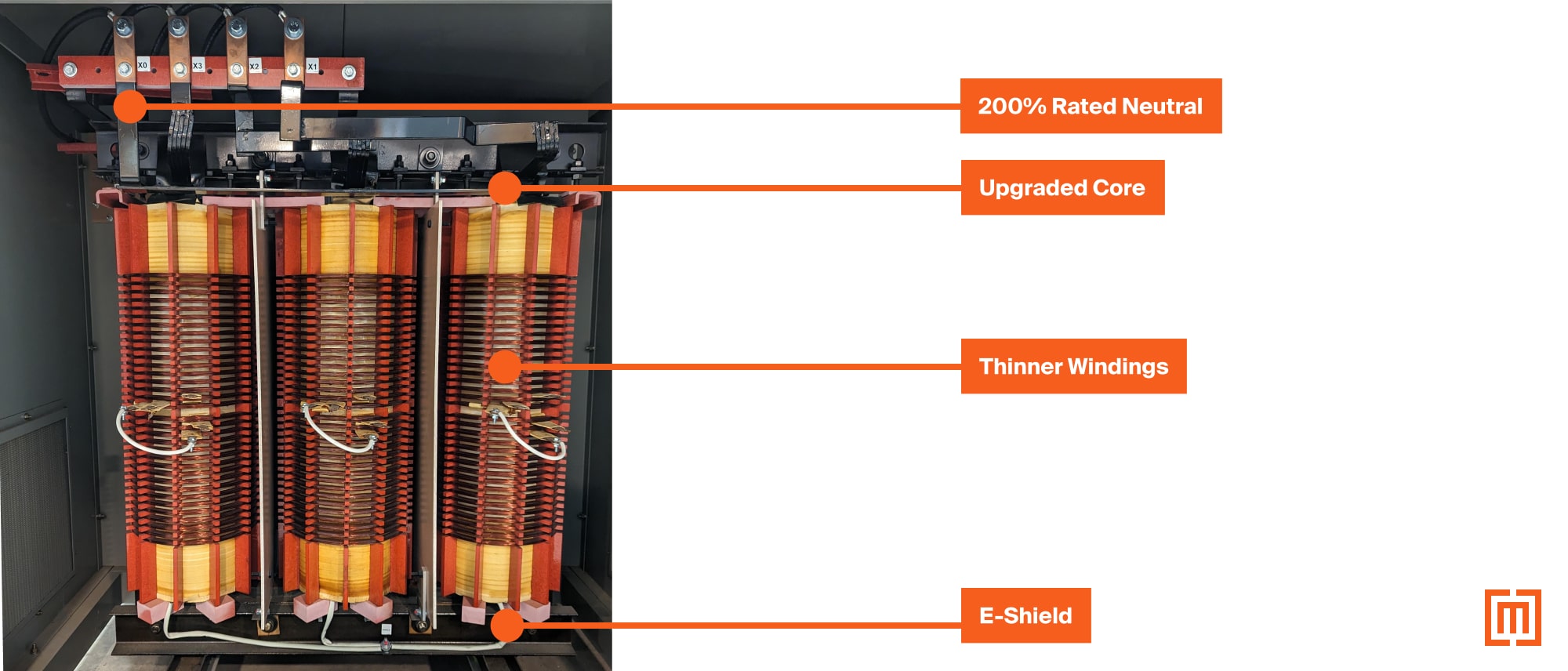
The global transformer market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by rising electricity demand, aging power infrastructure upgrades, and increased investment in renewable energy integration. According to Mordor Intelligence, the transformer market was valued at USD 45.6 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 7.2% from 2024 to 2029. Similarly, Grand View Research reports a CAGR of 7.5% from 2023 to 2030, fueled by smart grid development and grid modernization initiatives across North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific. Amid this growth, manufacturers with strong international certifications—particularly those with K ratings compliant with IEEE C57.12.00 standards—are gaining traction for their ability to handle harmonic distortions in commercial and industrial environments. As power quality becomes a critical concern, K-rated transformer producers are positioned at the forefront of reliable and efficient energy distribution. The following analysis highlights the top nine K-rated transformer manufacturers leading innovation, quality, and market share in this expanding sector.
Top 9 K Rated Transformer Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Transformers & Custom Magnetics
Domain Est. 1995
Website: hubbell.com
Key Highlights: Custom magnetics. We help OEMs develop, test, and manufacture transformers, inductors and filters to support their product development and exact specifications….
#2 Transformer Supplier
Domain Est. 1999
Website: olsun.com
Key Highlights: Olsun, a transformer manufacturer & supplier, provides dry type transformers & electrical transformers-the leading dry transformer manufacturer in the USA….
