The global laser manufacturing market has experienced robust growth over the past decade, driven by increasing demand across industries such as automotive, electronics, healthcare, and precision manufacturing. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global laser market was valued at USD 16.3 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 23.8 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of approximately 6.5% during the forecast period. China has emerged as a pivotal player in this expansion, leveraging its strong industrial base, government support for high-tech manufacturing, and cost-efficient production capabilities. As one of the largest producers and consumers of laser technology, China accounts for over 30% of global laser equipment production, with domestic manufacturers increasingly competing on quality, innovation, and scalability. This growth is further bolstered by rising adoption of fiber lasers and advancements in laser-based automation within Chinese manufacturing ecosystems. Against this backdrop, a closer look at the top 10 laser manufacturers in China reveals key innovators shaping both regional and international laser technology trends.
Top 10 Laser China Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Focus on laser
Founded: 1996
Website: hanslaser.net
Key Highlights: Han’s Laser Technology Industry Group Co., Ltd, a public company which was established in 1996, has now became the flagship of Chinese national laser industry ……
#2 Demark (Wuhan) Technology Co., Ltd.
Website: demarkchina.cn
Key Highlights: Demark (Wuhan) Technology Co.,ltd has focused on laser technology for over 20 years in China, including laser marking, laser engraving, laser welding and laser ……
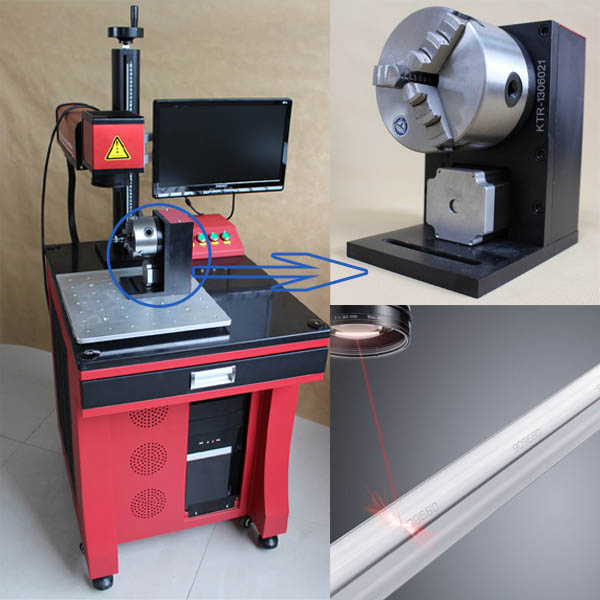
#3 International Laser Marking Machine Manufacturer & Supplier …
Website: hunstlaser.com
Key Highlights: Hunst Laser Co., Ltd is one of the leading and top-notch laser marking machine manufacturer and supplier in China. We excel in introducing the innovative and ……
#4 China Laser Welding
Website: laserchina.com
Key Highlights: LASERCHINA is a China-based laser manufacturer that specializes in developing and manufacturing laser machine, parts, custom solutions and repair service….
#5 JPT Laser
Website: en.jptoe.com
Key Highlights: As a leading laser manufacturer in China, JPT offers a full range of lasers, including MOPA laser, CW laser, DPSS laser, and diode lasers. JPT delivers high- ……
#6 Wuhan Raycus Fiber Laser Technologies Co., Ltd.
