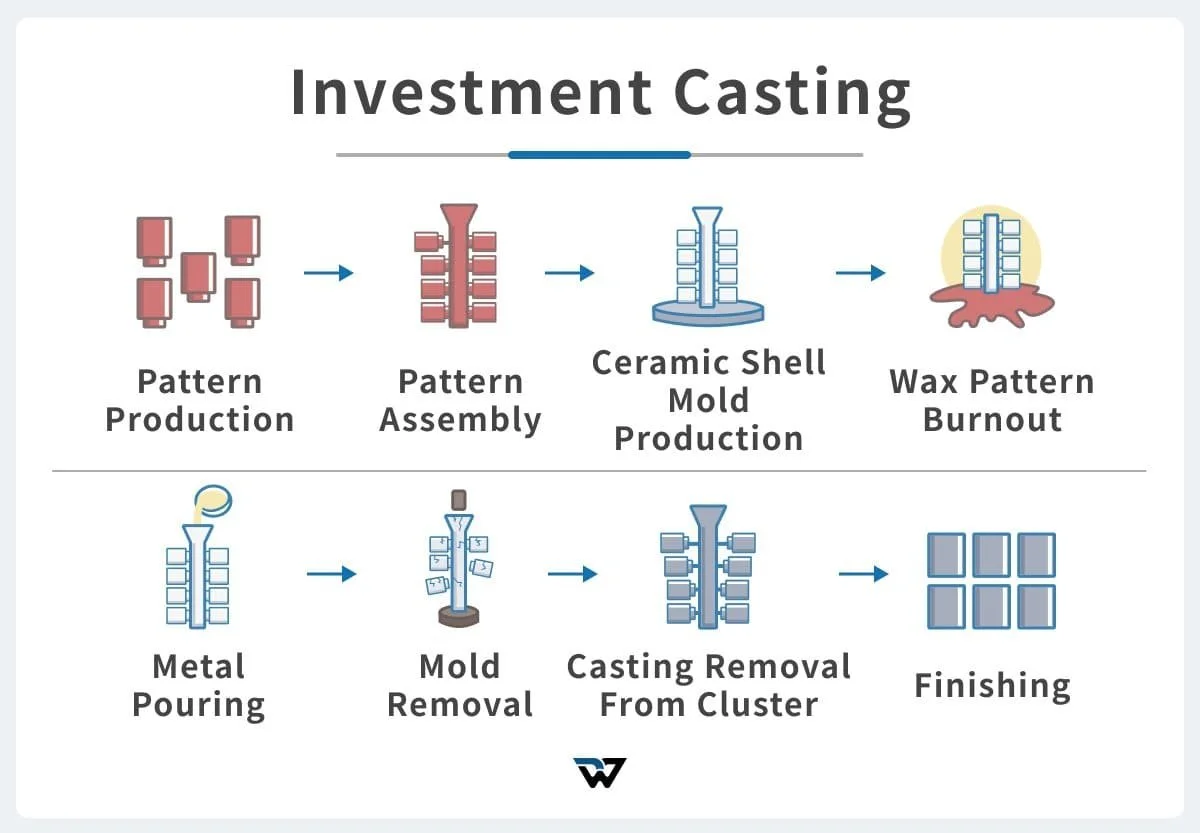
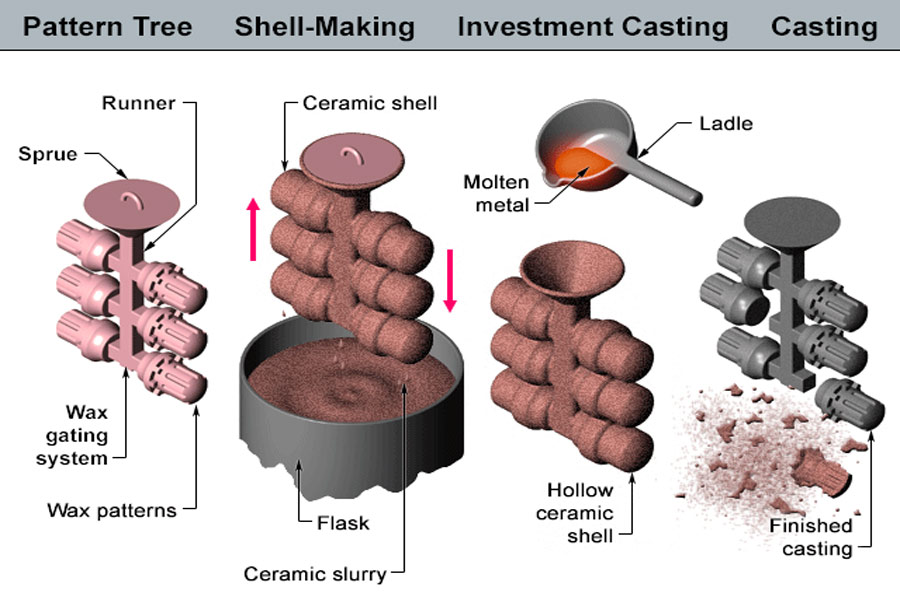
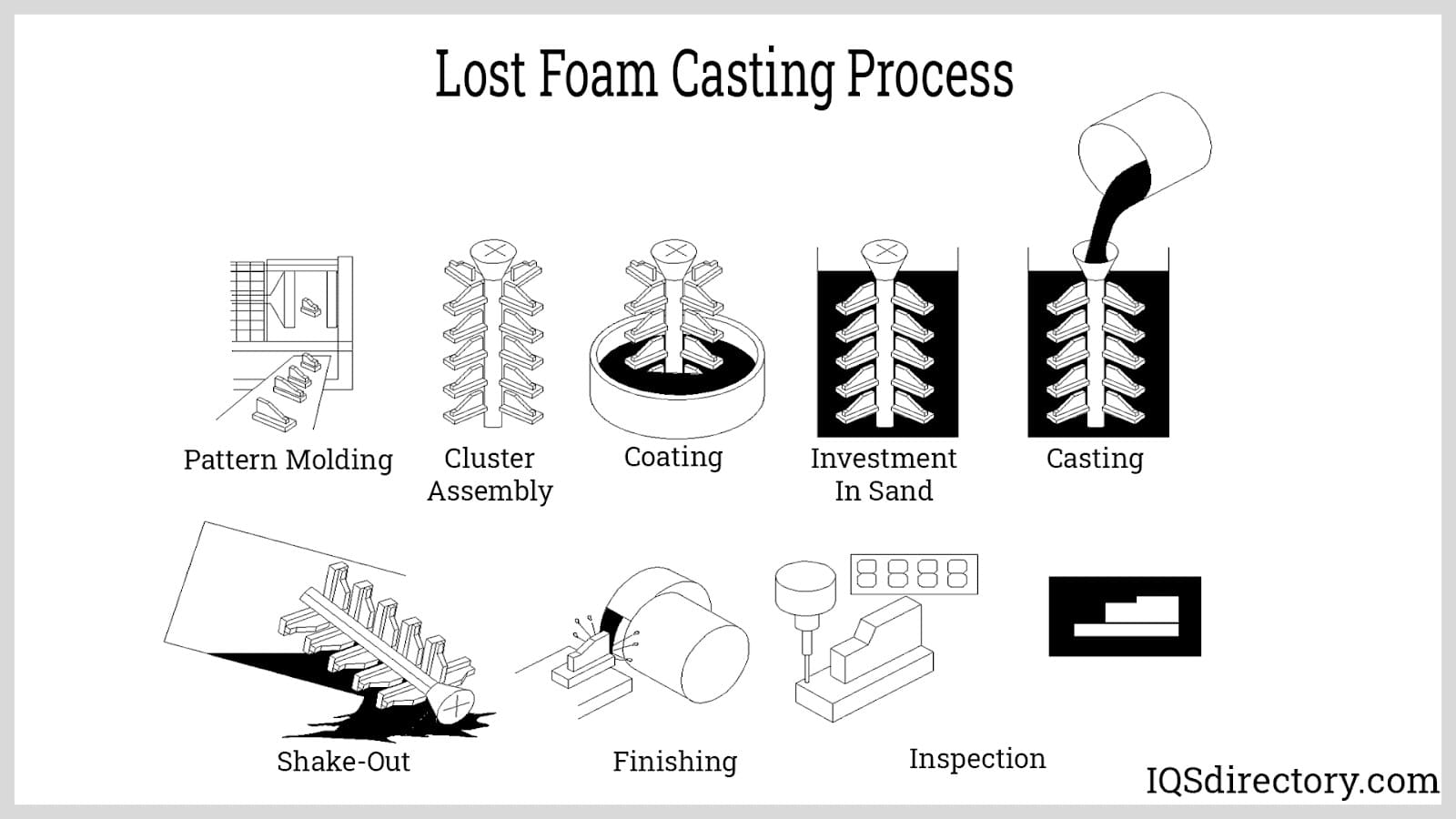
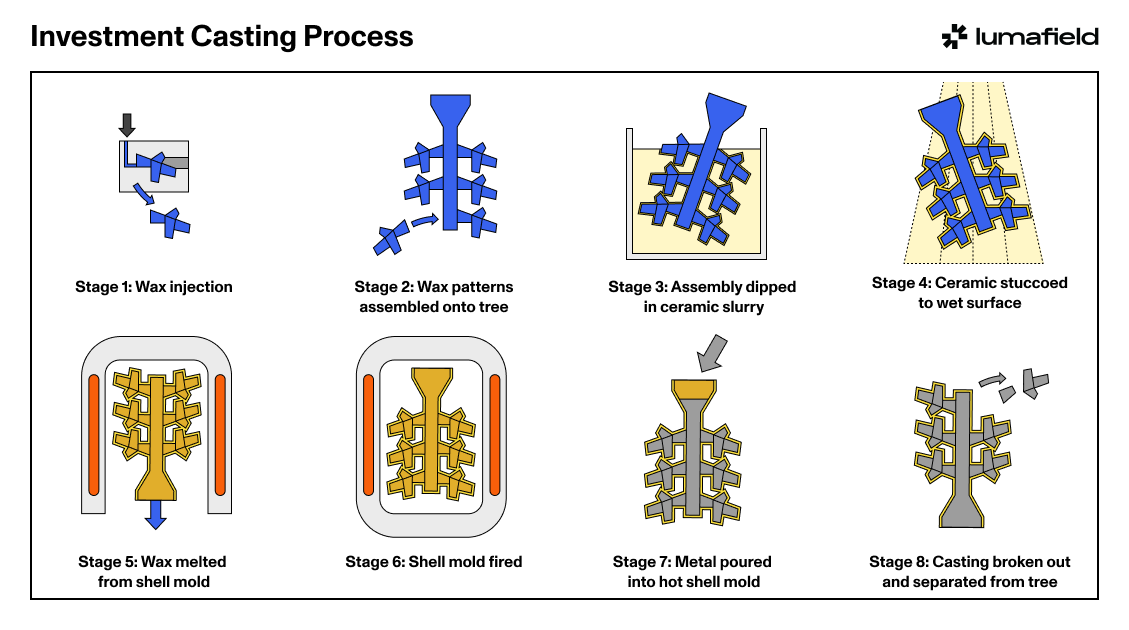
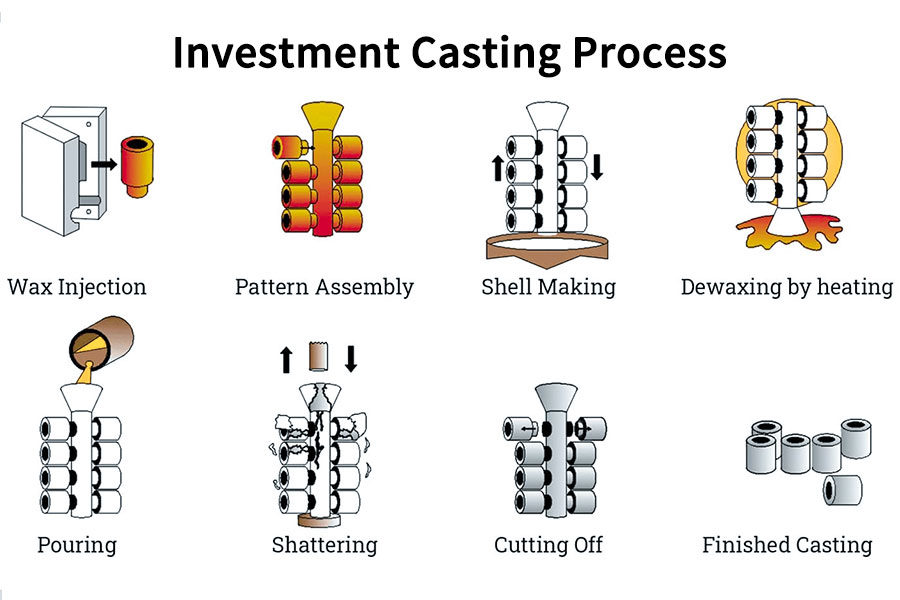
The global investment mold casting market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for high-precision, complex metal components in aerospace, defense, medical, and power generation industries. According to Grand View Research, the global investment casting market size was valued at USD 12.6 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030. This expansion is fueled by the increasing adoption of lightweight and high-strength alloys, particularly in aerospace applications, where precision and reliability are critical. Additionally, Mordor Intelligence projects continued