The global laser brazing market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for precision joining technologies in automotive, aerospace, and industrial manufacturing. According to Grand View Research, the global laser welding and brazing market size was valued at USD 3.2 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.8% from 2023 to 2030, fueled by advancements in automation and lightweight material integration. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence forecasts a CAGR of over 7% during the forecast period 2023–2028, citing rising adoption of laser-based processes in electric vehicle production and high-strength steel applications. As manufacturers seek faster, cleaner, and more energy-efficient joining solutions, laser brazing has emerged as a preferred alternative to traditional methods. This growing momentum has led to heightened innovation and competition among key players worldwide. Below is a data-driven overview of the top 8 laser brazing manufacturers leading technological advancement and market expansion in this evolving landscape.
Top 8 Laser Brazing Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laser Brazing
Website: cmw.fraunhofer.org
Key Highlights: High quality brazing is also possible using laser technology. Laser Brazing uses a lower melting point filler wire material which is melted by the laser ……
#2 Equipment & Systems
Website: amadaweldtech.com
Key Highlights: Manufacturer of equipment and systems for welding, cutting, marking, micromachining, sealing, and bonding. Resistance welding. Laser….
#3 Laser brazing
Website: industrial-laser-systems.com
Key Highlights: Laser brazing is a process of assembling identical or dissimilar materials by means of a supply of material….
#4 Laser Brazing Services
Website: titanovalaser.com
Key Highlights: Titanova, Inc. offers unique services of brass welding, laser brazing and laser soldering. The diode laser has a unique wavelength and beam shape….
#5 Laser Brazing
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Our laser brazing experts are ready to evaluate your application and offer a solution optimized for your requirements….
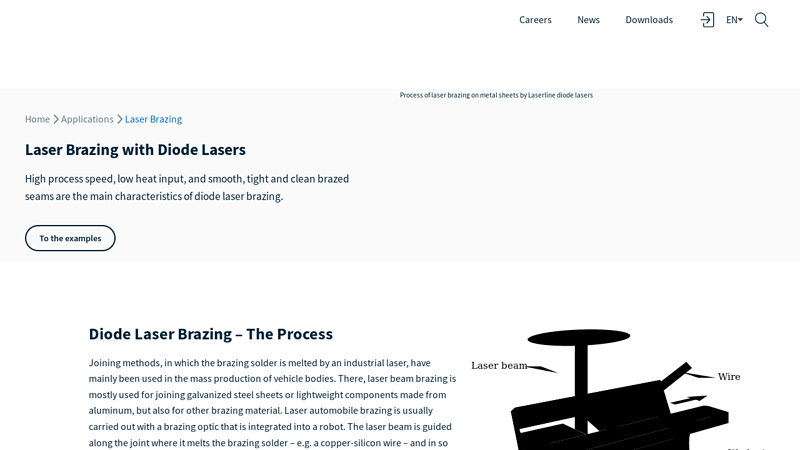
#6 Laser Brazing for the Automobile Industry
Website: laserline.com
Key Highlights: Laser beam brazing is mostly used for joining galvanized steel sheets or lightweight components made from aluminum, but also for other brazing material….
#7 MIG, TIG, Robotic, & Laser Welding Solutions
Website: binzel-abicor.com
Key Highlights: Explore ABICOR BINZEL USA for advanced welding solutions. We offer MIG, TIG robotic, and laser welding technologies, along with MIG guns and robotic torches ……
#8 Laser Brazing
Website: scansonic.de
Key Highlights: The laser brazing process uses a filler metal for joining without actually melting the base material. This process allows you to achieve high precision and ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Brazing

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Laser Brazing
The global laser brazing market in 2026 is poised for significant growth and transformation, driven by technological advancements, evolving industry demands, and a strong push towards automation and sustainability. Key trends shaping the market include:
1. Accelerated Adoption in Electric Vehicle (EV) Manufacturing: The rapid expansion of the EV market is a primary driver. Laser brazing is becoming the preferred method for joining dissimilar materials (e.g., aluminum to steel, copper to aluminum) used extensively in EV battery enclosures, power electronics, and lightweight body structures. Its precision, minimal heat-affected zone (HAZ), and ability to create strong, hermetic seals without damaging sensitive components make it ideal for high-reliability EV applications. Demand for automated, high-throughput brazing solutions in EV production lines will surge.
