The global laser cleaning machine market is experiencing rapid expansion, driven by increasing demand for eco-friendly, precise, and automated surface treatment solutions in metal manufacturing. According to Grand View Research, the market was valued at USD 458.2 million in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.2% from 2023 to 2030. This surge is fueled by stricter environmental regulations, the push to replace chemical cleaning methods, and the integration of laser systems into industrial automation. Mordor Intelligence further underscores this momentum, noting that rising adoption in automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery sectors is accelerating innovation and product development. As metal manufacturers seek non-abrasive, low-maintenance cleaning methods with minimal downtime, laser cleaning technology has emerged as a transformative solution. With numerous options entering the market, selecting the right machine is critical for optimizing performance, ensuring safety, and maximizing return on investment. Below, we present a data-driven analysis of the top 10 laser cleaning machines tailored for metal manufacturing applications in 2024.
Top 10 Laser Cleaning Machine For Metal Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
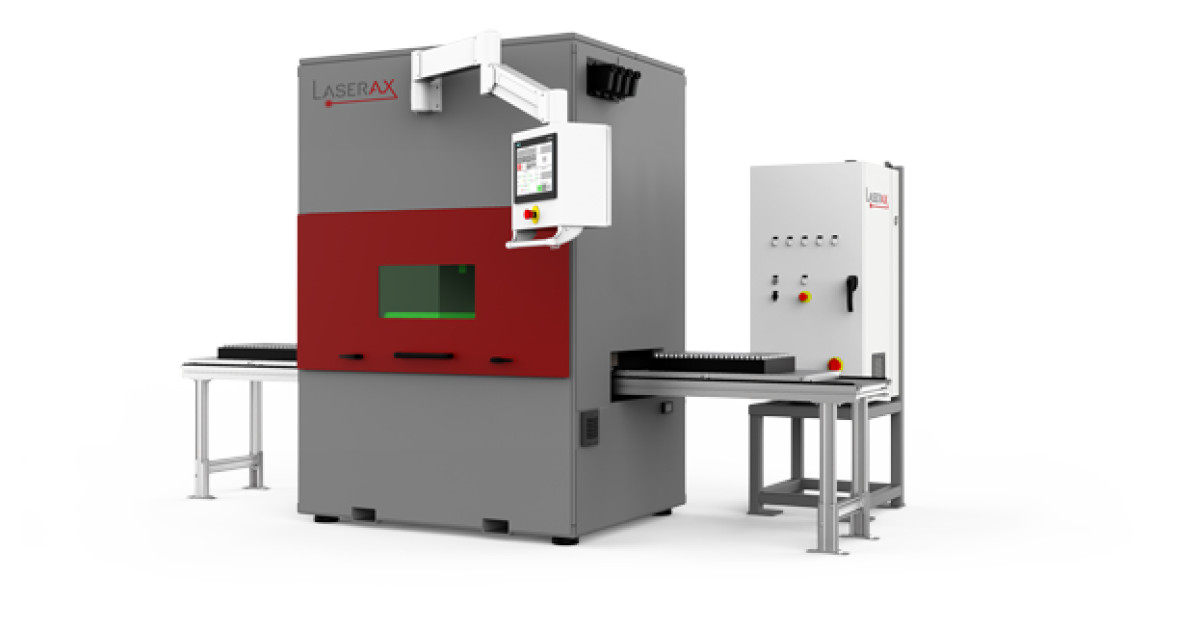
#1 Laserax
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Laserax works with the world’s leading manufacturers to implement laser cleaning, welding, texturing, and marking solutions….
