The global laser beam welding market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for precision joining technologies in automotive, aerospace, and industrial manufacturing sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global laser welding market size was valued at USD 1.78 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.8% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects a CAGR of over 7.5% during the forecast period of 2023–2028, citing rising automation, lightweight material usage, and advancements in high-power laser systems as key growth catalysts. As manufacturers seek faster, cleaner, and more energy-efficient welding solutions, laser beam technology has emerged as a preferred method for high-integrity applications. This growing demand has fostered a competitive landscape among equipment suppliers, pushing innovation in fiber lasers, beam delivery systems, and process integration. In this context, the following list highlights the top 10 laser beam welder manufacturers leading the industry through technological excellence, global reach, and strategic partnerships.
Top 10 Laser Beam Welder Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Focus on laser
Website: hanslaser.net
Key Highlights: With good beam quality, fiber transmission and high electro-optical conversion efficiency, It is mainly used for rapid welding thin materials. More · MOLD 301….
#2 Laserax
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Laserax works with the world’s leading manufacturers to implement laser cleaning, welding, texturing, and marking solutions….
#3 Denaliweld
Website: denaliweld.com
Key Highlights: DenaliWeld INC, is a proud employee-owned fiber laser welding machine manufacturer based in Chicago, USA. Bolstered by the most experienced engineers and design ……
#4 Equipment & Systems
Website: amadaweldtech.com
Key Highlights: Manufacturer of equipment and systems for welding, cutting, marking, micromachining, sealing, and bonding. Resistance welding. Laser….
#5 Laser Welder
Website: laser-welder.net
Key Highlights: Laser welders are incredibly versatile and essential in any fabrication shop or factory welding parts from sheet metal….
#6 Laser Welding
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser welding creates exceptionally high-quality joints with excellent physical and electrical properties, even when joining challenging materials like aluminum ……
#7 MIG, TIG, Robotic, & Laser Welding Solutions
Website: binzel-abicor.com
Key Highlights: Explore ABICOR BINZEL USA for advanced welding solutions. We offer MIG, TIG robotic, and laser welding technologies, along with MIG guns and robotic torches ……
#8 Laser Welding
Website: camvaceng.com
Key Highlights: Laser welding (LW) is a welding process that uses a high-power density laser beam to join two materials together, creating a deep, narrow weld….
#9 Handheld Laser Welding Machine, Handheld Laser Cleaning …
Website: kaihuanlaser.com
Key Highlights: Laser welding is a high-precision process using a focused laser beam to melt and join materials, known for its versatility and low heat impact in diverse ……
#10 Laser Welding Machines
Website: coherent.com
Key Highlights: Get manual to fully automated laser welding machines that weld plastics and metals with speed and precision while improving throughput….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Beam Welder

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Laser Beam Welders – Precision, Automation, and Industry 4.0 Driving Growth
The global laser beam welding (LBW) market is poised for significant transformation and robust growth by 2026, driven by escalating demands for precision, efficiency, and automation across key industrial sectors. Key trends shaping the market landscape include:
1. Dominance of High-Power Fiber Lasers: Fiber lasers will solidify their position as the technology of choice, surpassing CO2 and disk lasers. Their superior wall-plug efficiency (often >30%), lower maintenance requirements, smaller footprint, and exceptional beam quality make them ideal for high-speed, deep-penetration welding in automotive and heavy industry. Advancements in multi-kilowatt (10kW+) single-mode and brightness-optimized fiber lasers will enable faster processing of thicker materials and more complex geometries, particularly in e-mobility and aerospace.
2. Integration with Advanced Automation & Robotics: Laser welding systems will become increasingly integrated into fully automated production lines and collaborative robotics (cobots). Seamless integration with robotic arms (especially 6-axis and SCARA), automated part handling, and in-line quality control systems will be standard. This trend is fueled by the need for consistent quality, reduced labor costs, and the ability to handle complex 3D welding paths in high-volume manufacturing (e.g., battery packs, powertrains).
