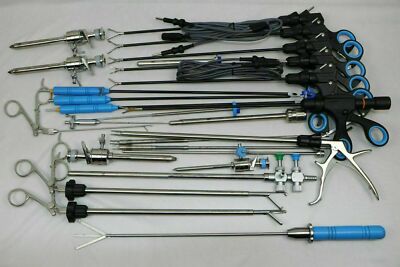
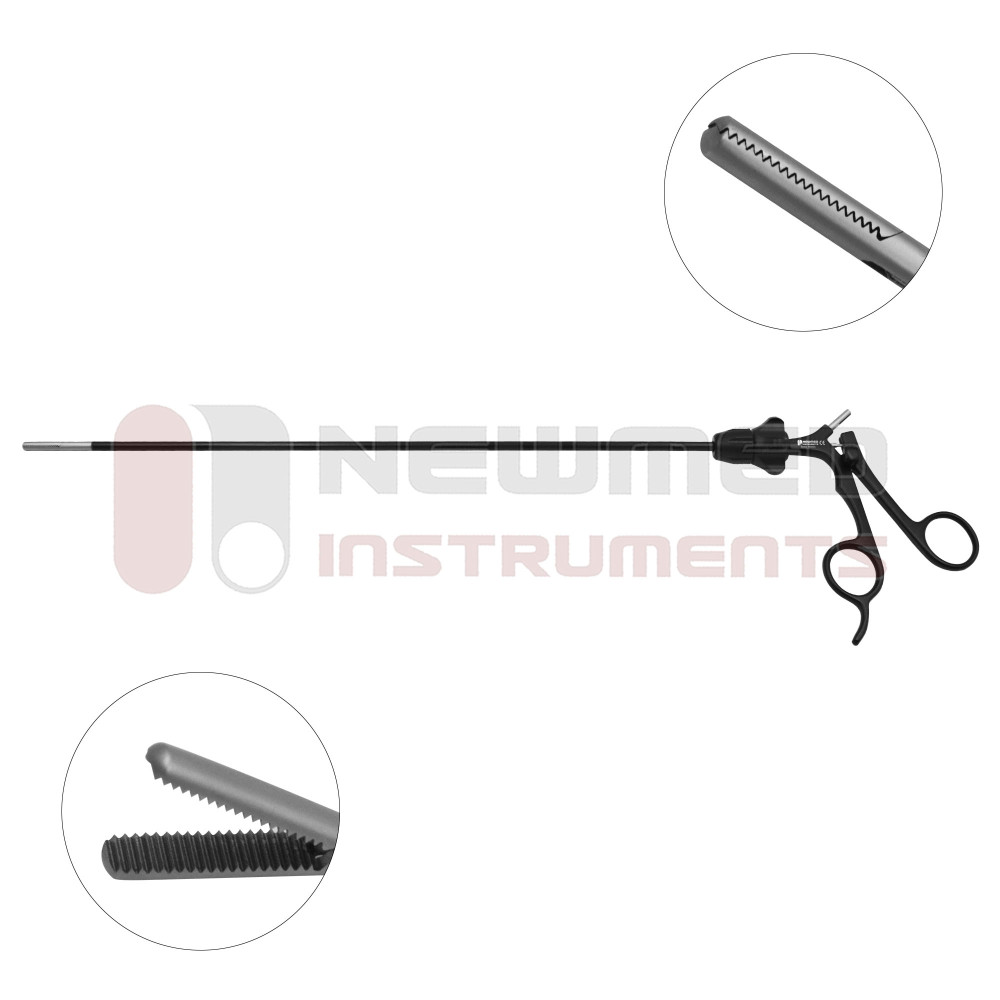
The global laparoscopic instruments market is experiencing robust growth, driven by the rising preference for minimally invasive surgeries, aging populations, and advancements in surgical technologies. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global laparoscopic devices market size was valued at USD 9.8 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.6% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects a CAGR of over 7.3% during the forecast period of 2023–2028, citing increasing procedural volumes and favorable healthcare reforms in emerging economies as key growth accelerators. With hospitals and ambulatory surgical centers adopting advanced laparoscopic tools to enhance precision and reduce recovery times, demand for high-quality instruments has surged. This growth has catalyzed intense innovation and competition among manufacturers, positioning the top players as critical enablers of modern surgical care. In this evolving landscape, identifying the leading laparoscopic instruments manufacturers becomes essential for healthcare providers aiming to optimize clinical outcomes and operational efficiency.