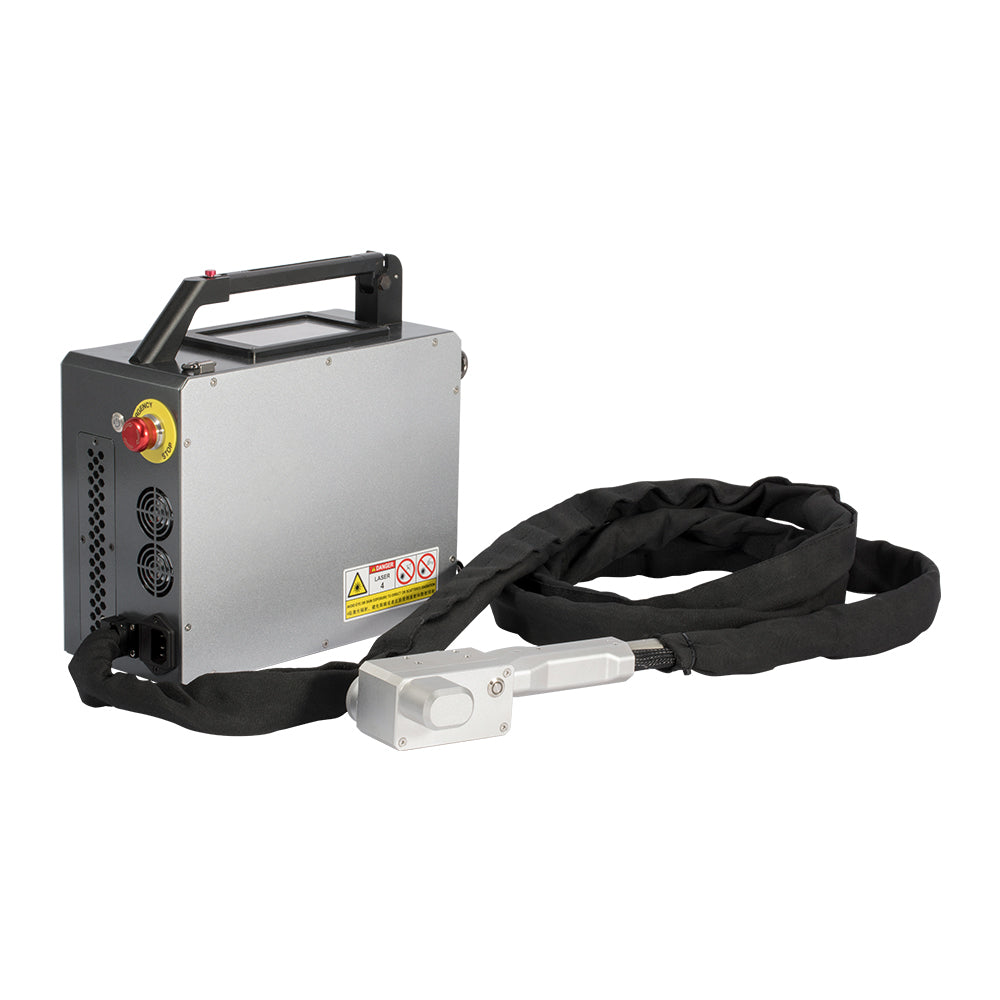
#2 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: we engineer and manufacture the most advanced—and most powerful—pulsed industrial laser cleaning systems on the market, built for both manual and automated ……
#3 SFX Laser
Website: sfxlaser.com
Key Highlights: SFX Laser is a 20+ years professional laser equipment manufacturer including laser cleaning machine, laser welding machine, fiber laser engraver, fiber laser…
#4 Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: SHARK P CL – a universal professional laser cleaning machine suitable for metal, wood, stone and mixed-material applications….
#5 Laser Cleaning Systems
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Our most powerful metal laser cleaning machine, the CleanTech Industrial Roughening Laser 3050, offers top speed and efficiency for surface treatment and more….
#6 Argento Lux
Website: argentolux.com
Key Highlights: Argento Lux, experts in laser cleaning, utilizing high-powered lasers to remove contamination from various surfaces. Similar to sandblasting without the ……
#7 Pulse Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: triumphlaser.com
Key Highlights: A pulse laser cleaning machine is an advanced, highly efficient tool designed for precision cleaning and removal of contaminants such as rust, paint, oil, and ……
#8 Laser Cleaning Machines
Website: wattsan.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaning uses powerful laser beams to remove contaminants such as rust, paint, dirt or oxidation from a variety of surfaces….
#9 Laser Cleaning
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaning is used across a variety of industries to remove unwanted surface materials like coatings, paints, rust, oil, and for surface preparation for ……
#10 Full List of Laser Machines
Website: hantencnc.com
Key Highlights: We are a laser machine manufacturer. Our products include laser cleaning machines, laser welding machines and laser marking machines. As a laser machine ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Cleaning Machine For Metal

H2: Market Trends for Laser Cleaning Machines for Metal (2026 Outlook)
The global market for laser cleaning machines for metal is poised for significant growth and transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, increasing environmental regulations, and rising demand across key industrial sectors. Several critical trends are shaping the trajectory of this market:
1. Rising Demand for Eco-Friendly Surface Preparation
Industries are increasingly shifting away from traditional cleaning methods—such as sandblasting, chemical solvents, and dry ice blasting—due to environmental and health concerns. Laser cleaning offers a non-abrasive, chemical-free, and waste-minimizing alternative, aligning with global sustainability goals. By 2026, stringent environmental regulations in regions like Europe and North America are expected to accelerate the adoption of laser cleaning technologies in metal fabrication, automotive, and aerospace sectors.