Website: en.raycuslaser.com
Key Highlights: (hereinafter referred to as “Wuhan Raycus”) is the first Chinese enterprise engaged in the research, development and scale production of high-power fiber lasers ……
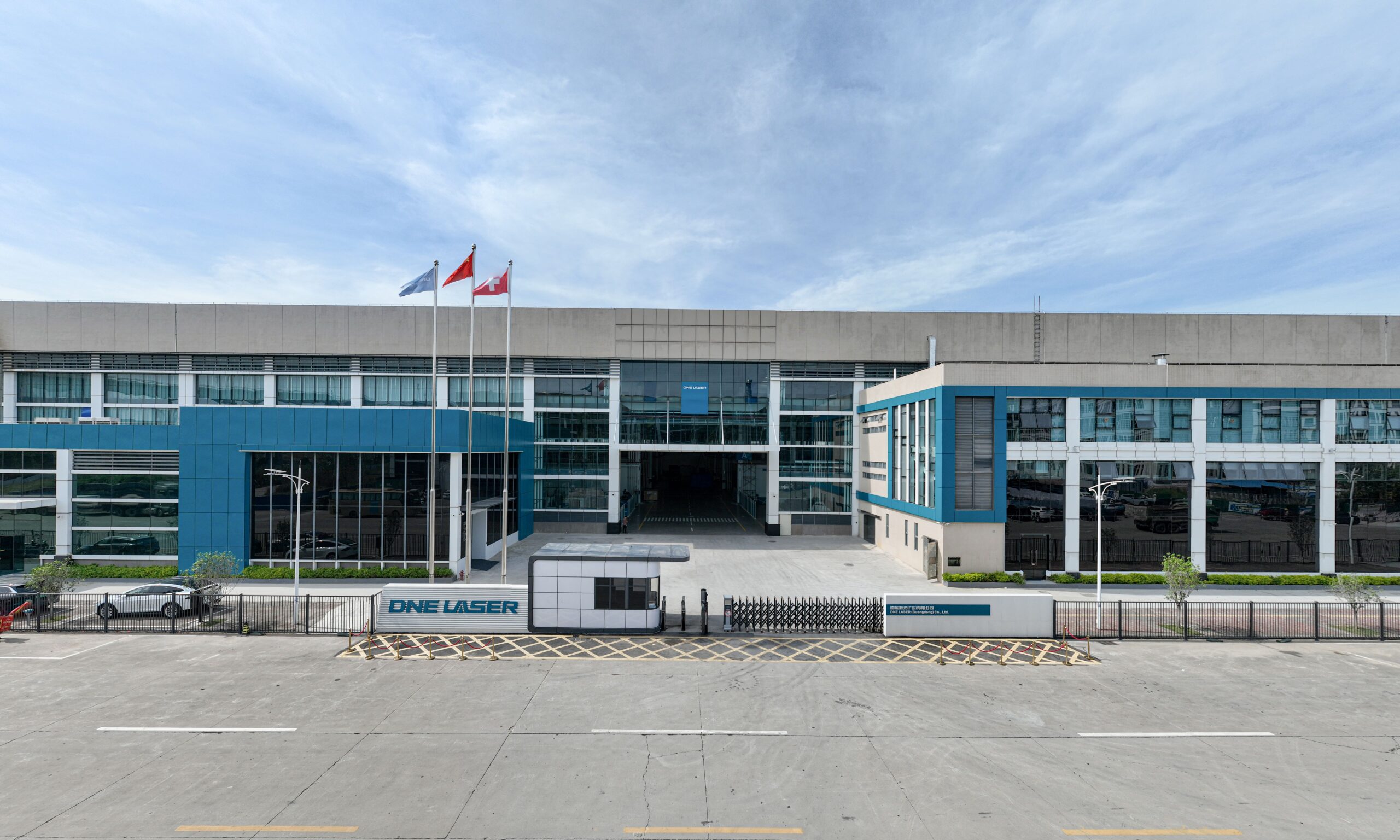
#7 DNE LASER
Website: dne.global
Key Highlights: DNE Laser (Guangdong) Co., Ltd. (Brand name: DNE LASER), a wholly owned subsidiary of the Swiss Bystronic Group, is headquartered in Shenzhen with its ……
#8 20 Years Experience Laser Cutting Machine Chinese Manufacturer
Website: jqlaser.com
Key Highlights: Protube. Learning from experience, simplifying your production. ; The elegance of metal. Tube laser cutting machines give shape to your design….
#9 IPG Photonics
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: IPG Photonics manufactures high-performance fiber lasers, amplifiers, and laser systems for diverse applications and industries. Discover your solution….
#10 Han’s Laser
Website: hansme.net
Key Highlights: The first laser cutting automatic production line in China. XCMG has chosen the laser automation production line provided by Han’s Laser, becoming the first ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser China

H2: Market Trends for Laser Technology in China (2026 Outlook)
As China continues to position itself as a global leader in advanced manufacturing and high-tech innovation, the laser technology market is poised for robust growth and transformation by 2026. The second half of the decade (H2) is expected to be defined by accelerated adoption across industries, domestic technological self-reliance, and strategic government support. Below is an analysis of key market trends shaping the laser industry in China through 2026.
1. Rising Demand in Advanced Manufacturing
China’s push toward intelligent manufacturing under initiatives like Made in China 2025 is driving widespread integration of laser systems in automotive, electronics, and aerospace sectors. By 2026, high-precision laser cutting, welding, and additive manufacturing (3D printing) will be standard in smart factories. The electric vehicle (EV) boom, in particular, is fueling demand for laser-based battery welding and component fabrication, with Chinese EV manufacturers investing heavily in automated laser solutions.
2. Growth of Domestic Laser Technology
China is rapidly reducing its reliance on imported laser components. Companies such as Han’s Laser, Maxphotonics, and Raycus have made significant strides in developing high-power fiber lasers and ultrafast lasers. By 2026, domestic firms are expected to capture over 70% of the mid-to-high-end laser market in China, supported by state-backed R&D programs and innovation clusters in cities like Wuhan and Shenzhen.