Top 10 Laparoscopic Instruments Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laparoscopic Instruments
Domain Est. 2004
Website: aesculapusa.com
Key Highlights: We offer a broad spectrum of laparoscopic instruments that enable minimally invasive surgery in a variety of specialties….
#2 Handcrafted precision
Domain Est. 2019
Website: ackermannsurgical.com
Key Highlights: Ackermann is a Full-Range-System Manufacturer … Industry-leading range of Laparoscopic specialty instruments including the all-new XPress Lock™ Mini Lap line….
#3 Laparoscopic Surgical Instruments for Precision
Domain Est. 1994
Website: steris.com
Key Highlights: Our industry-leading portfolio gives you over 300 configurations, from laparoscopes to laparoscopic scissors, to confidently accomplish nearly any surgical task ……
#4 Laparoscopic instrument
Domain Est. 1995
Website: karlstorz.com
Key Highlights: Here you will find an overview of all instruments for use in gynecological laparoscopy. Please select the desired subcategory….
#5 Laparoscopic & Robotic Instruments
Domain Est. 1995
Website: conmed.com
Key Highlights: For laparoscopic and robotic surgery, CONMED has a large portfolio of surgical instruments ranging from specimen bags to uterine manipulators to access and ……
#6 Encision
Domain Est. 1999
Website: encision.com
Key Highlights: Super sharp and exceptionally responsive, AEM enTouch Reposable 2x Scissors provide new levels of performance while reducing cost and waste….
#7 Advancing Perioperative Care with Aspen Surgical’s Portfolio of …
Domain Est. 1999
Website: aspensurgical.com
Key Highlights: Explore our broad array of perioperative products and solutions for hospitals, surgery centers and more — all from one trusted source….
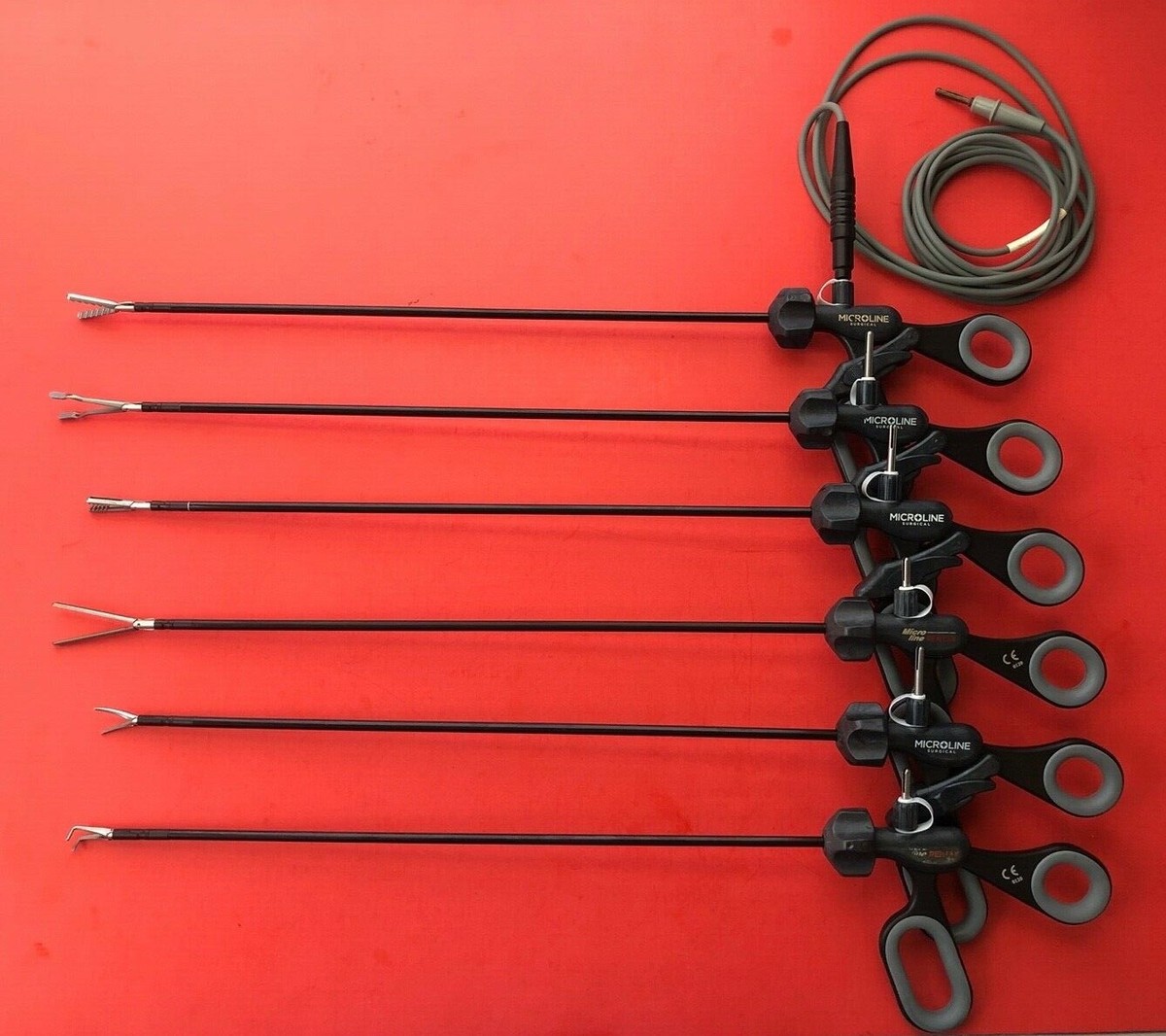
#8 Microline Surgical
Domain Est. 2009
Website: microlinesurgical.com
Key Highlights: Microline Surgical partners with healthcare providers to streamline intraoperative efficiencies and drive significant cost savings….
#9 Cipher Surgical
Domain Est. 2010
Website: ciphersurgical.com
Key Highlights: OpClear is the top choice for surgical equipment cleaners in laparoscopic procedures. Engineered for healthcare professionals worldwide….
#10 Laparoscopic Instruments & Surgical Solutions
