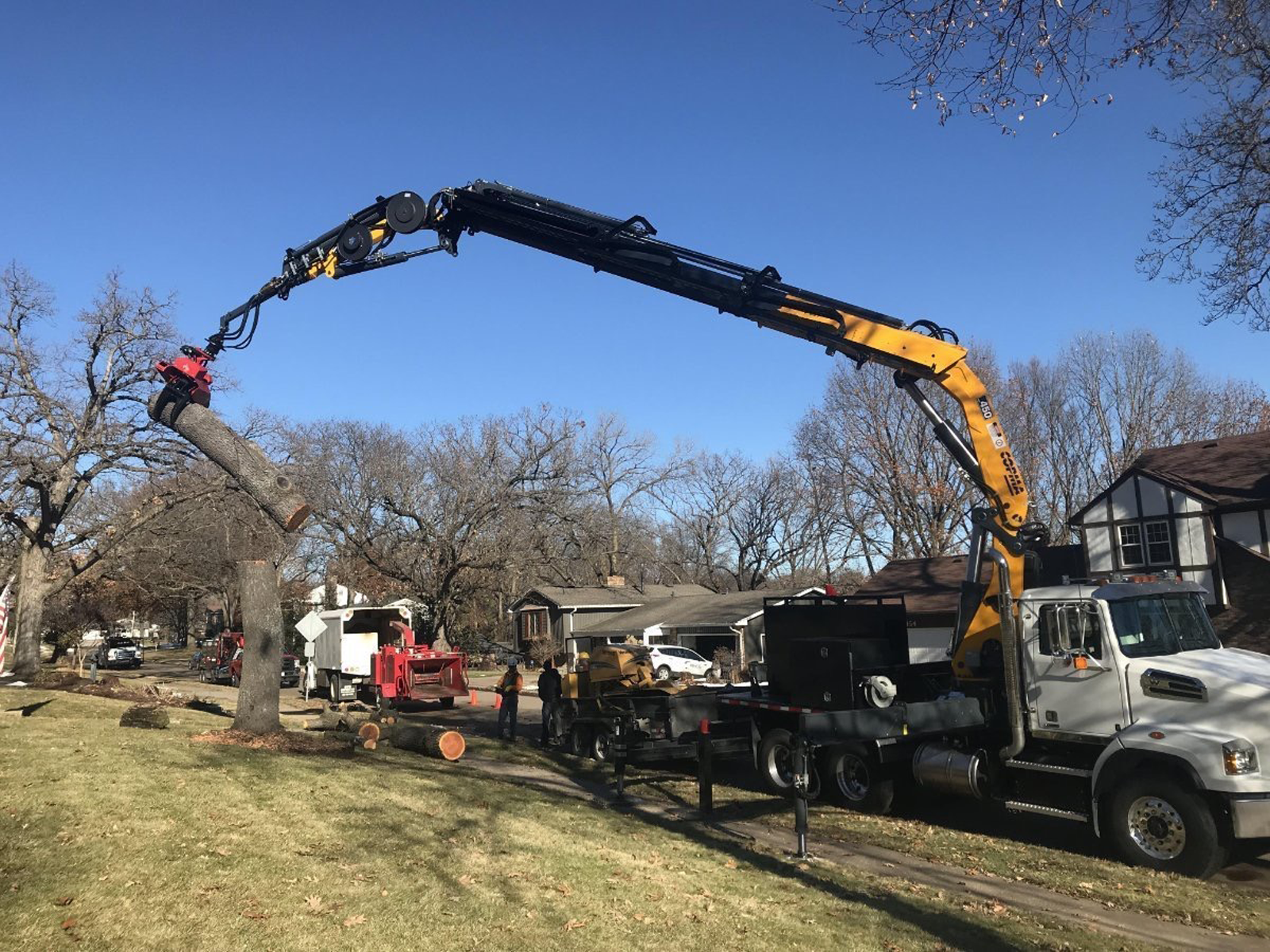
The global knuckle boom loader market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for versatile and efficient material handling equipment across forestry, construction, and waste management sectors. According to Mordor Intelligence, the knuckle boom loader market was valued at approximately USD 2.1 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 5.8% from 2024 to 2029. This expansion is fueled by rising investments in infrastructure development, technological advancements in hydraulic systems, and the growing preference for compact, multifunctional machinery that enhances operational efficiency in constrained environments. As demand intensifies, several manufacturers have emerged as leaders, combining innovation, durability, and smart integration features to capture significant market share. The following analysis highlights the top 8 knuckle boom manufacturers shaping the industry’s future through engineering excellence and global reach.
