The global laser cleaning market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by increasing demand for eco-friendly, precision-based surface treatment solutions across industries such as automotive, aerospace, manufacturing, and heritage conservation. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the laser cleaning market was valued at approximately USD 716.8 million in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 18.5% from 2024 to 2029. This surge is fueled by the technology’s advantages over traditional cleaning methods—namely, its non-abrasive nature, minimal waste generation, and reduced downtime. Grand View Research further supports this trajectory, noting that advancements in fiber laser technology and rising industrial automation are key growth enablers. As companies increasingly prioritize sustainability and operational efficiency, laser cleaning has transitioned from niche application to mainstream adoption. Against this backdrop, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders in innovation, scalability, and market reach. Here are the top 9 laser cleaning business manufacturers shaping the future of industrial cleaning.
Top 9 Laser Cleaning Business Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laserax
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Laserax works with the world’s leading manufacturers to implement laser cleaning, welding, texturing, and marking solutions….
#2 Clean Laser Systems
Website: cleanlaser.de
Key Highlights: IPG | cleanLASER has been developing and producing high-precision laser systems for cleaning and industrial surface treatment for more than 20 years….
#3 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: we engineer and manufacture the most advanced—and most powerful—pulsed industrial laser cleaning systems on the market, built for both manual and automated ……
#4 Laser Photonics
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser Photonics manufactures reliable, safe, and eco-friendly Laser Cleaning, Laser Cutting, Laser Engraving, Laser Marking, and Laser Welding solutions….
#5 IPG Photonics
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: IPG Photonics is the world leader of fiber laser technology, providing the most innovative and productive laser solutions for any industry application….
#6 Netalux
Website: netalux.com
Key Highlights: Discover our award-winning Laser Cleaning Solutions for the world’s most demanding industries. Discover our products and global service now….
#7 How to Start a Laser Cleaning Business?
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: This page summarizes the most important information for beginners who are considering the purchase of a professional laser cleaning machine and ……
#8 Laser cleaning
Website: p-laserusa.com
Key Highlights: Our laser machines are mainly used to remove the following contaminants: Rust – Paint – Coatings – Release Agents – Grease, Oils – Soot – Rubber- Organic ……
#9 Laser Cleaning Technologies
Website: lasercleaningtechnologies.com
Key Highlights: We offer the only fiber-coupled, compact, mobile or stationary laser cleaning units, with 20 to 1600watts of laser power for a wide-range of applications….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Cleaning Business
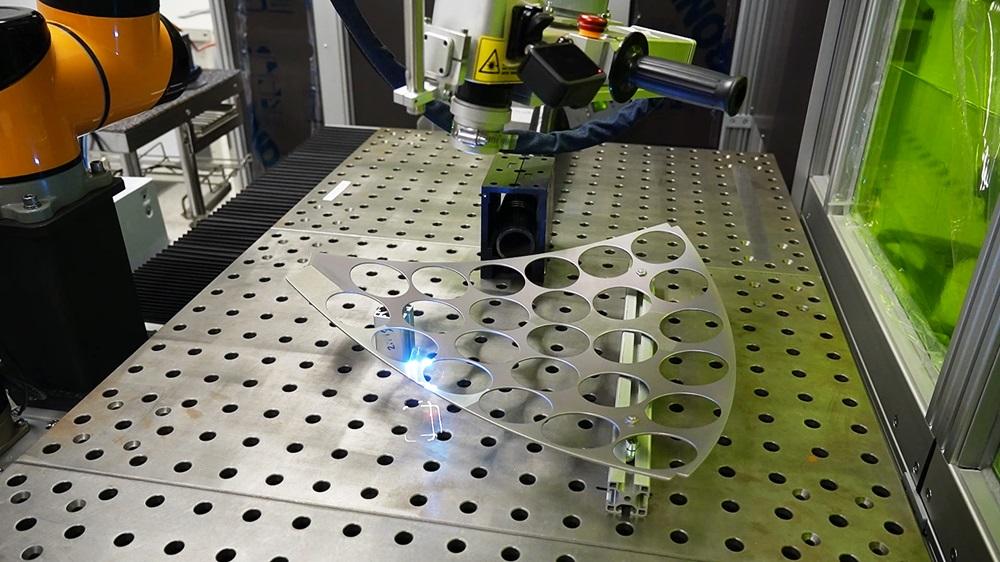

2026 Market Trends for the Laser Cleaning Business
The laser cleaning market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, increasing environmental regulations, and expanding industrial applications. Here are the key trends shaping the industry:
Rising Demand for Eco-Friendly Surface Preparation
Environmental concerns are accelerating the shift from traditional abrasive and chemical cleaning methods to laser solutions. With stricter global regulations on chemical usage (e.g., VOCs) and waste disposal, industries are adopting laser cleaning as a dry, non-abrasive, and chemical-free alternative. By 2026, this regulatory pressure will drive widespread adoption, particularly in automotive, aerospace, and cultural heritage restoration sectors seeking sustainable compliance.