Domain Est. 2024
Website: tecolimedical.com
Key Highlights: At TECOLI Medical, we have been dedicated to laparoscopic instruments for years, offering a full range of products from basic tools to advanced solutions….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laparoscopic Instruments

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Laparoscopic Instruments – Expansion Driven by Innovation, Minimally Invasive Demand, and Emerging Economies
The global laparoscopic instruments market is poised for robust growth by 2026, shaped by a confluence of technological advancements, shifting healthcare paradigms, and evolving patient preferences. Key trends indicate a market trajectory towards smarter, more precise, and accessible minimally invasive surgery (MIS).
1. Surge in Minimally Invasive Surgical Procedures: The dominant driver remains the overwhelming patient and provider preference for laparoscopic over open surgery. Benefits like reduced pain, shorter hospital stays, faster recovery, lower infection rates, and minimal scarring continue to fuel adoption across diverse procedures – from cholecystectomies and appendectomies to complex bariatric, colorectal, and gynecological surgeries. This fundamental shift ensures sustained demand for laparoscopic instruments.
2. Technological Innovation as a Key Growth Catalyst: The market is witnessing rapid innovation, pushing the boundaries of capability:
* Advanced Energy Devices: Integration of advanced bipolar energy (e.g., vessel sealing, tissue fusion) and ultrasonic devices into laparoscopic platforms enhances precision, reduces operative time, and improves hemostasis, becoming increasingly standard.
* Enhanced Visualization: High-definition (HD), 4K, and 3D laparoscopy are becoming mainstream, providing surgeons with superior depth perception and detail. Near-infrared (NIR) fluorescence imaging (e.g., ICG) is gaining traction for real-time perfusion assessment and lymph node mapping.
* Smart Instruments & Instrumentation: Development of “smart” instruments with integrated sensors for tissue feedback (e.g., force sensing, tissue characterization) and connectivity for data capture and workflow integration is emerging, paving the way for data-driven surgery.
