The global moisture analysis market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by increasing quality control demands across pharmaceuticals, food and beverages, chemicals, and energy sectors. According to a 2023 report by Grand View Research, the global moisture analyzer market was valued at approximately USD 540 million and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by regulatory requirements, advancements in analytical instrumentation, and the need for precise moisture content measurement to ensure product stability and compliance. Karl Fischer titration, recognized for its accuracy and specificity in water content determination, remains a gold standard in moisture analysis—making Karl Fischer moisture analyzers a critical tool in modern laboratories. As demand rises, several manufacturers have emerged as leaders, combining innovation, precision engineering, and global reach. Below are the top seven Karl Fischer moisture analyzer manufacturers shaping the industry landscape.
Top 7 Karl Fischer Moisture Analyzer Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
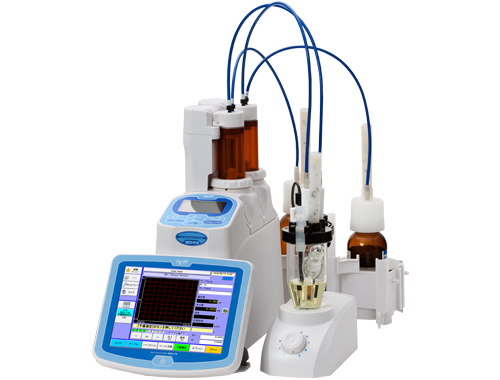
#1 Karl Fischer Titrators
Domain Est. 1993
Website: mt.com
Key Highlights: A Karl Fischer (KF) titrator is an instrument that is used to determine the water content in liquid or solid samples. Accurate determination of water ……
#2 Karl Fischer Titration
Domain Est. 1995
Website: fishersci.com
Key Highlights: Karl Fischer (KF) titration is the universally accepted method for determining water content in a variety of samples….
#3 Volumetric and coulometric Karl Fischer titrators
Domain Est. 1996
Website: metrohm.com
Key Highlights: Volumetric titrators and coulometric titrators for moisture determination from 0.001 to 100% water content in liquid, solid, or gaseous samples….
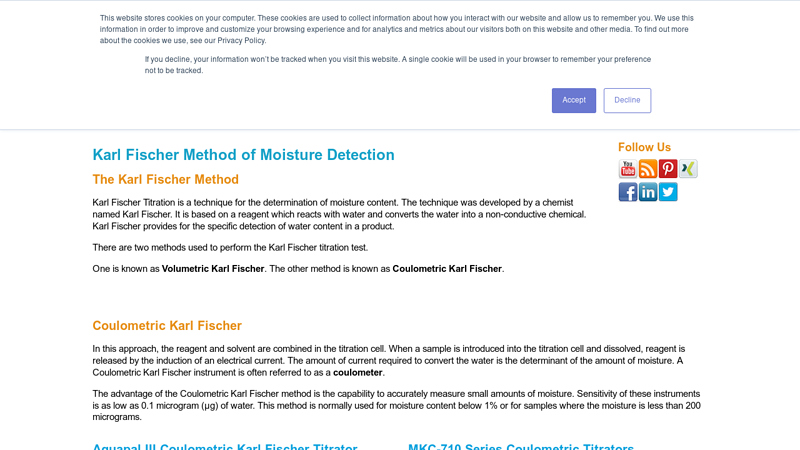
#4 Karl Fischer Method of Moisture Detection
Domain Est. 1997
Website: cscscientific.com
Key Highlights: Karl Fischer Titration is a technique for the determination of moisture content. The technique was developed by a chemist named Karl Fischer….
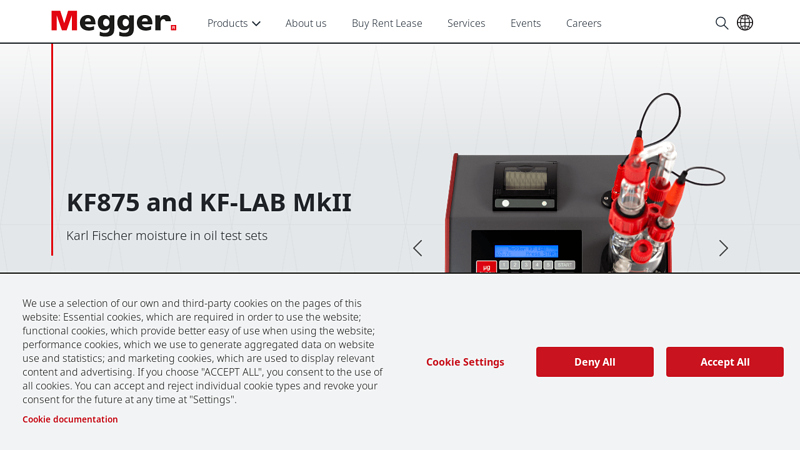
#5 KF875 and KF
Domain Est. 2001
Website: megger.com
Key Highlights: The KF875 and KF-LAB MkII Karl Fischer moisture test sets provide accurate on-site moisture measurement. They are portable with an integral printer….
