The global isolation transformers market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand for electrical safety, noise suppression, and reliable power supply across industrial, healthcare, and data center applications. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 2.1 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.8% from 2024 to 2029. This expansion is fueled by increasing investments in smart grid infrastructure, growing industrial automation, and stringent regulations surrounding electrical safety. As critical components in power distribution systems, isolation transformers play a vital role in preventing ground loops, reducing electrical noise, and protecting sensitive equipment—making them indispensable in mission-critical environments. With market players increasingly focusing on energy-efficient and compact designs, the competitive landscape is evolving rapidly. Based on market presence, product innovation, and global reach, the following are the top 10 isolation transformers manufacturers shaping the industry’s future.
Top 10 Isolation Transformers Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Virginia Transformer Corp
Domain Est. 1997 | Founded: 1971
Website: vatransformer.com
Key Highlights: The largest U.S.-owned custom power transformer manufacturer since 1971, with six advanced facilities across the U.S. and Mexico….
#2 Hammond Power Solutions Americas
Domain Est. 2000
Website: americas.hammondpowersolutions.com
Key Highlights: HPS is the largest manufacturer of dry-type transformers in North America. We engineer and manufacture a wide range of standard and custom transformers….
#3 Isolation Transformer Manufacturers
Domain Est. 2001
Website: osbornetransformer.com
Key Highlights: Isolation Transformer Manufacturers. Osborne Transformer is a market leader in the production of extremely durable isolation transformers….
#4 TMC Transformers
Domain Est. 2006
Website: tmctransformers.com
Key Highlights: TMC is specialised in the production of dry-type transformers and cast resin transformers for different applications and installation needs. Visit our website….
#5 Transformers
Domain Est. 1990
Website: electrification.us.abb.com
Key Highlights: Drive Isolation Transformer (DIT) is designed to specifically handle the mechanical stresses, voltage distortions, and harmonics associated with SCR ……
#6 Jensen Transformers
Domain Est. 1996
Website: jensen-transformers.com
Key Highlights: Jensen offers a complete range of transformers for the most demanding audio designs. Each transformer is manufactured and tested to deliver the utmost quality….
#7 Isolation Transformers
Domain Est. 1996
Website: tripplite.eaton.com
Key Highlights: Tripp Lite Isolation Transformers offer complete power line isolation, noise filtering and surge suppression, making them ideal for sensitive electronic ……
#8 Transformers
Domain Est. 1996
#9 Torus Power
Domain Est. 2005
Website: toruspower.com
Key Highlights: Torus Power Toroidal Isolation Power Transformers are engineered to perform and protect like no other to enhance audio, video, and control systems….
#10 Isolation transformers
Domain Est. 2021
Website: hitachienergy.com
Key Highlights: Isolation transformers are special transformers used to isolate the AC network from DC leakage currents caused by DC rails in close proximity to AC rails….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Isolation Transformers

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Isolation Transformers
The isolation transformer market is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by technological advancements, shifting energy landscapes, and increasing demands for electrical safety and power quality. Key trends shaping the market include:
1. Rising Demand in Renewable Energy Integration:
As solar and wind power installations expand globally, isolation transformers are increasingly critical for safely interfacing variable renewable sources with the grid. Their role in providing galvanic isolation, voltage matching, and fault protection makes them essential in inverters and grid-tie systems. By 2026, increased investments in utility-scale and distributed renewable projects—especially in Asia-Pacific and North America—are expected to significantly boost demand.
2. Growth in Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Infrastructure:
The global expansion of EV charging networks, particularly high-power DC fast chargers, is driving demand for isolation transformers. These transformers ensure user safety and electromagnetic compatibility in charging stations. With governments pushing for cleaner transportation, the deployment of public and private EV charging points will elevate the need for reliable and compact isolation solutions, especially those designed for harsh environments.
3. Emphasis on Power Quality and Industrial Automation:
Industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and data centers are increasingly reliant on sensitive electronic equipment. Isolation transformers mitigate electrical noise, surges, and ground loops, ensuring stable and clean power. The rise of Industry 4.0 and smart factories will continue to drive demand for high-efficiency, low-noise isolation transformers capable of supporting advanced automation and IoT devices.
4. Advancements in Material and Design Efficiency:
By 2026, market innovation will focus on improving energy efficiency and reducing size and weight. The adoption of amorphous metal cores, advanced winding techniques, and better thermal management will lead to transformers with lower losses and enhanced reliability. These improvements align with global energy efficiency regulations and sustainability goals, particularly in Europe and North America.
5. Regulatory and Safety Standards Driving Adoption:
Stricter electrical safety codes and standards—such as IEC 61558 and IEEE C57—will mandate the use of isolation transformers in critical applications like medical facilities and hazardous environments. Increased awareness of electrical safety in both developed and emerging markets will further support market growth.
6. Regional Market Diversification:
While North America and Europe remain strong markets due to infrastructure upgrades and renewable integration, Asia-Pacific is expected to witness the highest growth rate. Rapid industrialization in countries like India and Vietnam, coupled with government smart grid initiatives in China, will expand the regional footprint of isolation transformer applications.