* Disposable (Single-Use) Instruments: Driven by concerns over infection control (especially post-pandemic), reprocessing costs, and sterilization failures, the market for high-quality, reliable single-use laparoscopic instruments (especially trocars, graspers, dissectors) is expanding significantly, particularly in ambulatory surgery centers (ASCs) and regions with limited reprocessing infrastructure.
3. Rising Prevalence of Chronic Diseases: The growing global burden of obesity, cancer (colorectal, gynecological), and gastrointestinal disorders directly increases the need for surgical interventions, many of which are optimally treated laparoscopically. Bariatric surgery, in particular, is a major contributor to market growth.
4. Expansion in Ambulatory Surgery Centers (ASCs) and Outpatient Settings: The shift towards cost-effective, outpatient care is accelerating. ASCs are increasingly performing complex laparoscopic procedures. This trend favors instruments that are reliable, easy to use, and often disposable, reducing turnaround time and infection risk, further boosting demand for laparoscopic toolkits.
5. Growth in Emerging Economies: Markets in Asia-Pacific (especially India, China), Latin America, and parts of the Middle East & Africa are experiencing rapid growth. Factors include improving healthcare infrastructure, rising disposable incomes, increasing awareness of MIS benefits, government initiatives to expand surgical access, and growing medical tourism. Local manufacturing and partnerships are key strategies for market penetration.
6. Focus on Ergonomics and Surgeon Well-being: Recognition of surgeon fatigue and musculoskeletal injuries from prolonged laparoscopic procedures is driving demand for more ergonomic instrument designs, including wristed instruments, improved handle designs, and better articulation, enhancing surgical precision and reducing physical strain.
7. Regulatory and Reimbursement Landscape: Stringent regulatory requirements (FDA, CE Mark, MDR, NMPA) ensure safety and efficacy but can impact time-to-market. Reimbursement policies significantly influence adoption; favorable reimbursement for laparoscopic procedures compared to open surgery remains crucial for market growth, though cost-containment pressures persist.
8. Competitive Landscape Intensification: The market features a mix of large multinational players (Medtronic, Johnson & Johnson Ethicon, B. Braun, Stryker, Olympus) and innovative smaller companies. Competition is fierce, focusing on technological differentiation, cost-effectiveness (especially with disposables), service offerings, and strategic partnerships. Consolidation and collaborations are likely.
Conclusion: By 2026, the laparoscopic instruments market will be characterized by sustained growth driven by the irreversible shift towards minimally invasive surgery, accelerated by technological leaps in visualization, energy, and smart instrumentation, and fueled by the expanding needs of aging populations and rising healthcare access in emerging economies. The rise of single-use devices and the expansion of outpatient surgery will be defining features. Success will depend on innovation, cost-effectiveness, meeting evolving regulatory standards, and effectively addressing the needs of diverse global markets.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Laparoscopic Instruments (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing laparoscopic instruments involves navigating complex challenges related to both product quality and intellectual property (IP) rights. Overlooking these critical areas can lead to compromised patient safety, legal liabilities, financial losses, and reputational damage. Below are the key pitfalls to avoid:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inadequate Supplier Vetting and Audits
Failing to conduct thorough due diligence on manufacturers, especially those in low-cost regions, can result in partnering with suppliers lacking proper quality management systems. Without on-site audits, buyers may be unaware of poor manufacturing practices, substandard materials, or inconsistent quality control, leading to defective instruments.
2. Compromised Material and Manufacturing Standards
Sourcing instruments made from inferior-grade stainless steel or non-compliant materials can negatively impact durability, sterilization resistance, and biocompatibility. Instruments that do not meet ASTM or ISO standards (e.g., ISO 13485, ISO 7153) may fail during procedures, increasing the risk of complications.
3. Lack of Compliance with Regulatory Requirements
Procuring instruments that are not certified by regulatory bodies such as the FDA (USA), CE (Europe), or NMPA (China) can result in shipment seizures, market entry denials, or legal penalties. Mislabeling or incomplete documentation (e.g., missing UDI, IFU) further compounds compliance risks.
4. Inconsistent Quality Control and Testing
Suppliers may lack robust in-process and final product testing protocols. Instruments might not be tested for functionality (e.g., jaw alignment, insulation integrity, articulation smoothness), leading to intraoperative failures. Batch-to-batch variability is a common issue without stringent QC oversight.