2. Dominance of High-Power Fiber Lasers and Process Optimization: Fiber lasers will solidify their position as the dominant light source due to their superior beam quality, efficiency, reliability, and lower operating costs compared to CO2 lasers. Expect advancements in multi-kilowatt fiber lasers enabling faster processing speeds and deeper penetration for thicker materials. Concurrently, significant focus will be on process optimization through closed-loop monitoring systems (using camera-based seam tracking, temperature sensing, and plasma monitoring) and AI-driven predictive control to ensure consistent, defect-free joints, especially in high-volume production.
3. Integration with Advanced Robotics and Automation: Laser brazing systems will be increasingly integrated into fully automated robotic cells, particularly in automotive assembly lines. Collaborative robots (cobots) may find niche applications in smaller-scale or flexible production environments. Seamless integration with factory IoT platforms (Industry 4.0) will enable real-time data collection, remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and improved overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
4. Expansion Beyond Automotive into New Sectors: While automotive (especially EVs) remains the largest segment, laser brazing will see growing adoption in:
* Consumer Electronics: For hermetic sealing of high-end devices and joining heat-sensitive components.
* Aerospace & Defense: For lightweight, high-integrity joints in airframes and engine components.
* Medical Devices: For precise, clean joining of small, complex instruments and implants.
* HVAC & Appliances: For reliable, leak-free joints in heat exchangers and critical components.
5. Focus on Material Innovation and Hybrid Processes: Research and development will focus on optimizing laser brazing for new advanced materials (e.g., high-strength steels, magnesium alloys, composites) and dissimilar metal combinations. Hybrid processes, combining laser brazing with techniques like induction pre-heating or arc welding, may gain traction to improve wetting, reduce stress, and handle challenging joint configurations.
6. Emphasis on Sustainability and Cost Reduction: Manufacturers will prioritize solutions that minimize energy consumption, reduce waste (e.g., precise filler wire deposition), and lower consumable costs (e.g., longer-lasting optics, efficient shielding gas usage). The inherent advantages of laser brazing – lower heat input, reduced distortion (less post-processing), and higher material utilization – align well with sustainability goals.
7. Geopolitical and Supply Chain Dynamics: Regional manufacturing shifts (e.g., nearshoring, friendshoring) and supply chain resilience will influence investment in laser brazing equipment. Asia-Pacific (especially China, Japan, South Korea) will remain a major growth hub due to strong automotive and electronics manufacturing, while North America and Europe will see growth driven by EV production and industrial automation.
In conclusion, the 2026 laser brazing market will be characterized by robust growth, primarily fueled by the EV revolution and advancements in laser source technology and automation. Success will depend on providing reliable, integrated, and intelligent solutions that meet the demanding requirements of high-volume, high-precision manufacturing across diverse and expanding industrial sectors, with a strong undercurrent of sustainability.

H2: Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Laser Brazing Services – Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing laser brazing services offers numerous advantages in high-precision manufacturing, particularly in the automotive, aerospace, and energy sectors. However, companies often encounter significant challenges related to quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) protection. Understanding these pitfalls is critical to ensuring reliable production outcomes and safeguarding proprietary technologies.
