The global iron sand market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand from the steel industry and infrastructure development, particularly in Asia-Pacific. According to Grand View Research, the global iron ore market—of which iron sand is a key component—was valued at USD 109.2 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by increasing urbanization, industrialization, and government investments in construction and manufacturing. Iron sand, known for its high titanium and vanadium content, is gaining traction not only as a raw material for steelmaking but also in niche applications such as welding rods and heavy concrete. Geographically, countries like Japan, Indonesia, and New Zealand are key players due to abundant coastal iron sand deposits and established mining operations. As demand intensifies, a select group of manufacturers are scaling production, adopting sustainable extraction methods, and investing in beneficiation technologies to improve ore quality. The following profile highlights the top 8 iron sand manufacturers shaping the industry through innovation, operational scale, and strategic market positioning.
Top 8 Iron Sand Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
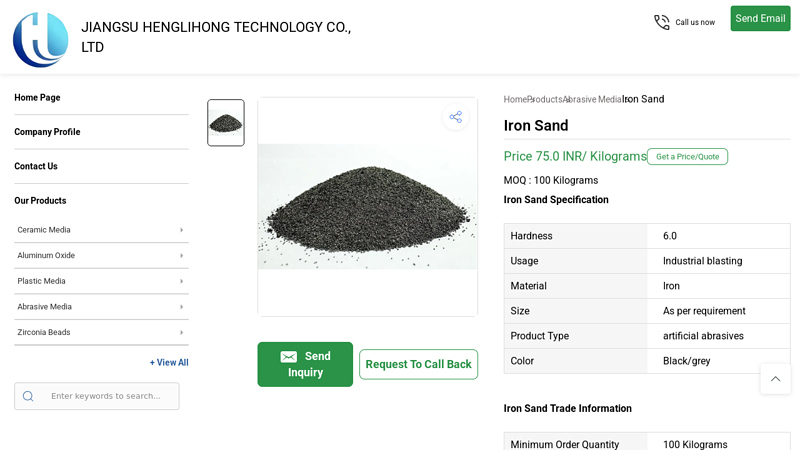
#1 Iron Sand Exporter, Manufacturer & Supplier, Wuxi, China
Website: henglihongtech.com
Key Highlights: Special iron sand is durable and reusable. Wide adaptability, suitable for a variety of materials. Meet the different needs of various industrial scenarios….
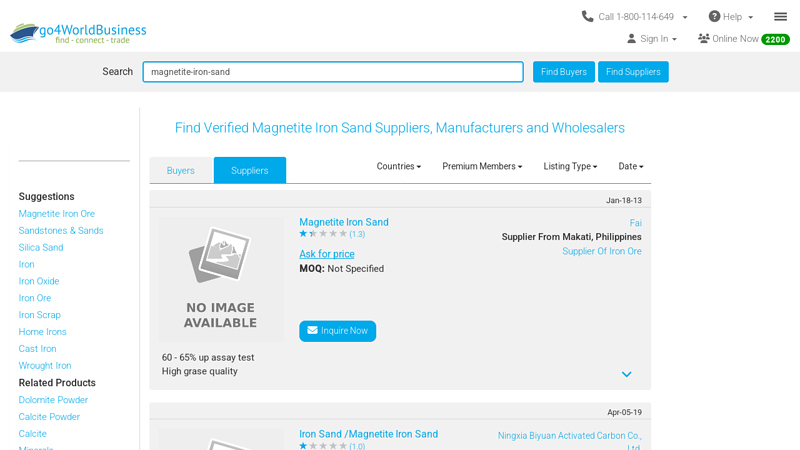
#2 Magnetite Iron Sand Wholesale Suppliers, Manufacturers …
Domain Est. 2001
Website: go4worldbusiness.com
Key Highlights: Iron sand is made from broken heat-treated iron shot. It is of high hardness with sharp angles, which make suitable for high-speed spray etching and ……
#3 FerroSand Iron Oxide Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2023
Website: ferrosand.com
Key Highlights: FerroSand Iron Oxide Manufacturer – Free from impurities, based on natural magnetite – Fractions up to 0.3 mm – Quality certificate for each batch….