3. Expansion in Emerging Applications
Beyond traditional industrial uses, new applications are emerging:
– Semiconductor and Microelectronics: As China invests heavily in semiconductor self-sufficiency, precision lasers for lithography, dicing, and inspection are in high demand.
– Biomedical and Life Sciences: Ultrafast lasers are increasingly used in medical device manufacturing, ophthalmic surgery, and bio-imaging.
– Green Energy: Lasers play a critical role in solar cell scribing, battery recycling, and hydrogen fuel cell production—sectors that align with China’s carbon neutrality goals.
4. Government Policy and Strategic Support
The 14th Five-Year Plan (2021–2025) and its extension into 2026 emphasize breakthroughs in core technologies, including photonics and optoelectronics. Special economic zones and innovation hubs offer tax incentives, subsidies, and infrastructure for laser startups and R&D centers. Export controls on critical technologies from Western nations are further incentivizing indigenous innovation.
5. Consolidation and Internationalization
The Chinese laser market is expected to see increased consolidation, with larger players acquiring smaller firms to expand capabilities. At the same time, Chinese laser companies are expanding globally, exporting to Southeast Asia, Europe, and Latin America. By 2026, Chinese laser equipment could represent over 40% of global exports, challenging traditional leaders like Germany and the U.S.
6. Technological Advancements
Key technological trends include:
– Higher Power and Efficiency: Multi-kilowatt fiber lasers (>20 kW) becoming standard for heavy industry.
– Ultrafast Lasers: Picosecond and femtosecond lasers gaining traction in precision machining.
– AI Integration: Smart laser systems with real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and adaptive control via AI and IoT.
7. Challenges and Risks
Despite growth, challenges remain:
– Supply Chain Vulnerabilities: Access to high-end optical components (e.g., laser diodes, crystals) may still depend on foreign suppliers.
– Intellectual Property (IP) Concerns: Ongoing IP disputes with Western firms could impact international expansion.
– Overcapacity Risks: Rapid expansion may lead to price competition and margin pressure in mid-range segments.
Conclusion:
By 2026, China’s laser market will be characterized by technological maturity, domestic leadership, and diversification across high-growth sectors. H2 of the decade will likely see the consolidation of China’s position as the world’s largest laser market, both in terms of production and application. Strategic investments, policy support, and innovation will continue to drive growth, making China a pivotal player in the global laser ecosystem.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Lasers from China: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing laser technology from China can offer cost advantages, but it comes with significant risks, particularly in the areas of quality control and intellectual property (IP) protection. Being aware of these common pitfalls is essential for making informed procurement decisions and safeguarding your business interests.
Quality Inconsistencies and Substandard Components
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing lasers from Chinese suppliers is inconsistent product quality. While many Chinese manufacturers produce high-quality lasers, others may cut corners to reduce costs. This can result in lasers that fail to meet performance specifications, have shorter lifespans, or exhibit reliability problems under continuous use. Variability between production batches is common, especially with less reputable suppliers who lack stringent quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001 certification). Buyers may receive units with inferior optical components, unstable power outputs, or poor thermal management, leading to increased maintenance costs and downtime.
Lack of Transparency in Manufacturing Processes
Some suppliers may outsource parts of the production process to unverified subcontractors, making it difficult to trace component origins or ensure consistent manufacturing standards. This lack of transparency can compromise the integrity of the final product and make root-cause analysis nearly impossible when failures occur. Buyers often discover that key components—such as laser diodes or control boards—are sourced from low-tier suppliers, undermining the overall performance and safety of the laser system.
Intellectual Property Infringement and Reverse Engineering
Sourcing laser technology from China carries a significant risk of IP theft or unauthorized replication. Some suppliers may reverse-engineer your designs or those of your competitors and produce counterfeit or clone versions. Even when working under non-disclosure agreements (NDAs), enforcement can be challenging due to differences in legal systems and limited recourse in Chinese courts. There have been documented cases where suppliers used customer-provided designs to develop competing products or sell them to other buyers, eroding competitive advantage.
Weak Protection of Technical Documentation and Software
Laser systems often include proprietary software, calibration algorithms, or embedded firmware that represent valuable IP. When partnering with Chinese manufacturers, there is a risk that this software can be copied, modified, or embedded into other products without authorization. Without strong contractual safeguards and technical protections (such as encryption or secure boot mechanisms), your software and technical know-how may be vulnerable to misuse.
