The global JTAG programmer market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand for advanced embedded systems, increased complexity in PCB testing, and the proliferation of IoT and automotive electronics. According to Grand View Research, the global automatic test equipment (ATE) market—which includes JTAG and boundary scan technologies—was valued at USD 4.9 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.1% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is further accelerated by the semiconductor industry’s shift toward miniaturization and higher integration, necessitating reliable, high-precision programming and testing tools. As JTAG (Joint Test Action Group) remains a cornerstone standard for debugging and in-circuit programming, manufacturers specializing in JTAG programmers are playing a critical role in enabling efficient product development cycles across aerospace, industrial automation, telecommunications, and automotive sectors. With competitive pressures and technological innovation intensifying, a select group of manufacturers has emerged at the forefront, combining performance, software integration, and scalability to meet evolving industry demands.
Top 4 Jtag Programmer Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Programming DSP from TMDSDSK6713 JTAG Emulator
Domain Est. 1986
Website: e2e.ti.com
Key Highlights: I have been using the TMDSDSK6713 for development purposes but have recently populated my PCB and am now trying to program my C6726 DSP….
#2 We are boundary
Domain Est. 1996
Website: jtag.com
Key Highlights: We are JTAG/Boundary-scan-1149.1 Test solutions for today’s electronics. Get new board and system designs up and in production running….
#3 Programming microcontrollers
Domain Est. 2009
Website: electronics.stackexchange.com
Key Highlights: JTAG is an in-system debugging tool which allows you to manipulate and examine the status of a supported AVR while it is running in a circuit….
#4 Technical Guide to JTAG
Domain Est. 2001
Website: xjtag.com
Key Highlights: This document provides you with interesting background information about the technology that underpins XJTAG….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Jtag Programmer

2026 Market Trends for JTAG Programmers
The market for JTAG (Joint Test Action Group) programmers is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by advancements in semiconductor technology, growing complexity in electronics design, and expanding applications across key industries. Here are the major trends expected to shape the JTAG programmer landscape:
1. Rising Demand from High-Complexity Electronics
As integrated circuits (ICs) and system-on-chips (SoCs) become more sophisticated—with multi-core processors, advanced FPGAs, and dense packaging—debugging and programming during development and production require robust JTAG solutions. By 2026, the demand for JTAG programmers capable of handling high-speed, multi-device chains and complex boundary-scan architectures will grow, especially in sectors like telecommunications, automotive, and industrial automation.
2. Expansion in Automotive and IoT Applications
The automotive industry’s shift toward electric vehicles (EVs), advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), and autonomous driving is increasing reliance on JTAG for in-system programming and testing of microcontrollers and ASICs. Similarly, the proliferation of IoT devices—many of which are resource-constrained and require secure, reliable firmware updates—will boost the need for compact, low-power JTAG programmers compatible with embedded development workflows.
3. Integration with AI and Automated Testing Platforms
By 2026, JTAG programmers are expected to integrate more closely with AI-driven test automation platforms. Machine learning algorithms will analyze boundary-scan data to predict failure points, optimize test coverage, and reduce debugging time. This trend will enhance manufacturing yield and improve product reliability, especially in high-volume production environments.
4. Emphasis on Security and Secure Programming
With rising concerns over firmware tampering and counterfeiting, secure JTAG programming will become a critical feature. JTAG programmers in 2026 will increasingly support encrypted communication, secure boot programming, and authentication protocols (e.g., integration with Trusted Platform Modules or hardware security modules), particularly for defense, medical, and industrial applications.
5. Growth of Portable and Cloud-Connected JTAG Tools
There will be a growing shift toward portable, USB-powered JTAG programmers with wireless or cloud connectivity. Remote firmware updates and diagnostics—enabled through cloud-managed JTAG interfaces—will become standard in distributed development teams and field service operations. This trend supports agile development and reduces time-to-market.
