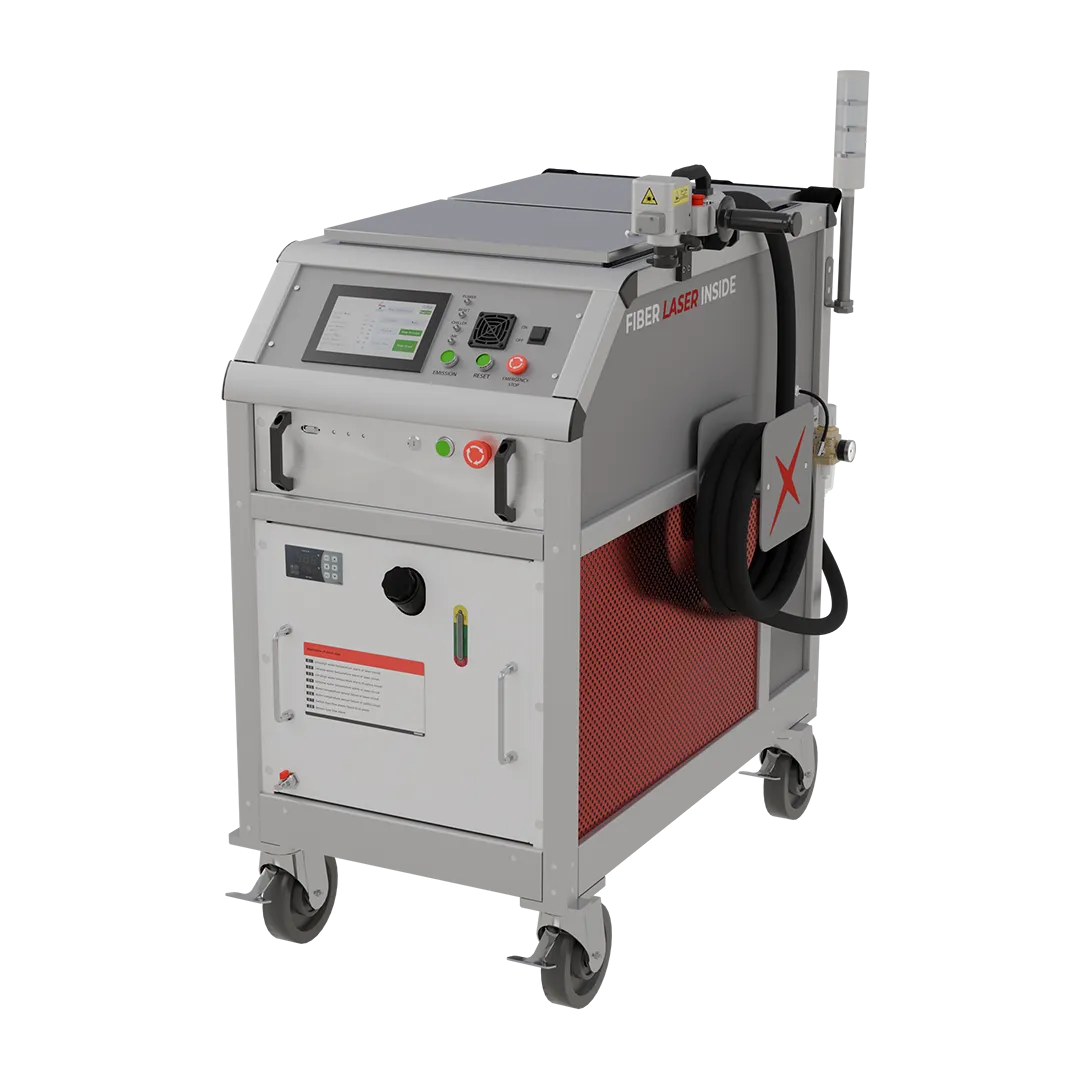
The global laser cleaning market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by increasing demand for eco-friendly, precise, and low-maintenance surface treatment solutions across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. According to Grand View Research, the market was valued at USD 507.2 million in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 21.8% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects continued momentum, attributing growth to technological advancements in portable laser systems and rising regulatory pressure to reduce chemical-based cleaning methods. This surge in adoption has catalyzed innovation and competition among manufacturers, leading to the emergence of high-performance laser cleaner tools that offer superior efficiency and operational safety. In this evolving landscape, the following eight manufacturers stand out for their cutting-edge technology, global reach, and strong market presence.