Expansion into New Industrial Applications
While already established in mold cleaning and rust removal, laser cleaning is gaining traction in emerging sectors. The automotive industry will increasingly use it for battery and electric motor component cleaning in EV manufacturing. In electronics, precision cleaning of circuit boards and connectors will grow. Additionally, the nuclear and energy sectors are exploring laser decontamination, opening high-value opportunities by 2026.
Advancements in Portable and Robotic Integration
Technology improvements are making laser cleaning systems more compact, user-friendly, and cost-effective. Portable handheld units are becoming mainstream, enabling on-site maintenance in shipyards and infrastructure. Simultaneously, integration with robotic arms and automation systems will surge, especially in smart factories. By 2026, AI-driven robotic laser cleaning cells are expected to become standard in high-volume production lines, improving precision and reducing labor costs.
Growing Focus on Cost Efficiency and ROI
As laser source efficiency improves and equipment prices decline, the total cost of ownership becomes more competitive with traditional methods. Businesses are recognizing the long-term savings from reduced consumables, waste disposal, and downtime. By 2026, comprehensive ROI calculators and service-as-a-solution (SaaS) models will make laser cleaning more accessible to SMEs, expanding market penetration beyond large corporations.
Regional Market Diversification
While North America and Europe lead in adoption due to stringent environmental policies, Asia-Pacific—especially China, Japan, and South Korea—is expected to experience the fastest growth by 2026. Government support for advanced manufacturing and rising industrial automation in the region will fuel demand. Localized manufacturing of laser components will also reduce costs and supply chain dependencies.
Increased Competition and Market Consolidation
The growing attractiveness of the laser cleaning market will intensify competition. New entrants and established laser manufacturers will expand their portfolios, leading to product differentiation through software, safety features, and ease of integration. By 2026, strategic partnerships, mergers, and acquisitions are likely as companies aim to scale rapidly and offer end-to-end cleaning solutions.
In conclusion, the 2026 laser cleaning market will be defined by sustainability, automation, and broader industrial integration. Companies that innovate in usability, affordability, and application-specific solutions will lead this high-growth sector.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing a Laser Cleaning Business: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
When sourcing or acquiring a laser cleaning business, buyers and investors must navigate several critical challenges, particularly concerning product quality and intellectual property (IP). Overlooking these areas can lead to significant financial, legal, and operational setbacks. Below are two major pitfalls to avoid:
Quality Inconsistencies and Technical Reliability
One of the most prevalent risks in sourcing a laser cleaning business is the variability in product quality and technical performance. Many suppliers, especially in competitive or emerging markets, may offer laser cleaning systems that appear cost-effective but fall short in real-world conditions. Common quality-related issues include inconsistent cleaning performance, premature component failure (such as diodes or cooling systems), inadequate safety features, and poor integration with industrial workflows. These shortcomings often stem from substandard manufacturing practices, lack of rigorous quality control, or the use of low-grade materials. Buyers may discover post-acquisition that systems require frequent maintenance, lack scalability, or fail to meet industry standards—damaging customer trust and increasing long-term costs. Conducting thorough technical due diligence, including on-site testing, review of failure rate data, and third-party performance audits, is essential to mitigate these risks.
Intellectual Property Vulnerabilities and Ownership Gaps
Another critical pitfall involves inadequately protected or contested intellectual property. Laser cleaning technologies often rely on proprietary algorithms, optical configurations, software controls, or unique beam delivery mechanisms that drive performance advantages. However, businesses may lack proper IP protection—such as patents, trademarks, or trade secrets—or have IP that is poorly documented, expired, or subject to third-party claims. In some cases, key innovations may have been developed by contractors or former employees without clear assignment agreements, creating ownership disputes. Acquiring a business with weak or contested IP not only diminishes its valuation but also exposes the buyer to litigation, loss of competitive edge, and barriers to future innovation. Comprehensive IP due diligence—reviewing patent portfolios, licensing agreements, employee contracts, and freedom-to-operate analyses—is crucial to ensure the business’s technology is both defensible and legally secure.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for a Laser Cleaning Business
Business Structure and Legal Registration
Establishing a legally compliant business structure is the first step. Choose a suitable entity—such as a sole proprietorship, LLC, or corporation—based on liability protection, tax implications, and scalability. Register your business with the appropriate state and federal authorities, obtain an Employer Identification Number (EIN) from the IRS, and ensure all local licenses and permits are secured.
