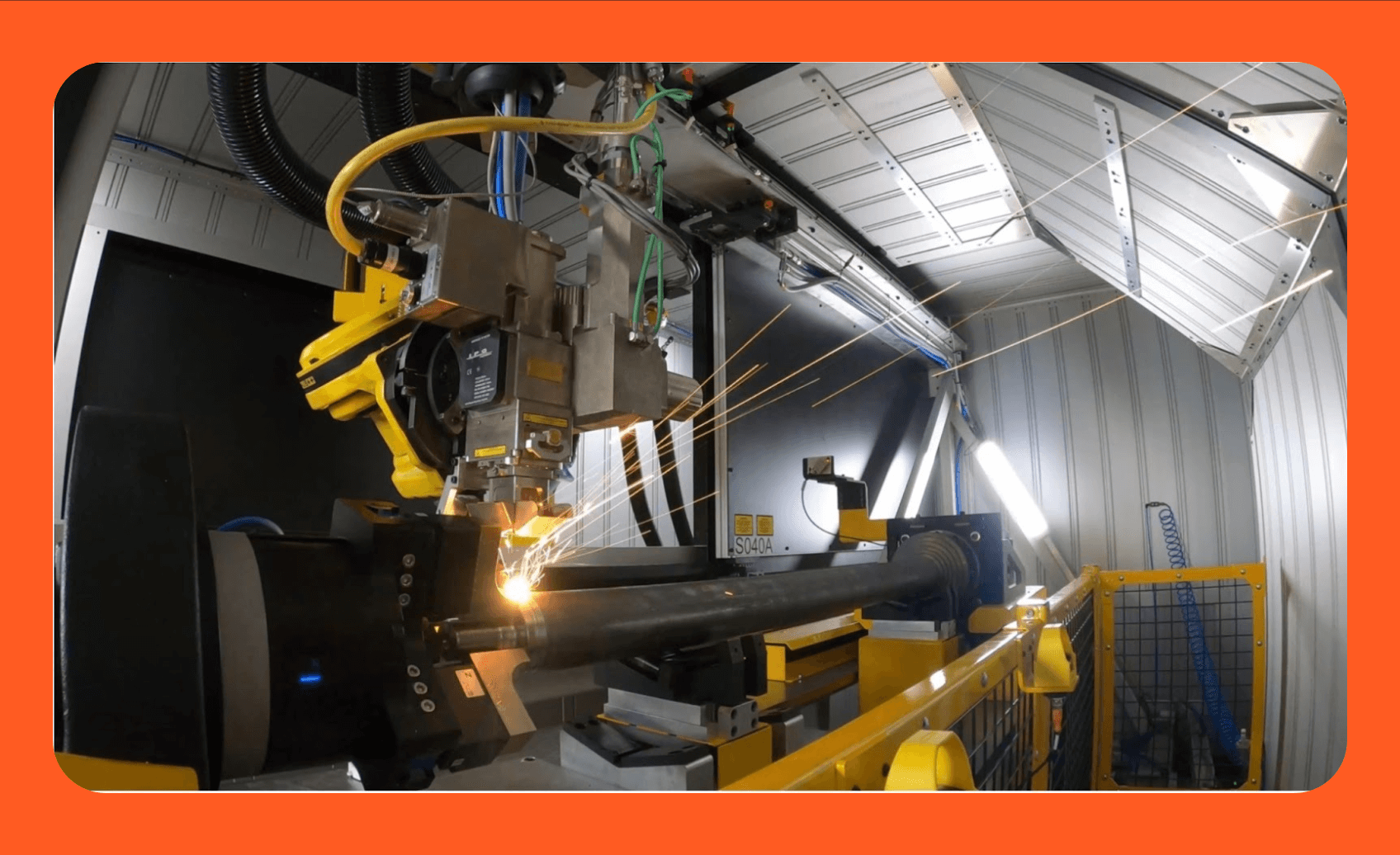
The global laser beam welding machine market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for precision joining solutions in high-tech industries such as automotive, aerospace, and medical devices. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 1.85 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% over the forecast period 2024–2029. This expansion is fueled by advancements in fiber laser technology, rising automation in manufacturing, and the need for high-speed, low-distortion welding processes. As industries shift toward lightweight materials and tighter tolerances, laser beam welding (LBW) has emerged as a critical technology, prompting manufacturers to invest heavily in R&D and scalable solutions. With Asia-Pacific emerging as a key growth region due to expanding industrial infrastructure and automotive production, the competitive landscape is rapidly evolving. Based on market presence, technological innovation, global reach, and customer reviews, the following ten companies represent the leading manufacturers shaping the future of laser beam welding.