market momentum, citing technological advancements in ceramic shell processes and growing outsourcing of casting production to specialized manufacturers. As demand intensifies, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders, combining scale, technical expertise, and innovation to dominate the investment casting landscape. These top players are setting industry benchmarks in quality, efficiency, and R&D investment.
Top 10 Investment Mold Casting Process Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 INDO
Domain Est. 2009
Website: indo-mim.com
Key Highlights: INDO-MIM Limited is a globally recognized manufacturer of Precision Engineering Components using Metal Injection Molding (“MIM”) technology….
#2 Learn About Investment Casting
Domain Est. 1995
Website: hitchiner.com
Key Highlights: Investment casting is a method of manufacturing parts by pouring molten metal into a hollow mold shell. The shell is made by an “investment” of ……
#3 Precision Investment Casting Process
Domain Est. 1998
Website: signicast.com
Key Highlights: Investment casting, or lost wax casting, involves creating a wax pattern, coating it with ceramic to form a mold, melting out the wax, pouring molten metal into ……
#4 Investment Casting Foundry
Domain Est. 2000
Website: americancastingco.com
Key Highlights: American Casting Company delivers premier quality investment castings with the industry’s shortest lead times. Located in Hollister, CA….
#5 Investment Casting
Domain Est. 2005
Website: vpic-group.com
Key Highlights: The investment casting process begins with the creation of a permanent mold, which matches the shape of the component. Once the mold is created, hot wax is ……
#6 Custom Investment Casting Manufacturing Company
Domain Est. 2008 | Founded: 1980
Website: tfgusa.com
Key Highlights: Trusted since 1980 for custom investment castings in stainless steel, aluminum & magnesium using advanced automated equipment….
#7 Investment Casting Foundry
Domain Est. 2008
Website: barron-industries.com
Key Highlights: Barron Industries offers precision-machined investment castings and assemblies, with over 200 alloys, including aluminum and stainless steel….
#8 Precision Investment Casting
Domain Est. 2014
Website: chemours.com
Key Highlights: Precision investment casting involves manufacturing of high-performance molds for casting of complex, intricate parts….