5. Poor Sterilization and Packaging Practices
Instruments that are improperly cleaned, sterilized, or packaged can introduce infection risks. Non-sterile or compromised packaging undermines the safety and usability of reusable and single-use devices alike.
6. Insufficient Training and Support
Suppliers may fail to provide adequate training or technical support, leading to incorrect use, premature wear, or damage. This is particularly critical for advanced instruments like articulating or energy devices.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
1. Sourcing Counterfeit or IP-Infringing Devices
Purchasing from unauthorized distributors or gray market suppliers increases the risk of acquiring counterfeit instruments that mimic branded products. These devices often violate patents, trademarks, and copyrights, exposing buyers to legal action and liability for distribution of infringing goods.
2. Unintentional Use of Patented Technologies
Generic or “compatible” instruments may incorporate patented mechanisms (e.g., specific articulation systems, sealing technologies, or handle ergonomics) without licensing. Buyers risk becoming complicit in patent infringement, leading to lawsuits and injunctions.
3. Lack of IP Clearance in Contracts
Failing to include IP warranties and indemnification clauses in sourcing agreements leaves buyers vulnerable. If a supplier’s product is later found to infringe third-party IP, the buyer—not the supplier—may bear legal and financial consequences.
4. Misuse of Branding and Trademarks
Rebranded or private-labeled instruments that use logos, trade dress, or names confusingly similar to established brands can trigger trademark infringement claims, damaging brand reputation and inviting litigation.
5. Inadequate Documentation of IP Ownership
When developing custom instruments, unclear agreements about IP ownership between buyer and supplier can result in disputes over design rights, tooling ownership, and future manufacturing rights.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should:
– Conduct comprehensive supplier audits and demand certification evidence (ISO 13485, FDA registration).
– Request material certifications and independent testing reports.
– Verify regulatory approvals and ensure full traceability and labeling compliance.
– Perform IP due diligence by consulting legal experts to screen for infringement risks.
– Include strong IP protection clauses in procurement contracts.
– Source exclusively from authorized and reputable channels.
Proactively addressing quality and IP concerns ensures safer surgical outcomes, regulatory compliance, and long-term supply chain resilience.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laparoscopic Instruments
Laparoscopic instruments are critical medical devices used in minimally invasive surgical procedures. Ensuring their safe, efficient, and compliant logistics is essential to patient safety, regulatory adherence, and operational effectiveness. This guide outlines key considerations in managing the logistics and compliance of laparoscopic instruments across the supply chain.
Regulatory Classification and Standards
Laparoscopic instruments are typically classified as Class II medical devices under regulatory frameworks such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Union Medical Device Regulation (EU MDR). Compliance with international standards is mandatory and includes:
- ISO 13485: Quality management systems for medical devices
- ISO 14971: Risk management for medical devices
- IEC 60601-1: Safety requirements for medical electrical equipment (if applicable)
- FDA 21 CFR Part 820: Quality System Regulation (QSR)
- EU MDR 2017/745: For CE marking and market access in Europe
Manufacturers and distributors must maintain documentation proving conformity, including Technical Files, Design Dossiers, and Declarations of Conformity.
Labeling and Packaging Requirements
Proper labeling and packaging are vital for traceability, sterility maintenance, and regulatory compliance. Requirements include:
- UDI (Unique Device Identification): Mandatory in the U.S. (FDA) and EU (MDR). Each instrument or kit must bear a UDI barcode containing the device identifier (DI) and production identifier (PI).
- Sterile Barrier System (SBS): Packaging must ensure sterility until point of use. Materials must comply with ISO 11607 standards.
- Label Content: Include product name, model/lot numbers, expiry date (if applicable), manufacturer details, UDI, and sterilization method (e.g., EtO, gamma).
- Language Requirements: Labels and instructions for use (IFU) must be in the official language(s) of the destination country.
Transportation and Storage Conditions
Laparoscopic instruments must be protected from physical damage, contamination, and environmental extremes during transit and storage.
- Temperature and Humidity: Store in a clean, dry environment with controlled temperature (typically 15–30°C) and relative humidity (30–70%). Avoid condensation.