6. Consolidation and Standardization Across Ecosystems
As JTAG standards evolve (e.g., IEEE 1149.x extensions), vendors will focus on interoperability and software ecosystem integration. By 2026, leading JTAG programmer manufacturers are expected to offer unified software platforms supporting multiple chip vendors, reducing the learning curve and improving developer productivity.
In summary, the 2026 JTAG programmer market will be defined by higher performance, enhanced security, smarter automation, and broader application reach—driven by the relentless pace of innovation in electronic systems design and manufacturing.
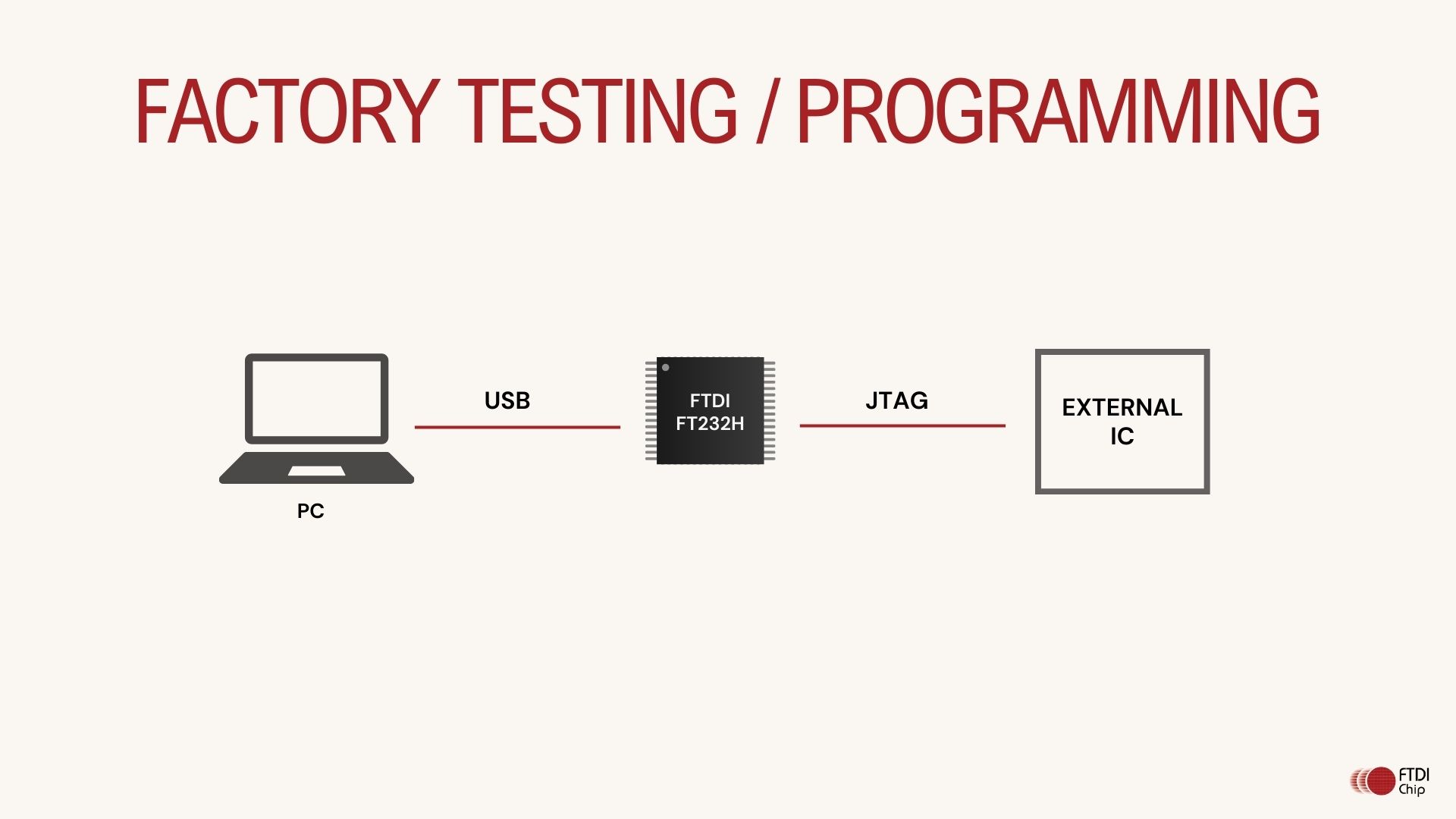
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing JTAG Programmers: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing JTAG programmers, especially from lesser-known or overseas suppliers, can introduce significant risks related to product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Being aware of these pitfalls is crucial for ensuring reliable operations and safeguarding sensitive designs.