#6 KF Moisture Titrator
Domain Est. 2020
Website: kem.kyoto
Key Highlights: Karl Fischer Reagent “KEMAQUA Series” is a reagent made by Kyoto Electronics Manufacturing for use with Karl Fischer Moisture titrator….
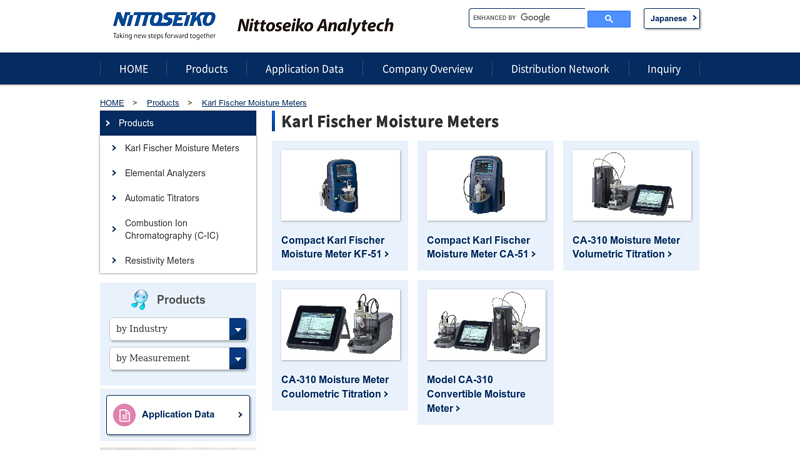
#7 Karl Fischer Moisture Meters
Website: n-analytech.co.jp
Key Highlights: Products · Compact Karl Fischer Moisture Meter KF-51 · Compact Karl Fischer Moisture Meter CA-51 · CA-310 Moisture Meter Volumetric Titration · CA-310 Moisture ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Karl Fischer Moisture Analyzer

H2: Market Trends for Karl Fischer Moisture Analyzers in 2026
As the global demand for precision in moisture content analysis continues to grow across regulated industries, the Karl Fischer (KF) Moisture Analyzer market is poised for significant evolution by 2026. Driven by advancements in automation, stringent quality control requirements, and expanding applications in pharmaceuticals, chemicals, food and beverages, and materials science, several key trends are shaping the landscape of this specialized analytical instrumentation sector.
-
Increased Adoption of Automated and Smart Analyzers
By 2026, automation is expected to dominate the KF moisture analyzer market. Fully automated systems integrated with robotic sample changers, AI-driven data interpretation, and IoT connectivity are enabling high-throughput laboratories to improve efficiency and reduce human error. These “smart” analyzers offer remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and seamless integration with Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS), aligning with the broader Industry 4.0 movement. -
Growth in Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology Applications
The pharmaceutical industry remains the largest end-user of KF analyzers due to strict regulatory compliance (e.g., USP <921>, EP 2.5.12). With the rise of biologics, mRNA vaccines, and personalized medicine, precise moisture control in lyophilized products and raw materials is critical. By 2026, demand for high-precision, low-maintenance KF titrators with compliance-ready software will accelerate, particularly in emerging markets with expanding pharma manufacturing capabilities. -
Expansion in Food and Beverage Quality Control
Food safety standards and consumer demand for longer shelf life are pushing manufacturers to adopt advanced moisture analysis. KF analyzers are increasingly used to measure water content in dairy, grains, confectionery, and dehydrated foods. Miniaturized and portable KF systems are expected to gain traction in on-site quality checks, supporting real-time decision-making in production environments. -
Shift Toward Coulometric and Volumetric Hybrid Systems
While volumetric KF remains common for high-moisture samples, coulometric methods dominate trace moisture analysis. By 2026, hybrid instruments capable of both techniques in a single platform are gaining popularity, offering laboratories greater flexibility and cost efficiency. These systems reduce reagent consumption and waste, aligning with green chemistry initiatives. -
Rise of Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Solutions
Environmental regulations are driving innovation in reagent formulations. Non-toxic, biodegradable alternatives to traditional pyridine-based reagents are being adopted to reduce environmental impact. Equipment manufacturers are responding by designing analyzers with lower solvent consumption and closed-loop reagent systems, appealing to sustainability-focused enterprises. -
Geographic Market Shifts and Regional Growth
Asia-Pacific, particularly China, India, and South Korea, is projected to be the fastest-growing region for KF moisture analyzers by 2026. This growth is fueled by expanding pharmaceutical production, increasing food safety regulations, and government investments in R&D infrastructure. Meanwhile, North America and Europe maintain strong markets due to established regulatory frameworks and continual technological upgrades. -
Integration with Complementary Analytical Technologies
To enhance analytical workflows, KF moisture analyzers are increasingly being paired with other technologies such as near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). These hybrid approaches allow for faster screening and cross-validation, improving data reliability and decision-making speed in quality assurance labs.
