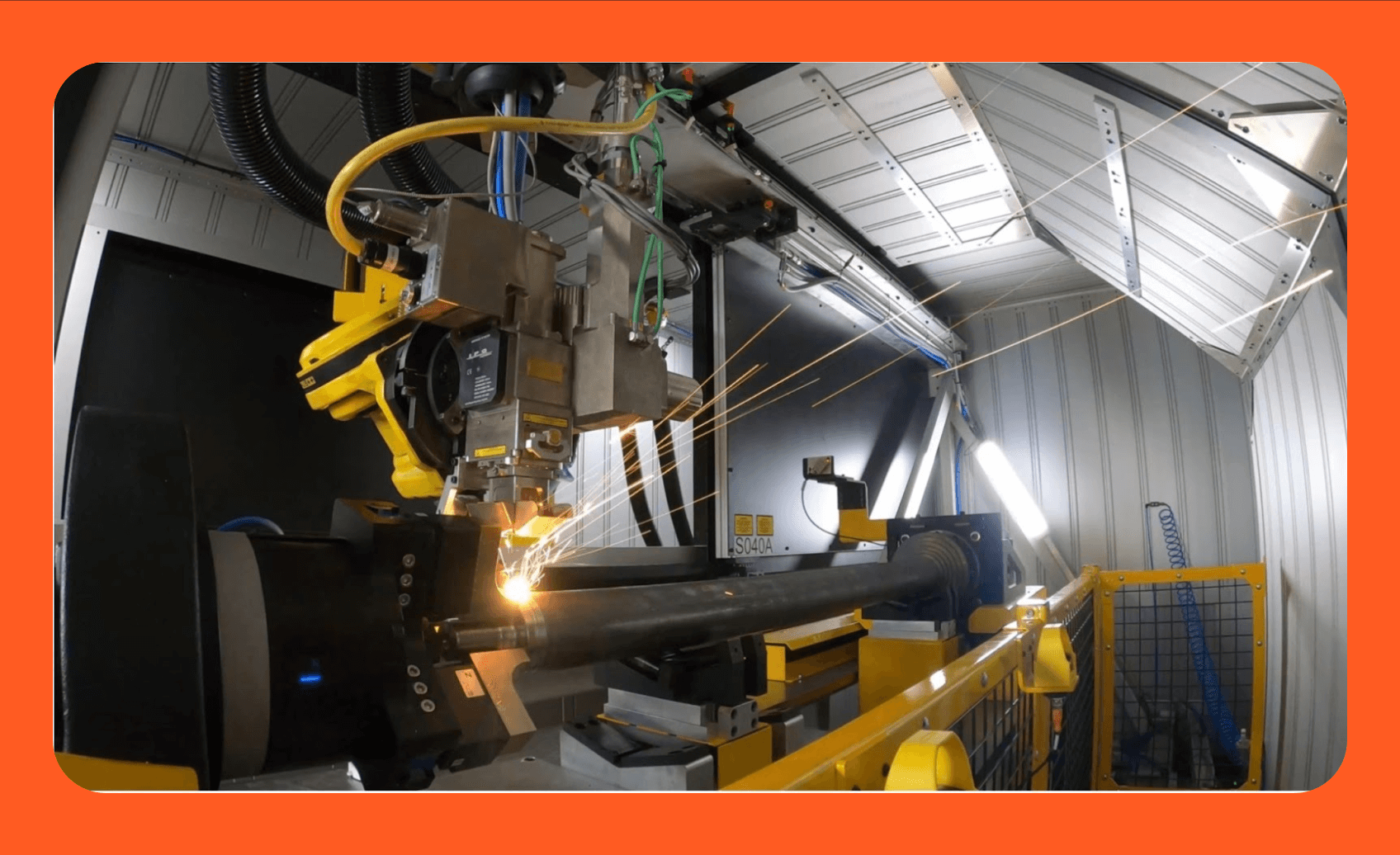
The laser arc welding market has experienced robust growth, driven by increasing demand for high-precision, efficient joining technologies across automotive, aerospace, and heavy manufacturing sectors. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global laser welding market was valued at USD 4.2 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.8% through 2028. This expansion is fueled by advancements in hybrid laser-arc welding (HLAW) techniques, which combine the deep penetration of laser beams with the gap-bridging capabilities of arc welding, resulting in superior weld quality and process stability. As industries prioritize automation and energy efficiency, manufacturers are investing heavily in integrated welding solutions. Grand View Research further supports this trend, noting that the growing adoption of fiber lasers and the shift toward lightweight materials in vehicle manufacturing are accelerating innovation in laser-based joining methods. In this competitive and rapidly evolving landscape, nine key players have emerged as leaders in laser arc welding technology—pioneering advancements in system integration, process control, and industrial scalability.