Top 8 Knuckle Boom Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Knuckle Boom Cranes With Superior Performance
Domain Est. 1996
Website: hiab.com
Key Highlights: HIAB Knuckle Boom Cranes are industry leaders in performance, safety, and efficiency, with superior design and build and cutting edge technology….
#2 Knuckleboom Crane
Domain Est. 2001
Website: knuckleboom.com
Key Highlights: We offer a broad range of Knuckleboom Cranes from all major manufacturers, custom built cranes and crane trucks, sales, service, parts and repair….
#3 Altec Truck Mounted Cranes
Domain Est. 1996
Website: altec.com
Key Highlights: Altec offers a wide variety of truck mounted cranes. We offer both telescopic boom truck cranes and articulating knuckle boom cranes….
#4 Knuckle Boom Cranes
Domain Est. 1997
Website: palfinger.com
Key Highlights: PALFINGER offers some of the most durable knuckle boom cranes in the industry. With a comprehensive range of models covering the entire range of working….
#5 Knuckleboom Crane
Domain Est. 1998
Website: alliedsystems.com
Key Highlights: A versatile crane with the ability to work in tight spaces, the Allied Marine Knuckleboom crane is a perfect solution for a number of applications….
#6 Knuckle Boom Mobile Cranes
Domain Est. 2000
Website: jomacltd.com
Key Highlights: The Only Knuckle Boom Articulating Cranes Manufactured and Engineered 100% in the USA. As a leader in service truck crane manufacturing, JOMAC is the only ……
#7 Knuckle Boom Loader Cranes
Domain Est. 2006
Website: hmfcranes.com
Key Highlights: The hydraulic knuckle boom (K) loader crane is our core product and most popular crane. See our selection of K-cranes with compact design, easy storage and ……
#8 COPMA
Domain Est. 2015
Website: cps-group.com
Key Highlights: COPMA knuckle booms are built tough while preserving an easy-to-use design for giving operators the power of handling heavy precast construction materials and ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Knuckle Boom

H2 2026 Market Trends for Knuckle Boom Cranes
The knuckle boom crane market in the second half of 2026 is expected to be shaped by a confluence of technological advancements, evolving regulations, economic shifts, and growing demand for efficiency and sustainability. Here’s an analysis of the key trends anticipated for this period:
1. Accelerated Electrification and Alternative Powertrains:
* Trend: H2 2026 will see a significant acceleration in the adoption of fully electric (battery-electric) knuckle booms, moving beyond niche applications. Expect wider availability from major manufacturers (e.g., HIAB, Palfinger, Fassi, Effer) across various lifting capacities.
* Drivers: Stricter urban emissions regulations (e.g., Low/Zero Emission Zones expanding in European and North American cities), corporate ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) targets, and decreasing battery costs will be primary drivers.
* Impact: Increased demand for electric models in urban logistics, utility work, and municipal applications. Hybrid solutions (diesel-electric) will remain relevant for applications requiring longer range or higher continuous power, but pure electric will gain substantial market share. Focus will shift to improving battery life, charging infrastructure integration, and total cost of ownership (TCO) calculations favoring electric.
2. Proliferation of Advanced Automation and Connectivity:
* Trend: Smart Crane Technology will become standard or highly desirable. This includes:
* Enhanced Telematics: Real-time monitoring of crane health (hydraulics, wear parts), operator behavior, fuel/energy consumption, and precise location tracking will be ubiquitous for fleet optimization and predictive maintenance.
