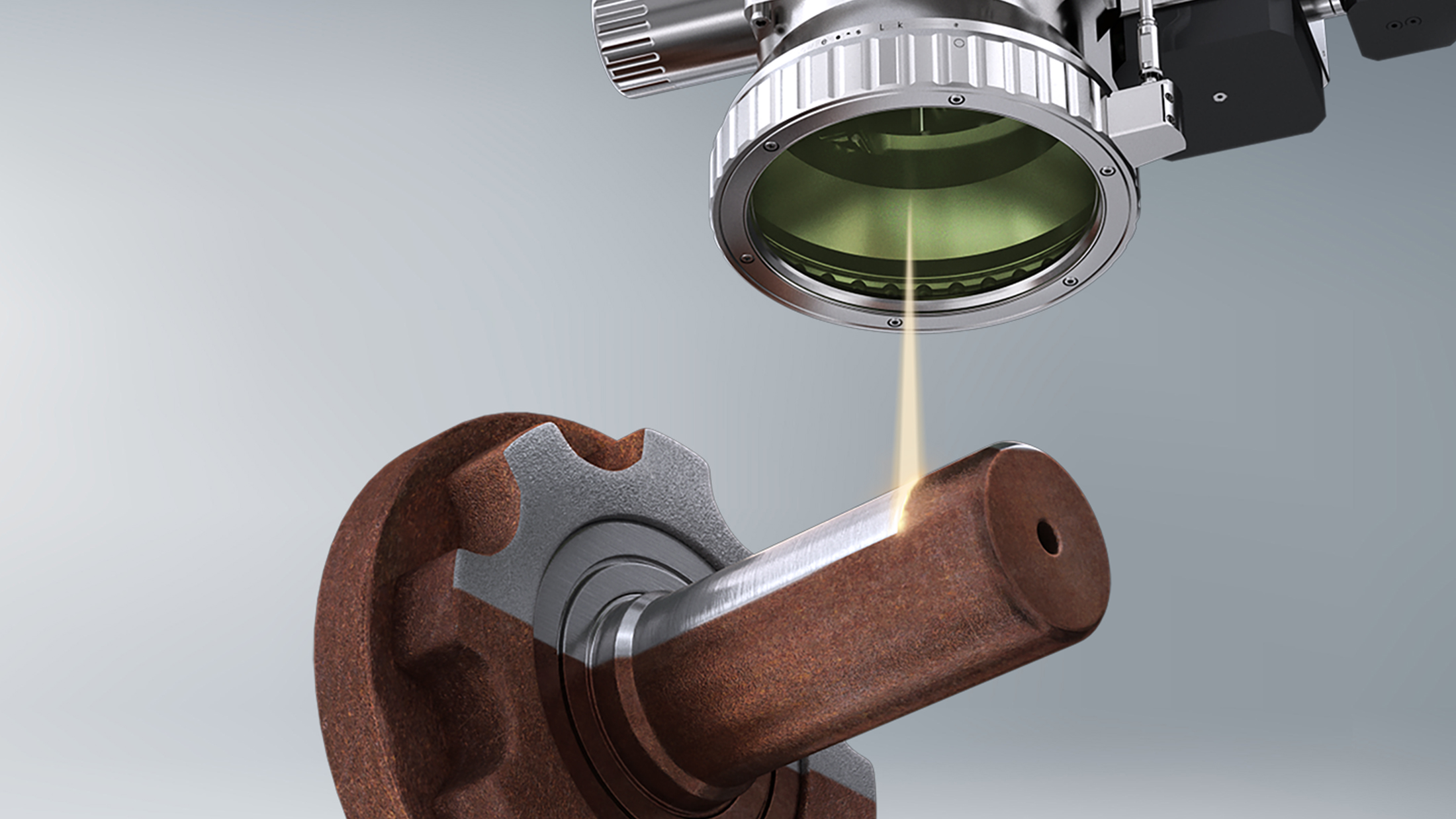
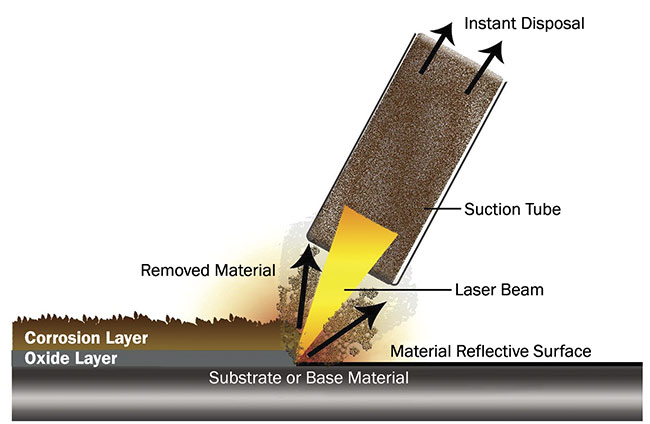
The global laser cleaning market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for environmentally friendly, precise, and efficient surface treatment solutions across industries. According to Grand View Research, the market was valued at USD 862.3 million in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 18.4% from 2023 to 2030. This surge is fueled by the adoption of laser cleaning in automotive, aerospace, electronics, and cultural heritage restoration, where traditional cleaning methods fall short in precision and sustainability. As industries prioritize automation and reduce reliance on chemical solvents, laser cleaning has emerged as a transformative technology. In this evolving landscape, a select group of manufacturers are leading innovation, scalability, and application-specific solutions—shaping the future of industrial maintenance and surface preparation. Here, we spotlight the top nine laser cleaning applications manufacturers at the forefront of this technological shift.
Top 9 Laser Cleaning Applications Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laserax
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Laserax works with the world’s leading manufacturers to implement laser cleaning, welding, texturing, and marking solutions….
#2 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: we engineer and manufacture the most advanced—and most powerful—pulsed industrial laser cleaning systems on the market, built for both manual and automated ……
#3 Clean Laser Systems
Website: cleanlaser.de
Key Highlights: IPG | cleanLASER has been developing and producing high-precision laser systems for cleaning and industrial surface treatment for more than 20 years….
#4 Laser Photonics
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser Photonics manufactures reliable, safe, and eco-friendly Laser Cleaning, Laser Cutting, Laser Engraving, Laser Marking, and Laser Welding solutions….
#5 Laser Cleaning
Website: keyence.com
