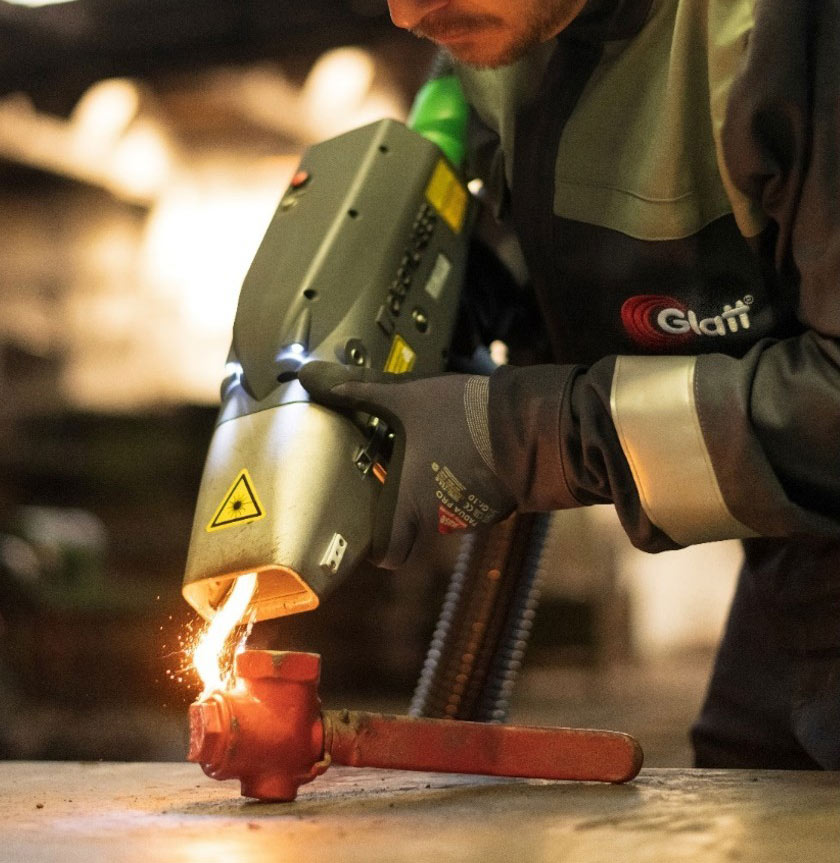
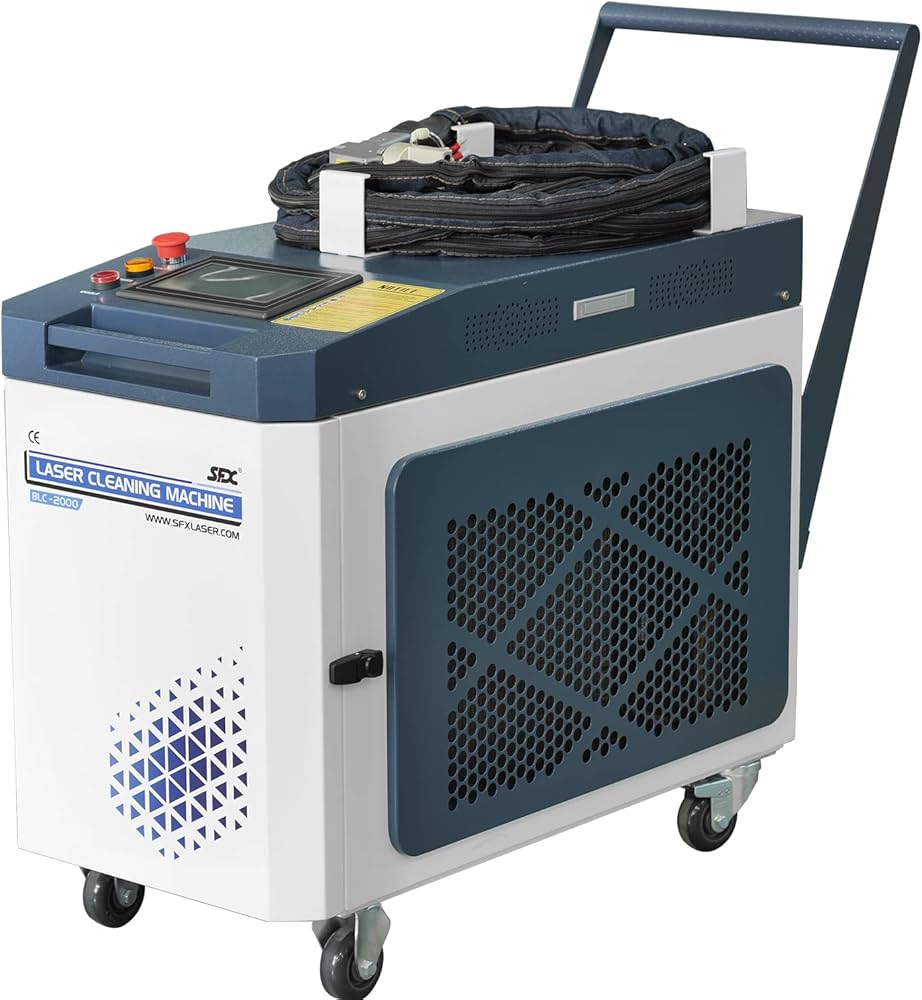
The global laser cleaning device market is experiencing robust growth, fueled by increasing demand for eco-friendly, precision-based cleaning solutions across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and heritage conservation. According to Grand View Research, the global industrial cleaning equipment market—under which laser cleaning falls—was valued at USD 13.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.2% from 2023 to 2030. Mordor Intelligence further highlights that the laser cleaning systems market is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of over 11% during the forecast period of 2023–2028, driven by the shift from chemical and abrasive methods toward non-contact, sustainable alternatives. As industries prioritize automation and environmental compliance, investment in high-efficiency laser cleaning technology is accelerating. This momentum has led to the emergence of innovative manufacturers pushing the boundaries of performance, portability, and application range. Below, we spotlight the top 9 laser cleaning device manufacturers shaping this dynamic landscape through technological advancement and global market presence.