* Semi-Autonomous Functions: Features like automated load leveling, optimized swing control, and guided positioning (using sensors and cameras) will improve safety and efficiency, reducing operator workload and training time.
* Remote Monitoring & Diagnostics: Cloud platforms will allow manufacturers and dealers to proactively identify potential issues and offer remote support.
* Drivers: Demand for improved safety, operational efficiency, reduced downtime, and data-driven fleet management. The rise of Industry 4.0 principles in construction and logistics.
* Impact: Cranes will generate valuable data for optimizing operations and maintenance. Cybersecurity will become a critical consideration. Training will increasingly focus on data interpretation and system management alongside traditional crane operation.
3. Focus on Lightweighting and Efficiency:
* Trend: Continued development and use of advanced high-strength steels (AHSS) and potentially composite materials to reduce crane weight without compromising strength or reach.
* Drivers: The need for improved fuel efficiency (for diesel models), increased payload capacity for electric trucks (where battery weight is significant), and meeting stricter vehicle CO2 regulations (especially in Europe).
* Impact: Lighter cranes will allow for more payload on the truck, extending range for electric models, or enabling smaller, more efficient carrier vehicles. This trend supports the overall sustainability push.
4. Customization and Application-Specific Solutions:
* Trend: Increased demand for highly customized cranes tailored to specific applications (e.g., specialized forestry, renewable energy installation, specialized utility work, waste management). This includes integrated tool carriers, specific hydraulic configurations, and unique mounting solutions.
* Drivers: Need for maximum productivity and safety in specialized tasks. Growth in niche sectors like offshore wind maintenance and solar farm construction.
* Impact: Manufacturers will offer more modular platforms and flexible configuration options. Partnerships between crane makers and specialized equipment providers will grow.
5. Supply Chain Maturation and Regional Dynamics:
* Trend: The supply chain for critical components (especially batteries, advanced electronics, specific steels) will be more mature than in 2025, leading to improved availability and potentially lower costs for new technologies. However, geopolitical factors and raw material (e.g., lithium, cobalt) availability will remain watchpoints.
* Drivers: Increased production volumes for EVs and related technologies benefiting the crane sector, coupled with ongoing efforts to diversify supply chains.
* Impact: Smoother production ramp-up for electric and advanced cranes. Regional manufacturing hubs (e.g., North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific) may see different adoption rates based on local regulations and economic conditions. Emerging markets might see growth in more affordable, efficient diesel models.
6. Sustainability as a Core Value Proposition:
* Trend: Sustainability will move beyond just emissions. Circular economy principles will gain traction, including:
* Design for easier disassembly and component reuse/recycling.
* Increased availability of certified remanufactured cranes and components.
* Focus on reducing the environmental impact throughout the entire lifecycle.
* Drivers: Regulatory pressure, corporate sustainability goals, and customer demand for greener solutions.
* Impact: “Green” credentials will be a major differentiator in marketing and procurement decisions. Lifecycle cost analysis will increasingly include environmental impact.
Conclusion for H2 2026:
The knuckle boom market in the latter half of 2026 will be characterized by a decisive shift towards electrification, intelligence, and sustainability. Electric models will transition from emerging to mainstream, particularly in urban and regulated environments. Data connectivity and automation will become standard features, fundamentally changing how cranes are operated, maintained, and managed. Efficiency, both in terms of energy consumption and operational productivity, will be paramount. Manufacturers who successfully integrate advanced technology, offer sustainable solutions, and provide robust data services will be best positioned to lead the market. Customers will increasingly evaluate cranes not just on lifting capacity and price, but on their total cost of ownership, environmental impact, and contribution to operational data and efficiency.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Knuckle Boom Cranes (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing knuckle boom cranes—whether for integration into larger machinery or as standalone equipment—can be complex. Buyers often encounter significant challenges related to quality standards and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to operational failures, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Below are key pitfalls to avoid.