Top 9 Laser Arc Welding Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Custom Automated Welding Manufacturer
Website: ametinc.com
Key Highlights: AMET is a welding manufacturer that provides custom automated welding machines. Our engineers design state of the art welding systems for various ……
#2 Micro Arc Welding, Inc.
Website: microarcwelding.com
Key Highlights: Micro Arc Welding manages to supply a mix of competitive-costing and low volume, high critical utility applications….
#3 Laser Welding
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser welding is the process of transferring a laser beam’s energy in the form of heat to fuse or join parts. This transferred heat melts the materials to ……
#4 MIG, TIG, Robotic, & Laser Welding Solutions
Website: binzel-abicor.com
Key Highlights: Explore ABICOR BINZEL USA for advanced welding solutions. We offer MIG, TIG robotic, and laser welding technologies, along with MIG guns and robotic torches ……
#5 Laser welding
Website: trumpf.com
Key Highlights: TRUMPF lasers can create fine weld points of just a millimeter in diameter in an instant, as well as deep-welded seams stretching over several meters….
#6 Sunstone Welders
Website: sunstonewelders.com
Key Highlights: Sunstone designs and manufactures high-tech micro welding and engraving solutions for many different industries. In short, wherever a very small spot weld ……
#7 Laser Welding
Website: precollc.com
Key Highlights: Preco provides laser welding processes including robotics, tooling and material handling. The process can be used with just about any materials that are ……
#8 Microtech Welding Corp.
Website: microtechwelding.com
Key Highlights: Quality Precision Welding. Your reliable partner for American-made welding solutions with unmatched speed, service, and proven expertise….
#9 Laser Welding Solutions
Website: laserweldingsolutions.com
Key Highlights: Laser Welding Solutions provides state-of-the-art surface technologies and 3D printing to assist in the product improvement efforts of our goal-driven ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Arc Welding
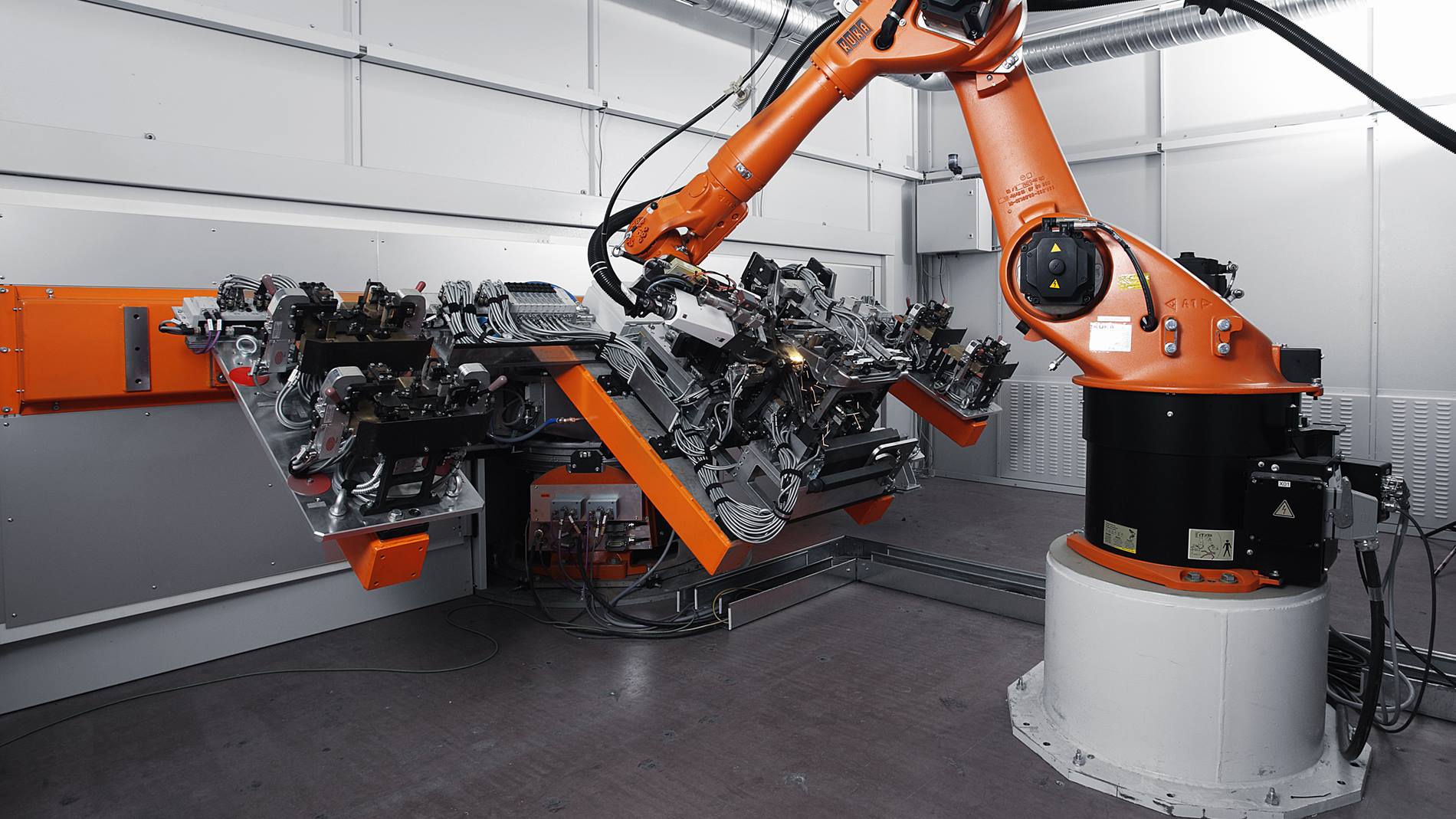
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Laser Arc Welding