Top 10 Laser Beam Welding Machine Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Focus on laser
Website: hanslaser.net
Key Highlights: With good beam quality, fiber transmission and high electro-optical conversion efficiency, It is mainly used for rapid welding thin materials. More · MOLD 301….
#2 Laserax
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Laserax works with the world’s leading manufacturers to implement laser cleaning, welding, texturing, and marking solutions….
#3 Equipment & Systems
Website: amadaweldtech.com
Key Highlights: Manufacturer of equipment and systems for welding, cutting, marking, micromachining, sealing, and bonding. Resistance welding. Laser….
#4 Denaliweld
Website: denaliweld.com
Key Highlights: We Specialize in Laser Welding & Cleaning. DenaliWeld INC, is a proud employee-owned fiber laser welding machine manufacturer based in Chicago, USA. Bolstered ……
#5 Handheld Laser Welding Machine, Handheld Laser Cleaning …
Website: kaihuanlaser.com
Key Highlights: Xingtai Kaihuan Laser Equipment Manufacturing Co., Ltd., is a professional laser processing application product research and development, production, sales, ……
#6 Laser Welding
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Discover Your Laser Welding Solution IPG is a partner for every stage of production from research and development to full-scale manufacturing….
#7 MIG, TIG, Robotic, & Laser Welding Solutions
Website: binzel-abicor.com
Key Highlights: Explore ABICOR BINZEL USA for advanced welding solutions. We offer MIG, TIG robotic, and laser welding technologies, along with MIG guns and robotic torches ……
#8 Laser Welding Machines
Website: coherent.com
Key Highlights: Get manual to fully automated laser welding machines that weld plastics and metals with speed and precision while improving throughput….
#9 Laser welding
Website: trumpf.com
Key Highlights: Our laser welding systems are the perfect tool for joining metal, plastic, and other materials with perfect seams and no distortion….
#10 Laser Welding
Website: camvaceng.com
Key Highlights: Laser welding (LW) is a welding process that uses a high-power density laser beam to join two materials together, creating a deep, narrow weld….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Beam Welding Machine

2026 Market Trends for Laser Beam Welding Machines
The global Laser Beam Welding (LBW) machine market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, rising industrial automation, and increasing demand across high-precision manufacturing sectors. As industries prioritize efficiency, accuracy, and sustainability, laser beam welding continues to emerge as a preferred joining technology over conventional methods. This analysis explores key market trends expected to shape the LBW machine landscape through 2026.
Technological Advancements Driving Adoption
One of the most influential trends shaping the 2026 LBW market is rapid innovation in laser source technology. Fiber lasers, in particular, are gaining prominence due to their superior energy efficiency, longer operational life, and lower maintenance requirements compared to traditional CO₂ and Nd:YAG lasers. By 2026, fiber laser-based welding systems are projected to dominate the market, especially in high-volume applications such as automotive and electronics manufacturing.
Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning into LBW systems enables real-time process monitoring, adaptive control, and predictive maintenance. These smart welding solutions enhance weld quality consistency and reduce scrap rates, making them highly attractive to precision-driven industries.
Expansion in Automotive and EV Manufacturing
The automotive sector remains a major driver of LBW machine demand, with electric vehicle (EV) production expected to surge through 2026. EV manufacturers rely heavily on laser welding for battery pack assembly, electric motor components, and lightweight structural parts. The need for high-speed, low-distortion joining techniques aligns perfectly with the capabilities of modern LBW machines.
Automakers are increasingly adopting hybrid and remote laser welding systems to improve production line flexibility and reduce footprint. As global EV adoption accelerates—supported by government regulations and consumer demand—the LBW market will benefit from sustained investment in next-generation manufacturing infrastructure.
Growth in Aerospace and Defense Applications
The aerospace and defense industries are also contributing significantly to LBW market growth. These sectors require materials with high strength-to-weight ratios, such as titanium and advanced aluminum alloys, which are best joined using laser welding due to its precision and minimal heat-affected zones.
By 2026, increased production of commercial and military aircraft, along with the development of reusable space vehicles, will drive demand for high-power, multi-axis LBW systems capable of complex 3D welding tasks. Moreover, the push for digital twin integration and Industry 4.0 practices in aerospace manufacturing will further boost adoption of intelligent laser welding cells.
Regional Market Dynamics
Geographically, Asia-Pacific is expected to lead the LBW machine market by 2026, fueled by robust industrialization in China, Japan, South Korea, and India. These countries are investing heavily in automation and high-tech manufacturing, particularly in electronics and automotive sectors. China, in particular, is expanding its domestic laser technology capabilities, reducing reliance on imported systems.