Top 8 Laser Cleaner Tool Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: PULSAR Laser is a manufacturer of professional laser cleaning machines, developed and engineered for industrial maintenance, manufacturing, restoration and ……
#2 Laserax
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Laserax works with the world’s leading manufacturers to implement laser cleaning, welding, texturing, and marking solutions….
#3 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: we engineer and manufacture the most advanced—and most powerful—pulsed industrial laser cleaning systems on the market, built for both manual and automated ……
#4 Laser Photonics
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser Photonics manufactures reliable, safe, and eco-friendly Laser Cleaning, Laser Cutting, Laser Engraving, Laser Marking, and Laser Welding solutions….
#5 Clean Laser Systems
Website: cleanlaser.de
Key Highlights: IPG | cleanLASER has been developing and producing high-precision laser systems for cleaning and industrial surface treatment for more than 20 years….
#6 SFX Laser
Website: sfxlaser.com
Key Highlights: SFX Laser is a 20+ years professional laser equipment manufacturer including laser cleaning machine, laser welding machine, fiber laser engraver, fiber laser…
#7 Netalux
Website: netalux.com
Key Highlights: Discover our award-winning Laser Cleaning Solutions for the world’s most demanding industries. Discover our products and global service now….
#8 Laser Cleaning
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Discover Your Laser Cleaning Solution IPG is a partner for every stage of production from research and development to full-scale manufacturing….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Cleaner Tool
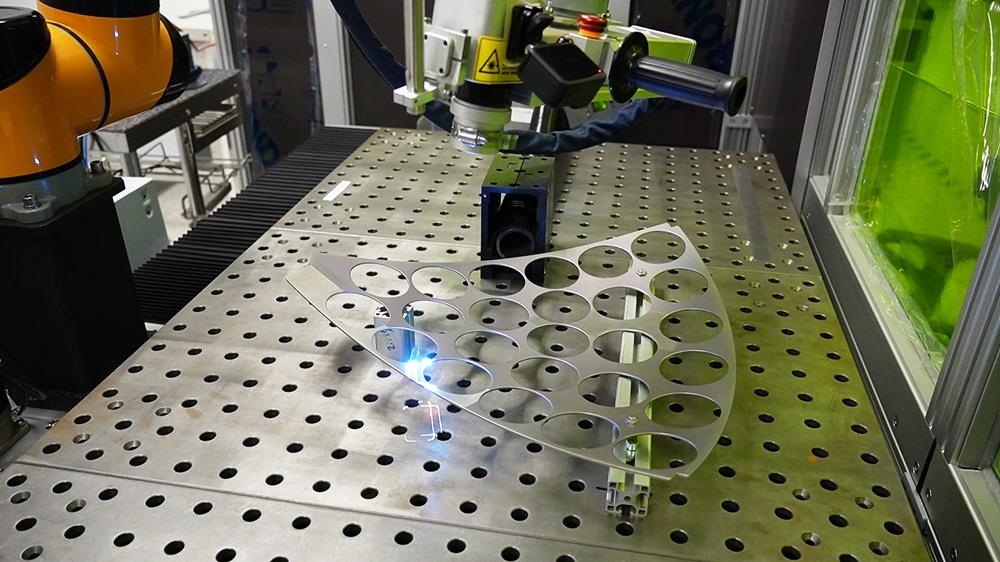

2026 Market Trends for Laser Cleaner Tools
The global laser cleaner tool market is poised for transformative growth and technological evolution by 2026, driven by increasing industrial automation, stringent environmental regulations, and advancements in laser technology. Here are the key trends expected to shape the landscape:
Rising Demand Across Industrial Sectors
Manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, and heritage conservation industries are rapidly adopting laser cleaning as a preferred method for surface preparation, rust removal, paint stripping, and mold cleaning. By 2026, the demand will be fueled by the need for non-abrasive, precise, and repeatable cleaning processes that minimize substrate damage. The automotive sector, in particular, is expected to see significant deployment for engine component refurbishment and weld preparation, while the aerospace industry will leverage laser cleaning for delicate turbine blade maintenance.