2. Technological Advancements and Cost Reduction
Ongoing innovations in fiber laser technology are improving cleaning efficiency, precision, and speed while reducing operational costs. By 2026, manufacturers are anticipated to deliver more compact, user-friendly, and energy-efficient systems with enhanced automation, including integration with robotics and AI-driven controls. These improvements will lower the total cost of ownership, making laser cleaning accessible to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
3. Expansion in Automotive and Aerospace Applications
The automotive industry is increasingly using laser cleaning for rust removal, paint stripping, and surface pretreatment before welding or coating. In aerospace, the technology is critical for maintaining high-precision components without causing microstructural damage. With ongoing investments in electric vehicle (EV) production and next-generation aircraft, demand for laser cleaning machines is expected to grow steadily through 2026.
4. Growth in Asia-Pacific Markets
China, India, Japan, and South Korea are emerging as key growth regions due to rapid industrialization, government support for advanced manufacturing, and increasing automation. Chinese manufacturers, in particular, are both major producers and consumers of laser cleaning equipment, driving down prices and increasing global competitiveness. By 2026, the Asia-Pacific region is projected to dominate market share in terms of volume and revenue.
5. Integration with Industry 4.0 and Smart Manufacturing
Laser cleaning systems are becoming integral components of smart factories, with capabilities for real-time monitoring, remote operation, and predictive maintenance. IoT-enabled machines will allow for seamless data integration into production workflows, improving efficiency and traceability. This trend is expected to gain momentum by 2026, especially in high-mix, low-volume manufacturing environments.
6. Increased Competition and Market Consolidation
The market is witnessing an influx of new players and product innovations, leading to intensified competition. At the same time, strategic partnerships, mergers, and acquisitions are expected to shape the competitive landscape. Established laser technology firms are likely to acquire niche startups to expand their product portfolios and geographic reach.
In conclusion, the laser cleaning machine market for metal applications is set for robust expansion by 2026, supported by environmental mandates, technological progress, and broadening industrial applications. Companies that invest in R&D, sustainability, and digital integration will be best positioned to capitalize on these emerging opportunities.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Laser Cleaning Machines for Metal: Quality and Intellectual Property (IP) Concerns
When sourcing laser cleaning machines for metal applications, businesses often focus on performance and cost, but overlook critical aspects related to quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. These oversights can lead to long-term operational, legal, and financial challenges. Below are the most common pitfalls in these two areas.
1. Compromised Machine Quality Due to Inadequate Specifications
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing laser cleaning machines is receiving equipment that fails to meet the required performance standards. This typically occurs due to:
- Vague or incomplete technical specifications: Suppliers may advertise high power (e.g., 1000W) lasers without clarifying whether this refers to peak or average power, or whether the system includes beam quality (M²) metrics.
- Use of substandard components: Some manufacturers cut costs by using lower-grade diodes, optics, or cooling systems, which reduces machine lifespan and cleaning efficiency.
- Lack of real-world testing data: Suppliers may provide lab-condition results that don’t reflect actual industrial use, such as inconsistent performance on rusted or painted metal surfaces.
Solution: Request third-party test reports, conduct on-site or video demonstrations with your materials, and verify component brands and certifications (e.g., CE, FDA, ISO).
2. Inconsistent Build Quality and Lack of Standardization
Many suppliers—especially in emerging manufacturing markets—lack standardized production processes. This results in:
- Machine-to-machine variability, even within the same model.
- Poor integration of subsystems (laser source, scanner, control software), leading to reliability issues.
- Inadequate thermal management, causing frequent overheating and downtime.
Solution: Prioritize suppliers with certified quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001) and request production line audits or factory inspection reports.
3. Hidden IP Risks in Laser Technology and Software
Laser cleaning machines often incorporate proprietary technologies in both hardware and software. Sourcing from unverified suppliers can expose buyers to serious IP risks:
- Use of counterfeit or cloned laser sources: Some manufacturers rebrand or reverse-engineer well-known laser modules (e.g., from IPG or Raycus), violating IP rights.