Top 9 Laser Cleaning Device Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laserax
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Laserax works with the world’s leading manufacturers to implement laser cleaning, welding, texturing, and marking solutions….
#2 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: Specializing in the production of premium-quality, Belgian-made industrial laser cleaning equipment, we take great pride in our craftsmanship and innovative ……
#3 Laser Photonics
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser Photonics manufactures reliable, safe, and eco-friendly Laser Cleaning, Laser Cutting, Laser Engraving, Laser Marking, and Laser Welding solutions….
#4 Clean Laser Systems
Website: cleanlaser.de
Key Highlights: IPG | cleanLASER has been developing and producing high-precision laser systems for cleaning and industrial surface treatment for more than 20 years….
#5 SHARK P CL Industrial Laser Cleaning Machines (100
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: SHARK P CL is an industrial pulsed laser cleaning machine series by PULSAR Laser with outputs from 100 W to 1000 W, air-cooled up to 500 W….
#6 SFX Laser
Website: sfxlaser.com
Key Highlights: SFX Laser is a 20+ years professional laser equipment manufacturer including laser cleaning machine, laser welding machine, fiber laser engraver, fiber laser…
#7 Netalux
Website: netalux.com
Key Highlights: Discover our award-winning Laser Cleaning Solutions for the world’s most demanding industries. Discover our products and global service now….
#8 Laser Cleaning
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Discover Your Laser Cleaning Solution IPG is a partner for every stage of production from research and development to full-scale manufacturing….
#9 Laser cleaning
Website: p-laserusa.com
Key Highlights: Our laser machines are mainly used to remove the following contaminants: Rust – Paint – Coatings – Release Agents – Grease, Oils – Soot – Rubber- Organic ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Cleaning Device
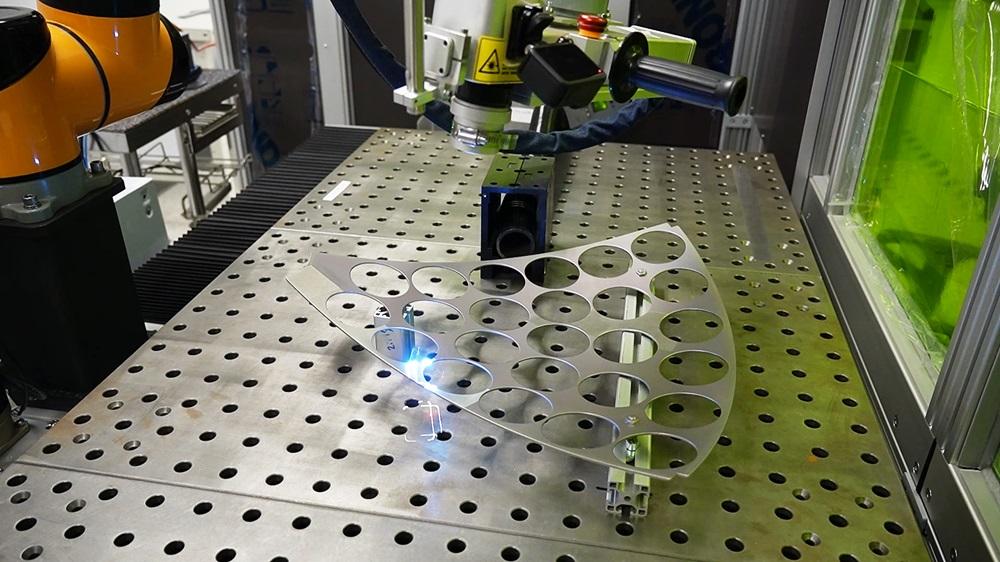

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Laser Cleaning Devices
The global laser cleaning device market is projected to experience robust growth by 2026, driven by increasing industrial automation, rising environmental regulations, and the demand for non-abrasive, eco-friendly cleaning solutions. Key trends shaping the market in 2026 include:
-
Expansion in Industrial Applications: Laser cleaning technology is gaining traction across diverse industries such as automotive, aerospace, precision manufacturing, and heritage conservation. By 2026, the automotive and aerospace sectors are expected to be major adopters, utilizing laser systems for paint stripping, rust removal, and mold cleaning due to their precision and minimal substrate damage.