North America and Europe will maintain strong market positions, driven by innovation in advanced manufacturing and stringent quality standards in medical and aerospace applications. Government initiatives promoting smart manufacturing and clean energy will further stimulate LBW adoption in these regions.
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Sustainability is becoming a core consideration in manufacturing, and LBW machines offer environmental advantages over traditional welding methods. With higher energy efficiency, reduced material waste, and lower emissions, laser welding supports green manufacturing goals. By 2026, companies seeking to meet environmental regulations and ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) targets will increasingly favor LBW solutions.
Challenges and Competitive Landscape
Despite strong growth prospects, the LBW market faces challenges such as high initial investment costs and the need for skilled operators. However, as automation and user-friendly interfaces improve, these barriers are gradually diminishing.
The competitive landscape is evolving, with key players such as TRUMPF, IPG Photonics, Coherent, and Han’s Laser expanding their product portfolios and investing in R&D. Strategic partnerships, mergers, and regional expansions are expected to intensify as companies vie for market leadership ahead of 2026.
Conclusion
By 2026, the Laser Beam Welding machine market will be characterized by technological sophistication, sector-specific customization, and global expansion. Driven by demand in electric vehicles, aerospace, and smart manufacturing, LBW systems will play a critical role in shaping the future of precision joining. As the industry embraces digitalization and sustainability, laser welding is set to become an indispensable tool in advanced industrial production.
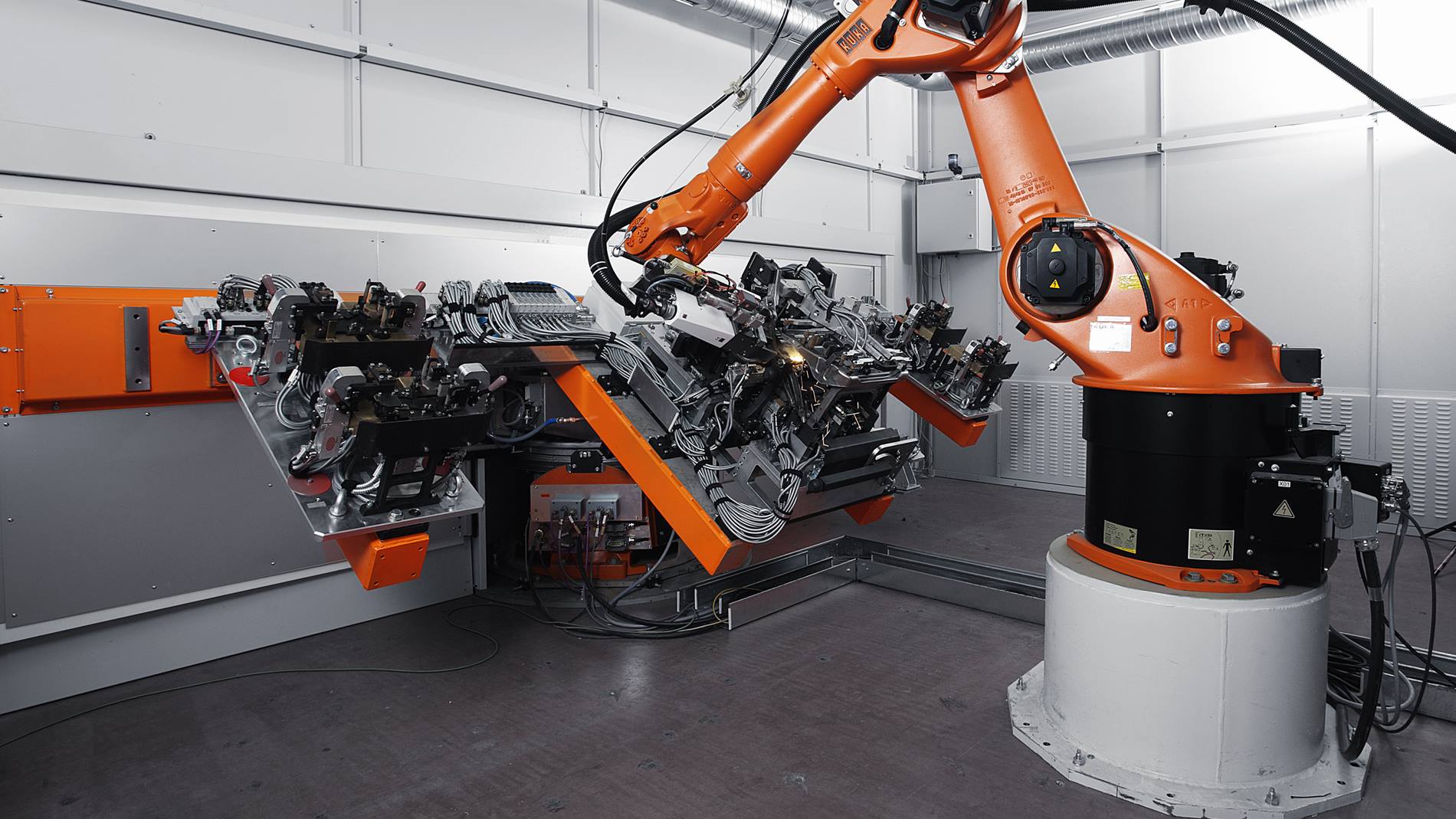
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Laser Beam Welding Machines: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing a Laser Beam Welding (LBW) machine is a significant investment, and overlooking critical quality and intellectual property (IP) aspects can lead to costly failures, operational downtime, and legal complications. Here are key pitfalls to avoid:
Overlooking Build Quality and Component Reliability
Purchasing a machine based solely on price often means compromising on core components. Low-cost lasers may use inferior diodes or optics that degrade quickly, leading to inconsistent beam quality, frequent maintenance, and shortened lifespan. Poorly engineered motion systems or cooling units can result in thermal drift, misalignment, and unreliable welds. Always verify the quality of critical subsystems—laser source, beam delivery optics, focusing head, motion control, and cooling—through technical specifications, third-party certifications, and user references.
Insufficient Verification of Performance Specifications
Suppliers may exaggerate key performance metrics such as laser power stability, beam quality (M² factor), spot size accuracy, and positioning repeatability. Without independent validation or on-site testing, you risk receiving a machine that cannot meet your production tolerances. Demand documented test reports, conduct factory acceptance tests (FAT), and where possible, trial the machine with your actual materials and joint configurations before finalizing the purchase.
Neglecting Software and Control System Integrity