Shift Toward Portable and Handheld Systems
A dominant trend by 2026 will be the proliferation of portable and handheld laser cleaning devices. Improvements in fiber laser efficiency, battery technology, and ergonomic design are making these tools more accessible for field service, maintenance operations, and small-to-medium enterprises. This shift democratizes access to laser cleaning technology, moving it beyond large industrial facilities into workshops and on-site repair environments.
Integration with Automation and Robotics
Laser cleaning systems will increasingly be integrated into automated production lines and robotic cells. By 2026, smart factories will deploy robotic arms equipped with laser cleaning heads for tasks such as pre-weld cleaning and post-processing, enhancing throughput and consistency. Integration with IoT platforms and AI-driven control systems will enable predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring, and adaptive cleaning parameters, improving operational efficiency.
Focus on Sustainability and Regulatory Compliance
As environmental regulations tighten globally—particularly restrictions on chemical solvents and abrasive blasting—laser cleaning offers a dry, chemical-free alternative with minimal waste. By 2026, companies will prioritize laser cleaning to meet sustainability goals and comply with regulations like REACH and OSHA standards. This eco-friendly profile will be a major selling point, especially in Europe and North America.
Advancements in Laser Source Technology
Fiber lasers will continue to dominate due to their reliability, efficiency, and lower maintenance needs. However, innovations in pulsed laser parameters (wavelength, pulse duration, frequency) will enhance cleaning efficacy on diverse materials—including composites, sensitive metals, and historical artifacts. Expect to see wider adoption of green and UV lasers for delicate applications where thermal damage must be minimized.
Price Reduction and Market Expansion
As production scales and component costs decline, laser cleaner tools will become more affordable. This downward pricing trend will open new markets in emerging economies and encourage adoption by smaller industrial players. Increased competition among manufacturers will also drive innovation in features and service models, such as leasing and pay-per-use options.
In conclusion, by 2026, the laser cleaner tool market will be defined by smarter, more mobile, and environmentally responsible solutions, positioning laser cleaning as a cornerstone technology in industrial maintenance and manufacturing hygiene.
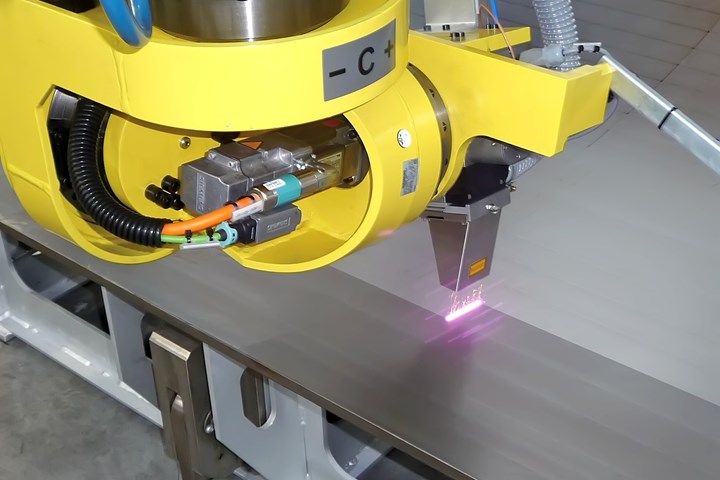

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Laser Cleaner Tools: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing laser cleaner tools from global suppliers—especially in cost-competitive markets—can present significant challenges related to product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Being aware of these pitfalls is crucial for ensuring a reliable, safe, and legally compliant procurement process.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Performance and Reliability
Many suppliers, particularly smaller or less experienced manufacturers, may offer laser cleaners that do not consistently meet advertised specifications. Issues such as unstable laser output, inconsistent cleaning speed, or premature component failure are common. Without proper quality control systems, units from the same batch can vary significantly in performance.