#3 Hammond Power Solutions Americas
Domain Est. 2000
Website: americas.hammondpowersolutions.com
Key Highlights: HPS is the largest manufacturer of dry-type transformers in North America. We engineer and manufacture a wide range of standard and custom transformers….
#4 Transformers
Domain Est. 1990
Website: electrification.us.abb.com
Key Highlights: ABB’s type QL K-Factor transformers are designed to withstand the additional heating that accompanies the presence of harmonics in electrical systems….
#5 Low-voltage transformer fundamentals
Domain Est. 1996
Website: eaton.com
Key Highlights: K-factor transformers are specifically designed to withstand the harmful overheating effects caused by harmonics generated by nonlinear (non-sinusoidal) loads….
#6
Domain Est. 1997
Website: delta.xfo.com
Key Highlights: Located in Granby, Quebec, Delta Transformers has been designing and manufacturing high-quality dry-type transformers and reactors for more than 40 years. Sign ……
#7 About Us
Domain Est. 1997
Website: vatransformer.com
Key Highlights: We offer ratings from 300 kVA up to 400 MVA/525 kV class for core-type liquid-filled transformers, from 60 MVA up to 500 MVA/500 kV for shell-type liquid-filled ……
#8 ELMAS
Domain Est. 2011
Website: elmas.co.in
Key Highlights: ELMAS’ K-Factor Rated transformers meet the UL 1561 standard and mitigate transformer losses from harmonic content. These transformers are essential in data ……
#9 K
Domain Est. 2023
Website: omexindustries.us
Key Highlights: A K-factor rated transformer is designed to handle a degree of harmonic load currents without overheating….
Expert Sourcing Insights for K Rated Transformer

H2: 2026 Market Trends for K-Rated Transformers
As the global electrical infrastructure evolves to meet increasing demands for energy efficiency, reliability, and compatibility with non-linear loads, K-rated transformers are poised to play a pivotal role in commercial and industrial power systems by 2026. These specialized transformers, designed to handle harmonic currents generated by modern electronic equipment such as variable frequency drives (VFDs), servers, LED lighting, and UPS systems, are becoming essential components in data centers, healthcare facilities, commercial buildings, and industrial plants.
1. Rising Demand Driven by Proliferation of Non-Linear Loads
By 2026, the widespread adoption of energy-efficient technologies and digital infrastructure is expected to significantly increase harmonic distortion in electrical systems. The growing deployment of IT equipment, automation systems, and power electronics in smart buildings and Industry 4.0 environments will drive demand for K-rated transformers. These transformers mitigate overheating and system inefficiencies caused by harmonic currents, offering enhanced durability and operational safety.
2. Growth in Data Centers and Edge Computing
The exponential expansion of cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and edge data centers is a key growth driver. Data centers generate high levels of harmonic distortion due to the dense concentration of servers and power conversion equipment. K-rated transformers are increasingly specified in these facilities to ensure reliable power distribution and to comply with energy codes and safety standards. With global data center investments projected to rise through 2026, demand for K-rated units will follow a parallel upward trajectory.
3. Regulatory and Energy Efficiency Standards
Stringent energy efficiency regulations and building codes—such as IE3 and IE4 efficiency standards, ASHRAE 90.1, and the International Energy Conservation Code (IECC)—are pushing facility designers toward optimized power solutions. K-rated transformers, often built with lower losses and enhanced thermal performance, align well with these requirements. Additionally, green building certifications like LEED are encouraging the use of robust, long-life electrical components, further supporting market adoption.
4. Regional Market Expansion
North America and Europe are expected to remain dominant markets due to mature infrastructure and strict electrical codes. However, rapid urbanization and industrialization in Asia-Pacific—particularly in India, China, and Southeast Asia—are creating new opportunities. Government initiatives promoting smart cities and digital infrastructure in these regions will fuel demand for harmonic-mitigating transformers, including K-rated models.
5. Technological Advancements and Product Differentiation
By 2026, manufacturers are anticipated to introduce advanced K-rated transformers with integrated monitoring systems, improved thermal management, and compatibility with IoT-enabled power management platforms. Hybrid designs that combine K-rating with features like low-noise operation or enhanced efficiency (e.g., DOE 2016 compliance) will gain market share. Customization for specific applications—such as healthcare facilities with sensitive equipment—will also differentiate leading suppliers.
6. Competitive Landscape and Supply Chain Dynamics
The market will see consolidation among transformer manufacturers, with an emphasis on offering comprehensive power quality solutions. Companies like Eaton, Schneider Electric, Hammond Power Solutions, and ABB are expected to expand their K-rated product lines. Supply chain resilience, particularly in sourcing high-quality magnetic materials and copper, will influence pricing and delivery timelines, especially amid fluctuating raw material costs.