Key Highlights: Elevate production quality with laser cleaning technology: remove dust, rust, and imperfections efficiently, reducing costs and improving precision….
#6 Laser Cleaning technology
Website: innotech-laser.de
Key Highlights: Laser cleaning has a wide range of applications, e.g. in facade cleaning, the automotive industry and medical technology. Galvo scanner / deflection units….
#7 Netalux
Website: netalux.com
Key Highlights: Discover our award-winning Laser Cleaning Solutions for the world’s most demanding industries. Discover our products and global service now….
#8 Laser Cleaning
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaning is used across a variety of industries to remove unwanted surface materials like coatings, paints, rust, oil, and for surface preparation for ……
#9 Laser cleaning
Website: trumpf.com
Key Highlights: How to achieve the perfect weld seam: laser cleaning allows you to very gently clean metal components of dirt, as well as oxidation and functional layers….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Cleaning Applications

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Laser Cleaning Applications
The laser cleaning market is poised for significant transformation and expansion by 2026, driven by technological advancements, stringent environmental regulations, and growing industrial demand for precision and automation. Key trends shaping the landscape include:
1. Accelerated Industrial Adoption & Market Expansion:
The global laser cleaning market is projected to experience robust compound annual growth rates (CAGRs) of 18–22% through 2026, reaching an estimated value of $2.1–$2.5 billion. This growth is fueled by increasing penetration across core sectors such as automotive (for paint stripping, rust removal, and surface preparation), aerospace (composite and turbine blade cleaning), heavy manufacturing (mold maintenance, weld seam preparation), and heritage conservation (artwork and monument restoration). Demand is particularly strong in North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific—especially China—where industrial modernization is prioritizing efficiency and sustainability.