Poor Build Quality and Component Sourcing
Many low-cost JTAG programmers on the market use substandard components and lack rigorous quality control. This can lead to inconsistent signal integrity, unreliable connections, or premature hardware failure. Users may experience intermittent programming issues, data corruption, or damage to target devices due to voltage irregularities. Additionally, counterfeit or recycled components may be used, further compromising reliability and longevity.
Inadequate or Incomplete Firmware and Software Support
Low-cost programmers often come with poorly documented, outdated, or closed-source software tools. This can limit compatibility with newer devices, operating systems, or development environments. Lack of firmware updates or community support hampers troubleshooting and integration into automated workflows. In some cases, essential features like boundary scan or flash programming may be unstable or entirely non-functional.
Intellectual Property Exposure and Security Risks
Using untrusted JTAG programmers poses a serious IP risk. Malicious firmware or hardware backdoors could potentially intercept and exfiltrate sensitive data during programming or debugging sessions—including bitstreams, firmware binaries, or configuration files. Since JTAG provides deep access to on-chip resources, a compromised tool could enable unauthorized readout of protected memory or reverse engineering of proprietary logic.
Reverse Engineering and Cloning Vulnerabilities
Some third-party programmers are clones of popular open hardware designs but may include undocumented modifications. These clones might not adhere to original security practices and could introduce vulnerabilities. Furthermore, using such devices in production environments risks violating licensing terms or exposing your organization to legal issues if the hardware or software infringes on existing patents or copyrights.
Lack of Compliance and Certification
Many budget JTAG tools lack proper electromagnetic compatibility (EMC), safety, or regulatory certifications (e.g., CE, FCC, RoHS). This not only affects performance in noise-sensitive environments but may also violate compliance requirements for commercial product development and deployment.
To mitigate these risks, it is advisable to source JTAG programmers from reputable vendors with transparent supply chains, strong software support, and clear security practices. Evaluating firmware openness, community trust, and available security audits can further reduce exposure to quality and IP-related issues.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for JTAG Programmer
This guide outlines the key logistics considerations and compliance requirements for the safe and legal handling, shipping, import/export, and use of JTAG (Joint Test Action Group) programmers. Adherence to these guidelines ensures regulatory compliance, product integrity, and operational efficiency.
Regulatory Classification & Export Controls
JTAG programmers may be subject to export control regulations due to their potential use in debugging, testing, or programming integrated circuits, including those with dual-use or military applications. Key compliance areas include:
- Export Control Classification Number (ECCN): Determine the appropriate ECCN under the U.S. Commerce Control List (CCL) or equivalent in other jurisdictions. JTAG programmers often fall under ECCN 3A991 or 3A001 depending on functionality and technical specifications.
- ITAR vs. EAR: Verify whether the device is subject to the International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) or Export Administration Regulations (EAR). Most commercial JTAG programmers are regulated under EAR.
- License Requirements: Evaluate if export, re-export, or transfer requires a license based on destination country, end-user, and end-use. Use tools like the Commerce Country Chart to assess licensing needs.
- Restricted Parties Screening: Conduct regular screenings against denied persons lists (e.g., BIS Denied Persons List, OFAC SDN List) before shipping to international customers.
Packaging & Handling Instructions
Proper packaging ensures the JTAG programmer arrives undamaged and ready for use.