By 2026, the Laser Arc Welding (LAW) market is poised for significant evolution, driven by the convergence of advanced manufacturing demands, technological innovation, and global industrial shifts. Key trends shaping the market include:
- Accelerated Adoption in Electric Vehicle (EV) Manufacturing: The explosive growth of the EV industry will be the primary catalyst. LAW’s ability to efficiently join dissimilar metals (e.g., aluminum to high-strength steel) and create high-integrity, lightweight structures with minimal distortion is critical for battery enclosures, chassis, and powertrain components. Demand from EV OEMs and Tier 1 suppliers will surge, making automotive (especially EVs) the dominant application segment.
- Technological Integration and Process Optimization: The market will see a shift beyond basic hybrid systems towards highly integrated, intelligent solutions. Key advancements include:
- Enhanced Process Monitoring & Control: Wider adoption of real-time monitoring (e.g., high-speed imaging, spectroscopy, acoustic sensing) combined with AI/ML for predictive quality control, adaptive parameter adjustment, and autonomous defect correction.
- Digital Twin & Simulation: Increased use of sophisticated simulation software for virtual process design, optimization, and troubleshooting, reducing setup time and material waste.
- Robotics & Automation: Tighter integration with collaborative robots (cobots) and advanced robotic cells for flexible, high-precision applications, particularly in complex geometries common in EVs and aerospace.
- Focus on Cost Reduction & Accessibility: While historically seen as expensive, efforts will intensify to lower the total cost of ownership (TCO):
- Modular & Scalable Systems: Development of more modular LAW systems allowing manufacturers to scale capabilities based on specific needs, improving ROI.
- Improved Efficiency: Higher power efficiency lasers, longer-lasting components, and reduced need for post-weld finishing will lower operational costs.
- Standardization: Emerging industry standards for processes and equipment will simplify integration and reduce engineering overhead.
- Expansion into New Materials and Applications: Beyond traditional steels and aluminum:
- Copper Processing: Growing demand for welding copper in EV motors, power electronics, and battery connections will drive LAW development for high-reflectivity materials.