#4 IRON SAND
Website: industrialsands.co.nz
Key Highlights: High quality, clean black iron sand. A very dense sand, with a consistent particle sizing between 75 to 150 microns. This sand has a very high Ferric Oxide ……
#5 Low
Domain Est. 1996
Website: ussilica.com
Key Highlights: We start with sand that is naturally low in iron and then utilize special processing techniques to ensure an even lower iron content….
#6 DISA Group
Domain Est. 2000
Website: disagroup.com
Key Highlights: Welcome to DISA. DISA develops and manufactures a complete range of metal casting production solutions for the ferrous and non-ferrous foundry industries….
#7 The Mining Operation
Website: nzsteel.co.nz
Key Highlights: The New Zealand Steel Mill at Glenbrook opened in 1970 with an ironsand mine located at the mouth of the Waikato River….
#8 Trusted Top 10 Iron Sand Casting Manufacturers and Suppliers
Domain Est. 2020
Website: hi.nblscasting.com
Key Highlights: Iron sand casting is a traditional metal casting process that involves pouring molten iron into a sand mold to create complex shapes….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Iron Sand
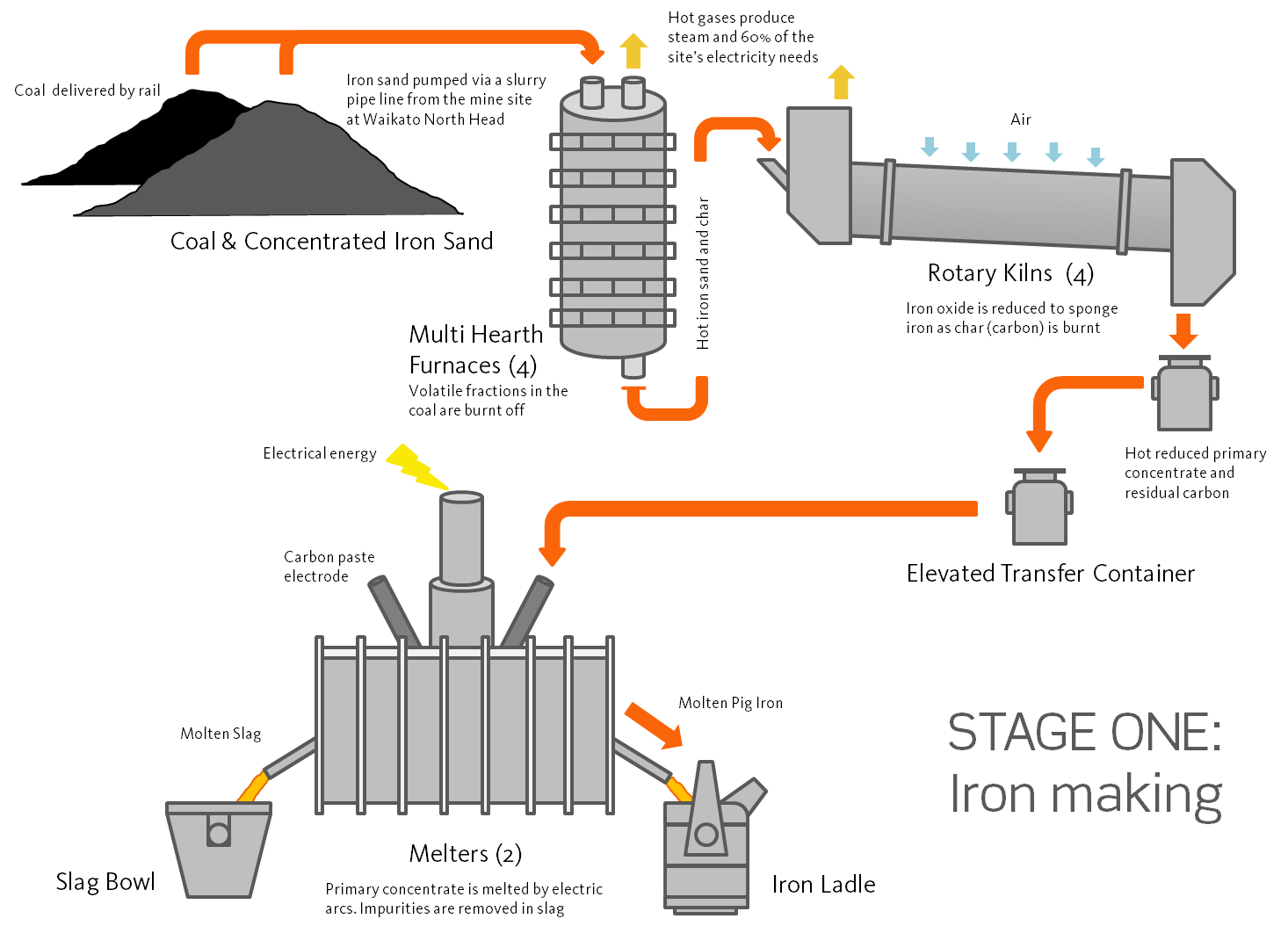
H2: Market Trends for Iron Sand in 2026
As the global economy continues to evolve in response to technological innovation, environmental regulations, and shifting industrial demand, the iron sand market is projected to undergo significant transformation by 2026. Iron sand, also known as titanomagnetite, is a key raw material rich in iron and titanium, primarily used in steel production and increasingly in advanced materials and renewable energy infrastructure. Below is an analysis of key market trends expected to shape the iron sand industry through 2026.
1. Rising Demand from Steel and Construction Sectors
Despite increasing efforts to decarbonize steelmaking, global demand for steel remains robust, particularly in emerging economies across Asia, Africa, and the Middle East. Iron sand, especially in countries like Japan, New Zealand, and Indonesia, serves as a vital iron ore alternative where conventional hematite or magnetite deposits are limited. By 2026, continued urbanization and infrastructure development are expected to sustain demand for iron sand, particularly in regional steel production hubs.
2. Technological Advancements in Processing and Beneficiation
One of the historical challenges with iron sand is its relatively low iron grade and high titanium content, which complicates traditional smelting. However, by 2026, advancements in beneficiation technologies—such as high-intensity magnetic separation, ilmenite upgrading, and plasma smelting—are expected to improve recovery rates and reduce processing costs. Countries like Japan and South Korea are investing heavily in direct reduction and electric arc furnace (EAF) technologies compatible with high-titanium iron sands, enhancing their economic viability.