In conclusion, the 2026 market for Karl Fischer Moisture Analyzers reflects a convergence of technological innovation, regulatory demands, and sustainability goals. Manufacturers who prioritize automation, compliance, and environmental responsibility are likely to lead the market, while end-users benefit from more accurate, efficient, and adaptable moisture analysis solutions.

H2: Common Pitfalls in Sourcing a Karl Fischer Moisture Analyzer – Quality and Intellectual Property (IP) Concerns
Sourcing a Karl Fischer Moisture Analyzer involves several technical, regulatory, and commercial considerations. Two critical areas where organizations often encounter pitfalls are product quality and intellectual property (IP) risks. Understanding these challenges is essential to ensure reliable performance, regulatory compliance, and protection against legal or operational setbacks.
1. Quality-Related Pitfalls
a. Substandard Instrument Performance
- Issue: Some suppliers, particularly low-cost manufacturers, may offer instruments with poor accuracy, repeatability, or stability due to inferior components (e.g., low-grade electrodes, pumps, or reagent handling systems).
- Impact: Inaccurate moisture measurements can compromise product quality in industries such as pharmaceuticals, food, and chemicals—where moisture content directly affects safety, shelf life, and compliance.
- Mitigation: Verify compliance with international standards (e.g., USP <921>, ASTM E1064, ISO 760) and request third-party calibration certificates. Prefer suppliers with documented quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001).
b. Lack of Validation Support
- Issue: Many vendors, especially those without a strong presence in regulated industries, fail to provide adequate documentation for instrument qualification (IQ/OQ/PQ).
- Impact: This creates hurdles in GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) environments, delaying deployment and risking audit findings.
- Mitigation: Source from manufacturers or distributors experienced in regulated sectors who provide full validation packages and 21 CFR Part 11 compliance (for software-enabled models).
c. Poor After-Sales Service and Spare Parts Availability
- Issue: Low-cost analyzers may be backed by limited technical support or long lead times for critical consumables (e.g., KF reagents, generator electrodes).
- Impact: Extended downtime and inconsistent performance reduce ROI and reliability.
- Mitigation: Evaluate supplier service networks, response times, and availability of local service engineers before procurement.
2. Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
a. Counterfeit or Clone Instruments
- Issue: Some suppliers offer devices that mimic the design and functionality of established brands (e.g., Mettler Toledo, Hanna Instruments) without proper licensing.
- Impact: These clones may infringe on patents, trademarks, or software copyrights, exposing the buyer to legal liability or product seizure, especially in regulated markets.
- Mitigation: Purchase through authorized distributors. Conduct due diligence on the manufacturer’s IP portfolio and verify original equipment manufacturer (OEM) status.
b. Proprietary Software and Firmware Concerns
- Issue: Certain analyzers use embedded software protected by IP laws. Unauthorized modifications or use of pirated software can violate licensing agreements.
- Impact: Non-compliance may lead to audit failures, software malfunctions, or legal action.
- Mitigation: Ensure software is genuine and regularly updated by the manufacturer. Avoid third-party firmware unless legally licensed.
c. Unclear Ownership of Method Data and Algorithms
- Issue: Some advanced KF analyzers include proprietary titration algorithms or method libraries. Buyers may unknowingly waive rights to data or face restrictions on data export or integration.
- Impact: Limits flexibility in data management and system integration (e.g., LIMS).
- Mitigation: Review licensing agreements carefully. Confirm data ownership and interoperability before purchase.
Conclusion
Sourcing a Karl Fischer Moisture Analyzer requires more than cost comparison. Quality pitfalls—such as unreliable performance and lack of validation support—can undermine analytical integrity. Meanwhile, IP risks—including counterfeit devices and software violations—pose legal and operational threats. To mitigate these, organizations should prioritize reputable suppliers, demand compliance documentation, and conduct thorough IP due diligence. Procuring from established, authorized vendors ensures both technical reliability and legal safety.

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Karl Fischer Moisture Analyzer
Proper logistics handling and regulatory compliance are essential for the safe, efficient, and legal transport, installation, and operation of a Karl Fischer (KF) Moisture Analyzer. This guide outlines key considerations to ensure adherence to international, national, and site-specific requirements.
H3: Logistics Considerations
- Packaging and Handling
- Ensure the analyzer arrives in its original manufacturer-approved packaging, including shock-absorbing materials and protective casing.
- Label packages as “Fragile” and “This Side Up” to prevent damage during transit.