- Thick Section Welding: Advancements will enable more efficient and reliable welding of thicker sections (e.g., >15mm) in heavy machinery, shipbuilding, and energy sectors, competing with traditional processes.
- Aerospace & Defense: Increased use for critical, high-value components requiring superior weld quality and strength-to-weight ratios.
- Sustainability as a Key Driver: LAW’s inherent advantages align with sustainability goals:
- Energy Efficiency: Significantly lower energy consumption compared to many conventional welding processes.
- Reduced Material Waste: Less filler metal consumption, minimal spatter, and lower post-weld machining requirements.
- Enabling Lightweighting: Critical for reducing vehicle emissions and improving fuel efficiency (ICE) or range (EV), a major sustainability benefit.
- Regional Market Dynamics:
- Asia-Pacific (APAC): Will remain the largest and fastest-growing market, driven overwhelmingly by massive EV production in China, Japan, and South Korea, coupled with strong industrial manufacturing bases.
- North America & Europe: Steady growth fueled by EV adoption, aerospace/defense, and a strong push for advanced manufacturing (Industry 4.0). Europe’s focus on green manufacturing regulations will further boost LAW adoption.
- Consolidation and Strategic Partnerships: The market will see increased activity through mergers, acquisitions, and partnerships between laser source manufacturers, arc welding equipment providers, robotics companies, and system integrators to offer comprehensive, optimized LAW solutions and capture larger market share.
In conclusion, the 2026 LAW market will be characterized by robust growth, primarily fueled by the EV revolution. Success will depend on technological advancements focused on intelligence, integration, and cost-effectiveness, expanding material capabilities, and a strong alignment with global sustainability and lightweighting imperatives.

H2: Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Laser Arc Welding (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing Laser Arc Welding (LAW) technology or services presents unique challenges due to its complexity, high performance demands, and the critical nature of the applications it often serves (e.g., automotive, aerospace, energy). Overlooking key pitfalls related to quality and intellectual property (IP) can lead to significant technical failures, project delays, financial losses, and legal exposure.
H3: Quality-Related Pitfalls
-
Insufficient Process Validation & Characterization:
- Pitfall: Assuming the supplier’s standard LAW process parameters are suitable for the specific material, joint geometry, and performance requirements of your component without rigorous validation.
- Risk: Inconsistent weld quality (porosity, cracks, lack of fusion), reduced mechanical properties (strength, fatigue life), and part rejection. The hybrid nature of LAW makes process windows sensitive.
- Mitigation: Demand detailed Process Qualification Reports (PQRs) and Procedure Qualification Records (PQRs) specific to your application. Require demonstration welds on actual or representative sample parts with destructive (tensile, bend, macro/micro) and non-destructive testing (NDT – UT, X-ray, VT) to agreed acceptance criteria (e.g., ISO 15614, AWS D1.1).
-
Inadequate Supplier Expertise & Experience:
- Pitfall: Selecting a supplier based solely on cost or general welding capability without verifying their specific expertise in the hybrid aspects of LAW (laser-arc interaction, plume dynamics, parameter synergies, specialized equipment).
- Risk: Suboptimal parameter selection, inability to troubleshoot complex defects, poor process stability, and inability to achieve required penetration or bead profile.
- Mitigation: Conduct thorough technical audits. Require evidence of successful LAW projects on similar materials and joint types. Interview the engineering team. Verify certifications (e.g., AWS Certified Welding Engineer/Fabricator with relevant special processes).
-
Poor Process Control & Monitoring:
- Pitfall: Relying on suppliers without robust, real-time process monitoring and control systems (e.g., laser power/position sensors, arc voltage/current feedback, seam tracking, melt pool monitoring).
- Risk: Undetected process drift, inconsistent weld quality, high scrap rates, and difficulty in root cause analysis for failures. LAW’s complexity demands active control.
- Mitigation: Specify requirements for process monitoring capabilities in the sourcing contract. Require access to process logs/data for critical production runs. Audit the supplier’s SPC (Statistical Process Control) practices for LAW.