In summary, by 2026, the isolation transformer market will be shaped by the convergence of energy transition, technological innovation, and heightened safety requirements. Manufacturers who adapt to these trends—offering efficient, compact, and application-specific solutions—will be well-positioned to capture emerging opportunities.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Isolation Transformers (Quality, IP)
Sourcing isolation transformers requires careful attention to avoid compromising safety, performance, and regulatory compliance. Overlooking key aspects related to quality and intellectual property (IP) can lead to significant risks. Below are common pitfalls to watch for:
Poor Build Quality and Material Substitutions
Many low-cost suppliers use inferior materials—such as lower-grade copper windings, substandard insulation, or undersized cores—to cut costs. This results in transformers that overheat, have poor efficiency, or fail prematurely. Always verify material specifications and request samples for testing.
Lack of Certification and Compliance
A major red flag is the absence of recognized safety certifications (e.g., UL, CE, IEC, CSA). Non-certified units may not meet electrical safety standards, posing fire or shock hazards. Ensure the transformer complies with regional regulations and is tested by accredited laboratories.
Inadequate IP Protection and Design Copying
When working with OEMs or offshore manufacturers, there’s a risk of design replication or unauthorized production. Suppliers may copy your specifications or re-sell identical units to competitors. Protect your designs with NDAs, patents where applicable, and clear contractual IP ownership clauses.
Misrepresentation of Isolation Ratings
Some suppliers exaggerate isolation voltage ratings or leakage current performance. Verify claims through third-party test reports and ensure the transformer meets the required dielectric strength (e.g., 4 kV isolation) for your application.
Poor Thermal Management Design
Transformers that lack proper thermal design or use low-temperature insulation materials can degrade quickly under continuous load. Check temperature rise ratings (e.g., class B, F, or H insulation) and confirm performance under full load conditions.
Inconsistent Quality Control Processes
Manufacturers without rigorous QC systems may produce inconsistent units, even within the same batch. Request documentation of quality control procedures, such as hipot testing, continuity checks, and batch traceability.
Hidden Costs Due to Rework or Downtime
Low upfront pricing can be misleading if the transformer fails in the field. Poor quality leads to higher long-term costs from equipment damage, maintenance, or system downtime. Factor in total cost of ownership, not just purchase price.
Supply Chain and Counterfeit Risk
Sourcing from unreliable suppliers increases the risk of receiving counterfeit or refurbished units misrepresented as new. Establish trusted supply chains, audit suppliers when possible, and verify authenticity through packaging, labeling, and performance testing.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence, technical validation, and strong contractual protections—especially when IP and long-term reliability are critical.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Isolation Transformers
Product Classification and Regulatory Overview
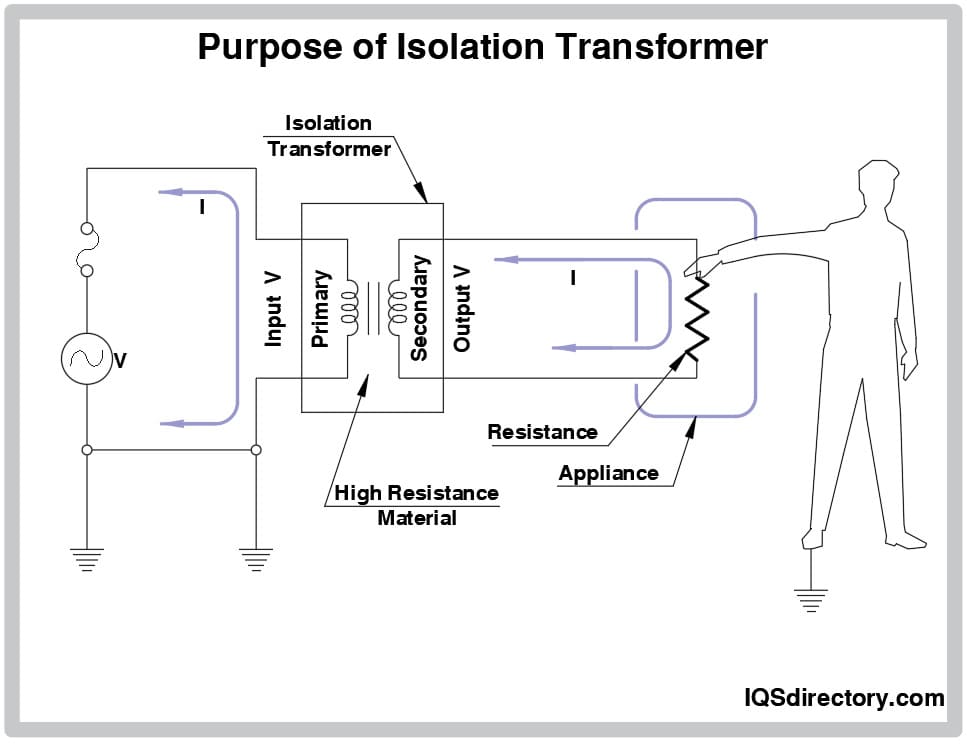
Isolation transformers are critical electrical components used to transfer electrical power from a source to a load while isolating the load from the power source. This isolation enhances safety by preventing electric shock and minimizing electrical noise. Due to their role in electrical systems, isolation transformers are subject to various international and regional regulations concerning safety, electromagnetic compatibility (EMC), and environmental standards. Key regulations include IEC 61558-2-4 (safety standards for isolating transformers), UL 5085 (North American safety standard), and compliance with the EU’s Low Voltage Directive (LVD) and Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive. Additionally, transformers may need to meet RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and REACH requirements in Europe.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Proper packaging is essential to prevent physical damage during transit. Isolation transformers should be packed in sturdy, moisture-resistant cartons with internal cushioning (e.g., foam inserts or molded pulp) to protect terminals and windings. Large or heavy units may require wooden crates and palletization for secure transport. Handling instructions such as “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Do Not Stack” must be clearly marked. For units with oil-filled cores (less common in modern isolation transformers), additional leak-proof packaging and hazardous material labeling may be required. Always follow manufacturer-specific handling guidelines to avoid compromising insulation integrity.