1. Quality-Related Pitfalls
-
Inconsistent Process Parameters:
Laser brazing is highly sensitive to variations in laser power, travel speed, focus position, and filler wire feed rate. Suppliers may lack standardized operating procedures or adequate process monitoring, leading to inconsistent joint quality, porosity, or incomplete fusion. -
Insufficient Operator Expertise:
The success of laser brazing heavily depends on operator skill and experience. Inadequately trained personnel at the supplier’s facility can result in defects such as undercutting, excessive spatter, or poor bead geometry. -
Lack of In-Process Monitoring and NDT Capabilities:
Many suppliers do not employ real-time monitoring systems (e.g., thermal imaging, seam tracking) or robust non-destructive testing (NDT) protocols. This increases the risk of undetected defects reaching final assembly. -
Material and Surface Preparation Variability:
Contamination, inconsistent joint fit-up, or improper surface cleaning can severely impact brazing quality. Suppliers may not enforce strict pre-braze preparation standards, especially when handling high-reflectivity materials like aluminum. -
Poor Traceability and Documentation:
Without comprehensive process documentation (e.g., laser logs, parameter records, inspection reports), it becomes difficult to trace quality issues or validate compliance with industry standards (e.g., ISO 3834, AWS C12.1).
2. Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
-
Exposure of Proprietary Designs and Processes:
Sharing detailed CAD models, joint designs, or process specifications with external suppliers increases the risk of IP leakage, especially if non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) are weak or unenforced. -
Lack of IP Clauses in Contracts:
Many sourcing agreements fail to clearly define IP ownership of custom tooling, process developments, or joint innovations, potentially leading to disputes or loss of competitive advantage. -
Reverse Engineering Vulnerabilities:
Laser brazing often involves unique joint geometries or material combinations. If not properly protected, competitors could reverse-engineer end products or processes developed in collaboration with the supplier. -
Inadequate Cybersecurity Measures:
Digital transfer of sensitive data (e.g., laser programs, inspection data) to suppliers may expose companies to cyber threats, particularly if the supplier lacks robust data protection protocols.
Mitigation Strategies
- Conduct thorough supplier audits focusing on quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001, IATF 16949) and technical capabilities.
- Require detailed process validation and first-article inspection reports before full-scale production.