-
Shift Toward Eco-Friendly Manufacturing: As environmental regulations tighten globally—especially in North America and Europe—industries are phasing out chemical-based and abrasive cleaning methods. Laser cleaning offers a solvent-free, waste-minimizing alternative, aligning with sustainability goals and contributing to regulatory compliance, thereby accelerating market adoption.
-
Technological Advancements and Portability: Ongoing R&D has led to the development of compact, handheld, and robotic-integrated laser cleaning systems. By 2026, portable devices are expected to dominate small- to mid-scale operations, offering flexibility and ease of use in field applications such as shipbuilding and pipeline maintenance.
-
Regional Market Growth: Asia-Pacific is anticipated to be the fastest-growing region by 2026, fueled by rapid industrialization in China, India, and South Korea. Government initiatives to modernize manufacturing infrastructure and increase automation are key growth drivers. Meanwhile, North America and Europe maintain strong market shares due to early adoption and high investment in advanced manufacturing technologies.
-
Cost Reduction and ROI Improvement: Although initial investment remains high, the total cost of ownership for laser cleaning systems is decreasing due to improved laser source efficiency and longer component lifespans. By 2026, increasing affordability and proven return on investment (ROI) are expected to encourage wider adoption, particularly among small and medium enterprises (SMEs).
-
Integration with Industry 4.0: Laser cleaning systems are increasingly being integrated with smart manufacturing ecosystems. By 2026, devices equipped with IoT connectivity, real-time monitoring, and AI-driven process optimization are expected to become standard, enabling predictive maintenance and enhanced operational efficiency.
In summary, the 2026 laser cleaning device market is characterized by technological innovation, regulatory support, and expanding industrial demand. As the technology becomes more accessible and adaptable, it is poised to replace conventional cleaning methods across multiple sectors, solidifying its position as a cornerstone of modern industrial maintenance and surface treatment.
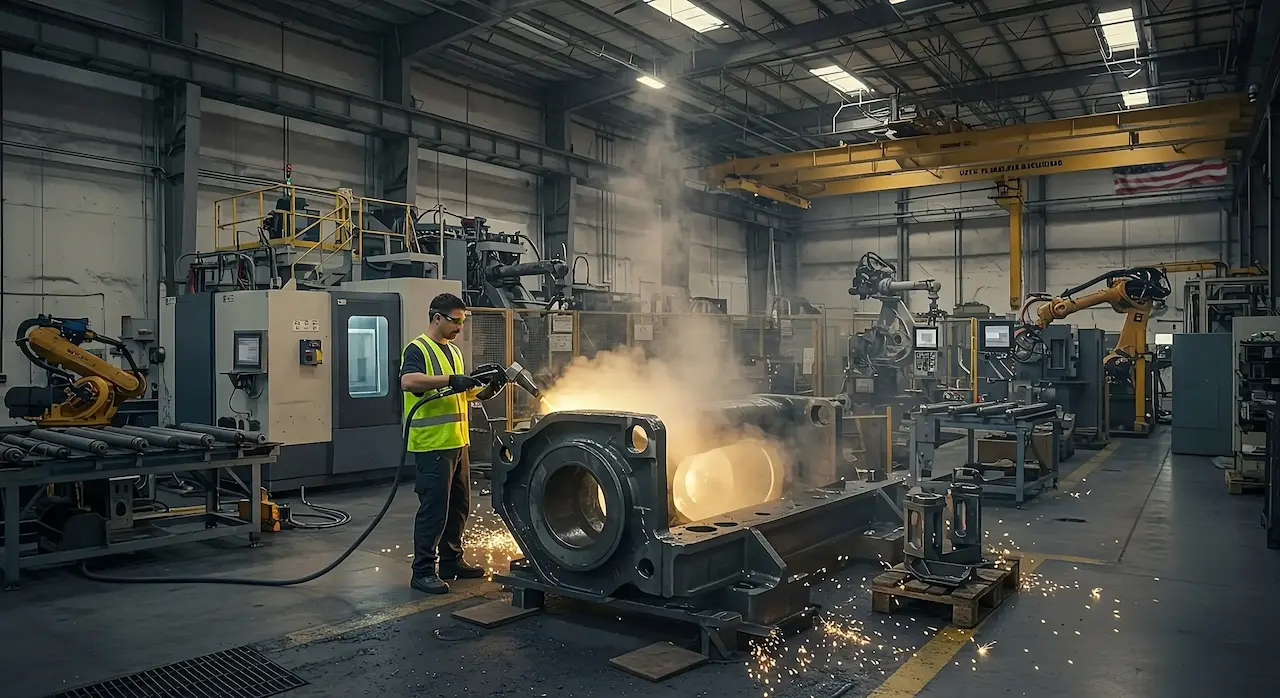

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Laser Cleaning Devices: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing laser cleaning devices, especially from emerging markets or unfamiliar suppliers, presents several critical risks related to product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Buyers must be vigilant to avoid costly mistakes.