3. Integration with Green Steel Initiatives
The push toward low-carbon steel production is reshaping raw material sourcing strategies. Iron sand, when processed using renewable-powered electric furnaces, offers a lower carbon footprint compared to conventional blast furnace methods reliant on imported high-grade iron ore. As green steel certification gains traction in the EU and North America, iron sand producers in regions with abundant renewable energy (e.g., New Zealand’s geothermal and hydro resources) may gain a competitive edge by 2026.
4. Geopolitical and Supply Chain Diversification
With increasing scrutiny on supply chain resilience, especially after disruptions in global shipping and trade tensions, countries are seeking alternative sources of critical minerals. Iron sand deposits in Southeast Asia, particularly Indonesia and the Philippines, are gaining attention as strategic assets. By 2026, regional governments may implement policies to develop domestic processing capabilities, reducing reliance on imported iron ore and enhancing resource security.
5. Co-Production of Titanium and Vanadium
Iron sand often contains valuable by-products such as titanium dioxide and vanadium, both of which are critical for aerospace, pigments, and energy storage (e.g., vanadium redox flow batteries). As demand for battery metals surges, integrated processing plants that extract multiple minerals from iron sand are expected to become more common. This trend will improve the overall economics of iron sand mining and support circular economy models.
6. Environmental and Regulatory Pressures
Environmental concerns, particularly around coastal mining and marine ecosystem impacts, are prompting stricter regulations. By 2026, iron sand projects will likely face increased scrutiny and require advanced environmental management systems. Sustainable mining practices, including land rehabilitation and reduced water usage, will be essential for securing social license to operate, particularly in ecologically sensitive areas.
7. Price Volatility and Market Competition
Iron sand prices are expected to remain sensitive to fluctuations in global iron ore prices, currency exchange rates, and energy costs. However, niche applications and technological differentiation may insulate certain high-purity or specialty iron sand products from broader commodity swings. Competition from recycled steel and alternative materials could also influence long-term demand dynamics.