- Implement strong contractual safeguards, including comprehensive NDAs and clear IP ownership terms.
- Limit data sharing to the minimum necessary and use secure data exchange platforms.
- Establish joint development agreements with defined IP rights when co-innovating with suppliers.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP-related pitfalls, organizations can leverage laser brazing effectively while minimizing operational and legal risks.
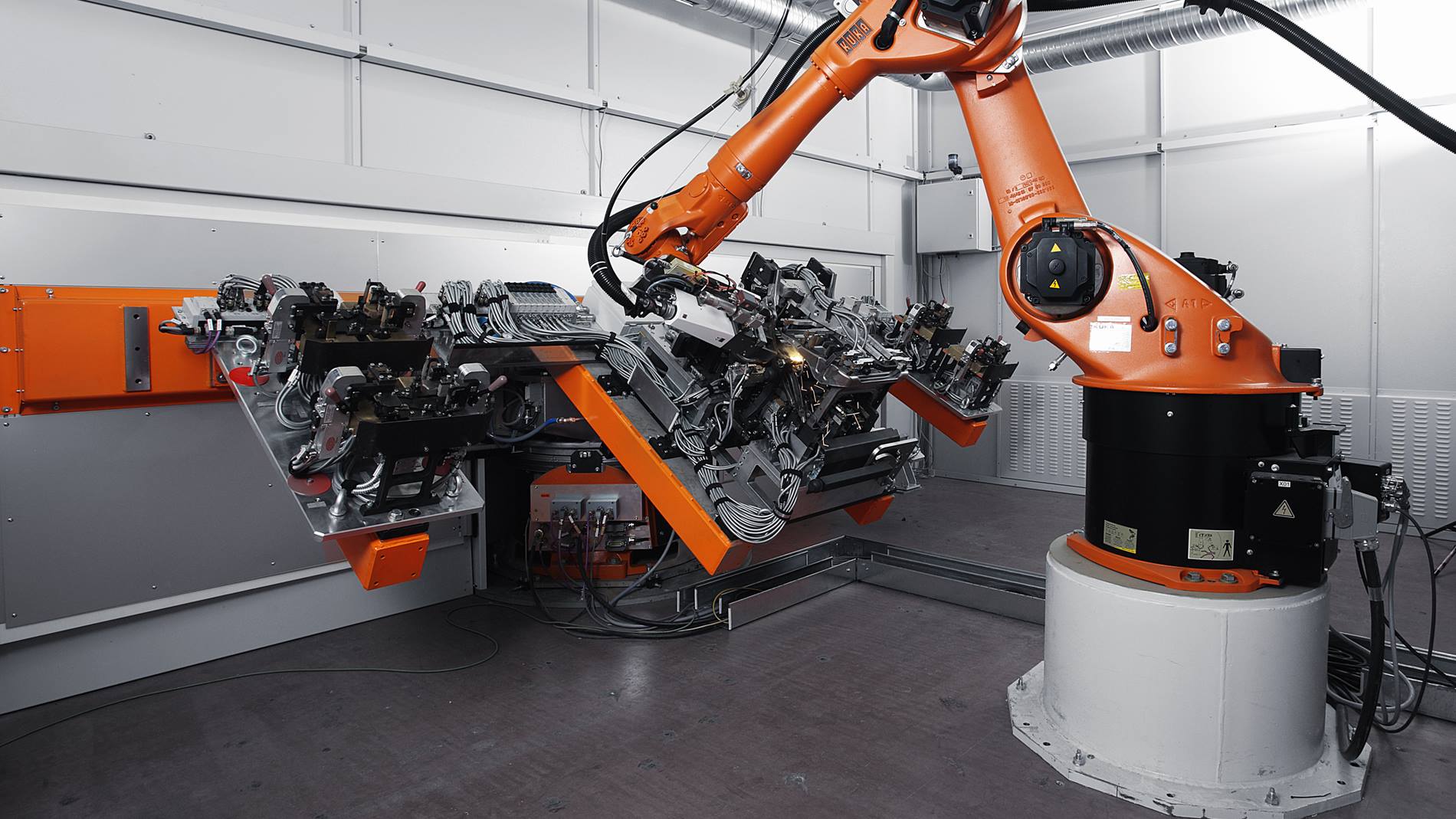
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Brazing
Introduction
Laser brazing is an advanced joining technique widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and heavy manufacturing due to its precision, speed, and high-quality joint formation. This guide outlines the logistics and compliance requirements for implementing and operating laser brazing processes safely, efficiently, and in accordance with international standards and regulations.
H2: Equipment & Material Logistics
Laser Brazing System Setup
- Laser Source: Ensure delivery, installation, and alignment of the appropriate laser source (e.g., fiber or disk laser) based on material thickness and joint design.
- Positioning Systems: Robotic arms or CNC stages must be calibrated and synchronized with the laser control system.
- Filler Material Supply: Maintain a consistent supply of brazing filler wire (typically CuSi3, CuAl8, or Ag-based alloys) with proper storage conditions to prevent oxidation or contamination.
- Cooling Systems: Install and maintain chiller units to manage laser head and system thermal loads.
- Fume Extraction: Integrate local exhaust ventilation (LEV) systems to capture metal fumes and particulates generated during brazing.
Material Handling & Storage
- Store filler wires in dry, temperature-controlled environments to prevent moisture absorption and oxidation.
- Label all materials with batch numbers, expiry dates, and compatibility information.
- Use non-magnetic containers and handling tools for ferrous-sensitive applications.
- Implement a first-in, first-out (FIFO) inventory system to minimize material degradation.
H2: Safety & Regulatory Compliance
Laser Safety (IEC 60825-1)
- Classify the laser system according to IEC 60825-1 standards (typically Class 4 for industrial lasers).
- Install interlocked enclosures, emergency stop buttons, and laser safety curtains.
- Use appropriate laser protective eyewear (wavelength-specific optical density).
- Post visible warning signs at entry points to laser operation zones.
- Conduct regular safety audits and risk assessments.
Occupational Health & Safety (OSHA / EU-OSHA)
- Train personnel in laser operation, hazard awareness, and emergency response.