2. Shift Towards Fiber Lasers and Higher Power Systems:
Fiber lasers continue to dominate the market due to their reliability, energy efficiency, compact size, and lower maintenance needs compared to older CO₂ or Nd:YAG systems. By 2026, there will be a noticeable shift toward higher-power fiber lasers (1,000W and above), enabling faster ablation rates and broader applicability to thick coatings, heavy rust, and large-scale industrial tasks. This evolution improves return on investment (ROI) for end-users by reducing processing time and labor costs.
3. Integration with Robotics and Smart Manufacturing (Industry 4.0):
Laser cleaning systems are increasingly being integrated into robotic arms and automated production lines. By 2026, smart laser cleaning solutions featuring IoT connectivity, real-time monitoring, and AI-driven process optimization will be commonplace. These systems enable predictive maintenance, adaptive cleaning parameters, and seamless data integration into digital twin platforms—key components of Industry 4.0 strategies aiming to enhance productivity and quality control.
4. Regulatory Tailwinds and Sustainability Drivers:
Stringent environmental regulations (e.g., REACH, EPA guidelines) restricting chemical solvents and abrasive blasting are accelerating the shift to eco-friendly alternatives. Laser cleaning produces no secondary waste, uses minimal consumables, and eliminates hazardous fumes or wastewater. As ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) compliance becomes a corporate imperative, laser cleaning will be positioned as a sustainable surface treatment solution across regulated industries.
5. Technological Innovation in Pulse Control and Beam Delivery:
Advancements in pulse shaping, beam modulation, and scanning optics are improving cleaning precision and substrate safety. By 2026, systems with intelligent pulse control will allow for selective material removal—preserving delicate underlying substrates such as copper or thin metal layers—expanding use cases in electronics and precision engineering. Handheld systems with enhanced ergonomics and safety features will also gain popularity for field maintenance and retrofit applications.
6. Cost Reduction and Accessibility:
While initial investment remains higher than traditional methods, the total cost of ownership (TCO) of laser cleaning is improving due to falling laser component prices, longer system lifespans, and reduced operational costs. By 2026, more affordable mid-range systems will enter the market, making laser cleaning accessible to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and niche applications like tooling maintenance and medical device manufacturing.
Conclusion:
By 2026, laser cleaning will transition from a specialized technique to a mainstream industrial process, driven by environmental mandates, digital integration, and continuous innovation. Companies investing in scalable, automated laser cleaning solutions will gain competitive advantages in quality, compliance, and operational efficiency. The convergence of sustainability, automation, and precision will solidify laser cleaning as a cornerstone of next-generation manufacturing and maintenance practices.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Laser Cleaning Applications: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
When sourcing laser cleaning systems or services, businesses often focus on cost and performance specifications while overlooking critical quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) concerns. Failing to address these aspects can lead to operational inefficiencies, legal disputes, and long-term financial losses. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Validation of Cleaning Performance
Many suppliers provide idealized results under laboratory conditions that don’t reflect real-world applications. Without third-party testing or on-site demonstrations, buyers risk acquiring systems that underperform on specific materials, contamination types, or production line speeds. Always request application-specific validation data and conduct pilot testing.
Lack of Standardized Quality Controls
Low-cost suppliers may skip essential manufacturing quality controls, leading to inconsistent beam quality, unreliable component lifespans, and safety hazards. Ensure the supplier adheres to international standards (e.g., IEC 60825 for laser safety) and offers comprehensive documentation on component sourcing and assembly processes.
Insufficient After-Sales Support and Training
Poorly trained operators can damage equipment or compromise cleaning efficacy. Some suppliers provide minimal training or lack local technical support, increasing downtime and maintenance costs. Confirm the availability of installation assistance, operator training, and responsive technical service before procurement.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
Ambiguous Ownership of Custom-Built Solutions
When working with suppliers to develop tailored laser cleaning systems, the IP rights to custom software, control algorithms, or mechanical designs may not be clearly transferred. This can restrict your ability to modify, repair, or scale the solution independently. Always define IP ownership in writing within the contract.