Conclusion
By 2026, the iron sand market is poised for strategic growth driven by technological innovation, decarbonization goals, and regional industrial policies. While challenges related to processing complexity and environmental impact persist, the integration of iron sand into green steel value chains and the recovery of critical co-products will enhance its market relevance. Producers who invest in sustainable practices, advanced technologies, and value-added processing are likely to capture significant opportunities in the evolving global metals landscape.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Iron Sand (Quality, IP)
Sourcing iron sand presents unique challenges due to its variable composition and potential intellectual property (IP) implications, especially when intended for advanced applications like direct reduction or magnetite production. Here are key pitfalls to avoid:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
- Inconsistent Chemical Composition: Iron sand deposits vary significantly in FeO/Fe₂O₃ ratio, total iron content, and impurities (TiO₂, V₂O₅, SiO₂, Al₂O₃, P, S). Relying on spot samples or outdated data can lead to procuring material unsuitable for your process, causing inefficiencies or product defects.
- Unverified Physical Properties: Critical characteristics like particle size distribution, density, and moisture content impact handling, processing efficiency (e.g., fluidization in reactors), and yield. Assuming specifications without rigorous testing leads to operational disruptions.
- Contamination and Impurities: Iron sand can contain problematic elements (e.g., high titanium, vanadium, or chlorine) or physical contaminants (plastics, organics). Failure to specify strict impurity limits and enforce testing results in downstream processing issues or off-spec final products.
- Lack of Standardized Specifications: The absence of universally accepted quality standards for iron sand (unlike iron ore pellets) makes defining “acceptable” quality difficult. Vague contracts lead to disputes and inconsistent supply.
- Inadequate Sampling and Testing Protocols: Poor sampling methods (not representative) or insufficient testing frequency/analysis depth (e.g., only total Fe, not mineralogy) provide a false sense of security about quality consistency.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
- Unprotected Processing Technology: Developing unique beneficiation, upgrading, or direct reduction processes for specific iron sand types creates valuable IP. Failing to secure patents (processes, equipment) or maintain trade secrets (specific parameters, know-how) before engaging suppliers or partners risks losing competitive advantage.
- Ambiguous IP Ownership in Joint Development: Collaborating with suppliers on process optimization or new applications requires clear contractual agreements upfront. Without defining who owns resulting IP (modifications, improvements), disputes arise, potentially blocking commercialization.
- Supplier Access to Sensitive Information: Sharing detailed process requirements or performance data with potential suppliers without robust Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) and clear scope limitations risks exposing core IP to competitors, especially if the supplier also works with others.
- Reverse Engineering Vulnerability: Unique physical or chemical characteristics of your processed material derived from iron sand might be protectable. If not patented or kept secret, competitors could potentially reverse-engineer the product and source similar sand to replicate it.
- Overlooking Geographical Indications or Local Regulations: In some regions, specific iron sand deposits or traditional processing methods might have protected status or be subject to local ownership/control rules, creating unexpected IP or access barriers.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Iron Sand
Overview of Iron Sand
Iron sand, also known as titanomagnetite sand, is a type of heavy mineral sand containing high concentrations of iron oxides. It is commonly used in steel production, construction, and as a raw material in various industrial applications. Due to its density and magnetic properties, iron sand requires specialized handling and transportation procedures to ensure safety, regulatory compliance, and environmental protection.
Classification and Regulatory Status
Iron sand is generally classified as a non-hazardous bulk solid cargo under the International Maritime Solid Bulk Cargoes (IMSBC) Code. However, its classification may vary depending on composition, moisture content, and particle size. Exporters and logistics providers must confirm the proper classification based on current testing and regulatory guidelines.
- IMSBC Code Category: Group C (non-liquefiable, non-chemically hazardous)
- UN Number: Not applicable (unless contaminated or mixed with hazardous substances)
- HS Code Example: 2601.11 or 2601.12 (for iron ores and concentrates, depending on country-specific tariff schedules)
Note: Always verify classification with local authorities and classification societies prior to shipment.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Iron sand is typically transported in bulk via open-top or covered hopper railcars, bulk carriers, or containerized in flexitanks or jumbo bags depending on volume and destination.