Use of Substandard Components
To reduce costs, some suppliers use low-grade optics, cooling systems, or laser diodes. These components degrade faster, reduce cleaning efficiency, and increase the risk of system failure. Inferior cooling mechanisms, for example, can lead to overheating and shortened device lifespan.
Lack of Safety Features and Certifications
Reputable laser cleaning tools must comply with international safety standards (e.g., IEC 60825 for laser safety). Some sourced products may lack essential safety features such as emergency stop functions, proper beam shielding, or interlock systems. Absence of recognized certifications can expose buyers to legal liability and workplace safety risks.
Insufficient Testing and Validation
Suppliers might not perform rigorous field testing under real-world conditions. As a result, performance claims—such as cleaning efficiency on rust, paint, or oxide layers—may be exaggerated or based on ideal lab scenarios, leading to disappointment upon deployment.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Counterfeit or Clone Products
A major concern when sourcing laser cleaners is the prevalence of cloned or reverse-engineered devices that infringe on patented technologies. These products often mimic the appearance and specifications of established brands but lack innovation, support, and legal legitimacy.
Unclear or Infringing Technology Provenance
Some suppliers may incorporate proprietary technologies (e.g., control software, scanning systems, or optical designs) without proper licensing. Purchasing such products can inadvertently involve your company in IP disputes, especially if the tools are used or resold in markets with strong IP enforcement.
Lack of IP Warranty or Legal Protection
Many suppliers, particularly in regions with weak IP enforcement, do not provide warranties against IP infringement. If a third party later claims ownership of the technology embedded in the tool, the buyer may face litigation, product recalls, or import bans—without recourse from the supplier.
Risk of Technology Misappropriation
When working closely with suppliers to customize laser cleaning tools, there is a risk that design specifications, software algorithms, or performance data could be copied or shared with competitors. Without robust non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) and IP clauses in contracts, your innovations may be compromised.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, conduct thorough due diligence:
– Audit supplier manufacturing facilities and quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001).
– Request third-party test reports and verify safety certifications.
– Perform independent performance testing before large-scale procurement.
– Conduct IP due diligence, including patent landscape analysis and supplier IP warranties.
– Include strong contractual protections regarding quality, performance, and IP indemnification.
By proactively addressing quality and IP concerns, businesses can secure reliable laser cleaning tools while minimizing operational and legal risks.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Cleaner Tool
Product Classification & Regulatory Overview
Laser cleaner tools are classified as industrial laser systems and are subject to multiple international and regional regulations. These tools typically fall under Class 4 laser products due to their high power output, requiring strict controls for safety, emissions, and transportation. Key regulatory frameworks include the IEC 60825 (laser safety), FDA/CDRH (U.S. radiation-emitting devices), CE marking directives (e.g., Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC, EMC Directive 2014/30/EU, and RoHS 2011/65/EU), and local occupational safety standards. Prior to shipment, ensure product documentation includes compliance declarations, technical files, and conformity assessments per destination market requirements.
Packaging & Handling Requirements
Laser cleaner tools must be packaged to prevent physical damage, moisture ingress, and electrostatic discharge during transit. Use rigid, shock-absorbent materials (e.g., custom foam inserts) within a double-walled corrugated container. Clearly label packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Laser Radiation” hazard symbols. Include desiccants if shipping to high-humidity regions. Always secure moving components and disconnect power sources or batteries per IATA/IMDG regulations. Handle with ESD-safe procedures in controlled environments to protect sensitive electronic controls.