Use of Unlicensed or Infringing Technology
Some suppliers may incorporate third-party software or patented subsystems without proper licensing. Purchasing such systems exposes your organization to infringement claims. Conduct due diligence on the supplier’s technology stack and request warranties confirming non-infringement.
Inadequate Protection of Your Proprietary Processes
Sharing detailed information about your production environment or materials with suppliers increases the risk of IP leakage. Ensure non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) are in place and limit data disclosure to what is strictly necessary for system design and integration.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls, organizations can secure reliable, compliant, and legally protected laser cleaning solutions that deliver sustainable value.
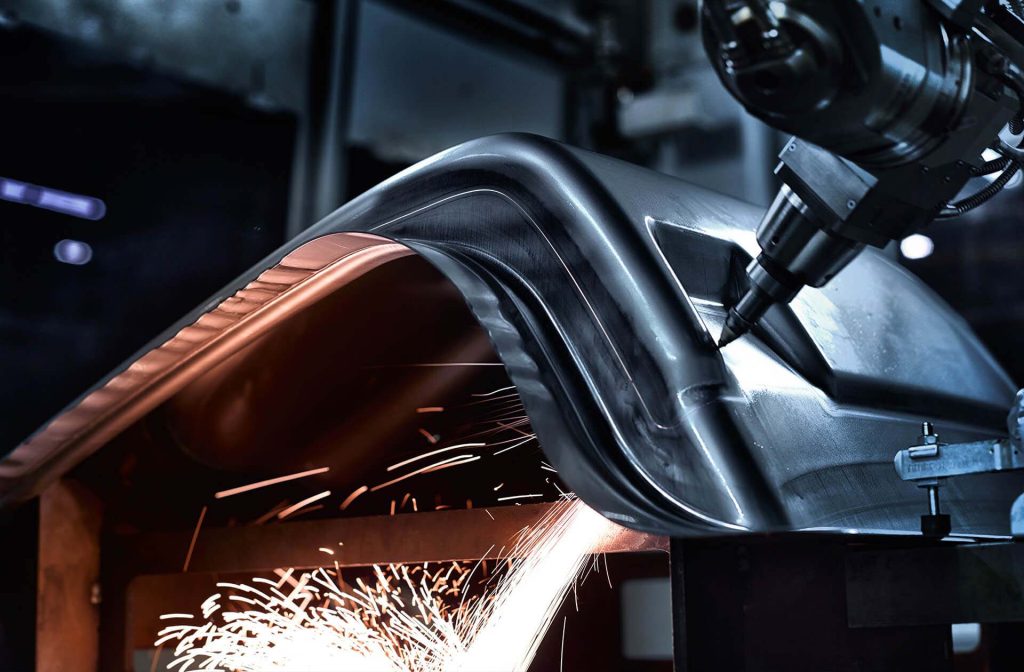

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Cleaning Applications
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Laser cleaning systems are subject to multiple regulatory frameworks depending on the region of operation. Key compliance areas include:
- Laser Safety Standards (IEC 60825-1 / ANSI Z136.1): Classify lasers according to hazard level and mandate appropriate safety controls, including labeling, interlocks, and protective housings.
- Occupational Health and Safety (OSHA, EU Directive 89/391/EEC): Require risk assessments, worker training, and implementation of engineering and administrative controls to minimize exposure to laser radiation and airborne contaminants.
- Air Quality & Emissions (EPA, EU Industrial Emissions Directive): Regulate the release of particulate matter and hazardous fumes generated during laser ablation. Use of fume extraction and filtration systems (e.g., HEPA filters) is typically required.
- Hazardous Waste Disposal (RCRA, EU Waste Framework Directive): Cleaned residues—especially when removing lead-based paint, asbestos, or heavy metals—may be classified as hazardous waste and must be handled, labeled, stored, and disposed of accordingly.
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC Directive 2014/30/EU): Ensure laser equipment does not interfere with other electronic systems and is immune to external interference.
Transportation and Handling of Laser Equipment
- Packaging: Laser systems must be shipped in shock-resistant, moisture-proof containers. Sensitive optical components should be secured and protected with anti-static materials.
