerce Control List under ECCN 6A003). Obtain necessary licenses for international shipment.
- Customs Documentation: Prepare commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin. Declare equipment accurately to avoid delays.
- Laser Classification Documentation: Provide IEC 60825 certification to customs authorities, especially in EU and Asia.
Operational Site Setup and Safety Zones
Controlled Access Zones
Establish a Laser Controlled Area with:
– Physical barriers (curtains, enclosures) rated for the laser wavelength and power
– Warning signs with laser class and hazard symbols (per ANSI Z535.1)
– Interlocked doors that disable the laser upon entry
Fume and Particulate Management
- Install HEPA filtration systems capable of capturing sub-micron particles.
- Conduct regular air quality monitoring to ensure compliance with OSHA PELs (Permissible Exposure Limits).
- Perform filter changeouts using proper containment procedures to avoid secondary contamination.
Training and Documentation
Operator Certification
Mandatory training programs should include:
– Laser safety fundamentals
– Equipment operation and emergency shutdown
– PPE use and maintenance
– Waste handling procedures
Maintain training records for audit purposes.
Recordkeeping and Audits
Keep logs of:
– Equipment maintenance and calibration
– Air quality and exposure monitoring
– Waste disposal manifests
– Incident reports (e.g., exposure, malfunctions)
Regular internal audits ensure ongoing compliance with safety and environmental standards.
Emergency Preparedness
Response Protocols
Develop site-specific emergency procedures for:
– Laser exposure incidents (eye/skin)
– Fire (laser ignition of materials)
– System malfunction or uncontrolled beam emission
Ensure first aid kits, emergency showers, and fire extinguishers (Class C for electrical fires) are accessible.
Spill and Contamination Response
In case of hazardous debris release:
– Evacuate and isolate the area
– Use HEPA vacuum (not brooms) for cleanup
– Dispose of contaminated materials as hazardous waste
– Report major incidents to regulatory bodies if required (e.g., EPA, local environmental agency)
Conclusion
Successful deployment of laser cleaning for rust removal hinges on meticulous logistics planning and unwavering compliance with safety, environmental, and transportation regulations. By implementing structured procedures for equipment handling, operator training, emission control, and emergency response, organizations can leverage the benefits of laser technology while minimizing risk and ensuring legal adherence. Regular review of evolving standards is recommended to maintain compliance across global operations.
In conclusion, sourcing laser cleaning technology for rust removal presents a highly effective, environmentally friendly, and sustainable solution for surface preparation and maintenance. Unlike traditional methods such as sandblasting or chemical treatments, laser cleaning offers precision, minimal substrate damage, and no secondary waste, reducing both operational costs and environmental impact. As industries continue to prioritize efficiency, safety, and compliance with environmental regulations, investing in reliable laser cleaning systems from reputable suppliers becomes increasingly advantageous. By carefully evaluating technical specifications, service support, and total cost of ownership, organizations can successfully integrate laser cleaning into their operations, achieving superior rust removal performance while future-proofing their maintenance processes.