- Provide personal protective equipment (PPE), including flame-resistant clothing, gloves, and face shields.
- Monitor workplace air quality for hazardous fumes (e.g., zinc oxide when brazing galvanized steel).
- Implement lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures for maintenance activities.
Environmental Compliance (EPA, REACH, RoHS)
- Comply with REACH and RoHS regulations regarding restricted substances in filler materials.
- Properly dispose of used filters, contaminated consumables, and waste materials through certified hazardous waste channels.
- Minimize energy consumption and optimize process efficiency to support sustainability goals.
H2: Process Validation & Quality Control
Welding Procedure Specification (WPS)
- Develop and document WPS in accordance with ISO 15609-4 or AWS C5.8/C5.8M.
- Include parameters such as laser power, travel speed, wire feed rate, beam focus, and shielding gas flow.
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT)
- Perform visual inspection, dye penetrant testing (PT), or radiographic testing (RT) as required.
- Use automated inline monitoring systems (e.g., seam tracking, thermal imaging) for real-time quality assurance.
Traceability & Documentation
- Record all process parameters, maintenance logs, and inspection results.
- Implement digital data management systems compliant with ISO 9001 and IATF 16949 (for automotive).
- Ensure full traceability from raw material to finished product.
H2: Transportation & International Shipping
Equipment Transport
- Secure laser systems and optical components using shock-absorbing packaging and climate control.
- Label containers with fragile, laser radiation, and orientation indicators.
- Comply with IATA/IMDG regulations when shipping internationally.
Filler Material Shipping
- Classify filler wires under proper UN numbers if containing regulated metals.
- Use moisture-resistant packaging and include safety data sheets (SDS) with shipments.
- Adhere to customs requirements for cross-border movement of industrial materials.
H2: Training & Personnel Certification
Operator Qualification
- Certify operators per ISO 14731 (Welding Coordination) or national equivalents.
- Include hands-on training in laser safety, process troubleshooting, and equipment maintenance.
- Conduct annual refresher courses and competency assessments.
Maintenance Technicians
- Train technicians in laser system diagnostics, optical alignment, and safety interlock verification.
- Ensure certifications align with manufacturer recommendations and national safety standards.
H2: Regulatory Standards & Audits
Key Compliance Standards
- ISO 13849: Safety of machinery – control systems
- ANSI Z136.1: Safe use of lasers
- EN 12198: Emission of dangerous substances from machinery
- ASME B31.3: Process piping (if applicable)
Internal & External Audits
- Schedule routine internal audits of safety, process control, and documentation practices.
- Prepare for third-party audits by certification bodies (e.g., TÜV, DNV, SGS).
- Maintain up-to-date compliance records and certificates.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and strict compliance are essential for the safe and efficient use of laser brazing technology. By adhering to this guide, organizations can ensure operational excellence, regulatory compliance, and high-quality manufacturing outcomes. Regular review and continuous improvement of procedures will further enhance performance and safety in laser brazing operations.
Conclusion for Sourcing Laser Brazing
In conclusion, sourcing laser brazing as a joining solution offers significant advantages in terms of precision, repeatability, and overall weld quality, particularly for high-value and performance-critical applications in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics. The process enables minimal heat input, reduced distortion, and excellent control over the brazed joint, contributing to enhanced product durability and aesthetics.
When evaluating potential suppliers or partners for laser brazing services, it is essential to assess not only their technical capabilities—including laser equipment, automation, and process expertise—but also their quality certifications, experience in relevant sectors, and ability to support scalable production. A reliable supplier should demonstrate consistent process control, robust quality assurance protocols, and a commitment to continuous improvement.
Ultimately, strategic sourcing of laser brazing services allows manufacturers to leverage advanced joining technology without substantial capital investment, improving product performance and competitiveness. By selecting the right partner, companies can ensure reliable, high-quality results that meet stringent industry standards while optimizing both operational efficiency and long-term costs.