The global market for industrial surface preparation solutions, including laser cabinet stripping technologies, is experiencing robust growth driven by increasing demand for precision, sustainability, and efficiency in manufacturing and maintenance operations. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global laser cleaning equipment market was valued at USD 392.5 million in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 1.16 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 19.8% during the forecast period. This expansion is fueled by stringent environmental regulations, the shift away from chemical-based and abrasive cleaning methods, and the rising adoption of laser cleaning in automotive, aerospace, and heavy equipment sectors. As companies prioritize non-contact, eco-friendly stripping processes with minimal downtime, the need for high-performance laser cabinet stripping systems has surged. In this competitive landscape, a select group of manufacturers are leading innovation—delivering reliable, scalable, and automated solutions aligned with Industry 4.0 standards. Based on technical capabilities, market presence, and customer adoption trends, here are the top 10 laser cabinet stripping manufacturers shaping the future of industrial surface treatment.
Top 10 Laser Cabinet Stripping Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
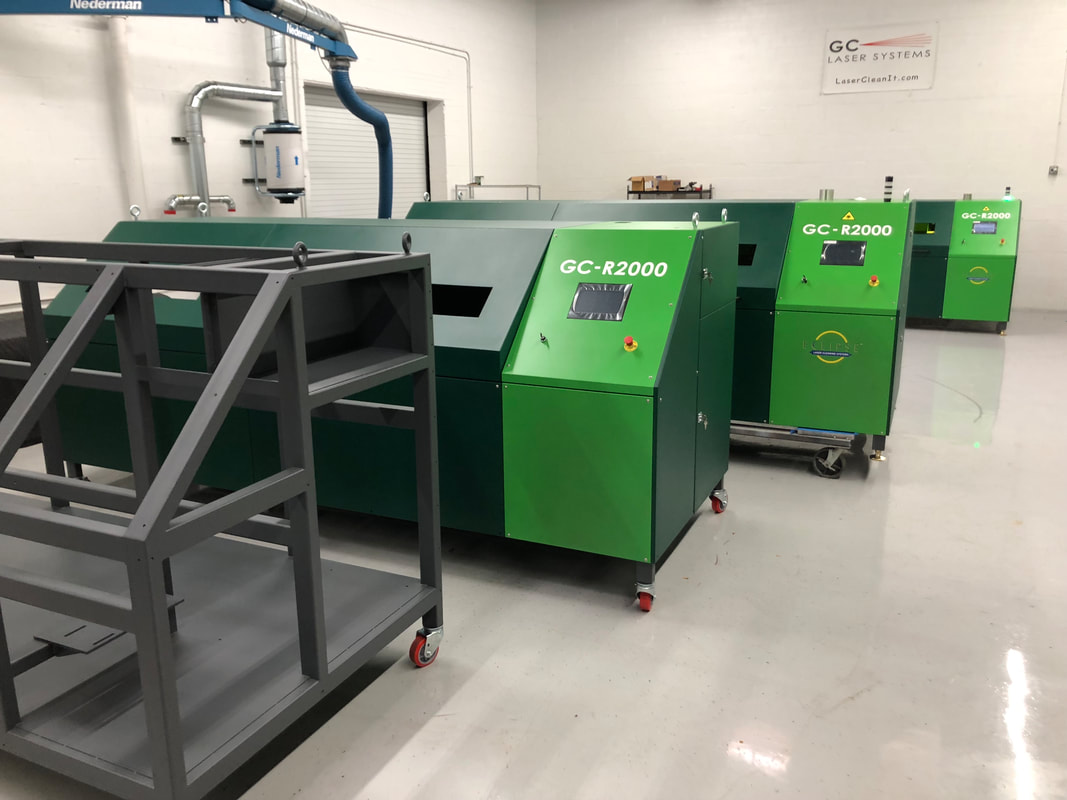
#1 G.C. Laser Systems
Website: gclasers.com
Key Highlights: G.C. Laser Systems Inc. manufactures unique laser cleaning technology that offers unmatched cleaning precision and surface prep. Our laser systems are ……
#2 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: we engineer and manufacture the most advanced—and most powerful—pulsed industrial laser cleaning systems on the market, built for both manual and automated ……
#3 Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: Explore PULSAR Laser P CL laser cleaning machines for industrial rust removal and paint stripping. Compare SHARK P CL, PANDA P CL and FOX P CL….