-
Neglecting Material & Joint Preparation Requirements:
- Pitfall: Overlooking the critical need for stringent material cleanliness (oil, oxide, moisture removal) and precise joint fit-up tolerances required for reliable LAW.
- Risk: Increased spatter, porosity, undercuts, and unstable keyhole formation, leading to weld discontinuities and reduced integrity.
- Mitigation: Clearly define and enforce material prep (cleaning methods, tolerances) and joint fit-up specifications in technical drawings and purchase orders. Include inspection requirements for incoming parts.
-
Underestimating Post-Weld Requirements:
- Pitfall: Focusing only on the welding process itself, neglecting necessary post-weld treatments (e.g., stress relieving, heat treatment, grinding, NDT) and their impact on final quality.
- Risk: Residual stresses causing distortion or cracking, surface defects going undetected, failure to meet dimensional or performance specifications.
- Mitigation: Define the complete Quality Assurance (QA) plan, including all post-weld steps, inspection points (IPs), and acceptance criteria. Verify the supplier’s capability and procedures for these steps.
H3: Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
-
Ambiguous Ownership of Developed IP:
- Pitfall: Failing to establish clear contractual terms defining who owns IP arising from the development work (e.g., optimized LAW parameters, unique fixtures, process improvements, new joint designs).
- Risk: Disputes over ownership, inability to use or license the developed IP freely, potential infringement claims, loss of competitive advantage. Supplier may claim ownership of process know-how developed using your requirements.
- Mitigation: Negotiate and include explicit IP clauses in the contract before work begins. Define ownership of background IP, foreground IP (developed during the project), and any improvements. Typically, client-owned requirements lead to client ownership of resulting IP, but this must be contractually secured.
-
Inadequate Protection of Background IP:
- Pitfall: Disclosing proprietary part designs, material specifications, or performance requirements to the supplier without adequate confidentiality protections (NDA) and clear limitations on use.
- Risk: Misuse or unauthorized disclosure of your confidential information, potential reverse engineering, loss of trade secrets.
- Mitigation: Implement a strong, project-specific Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) before sharing any sensitive information. Clearly define the scope of confidential information and the supplier’s obligations. Use “need-to-know” principles.
-
Lack of Transparency on Supplier’s Background IP:
- Pitfall: Not verifying the supplier’s rights to use their own equipment, software, and proprietary LAW processes. Assuming they have freedom to operate.
- Risk: Inadvertent infringement of third-party patents (e.g., on specific LAW techniques, beam delivery systems, monitoring tech). Your product could be subject to infringement claims or injunctions.
- Mitigation: Conduct IP due diligence on the supplier. Require warranties that their technology and processes used do not infringe third-party IP. Obtain indemnification clauses in the contract.
-
Failure to Secure Necessary Licenses:
- Pitfall: Overlooking the need for licenses to use specific patented LAW technologies, software algorithms, or consumables supplied by the welding equipment manufacturer (e.g., IPG, Trumpf, Fronius).
- Risk: Infringement liability, disruption of production if licenses are revoked, unexpected costs.
- Mitigation: Clarify with the supplier and original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) what licenses are required for the specific LAW process and equipment being used. Ensure these licenses are in place and properly assigned or sub-licensed to you if needed for production.
-
Poor Documentation and Traceability:
- Pitfall: Accepting results without comprehensive documentation linking specific process parameters, equipment settings, material batches, and operator actions to each weld or batch.
- Risk: Inability to reproduce results, difficulty in root cause analysis for failures, weak IP position (hard to prove what was developed), challenges in audits or disputes.
- Mitigation: Mandate detailed process documentation and data logging as part of the quality requirements. Ensure traceability from raw material to final weld is maintained.
Conclusion:
Successfully sourcing Laser Arc Welding requires a proactive approach that rigorously addresses both the demanding quality requirements inherent in the complex hybrid process and the significant intellectual property risks. Comprehensive technical due diligence, clear and robust contractual agreements (especially regarding IP ownership and confidentiality), and stringent quality assurance protocols are essential to mitigate these critical pitfalls and ensure a successful outcome.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Arc Welding
Overview
Laser Arc Welding (LAW) combines the precision of laser beam welding with the gap-bridging capabilities of arc welding, such as MIG or TIG. This hybrid process requires specialized equipment, trained personnel, and strict adherence to safety, environmental, and regulatory standards. This guide outlines the key logistics and compliance considerations for implementing and operating Laser Arc Welding systems.