The software controlling the LBW system is as critical as the hardware. Poorly designed or undocumented software can lead to operational inefficiencies, difficulty in process optimization, and lack of traceability. Ensure the control system is user-friendly, supports data logging, and allows for process parameter locking. Additionally, verify that software updates are provided regularly and that the supplier offers comprehensive training and technical support.
Ignoring Intellectual Property (IP) Ownership and Licensing
When integrating custom welding processes or software into the machine, clarify IP ownership upfront. Some suppliers may claim partial rights to process parameters, control algorithms, or user interfaces developed during commissioning. Ensure contracts explicitly state that your proprietary welding procedures and data remain your exclusive property. Beware of restrictive software licenses that limit your ability to modify, transfer, or service the machine independently.
Underestimating After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Even high-quality machines require maintenance and occasional repairs. Sourcing from suppliers with limited local support or opaque spare parts pricing can lead to extended downtime and inflated costs. Confirm the availability of technical support, response times, and the supply chain for critical consumables (e.g., protective windows, nozzles, optical fibers). Prefer suppliers with a strong regional service network or clear service-level agreements (SLAs).
Failing to Address Technology Transfer and Know-How Gaps
Advanced LBW systems often require specialized expertise to operate and optimize. If the supplier does not provide thorough training or knowledge transfer, your team may underutilize the machine’s capabilities or introduce process errors. Ensure the sourcing agreement includes comprehensive training programs, process documentation, and access to application engineers during ramp-up.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP-related pitfalls, organizations can ensure they select a reliable, high-performance Laser Beam Welding machine that supports long-term manufacturing success without exposing them to unnecessary technical or legal risks.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Beam Welding Machine
This guide outlines key logistics and compliance considerations for the shipment, import/export, installation, and operation of a Laser Beam Welding (LBW) Machine. Proper planning ensures smooth transport, regulatory adherence, and workplace safety.
Regulatory Compliance and Documentation
Ensure all applicable regulations are met before shipping or operating the machine. Key areas include:
- Export/Import Controls: Verify if the machine or its components (especially high-power lasers or optical parts) are subject to international trade regulations such as ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations) or EAR (Export Administration Regulations). Obtain necessary export licenses if required.
- Customs Documentation: Prepare accurate commercial invoices, packing lists, certificates of origin, and bills of lading. Clearly state the HS (Harmonized System) code for laser welding equipment (e.g., 8515.21 or 8515.80, depending on specifications).
- CE Marking (Europe): Confirm the machine complies with EU directives including Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC), Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive (2014/30/EU), and Low Voltage Directive (2014/35/EU). Documentation must include a Declaration of Conformity.