#9 Investment Castings
Domain Est. 2015
Website: investment-castings.net
Key Highlights: Investment casting is a metal working process that uses a ceramic shell built over a wax pattern to produce parts with extraordinarily uniform and smooth ……
#10 Niagara Investment Castings
Domain Est. 2015
Website: niagarainvestmentcastings.com
Key Highlights: We are your dependable single source for any investment cast solution you require, with the expertise to bring that solution to you fast and cost effectively….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Investment Mold Casting Process

H2: Emerging Market Trends in Investment Mold Casting Process (2026 Outlook)
The investment mold casting process, also known as lost-wax casting, is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, evolving industry demands, and global economic shifts. As industries such as aerospace, defense, medical devices, and energy continue to require high-precision, complex components, investment casting remains a critical manufacturing solution. Here’s an in-depth analysis of key market trends shaping the investment mold casting sector in 2026:
-
Increased Adoption of Automation and Digitalization
By 2026, automation is expected to play a pivotal role in enhancing the efficiency and consistency of investment casting operations. Foundries are increasingly integrating robotics for wax pattern assembly, shell building, and post-casting finishing. Digital twin technology and AI-driven process monitoring are being adopted to predict defects, optimize cycle times, and reduce scrap rates, improving overall yield and lowering production costs. -
Growth in Aerospace and Defense Applications
The aerospace and defense sectors remain the largest end-users of investment casting, particularly for turbine blades, engine components, and structural parts. With rising demand for fuel-efficient aircraft and next-generation defense systems, the need for high-performance, lightweight, and heat-resistant superalloys (e.g., Inconel, titanium) is driving innovation in casting techniques. OEMs are partnering closely with casting suppliers to ensure supply chain resilience and compliance with stringent quality standards. -
Expansion in Medical and Dental Industries
The medical device segment is emerging as a high-growth area for investment casting, especially for orthopedic implants, surgical instruments, and dental prosthetics. The demand for biocompatible materials like cobalt-chrome and titanium alloys, coupled with the need for patient-specific designs, is pushing foundries to adopt additive manufacturing (3D printing of wax or ceramic patterns) and precision casting techniques. -
Sustainability and Green Manufacturing Initiatives
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals are influencing investment casting practices. By 2026, there is a growing shift toward energy-efficient furnaces, recyclable ceramic shell systems, and closed-loop water and wax recovery systems. Additionally, companies are investing in cleaner energy sources and carbon footprint tracking to meet ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) benchmarks. -
Regional Shifts in Manufacturing and Supply Chains
Asia-Pacific, particularly China and India, continues to expand its investment casting capacity due to lower production costs and growing domestic demand. However, reshoring trends in North America and Europe—driven by geopolitical risks and the need for supply chain security—are leading to renewed investments in local foundry infrastructure. This dual dynamic is creating opportunities for global players with diversified manufacturing footprints. -
Advancements in Materials and Alloys
Ongoing R&D in advanced alloys and composite materials is expanding the performance envelope of investment cast parts. High-entropy alloys (HEAs) and oxide-dispersion-strengthened (ODS) materials are being explored for extreme environments. Simultaneously, improved modeling software enables better prediction of solidification behavior and microstructure evolution, enhancing material performance and reliability. -
Integration with Additive Manufacturing
Hybrid manufacturing—combining 3D printing with traditional investment casting—is gaining traction. 3D-printed wax or ceramic patterns allow for faster prototyping, reduced lead times, and greater design freedom. This synergy is particularly beneficial for low-volume, high-complexity parts in aerospace and energy applications, enabling rapid iteration and customization. -
Rising Demand in Renewable Energy and EV Sectors
While historically dominated by aerospace, investment casting is finding new applications in wind turbines, hydrogen fuel cells, and electric vehicle (EV) powertrains. Components such as turbine housings, sensor housings, and electric motor parts benefit from the precision and material versatility offered by investment casting, supporting the clean energy transition.
Conclusion
By 2026, the investment mold casting market is expected to grow steadily, fueled by innovation, sustainability, and cross-industry demand. Companies that embrace digital transformation, sustainable practices, and strategic partnerships will be best positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities. With an estimated CAGR of 5–7% through 2026, the sector remains a cornerstone of advanced manufacturing in high-tech industries.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Investment Mold Casting: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing investment mold casting (also known as lost-wax casting) from external suppliers, particularly overseas, offers cost advantages but introduces significant risks related to quality control and intellectual property (IP) protection. Understanding these common pitfalls is essential for mitigating potential issues and ensuring a successful supply chain.
Quality Inconsistencies and Process Variability
One of the most prevalent challenges in sourcing investment casting is maintaining consistent quality across production batches. Variations in raw materials, foundry practices, and environmental controls can lead to defects such as porosity, incomplete fills, dimensional inaccuracies, or surface imperfections. Suppliers may lack standardized quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001), resulting in inconsistent adherence to technical specifications. Without robust incoming inspection protocols or on-site audits, buyers risk receiving non-conforming parts that compromise end-product performance or require costly rework.