Key Handling Considerations:
- Moisture Control: While generally non-liquefiable, high moisture content can lead to shifting during transit. Load moisture content should remain below the Transportable Moisture Limit (TML).
- Dust Suppression: Iron sand can generate dust during loading/unloading. Use water sprays or dust suppressants and ensure workers wear appropriate PPE.
- Segregation: Keep iron sand separate from foodstuffs, corrosive materials, and moisture-sensitive goods.
Transportation Modalities
Maritime Transport
- Use bulk carriers compliant with IMSBC Code regulations.
- Submit a Cargo Declaration stating the cargo’s group classification, moisture content, and certification of test results.
- Ensure vessel holds are clean, dry, and free from contaminants.
- Monitor for cargo shift during transit, especially in rough seas.
Rail and Road Transport
- Use covered or enclosed trucks/railcars to prevent spillage and environmental contamination.
- Secure loads properly to prevent shifting.
- Follow national road and rail safety regulations (e.g., FMCSA in the U.S., ADR in Europe).
Air Transport
Iron sand is not typically air-shipped due to weight and volume constraints. If required for small samples, it must be packaged in UN-certified containers and declared in accordance with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations (usually as “not restricted” if non-hazardous).
Export and Import Compliance
Export Requirements
- Obtain necessary export licenses (varies by country; e.g., New Zealand requires permits for iron sand exports).
- Provide a Certificate of Origin.
- Submit a Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) or Safety Data Sheet (SDS), even if non-hazardous.
- Conduct and document moisture content and granulometry tests.
Import Requirements
- Comply with destination country customs regulations.
- Provide import declaration, commercial invoice, packing list, and bill of lading.
- Some countries may require environmental or mineral import permits.
- Check for restrictions (e.g., China, India, and EU may have specific rules on raw mineral imports).
Environmental and Safety Regulations
- EPA/Environmental Permits: Ensure compliance with local environmental protection laws during mining, storage, and loading.
- OSHA/Workplace Safety: Enforce use of respiratory protection, eye protection, and proper ventilation in handling facilities.
- MARPOL Annex V: Prevent illegal discharge of residue into the sea; wash water may require treatment before disposal.
Documentation Checklist
- Bill of Lading
- Commercial Invoice
- Packing List
- Certificate of Origin
- Cargo Test Reports (moisture content, granulometry)
- Export/Import Licenses
- SDS/MSDS
- Vessel Loading Plan (for bulk shipments)
- Customs Clearance Forms
Storage Guidelines
- Store in dry, covered areas to prevent moisture absorption.
- Use lined stockpiles on impermeable surfaces to avoid soil contamination.
- Control dust with windbreaks or sprays.
- Monitor for spontaneous heating (rare, but possible with fine particles and organic contamination).
Risk Management and Best Practices
- Conduct regular cargo testing before loading.
- Train staff in IMSBC Code procedures and emergency response.
- Use GPS tracking and cargo monitoring for high-value shipments.
- Insure cargo against loss, damage, and delay.
Conclusion
Iron sand logistics require careful attention to classification, moisture control, regulatory compliance, and environmental stewardship. By adhering to international standards and maintaining accurate documentation, shippers can ensure safe, efficient, and lawful transportation of iron sand across global supply chains. Always consult with regulatory bodies and logistics experts to stay updated on evolving requirements.
In conclusion, sourcing iron sand presents a promising opportunity for the development of iron and steel production, particularly in regions with abundant coastal or alluvial deposits. Its unique composition, rich in magnetite and other iron-bearing minerals, makes it a viable alternative to conventional iron ore, especially as traditional reserves become depleted. However, successful sourcing requires careful consideration of geological reliability, environmental impact, extraction technologies, and economic feasibility. Sustainable practices, including responsible mining and processing methods, must be implemented to minimize ecological disruption. Furthermore, establishing strong supply chains, complying with regulatory standards, and investing in beneficiation technologies are critical to ensuring consistent quality and scalability. With strategic planning and technological advancement, iron sand can play a significant role in meeting global iron demand and supporting the growth of resource-efficient metallurgical industries.