- FDA/CDRH Registration (USA): For Class I, III, or IV lasers, registration with the U.S. FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH) is mandatory. Submission of a Laser Product Report (Form FDA 2877) may be required prior to import.
- Laser Safety Standards: Comply with IEC 60825-1 (Safety of Laser Equipment) and ANSI Z136.1 (Safe Use of Lasers). Ensure proper laser classification labeling (e.g., Class 4) and interlocks are in place.
Packaging and Transportation
Proper packaging and handling are essential to prevent damage during transit.
- Crate Specifications: Use strong, weather-resistant wooden or composite crates with internal bracing. Machines should be securely mounted to avoid internal movement.
- Environmental Protection: Include desiccants and moisture barriers to protect sensitive optical and electronic components, especially during ocean freight.
- Handling Labels: Clearly mark crates with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” “Do Not Stack,” and “Laser Equipment – Avoid Direct Sunlight.”
- Transport Mode: Choose transport method (air, sea, or ground) based on urgency, cost, and machine size. For oversized units, coordinate with freight forwarders for special handling or permits.
- Insurance: Obtain comprehensive cargo insurance covering damage, loss, or delay during transit.
Import Clearance and Duties
Efficient customs clearance prevents delays.
- Local Regulations: Research country-specific import requirements (e.g., conformity assessment, local representative, or technical inspection).
- Duty and Tax Assessment: Determine applicable import duties, VAT, or GST based on the declared value and HS code. Consider bonded shipments or duty-free status if eligible (e.g., under R&D equipment exemptions).
- Pre-Arrival Submission: Submit documentation to customs authorities in advance to expedite clearance. Engage a licensed customs broker if necessary.
Installation and Site Preparation
Prepare the receiving site to meet technical and safety requirements.
- Facility Requirements: Ensure adequate floor loading capacity, clean and level flooring, and sufficient ceiling height. Maintain a dust-free, temperature-controlled environment (typically 18–25°C).
- Utility Supply: Confirm availability of required power supply (voltage, phase, grounding), compressed air, cooling water, and exhaust ventilation.
- Laser Safety Zone: Designate a controlled access area with interlocked doors, laser warning signs, and emergency stops. Install beam enclosures and protective barriers compliant with ANSI Z136.1 or IEC 60825.
- Permits and Inspections: Obtain local building, electrical, and fire safety permits. Schedule a post-installation inspection by a qualified laser safety officer (LSO) or regulatory body if required.
Operational Compliance and Maintenance
Ensure ongoing safety and regulatory adherence during machine operation.
- Laser Safety Officer (LSO): Appoint a trained LSO to oversee safety protocols, conduct risk assessments, and maintain compliance records.
- Training: Provide certified laser safety training for all operators and maintenance personnel.
- Maintenance Logs: Keep detailed records of service, calibration, and repairs. Follow manufacturer-recommended maintenance schedules.
- Waste and Emissions: Manage fumes and particulates using certified fume extraction systems. Dispose of contaminated filters and waste materials according to environmental regulations (e.g., EPA or equivalent).
- Periodic Audits: Conduct regular safety audits and equipment inspections to maintain compliance with local and international standards.
Emergency Preparedness
Establish protocols for equipment-related incidents.
- Emergency Procedures: Post clear instructions for laser shutdown, fire response, and injury reporting.
- Fire Suppression: Equip the area with Class C (electrical) fire extinguishers. Avoid water-based systems near high-voltage components.
- First Aid and Eye Protection: Provide laser-specific first aid kits and emergency eyewash stations. Ensure appropriate laser safety eyewear is available for all personnel.
By following this guide, organizations can ensure the safe, legal, and efficient deployment of Laser Beam Welding Machines across international and domestic operations.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Laser Beam Welding Machine
After a thorough evaluation of technical requirements, production needs, and market options, sourcing a laser beam welding machine represents a strategic investment in precision, efficiency, and long-term manufacturing capability. The decision to implement laser beam welding technology will significantly enhance weld quality, improve process repeatability, and reduce post-welding finishing requirements—leading to overall cost savings and increased throughput.
Key factors such as laser type (fiber, CO2, or disk), power output, integration capabilities with existing automation systems, vendor support, and total cost of ownership have been carefully considered. After comparing multiple suppliers and conducting site visits or demonstrations where possible, the selected machine offers the optimal balance of performance, reliability, and scalability for current and future production demands.
In conclusion, proceeding with the procurement of the recommended laser beam welding machine will position the organization at the forefront of advanced joining technologies, supporting high-quality manufacturing standards and enabling competitiveness in demanding markets such as automotive, aerospace, or medical device production. Proper training, maintenance planning, and process validation will ensure a successful implementation and maximum return on investment.