Equipment & Facility Requirements
- Laser Safety Enclosure: Install interlocked laser safety enclosures compliant with IEC 60825-1 to prevent exposure to Class 4 laser radiation.
- Ventilation & Fume Extraction: Use local exhaust ventilation (LEV) systems designed for metal fume extraction, especially when welding materials like aluminum or stainless steel. Ensure compliance with OSHA or local air quality regulations.
- Power Supply & Cooling: Provide stable electrical power and chiller systems to maintain optimal laser and arc source performance.
- Robotic Integration: If automated, ensure robotic cells meet ISO 10218-1 safety standards for industrial robots.
Personnel Training & Certification
- Laser Safety Officer (LSO): Appoint a certified LSO to oversee laser safety programs, conduct risk assessments, and ensure compliance with ANSI Z136.1 or equivalent standards.
- Welder Certification: Operators must be certified in both arc welding (e.g., AWS D1.1) and laser safety procedures.
- Emergency Response Training: Train staff in emergency shutdown procedures, fire response (Class D extinguishers for metal fires), and first aid for laser or arc-related injuries.
Regulatory Compliance
- Laser Safety Standards: Follow IEC 60825 (international) or FDA/CDRH 21 CFR 1040.10 (U.S.) for laser classification, labeling, and safety controls.
- Electrical Safety: Comply with NFPA 70 (NEC) and local electrical codes for high-power welding equipment.
- Hazardous Materials: Manage shielding gases (e.g., argon, helium) according to OSHA 29 CFR 1910.101 and CGA standards for storage and handling.
- Noise Exposure: Monitor noise levels from arc and cooling systems; comply with OSHA 29 CFR 1910.95 or EU Directive 2003/10/EC.
Environmental & Waste Management
- Fume Filtration: Use HEPA-filtered extraction systems to capture nanoparticles and metallic particulates. Dispose of filter waste as hazardous material if applicable.
- Coolant Disposal: Recycle or dispose of laser cooling fluids per EPA or local environmental regulations.
- Scrap Metal Handling: Segregate and recycle welding scrap in accordance with RCRA (U.S.) or WEEE (EU) directives.
Operational Best Practices
- Pre-Operation Checks: Inspect lenses, nozzles, and shielding gas flow before each shift.
- Process Documentation: Maintain logs of welding parameters, maintenance, and safety inspections for traceability and audit readiness.
- Lockout/Tagout (LOTO): Implement LOTO procedures per OSHA 29 CFR 1910.147 during maintenance.
Audits & Continuous Compliance
- Conduct quarterly safety audits of laser enclosures, ventilation systems, and emergency controls.
- Review and update safety protocols annually or after process changes.
- Maintain records of certifications, training, and incident reports for at least five years.
Adhering to this logistics and compliance framework ensures safe, efficient, and legally compliant Laser Arc Welding operations across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and heavy manufacturing.
Conclusion on Sourcing Laser-Arc Hybrid Welding Technology:
Sourcing laser-arc hybrid welding technology represents a strategic investment for industries seeking high-precision, efficient, and robust joining solutions. This advanced welding process combines the deep penetration and speed of laser beam welding with the gap-bridging capability and tolerance to joint imperfections of arc welding, resulting in superior weld quality, increased productivity, and reduced operational costs over time.
When sourcing this technology, key considerations include selecting reliable equipment suppliers with proven expertise, ensuring compatibility with existing production systems, and investing in workforce training to fully leverage the process’s capabilities. While the initial capital expenditure may be higher compared to conventional welding methods, the long-term benefits—such as improved process stability, lower distortion, reduced post-weld rework, and greater automation potential—justify the investment for high-value manufacturing sectors like automotive, shipbuilding, aerospace, and heavy machinery.
Moreover, ongoing advancements in fiber lasers, process monitoring, and integration with robotics continue to enhance the accessibility and performance of laser-arc hybrid systems. Therefore, organizations that proactively adopt and integrate this technology position themselves at the forefront of manufacturing innovation, achieving competitive advantages in quality, efficiency, and sustainability.