Inadequate Material Traceability and Certification
Investment castings are often used in demanding applications (e.g., aerospace, medical, or energy) where material composition is critical. A common pitfall is the absence of proper material traceability—suppliers may not provide valid mill test reports (MTRs) or may use substandard alloys to cut costs. Without verified documentation, companies expose themselves to compliance failures, product recalls, or safety hazards, especially in regulated industries.
Poor Dimensional Accuracy and Tolerance Control
Achieving tight tolerances in investment casting requires precision in wax pattern making, shell building, and thermal processing. Some suppliers, especially those with outdated equipment or insufficient process controls, struggle to maintain dimensional consistency. This results in parts that require extensive post-casting machining or fail to meet assembly requirements, undermining the cost and design benefits of near-net-shape casting.
Weak or Misaligned Quality Assurance Processes
Buyers often assume that suppliers perform comprehensive in-process and final inspections, but many lack proper non-destructive testing (NDT) capabilities such as X-ray, MPI, or fluorescent penetrant inspection. Even when testing is performed, inconsistent calibration, untrained personnel, or falsified reports can lead to undetected defects. Relying solely on final inspection without process validation increases the risk of latent failures in the field.
Intellectual Property Exposure and Theft
Sharing detailed CAD models, drawings, and proprietary alloy specifications with casting suppliers exposes companies to IP theft. Unscrupulous suppliers may reproduce and sell parts to competitors or reverse-engineer designs for their own product lines. In jurisdictions with weak IP enforcement, legal recourse is often limited or impractical, making prevention critical during the sourcing phase.
Lack of Contractual Safeguards for IP Protection
Many sourcing agreements fail to include robust IP clauses, such as clear ownership of tooling, molds, and design data, or restrictions on subcontracting and third-party access. Without non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) and explicit IP licensing terms, companies may lose control over their innovations. Additionally, failing to register IP in the supplier’s country can further weaken legal protection.
Supply Chain Transparency and Subcontracting Risks
Suppliers may subcontract parts of the casting process (e.g., wax modeling, shell coating, or heat treatment) without buyer knowledge, introducing unvetted third parties into the supply chain. This lack of transparency increases quality and IP risks, as oversight becomes diluted and accountability is unclear. Buyers may unknowingly source from unauthorized or lower-tier vendors, undermining quality and compliance.
Ineffective Communication and Technical Alignment
Misunderstandings due to language barriers, cultural differences, or inconsistent interpretation of engineering specifications can lead to incorrect casting designs or process deviations. Without regular technical dialogue and clear documentation (e.g., using ASME Y14.5 standards), even minor misalignments can result in major quality issues, delays, or rejections.
Failure to Conduct Onsite Audits and Qualification
Relying solely on paper certifications or remote assessments often leads to overestimating a supplier’s capabilities. Without onsite audits to evaluate equipment, workforce training, process controls, and quality records, buyers may partner with foundries that cannot meet required standards. Proper supplier qualification—including sample production runs and First Article Inspections (FAI)—is essential to validate performance before full-scale production.
Conclusion
Successfully sourcing investment mold casting requires proactive management of both quality and IP risks. Implementing strong supplier qualification processes, enforcing rigorous quality agreements, securing IP through legal and technical safeguards, and maintaining supply chain visibility are critical steps to avoid these common pitfalls and ensure reliable, protected manufacturing outcomes.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Investment Mold Casting Process
Overview of Investment Mold Casting
Investment mold casting, also known as lost-wax casting, is a precision manufacturing process used to produce complex metal components with high dimensional accuracy and excellent surface finish. Due to the intricate nature of the process and the materials involved, strict logistics and compliance protocols are essential to ensure safety, quality, environmental protection, and regulatory adherence.
Raw Material Sourcing & Transportation
Ensure all raw materials—wax patterns, ceramic slurries, refractory materials, and metal alloys—are sourced from certified suppliers complying with international standards (e.g., ISO 9001, ASTM, ASME). Transport materials under controlled conditions to prevent contamination or degradation. Maintain proper documentation, including material safety data sheets (MSDS/SDS), certificates of conformance (CoC), and chain-of-custody records.