Conclusion
The K-rated transformer market in 2026 will be shaped by the convergence of digitalization, energy efficiency mandates, and the need for resilient power systems. As harmonic pollution becomes a critical concern across sectors, K-rated transformers will transition from niche solutions to standard components in modern electrical designs. Stakeholders who invest in innovation, sustainability, and application-specific engineering will be best positioned to capitalize on this growing market.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing K-Rated Transformers (Quality, IP)
Sourcing K-rated transformers—designed to handle harmonic currents generated by non-linear loads such as variable frequency drives, UPS systems, and data centers—requires careful attention to both quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Failure to address these aspects can lead to performance issues, safety hazards, and legal risks. Below are common pitfalls encountered during the procurement process.
1. Overlooking Core Quality and Material Specifications
One of the most critical quality pitfalls is assuming all K-rated transformers are built to the same standard. Low-cost suppliers may use substandard core materials (e.g., inferior-grade silicon steel) or undersized windings, which compromise efficiency and thermal performance. These transformers may fail prematurely under harmonic stress, leading to downtime and safety risks.
Best Practice: Verify material certifications (e.g., ASTM standards), request test reports (temperature rise, harmonic load testing), and favor manufacturers with recognized quality management systems (ISO 9001).
2. Inadequate Thermal Design for Harmonic Loads
K-rated transformers are rated based on their ability to handle harmonic currents without overheating. A common mistake is selecting a transformer with an insufficient K-factor (e.g., K-4 instead of K-13) for the actual load profile.
Best Practice: Conduct a power quality audit to determine the actual harmonic content before specifying the K-rating. Ensure the transformer is derated appropriately and has adequate cooling mechanisms.
3. Misinterpreting IP (Ingress Protection) Ratings
The IP rating indicates protection against solid objects and moisture. A frequent oversight is selecting a transformer with an insufficient IP rating for the installation environment (e.g., IP20 for outdoor or dusty areas).
Best Practice: Match IP ratings to environmental conditions—IP54 or higher for outdoor or industrial environments. Confirm that enclosures are sealed properly and tested to IEC 60529 standards.
4. Risk of Counterfeit or Copycat Products
Due to the specialized nature of K-rated transformers, some suppliers may offer counterfeit or reverse-engineered units that mimic reputable brands. These often lack proper design validation and can pose serious safety and compliance risks.
Best Practice: Source directly from authorized distributors or OEMs. Request documentation such as type test reports, UL/cUL listings, and factory audit records. Be wary of unusually low prices.
5. Ignoring Intellectual Property (IP) Rights
Using or sourcing transformers that infringe on patented designs—such as specific winding configurations, cooling systems, or core geometries—can expose buyers to legal liability. Some manufacturers may replicate proprietary technologies without licensing.
Best Practice: Ensure suppliers can demonstrate IP compliance. Request evidence of design ownership or licensing agreements, especially when dealing with custom or high-performance units.
6. Lack of Long-Term Support and Technical Documentation
Poor documentation (e.g., missing schematics, test data, or maintenance manuals) and lack of after-sales support can hinder installation, troubleshooting, and compliance audits.
Best Practice: Require comprehensive documentation packages and verify the supplier’s technical support capabilities before purchase.
Conclusion
Sourcing K-rated transformers involves balancing technical performance, environmental suitability, and legal compliance. Avoiding these common quality and IP pitfalls ensures reliable operation, regulatory adherence, and protection against financial and legal exposure. Always prioritize transparency, certifications, and supplier credibility in the procurement process.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for K-Rated Transformers
Overview of K-Rated Transformers
K-Rated transformers are specifically designed to handle non-linear loads generated by modern electronic equipment such as computers, LED lighting, variable frequency drives, and other harmonic-producing devices. The “K” rating (e.g., K-4, K-13, K-20) indicates the transformer’s ability to withstand harmonic currents without overheating. Proper logistics and compliance are crucial during transportation, storage, installation, and operation to ensure safety, performance, and regulatory adherence.
Transportation & Handling Requirements
- Packaging: Ensure the transformer is securely mounted on a skid or pallet with protective covers over bushings, terminals, and radiators. Use weather-resistant packaging for outdoor transport.
- Lifting & Rigging: Always use lifting lugs or designated rigging points. Never lift by the tank, radiators, or bushings. Confirm lifting equipment capacity exceeds the transformer’s total weight.
- Vehicle Suitability: Use flatbed trucks or enclosed trailers with adequate suspension. Secure the unit with straps or chains to prevent shifting.
- Environmental Protection: Avoid exposure to moisture, dust, and extreme temperatures during transit. Cover the unit if transported in open vehicles.
- Documentation: Maintain shipping manifests, packing lists, and certificates of conformance during transport.