- Proprietary software with unclear licensing: Control software may include unlicensed code or lack proper documentation, creating legal exposure.
- Infringement liability: If the machine uses patented technologies (e.g., specific beam delivery or scanning systems), the end-user may be held liable in some jurisdictions.
Solution: Require suppliers to provide IP compliance documentation, including laser source authenticity certificates and software licensing agreements. Conduct due diligence on the supplier’s R&D capabilities and patent portfolio.
4. Lack of After-Sales Support and Technical Documentation
Even if a machine meets initial quality standards, poor documentation and support can compromise long-term usability:
- Missing or poor-quality user manuals, maintenance guides, or safety certifications.
- No access to firmware updates or software debugging tools.
- Unavailability of spare parts or trained technicians.
This not only affects operational continuity but may also void warranties or insurance coverage.
Solution: Include service-level agreements (SLAs) in contracts, verify local support networks, and ensure full documentation is delivered with the machine.
5. Misrepresentation of Capabilities and Certification Claims
Some suppliers exaggerate machine performance or falsely claim compliance with international standards. Common red flags include:
- Claims of “military-grade” or “industrial ISO-certified” systems without verifiable proof.
- Misleading marketing terms like “zero maintenance” or “100% rust removal” without context.
- Absence of test data under real-world conditions.
Solution: Verify certifications through official databases, request customer references, and insist on performance validation under your specific use case.
Conclusion
Sourcing a high-quality laser cleaning machine for metal requires more than just comparing price and power ratings. Buyers must rigorously evaluate both the technical quality and IP integrity of the equipment. Due diligence in supplier selection, demand for transparency, and legal safeguards can prevent costly setbacks and ensure long-term reliability and compliance.

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Cleaning Machines for Metal
Importing, exporting, or operating laser cleaning machines for metal involves navigating complex logistics and strict regulatory compliance. This guide outlines key considerations to ensure safe, legal, and efficient handling.
H2: International Shipping & Logistics
- Packaging: Machines must be shipped in robust, weatherproof, IP-rated containers (often IP65 or higher) with internal shock-absorbing materials (e.g., custom foam, wooden crating). Desiccant packs prevent moisture damage.
- Labeling: Clearly label packages as “Fragile,” “This Way Up,” “Contains Laser Equipment,” and include hazard symbols (laser radiation, high voltage, pinch points). Include FOB/CIF terms and consignee details.
- Transport Mode: Air freight (fastest, highest cost, strict IATA regulations), Sea freight (FCL/LCL containers, cost-effective for large volumes, longer transit), or Land freight (regional road/rail, requires route planning).
- Customs Clearance: Provide accurate commercial invoices, packing lists, bill of lading/air waybill, and certificates of origin. Classify the machine correctly under HS Code (e.g., 8515.21 – Laser machines for engraving, marking or cutting; local variations exist).
- Insurance: Obtain comprehensive cargo insurance covering loss, damage, and delays during transit.
H2: Regulatory Compliance
- Laser Safety (IEC 60825-1 / FDA 21 CFR 1040.10 & 1040.11):
- Classification: Metal cleaning lasers are typically Class 4 (high-power, hazardous). Must comply with international (IEC) and national (e.g., FDA in USA) standards.
- Labeling: Permanent, visible labels indicating Class 4 Laser, wavelength, maximum output power, and beam aperture.
- Interlocks & Safety Features: Mandatory safety interlocks on access panels, emergency stop buttons, key control, beam shrouds, and remote start/stop capability.
- User Documentation: Comprehensive safety manual in local language(s) detailing hazards, safety procedures, PPE requirements, and maintenance.
- Electrical Safety (CE, UKCA, UL/CSA, CCC):
- Conformity: Must meet regional electrical safety standards (e.g., CE Marking under EU Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC and Low Voltage Directive 2014/35/EU; UKCA for UK; UL/CSA for North America; CCC for China).
- Certification: Requires testing and certification by notified bodies (e.g., TÜV, SGS, Intertek) for CE/UKCA; UL/CSA Listing or Recognition in North America.
- EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility) – (CE: EMC Directive 2014/30/EU, FCC Part 15 Subpart B):
- Machine must not emit excessive electromagnetic interference and must be immune to typical environmental interference. Requires testing and declaration.
- RoHS & REACH (EU):
- RoHS: Restricts hazardous substances (e.g., lead, mercury, cadmium) in electrical equipment. Requires material declarations.