- Transportation: Use validated packaging and shipping methods. Instruments should be secured to prevent movement. For sterile devices, ensure integrity of the sterile barrier is maintained.
- Cold Chain (if applicable): While most laparoscopic tools do not require refrigeration, specific accessories or components (e.g., camera sensors, light cables) may have temperature-sensitive electronics.
- Shock and Vibration Protection: Use cushioning materials and rigid outer packaging to prevent mechanical damage.
Import and Export Compliance
Cross-border movement of laparoscopic instruments requires adherence to customs and trade regulations.
- Customs Documentation: Include commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading/airway bill, and certificates of origin.
- Regulatory Permits: Some countries require import licenses or prior notification to health authorities (e.g., ANVISA in Brazil, Health Canada).
- Tariff Classification: Use correct HS (Harmonized System) codes (e.g., 9018.90 for surgical instruments) to determine duties and taxes.
- Restricted Substances: Ensure compliance with REACH (EU), RoHS (electronics), and other chemical restriction regulations.
Sterilization and Reuse Protocols
For reusable laparoscopic instruments, strict reprocessing protocols must be followed:
- Cleaning: Manual or automated (washer-disinfector) cleaning per manufacturer IFU. Remove all organic debris.
- Inspection and Maintenance: Visual and functional checks for damage, insulation integrity (for electrosurgical tools), and moving parts.
- Sterilization: Typically via steam autoclaving (121–134°C) or low-temperature methods (e.g., hydrogen peroxide plasma). Follow validated cycles per IFU.
- Validation: Sterilization processes must be regularly monitored and validated per ISO 17665 (steam) and ISO 14937 (chemical sterilization).
Single-use devices must not be reprocessed unless explicitly cleared by regulatory authorities and the original manufacturer.
Traceability and Recall Management
Robust traceability systems are essential for patient safety and regulatory reporting.
- UDI Implementation: Enables tracking from manufacturer to patient.
- Distribution Records: Maintain logs of consignees, quantities shipped, and delivery dates.
- Recall Procedures: Establish a formal process for initiating, communicating, and executing field safety corrective actions (FSCAs). Report to relevant authorities (e.g., FDA MedWatch, EUDAMED).
- Post-Market Surveillance (PMS): Monitor adverse events and implement corrective actions per regulatory requirements.
Environmental and Disposal Considerations
- Waste Classification: Reusable instruments are maintained; single-use devices are treated as medical waste after use.
- Disposal Compliance: Follow local regulations for biohazardous and electronic waste (e.g., WEEE Directive in EU for devices with electronics).
- Sustainability: Consider reprocessing programs for single-use devices where legally permitted and validated.
Training and Competency
All personnel involved in handling, transporting, sterilizing, or using laparoscopic instruments must be trained in:
- Device-specific handling and storage
- Infection control and aseptic technique
- Regulatory requirements and documentation
- Emergency response (e.g., recalls, device malfunctions)
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance for laparoscopic instruments require a cross-functional approach integrating regulatory knowledge, quality systems, and supply chain best practices. Adherence to international standards, proper documentation, and vigilant monitoring ensure patient safety, legal compliance, and operational continuity throughout the product lifecycle.
Conclusion for Sourcing Laparoscopic Instruments:
Sourcing high-quality laparoscopic instruments is a critical factor in ensuring the success, safety, and efficiency of minimally invasive surgical procedures. A strategic and well-informed procurement process—taking into account instrument quality, regulatory compliance, supplier reliability, cost-effectiveness, and compatibility with existing surgical systems—is essential for healthcare institutions aiming to deliver optimal patient outcomes. By prioritizing vendors with proven track records, adherence to international standards (such as ISO and FDA), and strong post-purchase support, hospitals and surgical centers can maintain operational excellence and reduce long-term expenses related to instrument failure or frequent replacements. Furthermore, investing in reusable, durable instruments with proper sterilization and maintenance protocols not only supports sustainability but also enhances cost efficiency over time. In conclusion, a comprehensive and diligent approach to sourcing laparoscopic instruments ensures clinical reliability, cost savings, and improved surgical performance, ultimately contributing to higher standards of patient care.