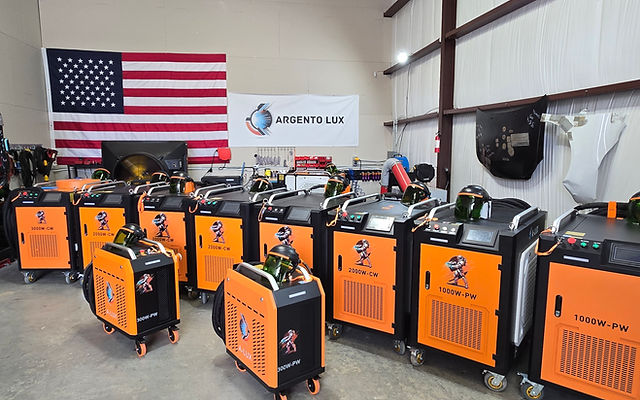
#4 Argento Lux
Website: argentolux.com
Key Highlights: It’s precise, fast, and perfect for stripping finishes without damaging the wood. We’ve reduced labor by 70%, and now 80% of our projects run through this laser ……
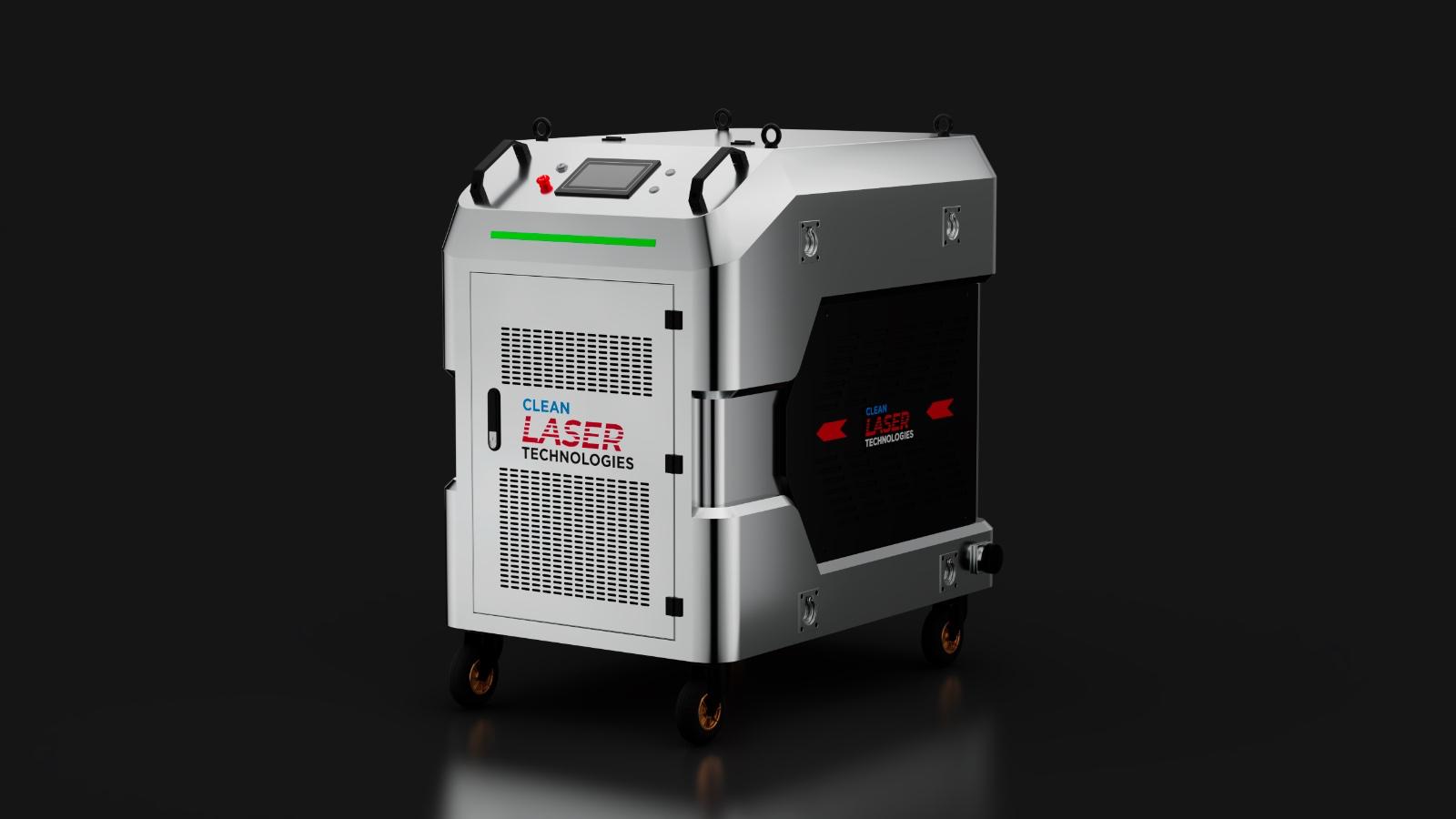
#5 Clean Laser Technologies
Website: cleanlasertechnologies.com
Key Highlights: Clean Laser Technologies is a Mississippi-based company specializing in laser cleaning technology, providing state of the art laser cleaning machines, training ……
#6 Laser cleaning
Website: narran.cz
Key Highlights: We can design and integrate a laser cleaning system into production, build a robotic workstation or supply a mobile laser for a wide range of applications….