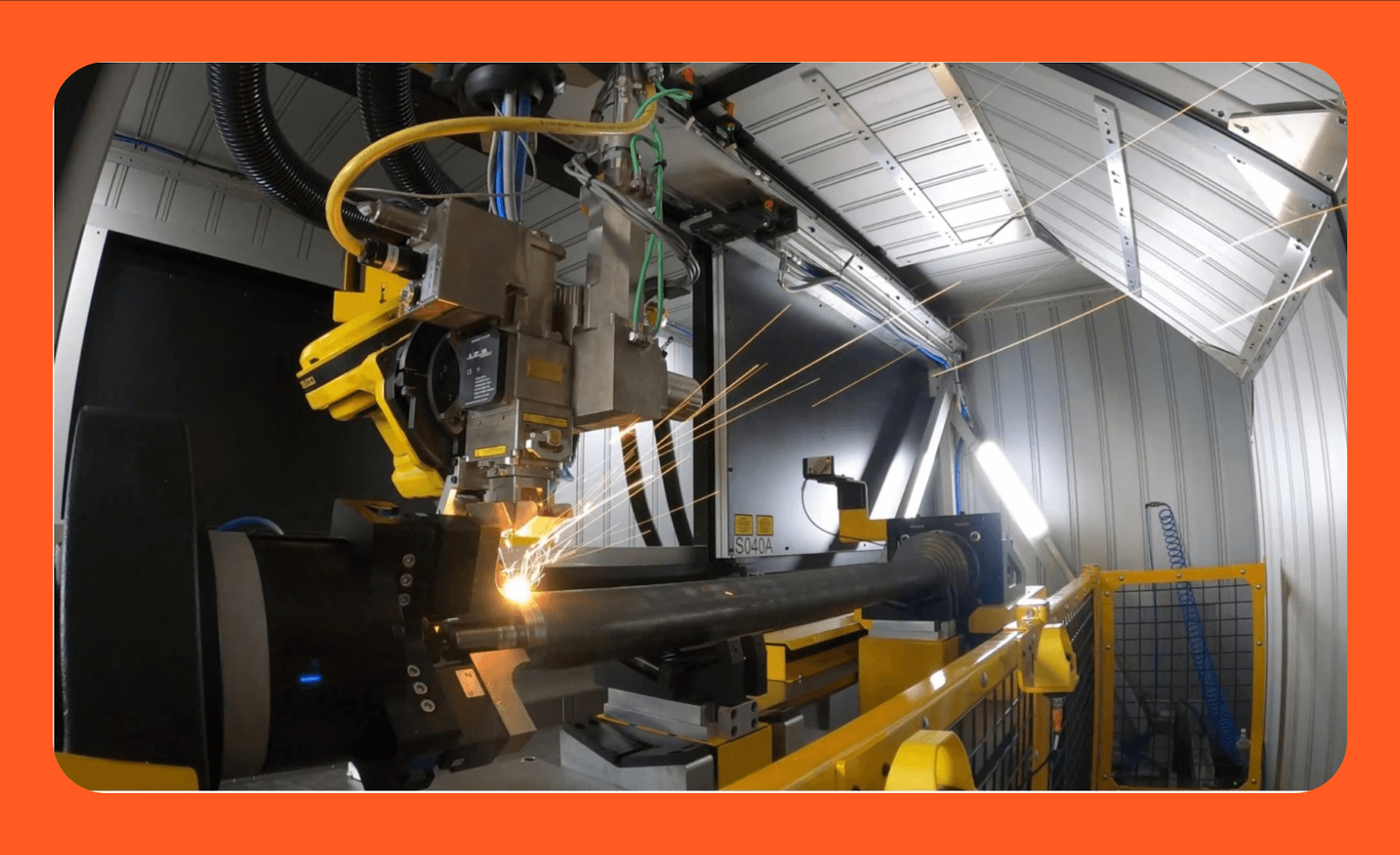
3. Rise of Remote Laser Welding (RLW) & Scanning Optics: The adoption of remote scanning heads using galvanometer mirrors will accelerate. RLW allows for extremely high-speed welding (meters per second) over large areas without moving the entire heavy laser source or robot. This is particularly crucial for automotive body-in-white (BIW) applications, enabling lightweight design with tailored blanks and aluminum structures, significantly reducing cycle times and increasing throughput.
4. Focus on Process Monitoring, Control, and Industry 4.0: Real-time process monitoring using integrated sensors (e.g., high-speed cameras, photodiodes, spectroscopy, pyrometry) will become essential. AI and machine learning algorithms will analyze this data for predictive quality assurance, automatic parameter optimization, and closed-loop process control, minimizing defects and rework. Connectivity to factory MES/SCADA systems for data logging, traceability, and predictive maintenance will be a key differentiator.