Facility Layout & Workflow Planning
Design the production facility to support a logical flow from pattern making to dewaxing, shell building, firing, pouring, cooling, and finishing. Segregate clean and dirty zones to prevent cross-contamination. Ensure adequate ventilation, fire suppression systems, and emergency exits, particularly in high-temperature areas such as kilns and foundries.
Environmental Compliance
Adhere to local, national, and international environmental regulations (e.g., EPA, REACH, RoHS). Properly manage emissions from dewaxing and metal melting processes using afterburners or filtration systems. Recycle spent shell material and reclaim metal runoff where possible. Treat and dispose of wastewater from slurry preparation and cleaning operations in accordance with environmental permits.
Occupational Health & Safety (OHS)
Implement a comprehensive safety program aligned with OSHA (or equivalent) standards. Train personnel on handling hot metals, operating furnaces, and using personal protective equipment (PPE) such as heat-resistant gloves, face shields, and respirators. Conduct regular equipment inspections and safety drills. Monitor indoor air quality for silica, metal fumes, and wax-related hydrocarbons.
Quality Control & Traceability
Establish a quality management system (QMS) per ISO 9001 or NADCAP standards for aerospace applications. Implement full traceability from raw material batch numbers through final inspection reports. Use non-destructive testing (NDT) methods such as X-ray, ultrasonic, or dye penetrant testing to validate casting integrity. Maintain detailed records for audits and customer compliance.
Waste Management & Recycling
Classify all waste streams (hazardous vs. non-hazardous) and dispose of them through licensed waste handlers. Recycle reusable materials such as wax, metal sprues, and gates. Document waste manifests and disposal certificates to demonstrate compliance with environmental laws and support sustainability initiatives.
Packaging, Labeling & Shipping
Package finished castings to prevent damage during transit, using anti-corrosion measures such as VCI paper or desiccants where necessary. Label shipments with proper handling instructions, material composition, and compliance markings (e.g., CE, FAA, ITAR if applicable). Ensure transport complies with IATA, IMDG, or DOT regulations when shipping hazardous materials or internationally controlled goods.
Regulatory & Industry Standards Compliance
Maintain compliance with relevant industry-specific standards, including:
– Aerospace: AS9100, AMS standards
– Medical: ISO 13485, FDA 21 CFR Part 820
– Defense: ITAR/EAR regulations
– General: ISO 14001 (Environmental), ISO 45001 (Safety)
Conduct internal audits and prepare for third-party certifications as required by customers or jurisdictions.
Documentation & Recordkeeping
Keep comprehensive records of all process parameters, inspection results, non-conformance reports (NCRs), corrective actions (CAPA), and employee training. Store digital and physical records securely for the required retention period (typically 10+ years in aerospace and medical sectors).
Continuous Improvement & Risk Management
Regularly review logistics and compliance performance using key performance indicators (KPIs). Conduct risk assessments for supply chain disruptions, regulatory changes, and process failures. Implement corrective and preventive actions to enhance efficiency, safety, and compliance over time.
Conclusion for Sourcing Investment Mold Casting Process:
Sourcing the investment mold casting process offers a highly effective solution for producing complex, high-precision metal components with excellent surface finish and dimensional accuracy. This method is particularly advantageous for industries such as aerospace, medical, automotive, and energy, where part integrity and performance are critical. By leveraging investment casting, companies can reduce material waste, minimize secondary machining operations, and achieve near-net-shape components, leading to long-term cost savings despite higher initial tooling and labor costs.
When sourcing this process, it is essential to partner with experienced and certified suppliers who maintain stringent quality controls, utilize advanced materials and technologies, and comply with industry standards (e.g., ISO, ASTM). Evaluating supplier capabilities in wax pattern production, shell building, alloy selection, and post-casting finishing ensures consistent product quality and reliability.
In conclusion, investment mold casting remains a superior choice for producing intricate and high-performance metal parts. Strategic sourcing from qualified manufacturers enables businesses to balance cost-efficiency with high-quality output, supporting innovation and competitiveness in demanding markets.