- ESD Protection: Always package JTAG programmers in anti-static bags or containers to prevent electrostatic discharge damage.
- Cushioning Material: Use foam inserts, bubble wrap, or molded pulp to immobilize the device and protect against shock and vibration during transit.
- Sealed Enclosures: Ensure packaging is sealed to prevent dust, moisture, and contaminants from entering.
- Labeling: Include clear labels indicating “Fragile,” “Electrostatic Sensitive Device,” and orientation arrows if applicable.
Shipping & Transportation
Follow best practices for domestic and international shipping.
- Carrier Compliance: Use carriers compliant with IATA, IMDG, or other relevant transportation regulations—even if not hazardous, proper documentation is essential.
- Documentation: Include commercial invoices, packing lists, and export declarations with accurate Harmonized System (HS) codes (e.g., 8471.80 for data processing equipment components).
- Insurance: Ship with declared value and insurance to cover loss or damage.
- Tracking: Use trackable shipment methods for accountability and delivery confirmation.
Import Compliance
For international recipients, ensure import regulations are met.
- Customs Clearance: Provide necessary documentation (e.g., Certificate of Origin, import licenses if required) to facilitate customs clearance.
- Duties & Taxes: Accurately declare value and classification to calculate applicable duties, VAT, or GST.
- Local Regulations: Confirm compliance with local electronic equipment standards (e.g., CE in Europe, KC in South Korea, CCC in China).
Product Compliance & Certifications
Ensure the JTAG programmer meets relevant safety and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standards.
- CE Marking (EU): Comply with the Low Voltage Directive (LVD) and EMC Directive. Maintain a Declaration of Conformity.
- FCC Certification (USA): Ensure compliance with Part 15 of FCC rules for electromagnetic interference.
- RoHS & REACH (EU): Confirm the product is free from restricted substances and includes necessary chemical disclosures.
- UL/CSA (North America): If applicable, verify safety certification for power supplies or connected accessories.
End-of-Life & Environmental Compliance
Adhere to environmental regulations for disposal and recycling.
- WEEE Compliance (EU): Label products with the crossed-out wheeled bin symbol and provide take-back or recycling options.
- Battery Handling: If the programmer includes a rechargeable battery, follow transport and disposal guidelines under UN 38.3 for lithium batteries.
- Recycling Programs: Partner with certified e-waste recyclers for responsible end-of-life management.
Recordkeeping & Audit Trail
Maintain comprehensive records for compliance verification and audits.
- Export Records: Retain export documentation for a minimum of five years (as required by EAR).
- Compliance Certificates: Keep copies of test reports, certifications (FCC, CE, etc.), and Declarations of Conformity.
- Training Logs: Document staff training on export controls, ESD handling, and logistics procedures.
By following this guide, organizations can ensure efficient logistics operations and full compliance with international regulations when distributing or using JTAG programmers.
Conclusion for Sourcing a JTAG Programmer
After evaluating various options, it is clear that selecting the right JTAG programmer depends on the specific requirements of the project, including target devices, operating environment, budget, and desired features such as speed, compatibility, and software support. Commercial programmers from reputable manufacturers like SEGGER (J-Link), Xilinx (Platform Cable USB), and Texas Instruments (XDS110) offer robust performance, extensive documentation, and strong technical support, making them ideal for professional development and production environments. On the other hand, open-source or budget-friendly alternatives such as FT2232HL-based adapters or J-Link clones may be suitable for hobbyists or low-volume prototyping, though they may lack reliability or full protocol compliance.
Ultimately, investing in a high-quality, well-supported JTAG programmer ensures faster debugging, broader device compatibility, and long-term maintainability. For most professional applications, sourcing a proven solution like the SEGGER J-Link or equivalent vendor-specific tool provides the best balance of performance, reliability, and ecosystem integration. Proper due diligence in selecting and sourcing the programmer will contribute significantly to development efficiency and product success.