- Labeling: Clearly mark all packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Laser Product” labels. Include required hazard symbols based on laser class (e.g., Class 4 laser warning).
- Battery & Power Components: If the system contains lithium-ion batteries, comply with IATA/ICAO regulations for air transport (UN38.3 testing, proper packaging, documentation).
- Import/Export Controls: Check for dual-use or technology-specific export restrictions (e.g., under EAR or Wassenaar Arrangement). Some high-power lasers may require export licenses.
On-Site Installation and Operational Logistics
- Site Assessment: Conduct pre-installation evaluation for power supply requirements (voltage, grounding), ventilation, space, and access. Confirm compatibility with local electrical codes (e.g., NEC, IEC).
- Controlled Access: Designate a laser-controlled area with restricted access, proper signage, and physical barriers (e.g., interlocked doors, light curtains).
- Fume Extraction Setup: Install local exhaust ventilation (LEV) systems with high-efficiency filters. Ensure ducting is grounded to prevent static buildup and regularly inspect for blockages.
- Calibration & Maintenance: Maintain logs for laser calibration, mirror alignment, and filter replacement. Follow manufacturer-recommended maintenance schedules to ensure performance and safety.
Personnel Training and Documentation
- Operator Certification: All personnel must complete laser safety training (e.g., Certified Laser Safety Officer – CLSO) and receive site-specific instruction on equipment use and emergency procedures.
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Develop and enforce SOPs covering startup, operation, shutdown, waste handling, and response to laser or fume system failures.
- Record Keeping: Maintain documentation of safety audits, training records, maintenance logs, emission monitoring, and waste disposal manifests for regulatory inspections.
Environmental and Waste Management
- Waste Characterization: Analyze debris from cleaning processes (e.g., via material safety data sheets or lab testing) to determine hazardous status.
- Containment: Use vacuum collection systems or drop cloths with adhesive backing to capture debris during operation, especially in outdoor or sensitive environments.
- Storage and Disposal: Store waste in labeled, sealed containers. Partner with licensed hazardous waste disposal providers and retain disposal certificates.
- Spill Response Plan: Prepare protocols for accidental release of hazardous residues, including containment, cleanup procedures, and reporting obligations.
International Considerations
- CE Marking (EU): Required for placing laser equipment on the European market. Involves conformity assessment, technical file compilation, and declaration of performance.
- FDA Registration (USA): Manufacturers and initial distributors of laser products must register with the FDA and submit product reports under 21 CFR 1040.10.
- Local Permits: Verify requirements for industrial operations, emissions, and noise levels with local authorities prior to deployment, especially in urban or environmentally sensitive areas.
Adherence to this guide ensures legal operation, protects personnel and the environment, and supports sustainable deployment of laser cleaning technologies. Regularly review and update compliance protocols in line with evolving regulations.
Conclusion: Sourcing Laser Cleaning Applications
In conclusion, sourcing laser cleaning technology presents a compelling opportunity for industries aiming to enhance efficiency, sustainability, and precision in surface treatment processes. As a non-abrasive, environmentally friendly alternative to traditional cleaning methods, laser cleaning eliminates the need for chemicals, reduces waste, and minimizes substrate damage—making it ideal for sectors such as automotive, aerospace, heritage conservation, and precision manufacturing.
When sourcing laser cleaning solutions, it is essential to evaluate key factors including laser power, wavelength, portability, safety features, and vendor support. Selecting the right system requires alignment with specific application needs, such as rust removal, paint stripping, or mold cleaning, as well as consideration of operational costs and return on investment.
The growing availability of advanced, user-friendly systems from reliable suppliers—both established manufacturers and innovative startups—makes it easier than ever to adopt this transformative technology. As automation and Industry 4.0 integration continue to evolve, laser cleaning is poised to become a standard in modern industrial maintenance and manufacturing.
Ultimately, investing in the right laser cleaning solution not only improves operational performance but also supports long-term sustainability goals, ensuring a cleaner, safer, and more efficient working environment. Careful due diligence in sourcing will enable organizations to harness the full potential of this innovative technology.