#7 Laser Cleaning and Laser Ablation Systems
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Remove rust and surface contaminants with our laser cleaning & laser ablation systems. Experience superior cleaning tech, automation, and eco-friendly ……
#8 Laser Paint Removal from Metals with Laser Cleaning
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: High-power Laser Cleaning Systems Laserax manufactures high-power fiber laser systems specifically designed to remove coatings from metal surfaces….
#9 Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: lmelaser.com
Key Highlights: LME Laser is a laser cleaning machine manufacture with 17 years experience. The Products including continuous laser cleaner and pulse laser cleaner….
#10 Fonon
Website: fonon.us
Key Highlights: Fonon specializes in creating advanced laser technologies and laser solutions for the military & defense industry. Laser cleaning, marking and defense ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Cabinet Stripping

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Laser Cabinet Stripping
The laser cabinet stripping market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by environmental regulations, technological advancements, and shifting industrial priorities. This analysis identifies key H2 (Hydrogen) market trends shaping the sector, emphasizing sustainability, efficiency, and integration.
1. Accelerated Shift Toward Green Manufacturing (H2 Trend: Decarbonization & Emission Reduction)
- Regulatory Pressure: Stricter global VOC (Volatile Organic Compound) and hazardous waste regulations (e.g., EU Green Deal, US EPA updates) will make traditional chemical stripping increasingly costly and complex. Laser stripping, producing minimal waste (primarily vaporized coating particulates) and no liquid effluent, aligns perfectly with decarbonization goals.
- Corporate Sustainability Targets: Manufacturers, especially in automotive, aerospace, and high-end engineering, will prioritize technologies reducing their environmental footprint. Laser stripping supports Scope 1 & 2 emission reduction targets by eliminating solvent use and associated disposal emissions.
- H2 Synergy: As green hydrogen production and use scales up in industry, facilities adopting H2 will demand cleaner, complementary processes. Laser stripping fits seamlessly into hydrogen-powered or hydrogen-integrated green factories.
2. Cost Competitiveness and ROI Focus (H2 Trend: Economic Efficiency & Industrialization)
- Reduced Operational Costs: While initial investment is higher, the elimination of solvent procurement, hazardous waste disposal fees (often 5-10x the cost of the solvent itself), PPE, and ventilation maintenance will drive compelling Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) advantages by 2026.
- Improved Throughput & Labor Efficiency: Advancements in laser power, beam delivery (robotics, scanners), and process automation will significantly increase stripping speed and consistency. This reduces labor dependency and boosts overall equipment effectiveness (OEE), improving ROI.
- Predictable Costs: Laser operating costs (electricity, maintenance) are more stable and predictable than volatile solvent and disposal markets, appealing to financially focused H2-era manufacturing.
3. Advancements in Laser Technology & Process Intelligence (H2 Trend: Digitalization & Smart Manufacturing)
- Higher Power & Efficiency: Continued development of fiber lasers (especially pulsed) will offer higher average powers with better wall-plug efficiency, enabling faster stripping of thicker or more resilient coatings (e.g., powder coats, epoxies).
- Intelligent Process Control: Integration of real-time monitoring (spectral analysis, acoustic sensors, machine vision) will allow for closed-loop control. Systems will automatically adjust parameters (power, speed, focus) based on coating type, thickness, and substrate condition, ensuring optimal results and substrate safety – crucial for high-value cabinets.
- AI & Machine Learning: Predictive maintenance for laser sources and robotic arms, optimized path planning for complex cabinet geometries, and adaptive learning from previous stripping jobs will become standard, maximizing uptime and quality.
4. Focus on Precision, Selectivity, and Substrate Preservation (H2 Trend: Quality & Material Integrity)
- Selective Stripping: Demand will grow for lasers that can selectively remove paint or coatings from specific areas (e.g., around welds, on intricate trim) without damaging underlying materials (aluminum, stainless steel, composites). This is vital for repair, refurbishment, and high-precision applications.