5. Expansion into New Materials & Applications: While steel and aluminum remain dominant, demand will grow for welding dissimilar materials (e.g., steel-to-aluminum for lightweighting) and advanced materials like copper (critical for EV motors and batteries), titanium (aerospace, medical), and high-strength steels. This will drive development of specialized laser sources (e.g., green lasers for copper) and process parameter databases.
6. Growth in Electric Vehicle (EV) Manufacturing: The EV revolution is the single largest driver. Laser welding is indispensable for manufacturing high-voltage battery packs (busbar welding, cell tab welding, casing sealing), electric motors (stator, rotor welding), and lightweight vehicle structures. The stringent quality and safety requirements of EVs perfectly align with the precision and reliability of LBW.
7. Increased Demand for Compact, Modular, and Flexible Systems: Manufacturers will seek systems that are easier to integrate, require less floor space, and offer greater flexibility for product changeovers. Modular laser sources, compact beam delivery systems, and software-defined processes will cater to the needs of job shops and manufacturers producing lower volumes of diverse products.
8. Sustainability and Energy Efficiency: The inherent energy efficiency of fiber lasers compared to traditional welding methods (like MIG/MAG) will be a major selling point. Manufacturers will increasingly highlight the reduced carbon footprint and lower operating costs (power, gas, consumables) of LBW systems as part of their sustainability initiatives.
In summary, the 2026 laser beam welding market will be characterized by smarter, faster, more connected, and more efficient systems. The convergence of high-power fiber lasers, advanced automation, real-time intelligence, and the insatiable demand from the EV and advanced manufacturing sectors will propel the market towards greater adoption, higher performance, and deeper integration into the core of modern industrial production.
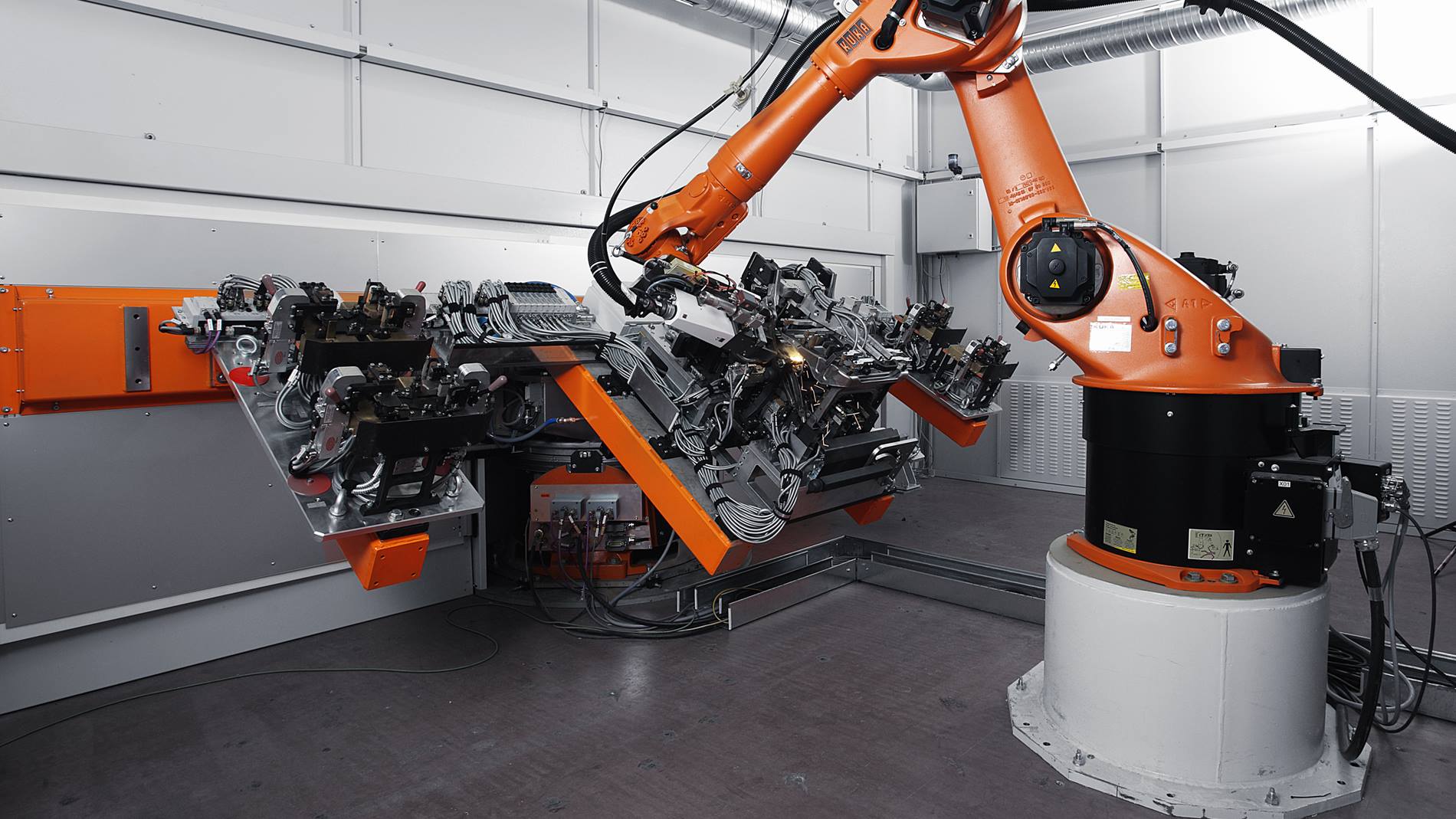
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Laser Beam Welder: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing a laser beam welder involves complex technical, financial, and legal considerations. While advanced capabilities and precision are major drivers, overlooking key pitfalls—particularly in quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection—can lead to significant operational disruptions, legal exposure, and financial loss.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Supplier Vetting and Certification
Choosing a supplier based solely on price or marketing claims without verifying technical expertise and manufacturing standards is a common mistake. Buyers may overlook the importance of certifications such as ISO 9001 (quality management) or compliance with laser safety standards (e.g., IEC 60825). Without these, there’s no assurance of consistent build quality, reliability, or adherence to safety protocols, increasing the risk of equipment failure or workplace hazards.
Insufficient Testing and Validation Protocols
Failing to define and enforce rigorous acceptance testing (e.g., weld consistency, beam stability, cycle testing) during procurement can result in receiving underperforming systems. Some suppliers may provide “showroom-ready” units that perform well in demonstrations but fail under real production conditions. Without documented validation processes, resolving disputes over performance becomes difficult.