Inadequate Compliance and Certification Standards
Chinese-made lasers may not always comply with international safety and regulatory standards (e.g., FDA, CE, IEC). Some suppliers may provide falsified certifications or misrepresent compliance status. Using non-compliant lasers can expose your company to legal liabilities, product recalls, or market access restrictions, particularly in highly regulated industries like medical devices or aerospace.
Mitigation Strategies
To minimize these risks, consider the following steps:
– Conduct thorough due diligence on potential suppliers, including on-site audits.
– Require third-party testing and certification for quality and compliance.
– Work with legally enforceable contracts that include IP clauses, confidentiality, and liability provisions.
– Limit the release of sensitive technical information and use modular designs to protect core IP.
– Partner with established sourcing agents or legal experts familiar with Chinese manufacturing and IP law.
By proactively addressing quality and IP concerns, businesses can leverage cost-effective manufacturing in China while protecting their technological investments and brand reputation.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser China
Overview of Laser Equipment Regulations in China
China strictly regulates the import, export, and domestic use of laser equipment due to safety, health, and security concerns. Compliance with Chinese standards and licensing requirements is essential for businesses involved in the logistics of laser products. This guide outlines key considerations for legal and efficient shipment and operation of laser devices in China.
Classification of Laser Products
Laser products are classified according to the national standard GB 7247.1 (equivalent to IEC 60825-1). Classification ranges from Class 1 (safest) to Class 4 (highest risk). The classification determines regulatory requirements, including labeling, documentation, and control measures. Accurate classification is mandatory for import clearance and market access.
Import Licensing and Required Documentation
Importing laser equipment into China requires approval from the State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR) and, in some cases, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT). Key documents include:
– Certificate of Conformity to GB 7247.1
– Technical specifications and user manuals (in Chinese)
– Import license (if applicable, especially for Class 3B and Class 4 lasers)
– Bill of Lading, Commercial Invoice, Packing List
– Product registration or filing with SAMR
High-powered lasers may also require dual-use and export control approvals.
Customs Clearance Procedures
Customs authorities at Chinese ports inspect laser shipments for compliance with safety and labeling standards. Delays may occur if documentation is incomplete or if the product lacks proper Chinese labeling. Engage a licensed customs broker familiar with high-tech and regulated goods to facilitate clearance. Pre-shipment verification is recommended.
Labeling and Language Requirements
All laser products must bear permanent labels in Chinese, indicating:
– Laser class (per GB 7247.1)
– Wavelength and output power
– Manufacturer name and address
– Safety warnings and precautions
User manuals and technical documentation must also be provided in Mandarin Chinese.
Radiation Safety and Environmental Compliance
Laser equipment may require registration with local environmental protection bureaus if it emits ionizing or non-ionizing radiation. Facilities using Class 3B and Class 4 lasers must implement safety measures, including controlled access, interlocks, and operator training. Regular safety audits may be required.
Export Controls and Dual-Use Considerations
Certain high-powered or military-grade lasers are subject to China’s Export Control Law. Exporters must determine if the laser falls under the Controlled Items List. Licenses are required for dual-use items, particularly those with potential military applications. Non-compliance can result in penalties, shipment seizure, or legal action.
After-Sales Service and Maintenance Compliance
Service and repair of laser equipment in China must be conducted by certified technicians. Spare parts shipments may also require documentation and classification. Maintain records of all servicing activities to demonstrate ongoing compliance.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Failure to comply with Chinese laser regulations can result in:
– Customs rejection or seizure of goods
– Fines and legal liability
– Suspension of import/export licenses
– Blacklisting from future trade activities
Recommended Best Practices
- Conduct a regulatory assessment before shipping
- Partner with local compliance experts or legal counsel
- Maintain up-to-date technical documentation in Chinese
- Train staff on Chinese safety and labeling requirements
- Monitor regulatory updates from SAMR, MIIT, and GACC
Adhering to this guide ensures smooth logistics operations and minimizes risks when dealing with laser products in China.
In conclusion, sourcing lasers from China offers significant advantages, including cost-effectiveness, a wide range of product options, and access to advanced manufacturing capabilities. Chinese suppliers provide diverse laser solutions—such as fiber, CO2, and diode lasers—suitable for various industrial, medical, and commercial applications. However, successful sourcing requires due diligence in selecting reliable suppliers, verifying product quality, and ensuring compliance with international standards and certifications. Working with trusted manufacturers, conducting factory audits, and using secure payment methods can mitigate potential risks such as intellectual property concerns or inconsistent quality. When managed strategically, sourcing lasers from China can enhance competitiveness by reducing production costs and accelerating time to market, making it a viable option for businesses worldwide.