- REACH: Requires registration of chemical substances and communication of SVHCs (Substances of Very High Concern) in articles.
- WEEE (EU):
- Comply with waste electrical and electronic equipment directives, including funding take-back schemes and providing recycling information.
- Country-Specific Requirements:
- USA: FDA laser product reporting (Varian Report), state-specific environmental regulations (e.g., California Prop 65).
- China: CCC certification, China RoHS.
- Canada: ICES-003 (EMC), Health Canada laser safety.
- Korea: KC Mark (safety & EMC), KCC (EMC).
- Japan: PSE Mark (safety), VCCI (EMC), Radio Law.
- Australia/NZ: RCM Mark (safety, EMC, radio), AS/NZS IEC 60825.1.
H2: Import/Export Controls & Documentation
- Export Controls (ITAR/EAR):
- EAR (US): Most metal cleaning lasers fall under ECCN 2B201 (Laser systems) on the Commerce Control List. Check if export license is required based on destination, end-user, and end-use (especially for very high power or specific wavelengths).
- ITAR: Generally not applicable unless the laser has military applications or is specifically designed for defense.
- Import Duties & Taxes: Research applicable tariffs, VAT/GST, and customs duties in the destination country based on HS code and origin.
- Essential Documentation:
- Commercial Invoice (detailed description, value, Incoterms).
- Packing List.
- Bill of Lading (Sea) / Air Waybill (Air).
- Certificate of Origin.
- Test Reports (Laser Safety, EMC, Electrical Safety).
- Declaration of Conformity (CE/UKCA/RCM/Other).
- User Manuals & Safety Instructions.
- Export License (if required by EAR or destination country).
H2: End-User Compliance & Safety
- Laser Safety Officer (LSO): Appoint a designated LSO (especially for Class 4 lasers) responsible for safety program implementation.
- Controlled Access: Establish a designated Laser Controlled Area (LCA) with interlocked access, warning signs (e.g., “Laser Radiation – Avoid Eye or Skin Exposure”), and entry procedures.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Mandatory use of laser safety eyewear (OD rated for the specific laser wavelength and power), protective clothing (flame-resistant), and hearing protection (if noise >85 dB).
- Fume Extraction: Mandatory high-efficiency fume extraction system (HEPA/ULPA filters) to capture hazardous metal oxides, particulates, and potential VOCs generated during cleaning. Regular filter maintenance is critical.
- Training: Comprehensive training for all operators on hazards, safe operating procedures, emergency response, PPE use, and maintenance protocols.
- Maintenance: Follow manufacturer’s schedule. Only qualified personnel should service the laser. Implement lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures during maintenance.
- Waste Disposal: Classify and dispose of collected dust/sludge as hazardous waste according to local environmental regulations (e.g., EPA, ECHA). Obtain proper disposal manifests.
Disclaimer: Regulations are subject to change and vary significantly by jurisdiction. Always consult with legal counsel, customs brokers, and regulatory experts specific to your countries of origin, transit, and destination before shipping or operating. This guide provides a general overview, not legal advice.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Laser Cleaning Machine for Metal
Sourcing a laser cleaning machine for metal surfaces proves to be a highly advantageous investment for industries seeking efficient, eco-friendly, and precise cleaning solutions. Unlike traditional methods such as sandblasting or chemical cleaning, laser cleaning offers non-abrasive, residue-free, and selective removal of rust, oxides, paint, and contaminants without damaging the underlying metal substrate. This results in improved surface quality, extended material lifespan, and reduced maintenance costs.
When sourcing a laser cleaning machine, key factors to consider include laser power (measured in watts), wavelength, pulse frequency, portability, safety features, and compatibility with different metal types. Opting for a reputable supplier with technical support, training, and warranty services ensures long-term reliability and optimal performance.
Moreover, the growing emphasis on sustainability and workplace safety further strengthens the case for adopting laser cleaning technology. With its ability to reduce waste, eliminate chemical usage, and minimize operator exposure to hazardous materials, laser cleaning aligns with modern environmental and regulatory standards.
In conclusion, sourcing a laser cleaning machine tailored to your specific metal cleaning needs not only enhances operational efficiency and product quality but also positions your business at the forefront of innovative and sustainable manufacturing practices. Making an informed procurement decision based on technical requirements and long-term value will yield significant returns in productivity, cost savings, and environmental responsibility.