- Minimized Substrate Impact: Refined pulse control (ultra-short pulses) and beam shaping will further reduce heat-affected zones (HAZ) and prevent warping, especially critical for thin-gauge sheet metal common in cabinets.
- Consistent Surface Preparation: Laser stripping provides a uniformly clean, contaminant-free surface ideal for subsequent processes like welding, bonding, or repainting, enhancing the quality and longevity of refurbished cabinets.
5. Expansion Beyond Traditional Markets & Integration (H2 Trend: Diversification & System Integration)
- Refurbishment & Circular Economy: As sustainability drives circular economy models, laser stripping will be essential for efficiently refurbishing industrial cabinets, enclosures, and machinery frames, extending product lifecycles.
- Integration into Production Lines: Laser stripping cells will increasingly be integrated as automated stations within larger manufacturing or remanufacturing lines (e.g., pre-weld cleaning, post-failure rework), moving beyond standalone “cleaning booths.”
- New Material Applications: Adoption will grow for stripping coatings from composite materials and advanced alloys used in next-gen cabinets for electronics, renewable energy, and transportation.
Conclusion for 2026:
By 2026, laser cabinet stripping will transition from a niche, environmentally motivated technology to a mainstream, economically driven solution. The H2 trends of decarbonization, economic efficiency, digitalization, quality focus, and integration will converge to make it the preferred method for environmentally conscious, cost-effective, and high-precision industrial cleaning. Success will depend on continued innovation in laser power, intelligence, automation, and the development of robust, user-friendly systems that deliver undeniable TCO benefits within integrated smart factories.
Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Laser Cabinet Stripping (Quality, IP)
Sourcing laser cabinet stripping services involves critical considerations around both quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to significant operational, financial, and legal risks. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Quality Control and Inconsistent Results
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing laser stripping is inconsistent quality due to inadequate process controls. Some suppliers may lack calibrated equipment, standardized operating procedures, or trained technicians, leading to problems such as incomplete stripping, damage to underlying materials, or variable edge quality. This inconsistency can compromise the performance and reliability of final products, especially in sensitive applications like electronics or medical devices.
Lack of Process Validation and Documentation
Many suppliers fail to provide comprehensive process validation data, such as first-article inspections, process capability (Cp/Cpk) studies, or material compatibility reports. Without this documentation, buyers cannot verify repeatability or compliance with industry standards (e.g., IPC, MIL-STD). This absence of traceability increases the risk of undetected defects and complicates root cause analysis in case of field failures.
Inadequate Handling of Intellectual Property
Laser stripping often involves proprietary designs, specialized tooling, or custom processing parameters developed by the buyer. A major pitfall arises when contracts do not clearly define IP ownership, confidentiality, or usage rights. Unscrupulous suppliers may reuse tooling, replicate processes, or share sensitive data with competitors, especially in offshore or low-cost regions with weaker IP enforcement.
Insufficient Data Security and Access Controls
Digital files required for laser processing—such as CAD models or laser paths—can contain sensitive design information. Suppliers without robust cybersecurity measures (e.g., encrypted data transfer, restricted network access, non-disclosure agreements) expose customers to the risk of data breaches or unauthorized replication. This is particularly concerning when working with high-value or innovative products.
Overlooking Regulatory and Compliance Requirements
Certain industries (e.g., aerospace, defense, medical) have strict requirements for material processing and documentation. Sourcing from suppliers who are unaware of or non-compliant with relevant standards (such as ITAR, REACH, or ISO certifications) can result in rejected batches, regulatory penalties, or supply chain disruptions.
Failure to Define Acceptance Criteria Upfront
Ambiguity in quality specifications—such as acceptable tolerances for strip width, edge charring, or substrate exposure—often leads to disputes. Without clearly defined and mutually agreed-upon acceptance criteria documented in the purchase order or quality agreement, buyers may receive parts that technically meet a vague specification but are functionally unsuitable.
Choosing Vendors Based Solely on Cost
Prioritizing the lowest price often leads to cutting corners in quality, training, or IP safeguards. Low-cost suppliers might use outdated equipment, skip validation steps, or lack proper audit trails. The short-term savings can result in higher total cost of ownership due to rework, scrap, or product recalls.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls through rigorous supplier qualification, clear contractual terms, and ongoing quality monitoring, companies can ensure reliable, secure, and high-quality laser cabinet stripping services.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Cabinet Stripping
This guide outlines the logistical considerations and compliance requirements for safely and effectively performing laser cabinet stripping operations. Adhering to these standards ensures operational efficiency, regulatory compliance, and personnel safety.