- Use trained personnel or certified freight handlers for loading/unloading; avoid dropping or tilting beyond manufacturer specifications.
-
Store in a climate-controlled, dry, and dust-free environment prior to installation (typically 15–25°C, 30–60% RH).
-
Transportation
- Use reputable carriers experienced in laboratory equipment logistics.
- For international shipments, comply with IATA (air) or IMDG (sea) regulations if shipping with reagents (see Compliance section).
-
Maintain a chain of custody and documentation (e.g., packing list, bill of lading, insurance).
-
Installation Site Preparation
- Verify power supply meets specifications (voltage, frequency, grounding).
- Ensure stable, vibration-free work surface capable of supporting analyzer weight.
- Provide adequate ventilation; avoid direct sunlight or heat sources.
-
Confirm availability of required consumables (KF reagents, solvents, electrodes, titration vessels).
-
Cold Chain (if applicable)
- Certain KF reagents (e.g., unsolvated reagents, electrodes) may require temperature-controlled transport. Monitor and document temperature throughout shipment.
H3: Compliance Requirements
- Chemical Safety (Reagents & Solvents)
- GHS/CLP Compliance: KF reagents (e.g., methanol, iodine, sulfur dioxide, pyridine-based or pyridine-free titrants) are often hazardous. Ensure all reagents are labeled with GHS pictograms, signal words, hazard statements (H-codes), and precautionary statements (P-codes).
- SDS Availability: Maintain updated Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for all reagents and solvents, accessible to all users.
-
Storage: Store flammable and toxic reagents in approved safety cabinets (flammable storage cabinets for methanol), segregated by compatibility. Follow local fire codes.
-
Environmental Regulations
- Waste Disposal: Used KF titration solutions and solvents are chemical waste. Dispose via certified hazardous waste handlers in accordance with EPA (USA), REACH/CLP (EU), or local environmental regulations.
-
Spill Management: Equip the lab with spill kits compatible with methanol and halogenated compounds. Train personnel on spill response procedures.
-
Electrical & Equipment Safety
- Ensure the analyzer meets regional electrical safety standards (e.g., CE marking in EU, UL/CSA in North America).
- Use grounded outlets and avoid extension cords.
-
Perform regular safety inspections (e.g., frayed cables, leaks).
-
Occupational Health & Safety
- Provide appropriate PPE: chemical-resistant gloves (nitrile), safety goggles, and lab coats.
- Install local exhaust ventilation or fume hoods if large volumes of volatile reagents (e.g., methanol) are used.
-
Train operators on safe handling, emergency procedures, and analyzer-specific risks (e.g., electrical components, glassware breakage).
-
Import/Export Regulations
- For cross-border shipments, classify KF reagents using proper UN numbers (e.g., UN 1230 for methanol) and transport hazard classes (e.g., Class 3 Flammable Liquid).
- Obtain necessary permits or notifications for controlled substances (e.g., methanol may be regulated depending on quantity and jurisdiction).
-
Verify customs documentation (commercial invoice, packing list, SDS) is complete and accurate.
-
Quality & Regulatory Standards
- Maintain calibration records traceable to national standards (e.g., NIST).
- Follow method validation protocols per pharmacopeial standards (e.g., USP <921>, Ph. Eur. 2.5.12, JP 2.47) if used in regulated environments (pharma, food, etc.).
- Implement instrument qualification (IQ/OQ/PQ) where required by GMP/GLP.
H3: Documentation & Records
- Retain shipping documentation, customs filings, and delivery receipts.
- Keep logs for:
- Reagent receipt and inventory
- Calibration and maintenance
- Waste disposal manifests
- Operator training
- Incident/spill reports
Adhering to this logistics and compliance guide ensures the Karl Fischer Moisture Analyzer is operated safely, legally, and in alignment with industry best practices. Always consult local regulations and manufacturer instructions for site-specific requirements.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Karl Fischer Moisture Analyzer
Sourcing a Karl Fischer Moisture Analyzer is a critical decision for laboratories and industries requiring precise and reliable moisture content analysis. After evaluating various suppliers, models, and technical specifications, it is evident that selecting the right instrument involves balancing accuracy, ease of use, maintenance requirements, and long-term cost of ownership.
Key considerations such as titration type (volumetric vs. coulometric), automation capabilities, compliance with regulatory standards (e.g., USP, EP, ISO), and compatibility with diverse sample types play a significant role in the final selection. Additionally, vendor support, calibration services, training, and software integration are essential for ensuring consistent performance and data integrity.
Ultimately, investing in a high-quality Karl Fischer analyzer from a reputable manufacturer—supported by strong technical service and validated performance—enhances analytical reliability, supports regulatory compliance, and improves overall operational efficiency. A well-informed sourcing decision will ensure long-term accuracy in moisture determination, contributing to product quality and process optimization across pharmaceutical, chemical, food, and materials industries.