Poor Manufacturing Quality and Substandard Components
One of the most frequent issues in sourcing knuckle boom cranes is receiving units built with inferior materials or inadequate workmanship. This often occurs when manufacturers cut costs by using low-grade steel, subpar hydraulic systems, or outdated control technologies. Such compromises result in reduced lifting capacity, shorter service life, and increased maintenance costs. Buyers may also face safety risks due to structural weaknesses or failure under load.
To mitigate this, conduct thorough supplier audits, request third-party certifications (e.g., ISO 9001, CE marking), and demand material test reports. Requiring factory acceptance tests (FATs) before shipment can verify performance and reliability.
Lack of Compliance with Regional Safety and Environmental Standards
Knuckle boom cranes must meet specific regional regulatory requirements, such as EU Machinery Directive, OSHA standards in the U.S., or local load safety regulations. Sourcing from manufacturers unfamiliar with these standards—or those who falsify compliance—can lead to rejected shipments, costly modifications, or operational shutdowns.
Ensure suppliers provide documentation proving compliance with applicable standards. Engage independent inspectors to verify adherence during production.
Inadequate After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Many buyers focus on initial price and technical specifications but overlook long-term serviceability. Sourcing from suppliers with weak global support networks can result in extended downtime due to unavailable spare parts or lack of trained technicians. This is especially critical for specialized components like hydraulic valves, control systems, and articulated joints.
Evaluate the supplier’s service infrastructure, including spare parts inventory, technical documentation, and response time guarantees. Consider entering into service-level agreements (SLAs) to secure ongoing support.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Sourcing knuckle boom cranes from regions with lax IP enforcement exposes buyers to legal and reputational risks. Some manufacturers reverse-engineer branded designs (e.g., HIAB, Palfinger) without licensing, producing “clone” units that infringe on patents, trademarks, or design rights. Purchasing such equipment—even unknowingly—can result in customs seizures, litigation, or liability for contributory infringement.
Conduct due diligence on the supplier’s IP portfolio. Request proof of design ownership, patents, or licensing agreements. Avoid suppliers offering “compatible” or “equivalent” models that closely mimic protected designs.
Hidden Design Copying and Lack of Innovation
Even when not outright infringing, some suppliers replicate functional aspects of established models without adding value or innovation. This “me-too” engineering often results in inferior performance, poor ergonomics, or inefficient hydraulics. Buyers may end up with cranes that look similar but underperform in real-world conditions.
Evaluate design documentation, engineering capabilities, and R&D investment. Request performance data from field tests and compare cycle times, fuel efficiency, and control responsiveness.
Incomplete or Misleading Technical Documentation
Poorly translated or incomplete manuals, schematics, and maintenance guides hinder safe operation and troubleshooting. Missing IP-related disclaimers or unclear origin of design can also complicate liability in case of accidents or failures.
Require comprehensive, multilingual technical documentation that includes safety instructions, exploded parts diagrams, and warranty terms. Verify that documentation clearly states original design ownership.
Failure to Secure IP Rights in Custom Designs
When sourcing custom-engineered knuckle boom cranes, buyers often assume they own the design. However, without clear contractual terms, suppliers may retain IP rights, limiting the buyer’s ability to modify, reproduce, or service the equipment independently.
Always include IP assignment clauses in procurement contracts. Ensure that custom designs, software, and technical drawings are explicitly transferred to the buyer upon full payment.
By addressing these quality and IP-related pitfalls proactively, businesses can source reliable, compliant, and legally secure knuckle boom cranes that deliver long-term value.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Knuckle Boom Cranes
Overview of Knuckle Boom Crane Transportation
Knuckle boom cranes, also known as articulated cranes, are specialized lifting equipment commonly mounted on trucks for material handling in construction, forestry, and utility sectors. Due to their size, weight, and configuration, transporting and operating these cranes involves strict logistics planning and regulatory compliance. This guide outlines key considerations for safe and legal transportation and use.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Federal and State Regulations
Transporting knuckle boom cranes across jurisdictions requires adherence to federal and state transportation laws. In the U.S., the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) and Department of Transportation (DOT) set baseline rules, while individual states may impose additional restrictions on dimensions, weight, and permitting.