Storage Guidelines
- Indoor Storage: Store in a clean, dry, and well-ventilated indoor environment. Maintain relative humidity below 60% to prevent condensation.
- Outdoor Storage: If unavoidable, elevate the unit on sleepers to avoid ground moisture. Use a breathable tarpaulin (not plastic) to allow ventilation and prevent condensation. Inspect regularly for damage or moisture.
- Preservation: If stored for more than 6 months, verify nitrogen blanket pressure (if applicable) or desiccant condition. Re-pressurize or replace desiccant as needed.
- Access Clearance: Maintain at least 3 feet (1 meter) of clearance around the unit for inspection and ventilation.
Regulatory & Safety Compliance
- National Electrical Code (NEC): Comply with NEC Article 450 for transformer installation, including clearances, ventilation, and overcurrent protection. K-rated transformers must be used in applications with significant harmonic content as specified in NEC guidelines.
- IEEE Standards: Adhere to IEEE C57.110 for recommended practices in powering and grounding non-linear loads with K-rated transformers.
- UL Certification: Ensure the transformer carries UL 1561 or UL 5085 certification, confirming compliance with safety and performance standards for dry-type transformers.
- NEMA TP-1: While not mandatory, adherence demonstrates energy efficiency and performance expectations.
- OSHA Regulations: Follow OSHA 29 CFR 1910.303 for general electrical safety requirements during handling and installation.
Installation Requirements
- Location: Install in a dedicated electrical room with proper fire-rated construction. Maintain required clearances (front, back, sides) per NEC and manufacturer specifications.
- Ventilation: Ensure adequate airflow to dissipate heat from harmonic losses. Avoid confined spaces without forced ventilation.
- Grounding: Bond the transformer frame and neutral point per local electrical codes and manufacturer instructions. Use appropriately sized grounding conductors.
- Connection Verification: Confirm input/output voltages, phase configuration, and terminal torque specifications. Use only listed connectors and conductors rated for temperature rise.
- Infrared Scanning: Perform thermal imaging after initial energization to detect loose connections or hotspots.
Environmental & Sustainability Compliance
- PCB-Free: Verify the transformer uses non-PCB insulating materials (standard for modern units).
- Recyclability: At end-of-life, recycle core, copper windings, and steel tank through certified e-waste handlers.
- Energy Efficiency: Select higher efficiency models where possible to reduce lifecycle energy consumption and carbon footprint.
Documentation & Recordkeeping
- Maintain copies of:
- Certificate of Compliance (UL, CSA, etc.)
- Test reports (temperature rise, impedance, turns ratio)
- Installation manual and wiring diagrams
- As-built commissioning report
- Maintenance logs (insulation resistance, thermography, loading)
Emergency & Risk Mitigation
- Fire Protection: Install in areas with automatic fire suppression (e.g., sprinklers or clean agent systems) if required by local code.
- Spill Containment: For oil-filled units (rare in K-rated dry types), ensure secondary containment per EPA Spill Prevention, Control, and Countermeasure (SPCC) rules.
- Labeling: Clearly mark nameplate data, K-rating, voltage, and warnings per NEC and OSHA requirements.
Conclusion
Proper logistics and compliance ensure the safe, efficient, and code-compliant use of K-Rated transformers. Adherence to handling, storage, regulatory, and installation standards maximizes reliability and protects personnel and equipment in environments with harmonic-rich loads. Always consult the manufacturer’s specifications and local authority having jurisdiction (AHJ) for project-specific requirements.
Conclusion for Sourcing K-Rated Transformers
Sourcing K-rated transformers is a critical step in ensuring reliable and efficient power distribution in environments with significant levels of harmonic distortion, such as data centers, healthcare facilities, commercial buildings, and industrial plants. These specialized transformers are designed to handle the additional heat and stress caused by harmonic currents generated by non-linear loads like variable frequency drives, computers, LED lighting, and other electronic equipment.
When sourcing K-rated transformers, it is essential to accurately assess the harmonic content of the electrical load to determine the appropriate K-factor rating (e.g., K-4, K-13, K-20). Selecting the correct rating ensures optimal performance, prevents overheating, and extends equipment lifespan. Additionally, considerations such as energy efficiency, physical footprint, compliance with standards (e.g., IEEE C57.110), and total cost of ownership should guide the procurement process.
Partnering with reputable manufacturers and suppliers who provide certified, well-tested K-rated transformers ensures reliability and safety. Proper installation, including adequate ventilation and adherence to electrical codes, further enhances performance.
In conclusion, sourcing the right K-rated transformer is a strategic investment in electrical system integrity. It mitigates risks associated with harmonic distortion, improves power quality, and supports the long-term efficiency and safety of modern electrical systems. Careful evaluation of technical specifications, load requirements, and supplier credibility will lead to a successful and sustainable power distribution solution.