Poor Build Quality and Performance Inconsistencies
Many low-cost laser cleaning devices suffer from substandard components and inadequate engineering. Common quality issues include inconsistent laser output, unreliable cooling systems, and fragile housings prone to damage. These flaws lead to frequent downtime, reduced cleaning efficiency, and higher total cost of ownership. Buyers may receive units that fail to meet advertised specifications or degrade rapidly under normal operating conditions.
Lack of Safety Certifications and Compliance
A major pitfall is sourcing devices without proper safety certifications (e.g., CE, FDA, IEC 60825). Non-compliant lasers pose serious health risks, including eye and skin injuries. Devices lacking certification may also be restricted from import or use in regulated industries, resulting in legal and operational setbacks.
Inadequate or Misrepresented Technical Support
Suppliers may promise comprehensive support but fail to deliver timely assistance, spare parts, or software updates. This is particularly problematic when troubleshooting technical issues or integrating the device into existing workflows. Language barriers and time zone differences can further exacerbate communication challenges.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Sourcing from manufacturers with questionable IP practices can expose buyers to legal liability. Some suppliers may produce devices that copy patented technologies, designs, or software from established brands. Purchasing such equipment may inadvertently involve the buyer in IP disputes, leading to seizures, fines, or reputational damage.
Absence of Genuine Warranty and Service Agreements