Transportation and Shipping Considerations
Isolation transformers can be shipped via air, sea, or ground freight depending on size, weight, and urgency. Standard units under 30 kVA are typically air-eligible if properly packed. Larger units may require sea or overland transport. When shipping internationally, ensure compliance with IATA (air), IMDG (sea), or ADR (road) regulations if applicable—especially for units containing insulating oils or other regulated materials. Use climate-controlled transport where possible to prevent condensation in humid environments. Declare the correct HS (Harmonized System) code—commonly 8504.23 or 8504.31—for customs clearance. Include technical specifications (kVA rating, input/output voltage, frequency) in shipping documents.
Import/Export Compliance
Exporting isolation transformers requires adherence to destination country regulations. In the EU, CE marking is mandatory, indicating conformity with LVD, EMC, and RoHS directives. In the U.S., UL or ETL listing is often required for market entry. Canada mandates compliance with CSA standards. Some countries (e.g., China, India, Russia) may require additional certifications such as CCC, BIS, or EAC. Export controls may apply if transformers are designed for military or dual-use applications—verify under EAR (U.S.) or equivalent regulations. Provide a detailed commercial invoice, packing list, and certificates of conformity (CoC) or test reports from accredited laboratories (e.g., TÜV, Intertek).
Installation and Site Compliance
Upon delivery, verify that the transformer matches site electrical specifications (voltage, frequency, phase). Installation must comply with local electrical codes such as the NEC (National Electrical Code) in the U.S., IEC 60364 internationally, or BS 7671 in the UK. Ensure proper grounding, clear ventilation, and protection from environmental hazards (moisture, dust, temperature extremes). Isolation transformers used in medical, industrial, or marine applications may require additional compliance with standards such as IEC 60601-1 (medical electrical equipment) or IEC 60092 (marine electrical installations). Qualified electricians should perform installation and final inspection.
Documentation and Record Keeping
Maintain comprehensive compliance documentation throughout the product lifecycle. Required documents include:
– Test reports (dielectric strength, temperature rise, insulation resistance)
– Certificate of Conformity (CoC) or Declaration of Conformity (DoC)
– UL/CE/CSA certification marks and supporting files
– RoHS/REACH compliance statements
– User manuals with safety warnings and maintenance instructions
– Shipping and customs documentation (bill of lading, commercial invoice, packing list)
Retain records for a minimum of 10 years for audit and traceability purposes, especially in regulated industries.
Disposal and End-of-Life Compliance
At end-of-life, isolation transformers must be disposed of according to environmental regulations. Units with copper windings and steel cores are recyclable but may contain small amounts of hazardous materials (e.g., PCBs in older models—now largely phased out). Follow WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directives in the EU and EPA guidelines in the U.S. for proper recycling. Never dispose of in general waste. Partner with certified e-waste recyclers who can safely dismantle and recover materials while documenting environmentally responsible disposal.
Conclusion on Sourcing Isolation Transformers
In conclusion, sourcing isolation transformers requires a careful evaluation of technical specifications, application requirements, quality standards, and supplier reliability. Isolation transformers play a critical role in enhancing electrical safety, reducing electrical noise, and providing galvanic isolation in sensitive environments such as medical facilities, industrial systems, laboratories, and HVAC systems. When selecting a supplier, it is essential to consider factors such as compliance with international standards (e.g., IEC, UL, CE), transformer efficiency, voltage ratings, kVA capacity, insulation class, and cooling methods.
Additionally, attention should be paid to customization capabilities, lead times, after-sales support, and cost-effectiveness to ensure long-term performance and reliability. Sourcing from certified and reputable manufacturers or distributors helps mitigate risks associated with counterfeit or substandard products. Ultimately, a well-informed procurement strategy ensures that the isolation transformers not only meet current operational needs but also support safety, compliance, and system longevity in diverse electrical environments.