Scope and Application
This guide applies to all personnel involved in the logistics, operation, and oversight of laser-based paint and coating removal from metal cabinets. It covers equipment handling, material movement, waste management, and regulatory adherence. The procedures detailed herein are designed for industrial or commercial environments utilizing Class 4 lasers for surface preparation.
Equipment and Material Handling
All laser stripping systems must be transported, stored, and deployed in accordance with manufacturer specifications. Prior to use, verify that the laser unit, power supply, extraction system, and safety enclosures are intact and undamaged. Use appropriate lifting equipment when moving laser cabinets or components to prevent injury. Store consumables (e.g., filters, protective covers) in a clean, dry environment, away from direct sunlight and flammable materials.
Site Preparation and Access
Ensure the work area is designated, clearly marked, and restricted to authorized personnel only. The site must provide adequate floor space for the laser system, ventilation/extraction units, and safe operator movement. Electrical supply must meet required specifications (voltage, grounding) and include emergency disconnects. Verify that access routes are unobstructed for emergency egress and equipment servicing.
Personnel Training and Authorization
Only personnel who have completed certified laser safety training (e.g., ANSI Z136.1 or equivalent) and site-specific operational training may operate or supervise laser stripping activities. Training records must be maintained and updated annually. All operators must wear appropriate laser防护 eyewear rated for the specific wavelength and power output of the laser in use.
Operational Controls and Safety Protocols
Implement engineering controls such as interlocks, beam shutters, and fume extraction systems to minimize exposure risks. Conduct a pre-operation safety check, including verification of enclosure integrity and emergency stop functionality. Never bypass safety systems. Maintain a log of all operations, including start/stop times, materials processed, and any anomalies observed.
Waste Management and Environmental Compliance
Collect all removed coating residues (paint chips, ablated material) as hazardous waste if containing regulated substances (e.g., lead, chromium). Segregate waste by composition and store in labeled, leak-proof containers. Follow local, state, and federal regulations (e.g., EPA, OSHA, RCRA) for disposal. Maintain waste manifests and disposal records for a minimum of three years.
Regulatory and Documentation Requirements
Ensure compliance with applicable regulations, including:
– OSHA 29 CFR 1910 (Occupational Safety and Health Standards)
– ANSI Z136.1 (Safe Use of Lasers)
– EPA NESHAP (National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants), if applicable
– Local fire and building codes
Maintain up-to-date documentation, including laser safety program, risk assessments, training records, maintenance logs, and compliance certifications.
Emergency Procedures
Post clear emergency procedures near the work area. In the event of fire, laser exposure, or system malfunction:
1. Activate the emergency stop
2. Evacuate the area
3. Notify safety personnel
4. Follow facility emergency response plan
First aid kits and eyewash stations must be accessible within 10 seconds of the work zone.
Inspection and Maintenance
Schedule routine inspections and preventive maintenance per the manufacturer’s guidelines. Document all maintenance activities, including replacement of optical components, filters, and safety sensors. Remove equipment from service immediately if defects are identified that could compromise safety or performance.
Transportation and Decommissioning
When transporting laser equipment off-site, secure all components to prevent movement. Cover optical surfaces and disconnect power sources. For decommissioning, follow environmental regulations for disposal of laser tubes, batteries, and electronic components. Recycle where possible through certified e-waste handlers.
Conclusion for Sourcing Laser Cabinet Stripping:
After a thorough evaluation of potential suppliers, technologies, and cost considerations, sourcing laser cabinet stripping presents a highly efficient and sustainable solution for paint and coating removal. Laser ablation technology offers precision, minimal substrate damage, reduced environmental impact, and compliance with health and safety regulations compared to traditional methods like sandblasting or chemical stripping.
The key factors in successful sourcing include selecting a vendor with proven experience in laser stripping applications, ensuring equipment compatibility with cabinet materials and coating types, and considering total cost of ownership—including training, maintenance, and throughput requirements. Additionally, integrating this technology supports long-term operational efficiency and aligns with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) goals by eliminating hazardous waste and reducing energy consumption.
Ultimately, investing in a reliable laser stripping solution enhances productivity, improves finish quality, and positions the organization at the forefront of advanced manufacturing practices. Strategic sourcing—focused on technology suitability, supplier expertise, and lifecycle benefits—will ensure a successful implementation and a strong return on investment.