Transportation & Shipping Compliance
Transport of laser cleaner tools is regulated under dangerous goods codes when batteries (e.g., lithium-ion) are included. If powered by rechargeable batteries, classify under UN 3480 (lithium-ion) or UN 3090 (lithium metal), packaged per IATA DGR (air), IMDG Code (sea), or ADR (road). Even without batteries, Class 4 lasers may require special handling documentation. Declare the product accurately on shipping manifests, noting laser classification and compliance with 21 CFR 1040.10 (U.S.) or equivalent standards. Use carriers experienced in handling industrial equipment and hazardous materials where applicable.
Import/Export Documentation
Prepare a complete set of export documentation including commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading/air waybill, and certificate of origin. Include a Laser Product Classification Certificate and Declaration of Conformity (DoC) referencing applicable standards (e.g., IEC 60825-1, FDA 21 CFR, CE directives). For exports to the U.S., file FDA pre-market notification (if required) and provide CDRH accession number. Check destination country requirements—some (e.g., China, Russia, India) may require additional product registration, local testing, or import licenses. Maintain records for audit and traceability per regulatory retention policies (typically 5–10 years).
Customs Clearance & Duties
Laser cleaner tools may attract variable import duties depending on the Harmonized System (HS) code. Common classifications include 8515.21 (laser soldering/welding machines) or 8479.89 (other machines). Confirm correct HS code with local customs authorities or a licensed broker. Provide all technical specifications to avoid misclassification. Be prepared for customs inspection, especially for Class 4 lasers. Duties, VAT, and anti-dumping fees (if applicable) must be paid prior to release. Use Incoterms clearly (e.g., DDP, DAP) to define responsibility for customs clearance and associated costs.
End-User Compliance & Safety Training
Ensure end users receive comprehensive safety documentation, including user manuals in local language, laser safety warnings, and maintenance procedures. Operators must be trained per OSHA (U.S.), EU Directive 89/391/EEC (workplace safety), or equivalent national standards. Provide appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as laser safety goggles rated for the tool’s wavelength. Maintain records of training and equipment use. Inform users of local regulatory reporting requirements, especially where laser operations may require facility registration or environmental permits.
Environmental & Disposal Regulations
Dispose of end-of-life laser cleaner tools in compliance with WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) and RoHS directives in applicable regions. Remove and recycle batteries separately per local hazardous waste rules. Laser components may contain hazardous materials (e.g., optical crystals, heavy metals); handle through certified e-waste recyclers. Document proper disposal for corporate sustainability reporting and regulatory compliance. Prohibit landfill disposal of electronic assemblies and laser modules.
Monitoring & Continuous Compliance
Establish a compliance monitoring program to track regulatory updates in key markets. Assign responsibility for maintaining product certifications, renewing registrations, and auditing supply chain partners. Conduct annual internal audits of logistics practices, labeling, and documentation accuracy. Subscribe to regulatory alert services for changes in laser safety, transport, or environmental laws. Update technical files and DoCs promptly to reflect design changes or new standards.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Laser Cleaner Tool:
Sourcing a laser cleaning tool is a strategic decision that can significantly enhance operational efficiency, improve surface preparation quality, and support sustainability goals by eliminating the need for chemicals or abrasive methods. Through careful evaluation of technical specifications, application requirements, safety features, and total cost of ownership, organizations can identify a suitable laser cleaning solution that aligns with their maintenance, restoration, or industrial production needs.
Key considerations such as laser power, portability, ease of integration, after-sales support, and compliance with safety standards should guide the procurement process. Additionally, partnering with reputable suppliers offering proven technology, training, and maintenance services ensures long-term reliability and return on investment.
Ultimately, investing in a high-quality laser cleaning tool not only modernizes cleaning processes but also positions the organization at the forefront of innovative, eco-friendly manufacturing and maintenance practices. As laser cleaning technology continues to evolve, early adoption can provide a competitive advantage in industries ranging from automotive and aerospace to heritage conservation and precision engineering.