Lack of After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
High-quality laser systems require ongoing maintenance, calibration, and technical support. Sourcing from suppliers with limited regional service networks or unclear spare parts policies can lead to prolonged downtime. This is especially critical with fiber or disk lasers, where proprietary components may have long lead times or be discontinued without notice.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
Ambiguous IP Ownership in Customized Systems
When commissioning a customized laser welding solution, the contract must clearly specify who owns the resulting designs, software, and process parameters. Without explicit clauses, suppliers may retain rights to modifications or innovations developed during integration, limiting your ability to replicate, modify, or transfer the system in the future.
Use of Counterfeit or Unlicensed Components
Unscrupulous suppliers may integrate counterfeit optics, control systems, or software to cut costs. These components not only compromise performance and safety but may also expose the buyer to IP infringement claims—especially if licensed technology (e.g., laser source firmware, CAD software) is used without proper authorization.
Inadequate Protection of Proprietary Processes
During demonstrations or trials, buyers may need to disclose sensitive production requirements or material specifications. Without robust non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) and clear data handling policies, suppliers could misuse this information to develop competing solutions or share it with third parties, eroding competitive advantage.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, implement a structured sourcing process that includes:
– Conducting technical audits of potential suppliers.
– Requiring third-party certification and performance validation.
– Defining IP ownership and licensing rights in procurement contracts.
– Enforcing NDAs and data protection clauses.
– Ensuring service-level agreements (SLAs) cover maintenance, training, and software updates.
By proactively addressing quality and IP concerns, organizations can secure reliable, compliant, and legally sound laser welding solutions that support long-term manufacturing goals.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Beam Welder
This guide outlines the key logistics and compliance considerations for the safe and legal transportation, handling, installation, and operation of a Laser Beam Welder.
Regulatory Compliance
Ensure adherence to all applicable local, national, and international regulations, including but not limited to:
– Laser Safety Standards: Comply with IEC 60825-1 (Safety of laser products) and ANSI Z136.1 (Safe Use of Lasers).
– Electrical Standards: Confirm conformity with IEC 60204-1 (Safety of machinery – Electrical equipment of machines) and local electrical codes.
– Machine Safety: Meet requirements of the Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC) in the EU or equivalent regulations in other regions (e.g., OSHA standards in the U.S.).
– EMC Regulations: Adhere to electromagnetic compatibility standards such as IEC 61326-1 to prevent interference with other equipment.