Industry Regulations and Safety Compliance
Laser cleaning involves Class 3B or Class 4 lasers, which are regulated by the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH) under the federal laser product standard (21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11). Ensure all laser equipment is registered with the FDA, includes proper labeling, and complies with safety features such as interlocks, beam shutters, and emergency stops. Maintain a Laser Safety Officer (LSO) if required, and follow ANSI Z136.1 guidelines for safe laser use.
Environmental, Health, and Safety (EHS) Requirements
Laser cleaning can generate hazardous airborne contaminants such as metal fumes, particulates, and ozone. Comply with OSHA standards (e.g., 29 CFR 1910.134 for respiratory protection) and implement engineering controls like fume extraction systems. Conduct regular air quality monitoring and provide appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including laser safety goggles, respirators, and fire-resistant clothing.
Transportation and Equipment Logistics
When transporting laser cleaning systems, ensure equipment is securely packaged and meets Department of Transportation (DOT) regulations for sensitive electronics and hazardous materials (if applicable). Use shock-absorbent packaging and climate-controlled vehicles when necessary. Maintain a detailed inventory and service log for all mobile units and comply with vehicle regulations if operating a fleet.
Waste Disposal and Environmental Compliance
Collected debris from laser cleaning may be classified as hazardous waste depending on the substrate (e.g., lead-based paint, cadmium coatings). Follow EPA guidelines under the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) for proper handling, storage, labeling, and disposal. Partner with licensed hazardous waste disposal companies and maintain manifests and disposal records for audits.
Insurance Coverage
Obtain comprehensive business insurance, including general liability, professional liability (errors and omissions), and equipment coverage. Given the high-power nature of lasers, consider additional umbrella policies and specific laser operation liability insurance. Workers’ compensation is mandatory in most states and essential for employee protection.
Client Site Compliance and Access
Before starting work, conduct site assessments to identify safety hazards, electrical requirements, and access limitations. Obtain site-specific permits and coordinate with facility managers to comply with their safety protocols. Provide clients with documentation of compliance, safety procedures, and equipment certifications to build trust and meet contractual obligations.
Training and Certification
Ensure all operators are trained in laser safety, equipment handling, emergency procedures, and regulatory compliance. Certification through accredited programs (e.g., Laser Safety Officer training per ANSI Z136) enhances credibility. Maintain training records and conduct regular refresher courses to keep staff updated on best practices and regulatory changes.
Recordkeeping and Audits
Maintain detailed records of equipment maintenance, safety inspections, employee training, waste disposal, and regulatory filings. These documents are critical during audits by OSHA, FDA, or environmental agencies. Implement a digital management system to organize compliance data and ensure quick access during inspections.
International Operations (if applicable)
If operating across borders, comply with local regulations such as the EU’s CE marking requirements, laser safety directives, and import/export controls. Understand International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) or Export Administration Regulations (EAR) if your equipment falls under controlled technology categories. Use customs brokers to navigate tariffs and documentation.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Laser Cleaning Business
Sourcing a laser cleaning business presents a promising and forward-thinking opportunity in the growing field of eco-friendly and advanced industrial cleaning solutions. As industries increasingly prioritize sustainability, efficiency, and precision, laser cleaning offers a chemical-free, non-abrasive, and highly effective alternative to traditional cleaning methods. The technology is rapidly gaining traction in sectors such as automotive, aerospace, manufacturing, heritage restoration, and mold maintenance.
By strategically sourcing reliable laser cleaning equipment suppliers, skilled personnel, and high-demand service niches, entrepreneurs can establish a competitive and scalable business. Key success factors include investing in quality technology, providing comprehensive training, ensuring regulatory compliance, and building strong client relationships through demonstrable results and ROI.
Furthermore, with continuous advancements in laser technology driving down costs and improving portability and ease of use, the market is becoming more accessible. Early entrants who understand the technical capabilities and can effectively communicate the long-term cost and environmental benefits will be well-positioned to capture market share.
In conclusion, sourcing a laser cleaning business is not only a smart commercial decision but also aligns with global trends toward sustainable industrial practices. With the right planning, investment, and execution, this venture can deliver significant value to clients and establish a profitable, future-ready enterprise.