Many low-cost suppliers offer vague or unenforceable warranty terms. In practice, this means limited recourse when defects arise. Additionally, the lack of local service centers can result in long repair times and extended equipment downtime.
Hidden Costs and Scalability Limitations
Initial purchase prices may appear attractive, but hidden costs—such as proprietary consumables, mandatory service contracts, or software licensing fees—can accumulate. Furthermore, low-end models may not scale effectively for industrial applications, necessitating premature replacement with higher-end systems.
To mitigate these pitfalls, buyers should conduct thorough due diligence, request third-party verification of specifications, insist on clear IP warranties, and prioritize suppliers with proven track records and transparent business practices.
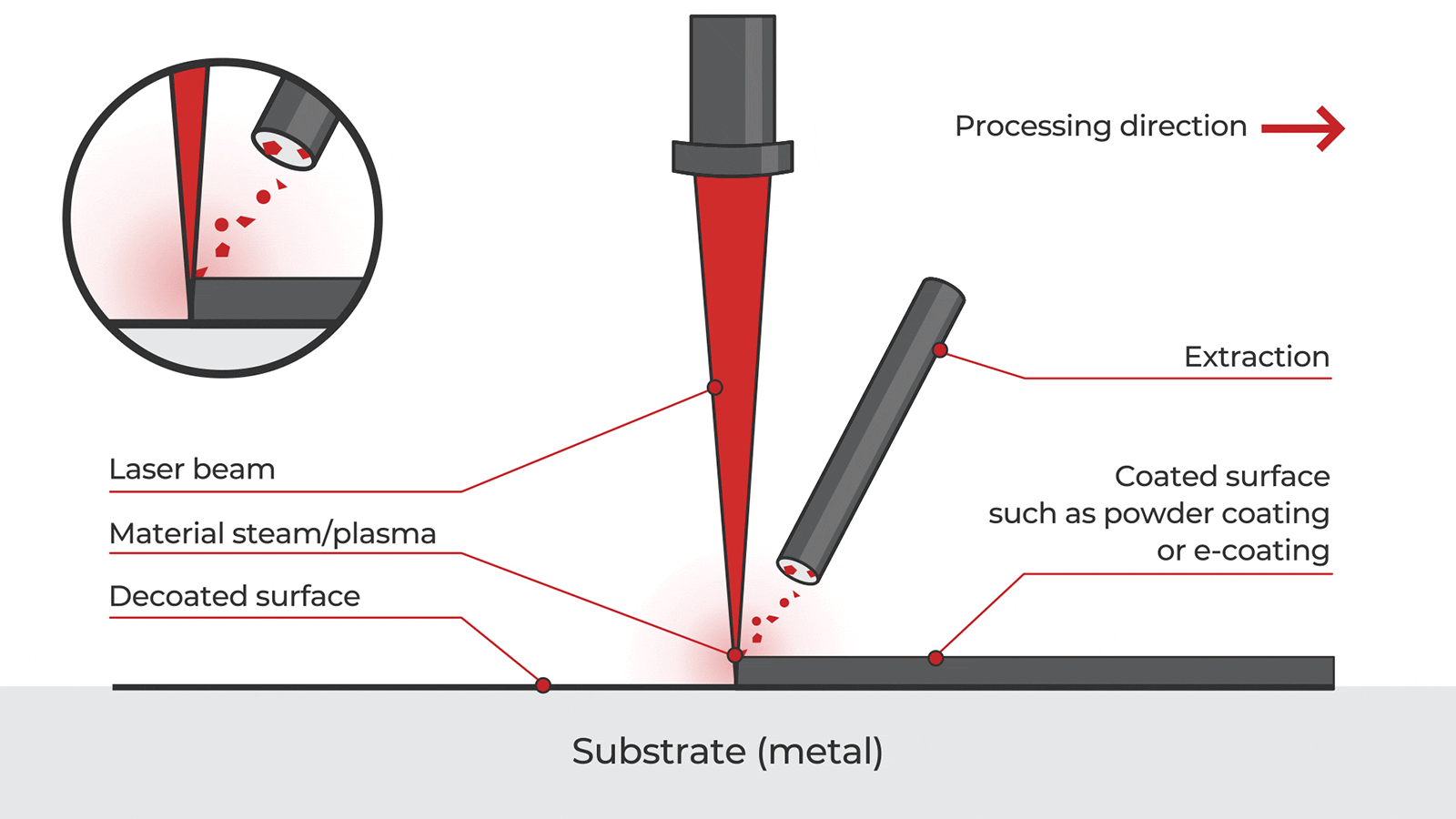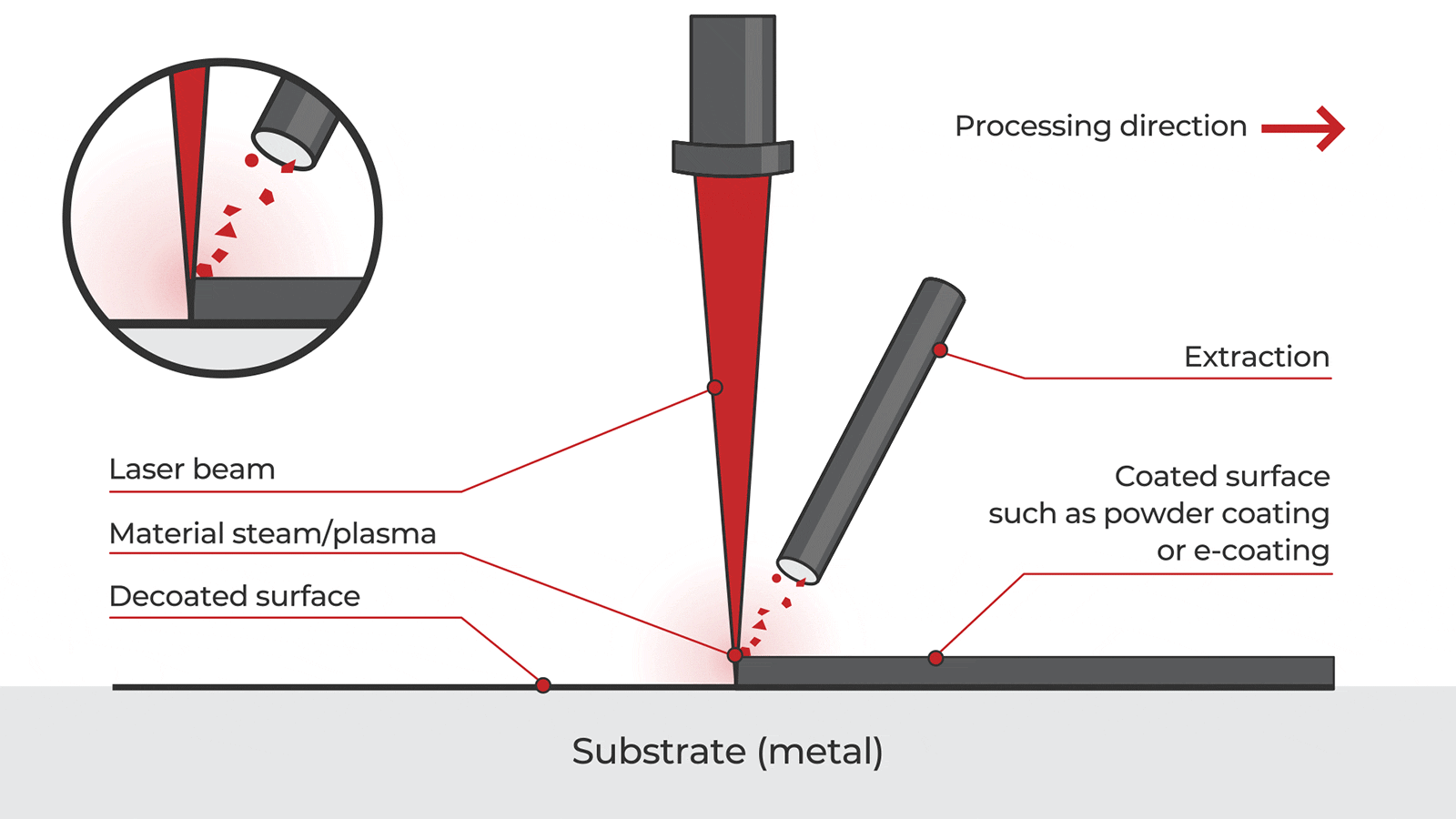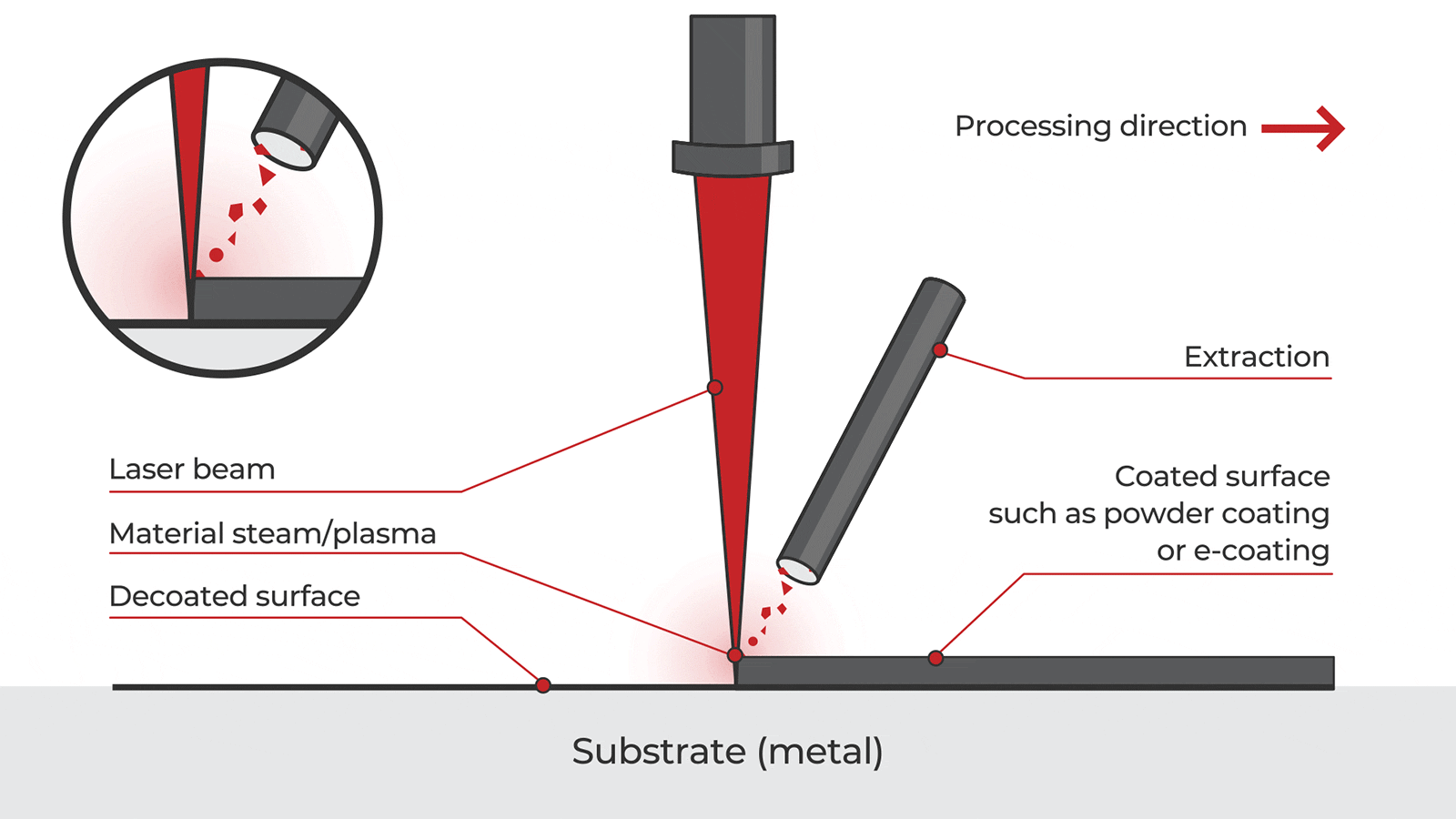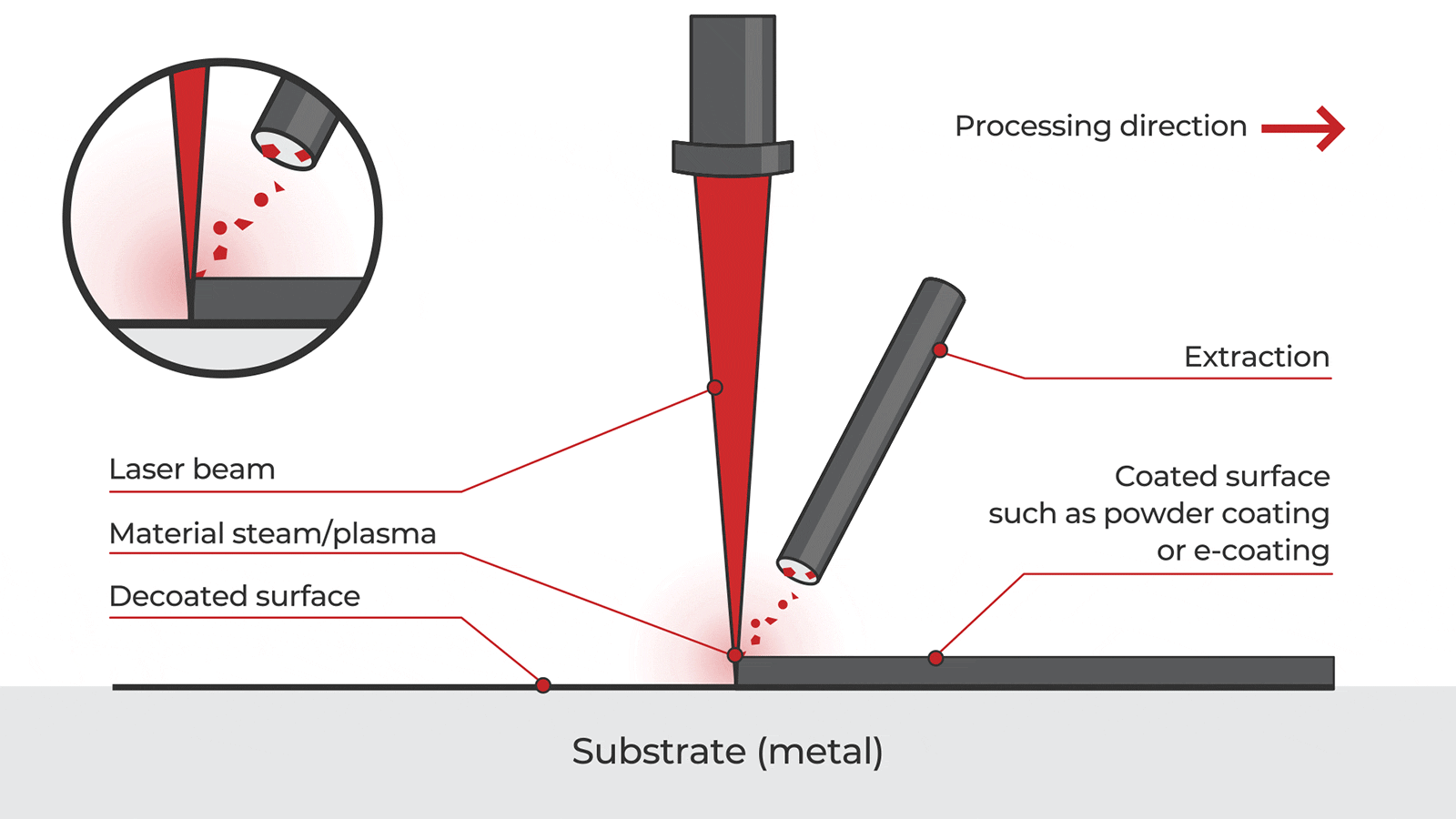
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Cleaning Devices
Regulatory Classification & Compliance
Laser cleaning devices are subject to multiple regulatory frameworks due to their use of high-powered lasers and potential industrial applications. Compliance is essential for legal import, export, sale, and operation.
Laser Safety (IEC/EN 60825-1 & FDA/CDRH):
All laser cleaning devices must comply with international laser safety standards such as IEC 60825-1 (or EN 60825-1 in the EU). In the United States, compliance with the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH) regulations (21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11) is mandatory. Devices must be classified (typically Class 4 lasers), labeled accordingly, and supplied with safety documentation, including user manuals and warning labels.