– Environmental and Waste Handling: Follow local regulations for disposal of consumables, coolant, and electronic waste.
Transportation and Handling
Plan logistics carefully to prevent damage and ensure personnel safety:
– Packaging: Use original manufacturer packaging or equivalent protective crating with shock-absorbing materials.
– Lifting and Moving: Employ certified lifting equipment (e.g., forklifts, hoists) and follow the manufacturer’s instructions for weight distribution and lifting points.
– Environmental Conditions: Maintain temperature and humidity within specified ranges during transit to protect sensitive components.
– Documentation: Include shipping manifests, packing lists, and import/export documentation (e.g., commercial invoice, bill of lading, certificates of origin) as required.
Import and Export Requirements
Verify customs and trade compliance for cross-border shipments:
– HS Code Classification: Use appropriate Harmonized System (HS) code (e.g., 8456.30 for laser cutting/welding machines).
– Import Permits and Duties: Check for required permits, tariffs, and taxes in the destination country.
– Export Controls: Confirm compliance with export regulations (e.g., EAR in the U.S., Dual-Use Regulation in the EU), especially if the laser exceeds certain power thresholds.
– CE, FCC, or Other Marks: Ensure the equipment bears necessary conformity markings for the target market.
Installation and Site Preparation
Prepare the facility to safely accommodate the laser welder:
– Space Requirements: Provide sufficient clearance around the machine for maintenance, ventilation, and emergency access.
– Power Supply: Ensure electrical service meets voltage, phase, frequency, and grounding specifications.
– Cooling System: Install and connect chillers or cooling loops as specified by the manufacturer.
– Ventilation and Fume Extraction: Implement local exhaust ventilation (LEV) systems to capture hazardous fumes and particulates in compliance with OSHA or equivalent standards.
– Laser Enclosure: Install interlocked safety enclosures and warning signs (e.g., “Laser Radiation” and “Danger” labels).
Operational Safety and Training
Implement safety protocols and ensure personnel are properly trained:
– Laser Safety Officer (LSO): Appoint a qualified LSO if required by local regulations.
– Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Provide appropriate laser safety eyewear, flame-resistant clothing, and respiratory protection as needed.
– Operator Training: Conduct comprehensive training on laser operation, emergency procedures, and maintenance.
– Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Develop and enforce documented SOPs for startup, operation, and shutdown.
Maintenance and Recordkeeping
Maintain compliance through regular upkeep and documentation:
– Scheduled Maintenance: Follow the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule for optics, cooling systems, and safety interlocks.
– Calibration Records: Keep logs of laser power calibration and safety system checks.
– Incident Reporting: Document any safety incidents, malfunctions, or exposure events per regulatory requirements.
– Compliance Audits: Conduct periodic internal audits to verify adherence to safety and environmental standards.
Decommissioning and Disposal
Safely retire the laser welder at end-of-life:
– Laser Deactivation: Follow proper procedures to discharge capacitors and disable the laser source.
– Hazardous Materials: Handle and dispose of batteries, coolant, and optical components according to environmental regulations.
– Recycling: Recycle electronic components and metal parts through certified e-waste facilities.
– Documentation: Retain records of disposal for compliance and audit purposes.
Adhering to this guide ensures safe, efficient, and legally compliant handling of laser beam welding equipment throughout its lifecycle.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Laser Beam Welder
After a thorough evaluation of technical requirements, production needs, supplier capabilities, and cost considerations, sourcing a laser beam welder represents a strategic investment in enhancing manufacturing precision, efficiency, and product quality. The technology offers significant advantages over conventional welding methods, including higher accuracy, reduced heat distortion, faster processing speeds, and improved repeatability—making it ideal for high-integrity applications in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and medical device manufacturing.
The selected laser beam welding system aligns with current production volumes and scalability goals, while also supporting future automation integration. Key factors such as laser type (e.g., fiber or disk laser), power output, beam delivery system, and compatibility with existing workflows were carefully assessed to ensure optimal performance and return on investment.
Furthermore, partnering with a reputable supplier that offers comprehensive technical support, training, and service maintenance will be critical to maximizing uptime and ensuring long-term success.
In conclusion, procuring a laser beam welder is a forward-thinking decision that strengthens manufacturing capabilities, supports innovation, and improves competitiveness in precision welding applications. With proper implementation and operational oversight, the investment is expected to deliver significant improvements in quality, productivity, and cost-efficiency over time.