Oversize/Overweight Permits
Most knuckle boom cranes exceed standard vehicle size or weight limits when mounted or in transit. Operators must obtain oversize/overweight permits from state transportation departments when necessary. Permits typically specify approved routes, travel times, and escort vehicle requirements.
Load Securement Standards
Per FMCSA’s Cargo Securement Rules (49 CFR Part 393, Subpart I), cranes must be properly secured during transit. This includes using rated tie-downs, chocks, and blocking to prevent shifting. The crane’s boom must be stowed in the travel position and locked with manufacturer-provided restraints.
Pre-Transportation Planning
Route Survey and Planning
Conduct a thorough route assessment to identify low bridges, narrow roads, sharp turns, and weight-restricted infrastructure. Use GPS tools with oversized load routing capabilities and consult state DOT databases for restrictions.
Vehicle and Crane Inspection
Prior to transport, inspect the carrier vehicle and crane for mechanical integrity. Check tires, brakes, lights, hydraulic systems, boom locks, and mounting bolts. Ensure all safety decals and load charts are visible and legible.
Operational Compliance
Operator Certification
Operators must be trained and certified per OSHA 29 CFR 1926.1400 (in the U.S.) for crane operation. Certification includes understanding load charts, stability, rigging, and signal communication. Employers must maintain records of training and evaluations.
Load Chart Adherence
Always operate the crane within the parameters of the manufacturer’s load chart. Never exceed rated capacities based on boom angle, radius, or configuration. Environmental factors like wind speed and ground conditions must also be considered.
Worksite Safety Protocols
Establish exclusion zones, use proper signaling, and conduct daily pre-use inspections. Ensure ground conditions support crane setup—use outriggers and crane pads on unstable or soft surfaces. Comply with site-specific safety plans and permit requirements.
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Required Documentation
Maintain up-to-date records including:
– Crane inspection logs (daily, monthly, annual)
– Operator certifications
– Maintenance and repair history
– Oversize/overweight permits
– Bill of lading and transport manifests
Compliance Audits
Regular internal audits ensure adherence to DOT, OSHA, and company safety policies. Audit findings should drive corrective actions and continuous improvement in logistics and operational procedures.
Special Considerations
Cross-Border Transport (U.S./Canada/Mexico)
When transporting internationally, comply with regulations from each country’s transportation authority. Harmonized standards exist under the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) framework, but permits, documentation, and safety requirements may vary.
Seasonal and Environmental Factors
Winter weather, high winds, and extreme temperatures impact crane transport and operation. Adjust logistics plans accordingly—use snow chains, delay travel during storms, and follow freeze-thaw protocols for hydraulic systems.
Conclusion
Proper logistics and compliance management for knuckle boom cranes ensures operational safety, regulatory adherence, and legal protection. By following federal and state guidelines, conducting thorough planning, and maintaining accurate documentation, companies can minimize risks and maximize efficiency in crane transportation and use.
Conclusion on Sourcing a Knuckle Boom Loader
Sourcing a knuckle boom loader requires a strategic approach that balances performance, cost, reliability, and long-term operational needs. After evaluating key suppliers, market options, and technical specifications, it is evident that selecting the right knuckle boom involves considering factors such as lifting capacity, reach, compatibility with existing machinery, maintenance requirements, and after-sales support.
Opting for reputable manufacturers ensures access to high-quality components, advanced hydraulic systems, and innovative features like intelligent controls and ergonomic design, which enhance productivity and safety. Additionally, evaluating total cost of ownership—including purchase price, fuel efficiency, service intervals, and spare parts availability—leads to a more sustainable investment.
For operations requiring versatility in forestry, construction, or material handling, a well-sourced knuckle boom significantly improves efficiency and reduces downtime. Therefore, conducting thorough due diligence, seeking references, and possibly engaging in product demonstrations or trial periods are recommended final steps before procurement.
In conclusion, a carefully sourced knuckle boom loader not only meets current operational demands but also supports scalability, safety, and cost-effectiveness in the long term. Choosing the right partner and model will ensure optimal performance and a solid return on investment.