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC):
In the European Union, devices must meet the EMC Directive 2014/30/EU. This requires conformity with standards like EN 61326-1 for industrial equipment. Testing ensures the device does not emit disruptive electromagnetic interference and is immune to common environmental interference.
Electrical Safety (Low Voltage Directive – LVD):
Devices operating within specified voltage ranges must comply with the EU’s Low Voltage Directive (2014/35/EU), adhering to standards such as EN 61010-1 for safety in measurement, control, and laboratory use. Similar requirements exist in other regions (e.g., UL/CSA standards in North America).
RoHS & REACH (EU):
Compliance with the Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive 2011/65/EU and the REACH Regulation (EC 1907/2006) is required for electronic components and materials used in the device. This includes limits on lead, mercury, cadmium, and other hazardous substances.
Export Controls (Dual-Use & ITAR):
High-powered laser systems may be classified as dual-use items under export control regimes such as the EU Dual-Use Regulation (Regulation (EU) 2021/821) or the U.S. Export Administration Regulations (EAR). Some advanced systems may require export licenses. Lasers with military applications may fall under ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations), requiring strict controls.
International Shipping & Logistics
Shipping laser cleaning devices requires attention to packaging, documentation, and carrier regulations due to their classification as sensitive electronic and laser equipment.
Proper Packaging:
Devices must be packed in shock-absorbent, moisture-resistant materials. Use anti-static packaging for electronic components. Secure all optical parts and ensure the device is immobilized within the container to prevent damage during transit.
Hazard Classification & Labeling:
While laser cleaning devices are typically not classified as hazardous goods under IATA/IMDG for transport, the Class 4 laser component requires specific warning labels. Include “Laser Radiation Avoid Direct Exposure to Beam” labels and Class 4 laser warning symbols on packaging.
Air & Sea Freight Documentation:
Prepare comprehensive shipping documents, including:
– Commercial Invoice (with HS code and value)
– Packing List
– Certificate of Conformity (CE, FCC, etc.)
– Safety Data Sheet (if applicable)
– Export License (if required under EAR or dual-use regulations)
HS Code Classification:
Use appropriate Harmonized System (HS) codes for customs clearance. Common codes include:
– 8543.70: Electrical machines and apparatus, having individual functions, not elsewhere specified (laser equipment)
– 9013.20: Lasers, other than laser diodes
Confirm the correct code with local customs authorities to avoid delays.
Customs Clearance:
Ensure all import regulations in the destination country are met. Some countries require pre-shipment inspections, additional certifications (e.g., KC for South Korea, CCC for China), or registration with local authorities.
Installation & Operational Compliance
Upon delivery, proper setup and compliance with local regulations are critical for safe and legal operation.
Site Assessment & Safety Zones:
Before installation, conduct a site safety assessment. Establish a controlled environment with interlocks, beam enclosures, and emergency shut-offs. Define a nominal hazard zone (NHZ) and implement access controls.
Training & Documentation:
Operators must be trained in laser safety (e.g., IEC 60825 or ANSI Z136.1 standards). Provide training certificates and maintain records. Supply user manuals, maintenance schedules, and laser safety officer (LSO) contact information.
Local Regulations & Permits:
Check with local authorities for additional requirements, such as industrial safety permits, environmental licenses (if fumes are generated), or workplace safety inspections (e.g., OSHA in the U.S.).
Maintenance & Record Keeping:
Maintain logs for service, repairs, safety checks, and laser output measurements. Retain compliance documentation for audits and regulatory inspections.
Summary of Key Actions
- Ensure device certification (CE, FDA, RoHS, EMC, LVD)
- Classify device correctly under export control regimes
- Use proper packaging and labeling for shipping
- Prepare complete customs and compliance documentation
- Conduct safety training and site evaluation
- Maintain compliance records and service logs
Adhering to this guide ensures safe, legal, and efficient international logistics and operation of laser cleaning devices.
Conclusion on Sourcing a Laser Cleaning Device:
In conclusion, sourcing a laser cleaning device represents a strategic investment in advanced, environmentally friendly, and efficient cleaning technology. Laser cleaning offers numerous advantages over traditional methods—including precision, non-abrasiveness, minimal maintenance, elimination of chemical solvents, and reduced waste—making it ideal for industries such as automotive, aerospace, manufacturing, and heritage conservation.
When sourcing a laser cleaning system, it is essential to evaluate key factors such as laser power, wavelength, portability, safety features, brand reputation, after-sales support, and total cost of ownership. Conducting thorough supplier assessments, requesting product demonstrations, and reviewing user feedback will help ensure the selected device meets operational requirements and delivers long-term value.
Ultimately, choosing the right laser cleaning device enhances productivity, supports sustainability goals, and contributes to improved workplace safety. With careful planning and due diligence, organizations can successfully integrate this innovative technology into their processes and gain a competitive edge in their respective markets.