The global fiberglass insulation market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for energy-efficient building solutions and stringent government regulations on carbon emissions. According to Grand View Research, the market was valued at USD 10.5 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is further accelerated by rising construction activities, especially in emerging economies, and the expanding use of fiberglass insulation in industrial and HVAC applications. As sustainability becomes a priority across industries, manufacturers are investing in innovative, low-emission production technologies and recyclable materials to meet evolving environmental standards. Amid this dynamic landscape, a select group of industry leaders continues to shape the future of insulation through advanced manufacturing capabilities, global supply chains, and strong R&D initiatives—solidifying their positions in the highly competitive market. Here’s a look at the top nine fiberglass insulation manufacturers driving innovation and growth worldwide.
Top 9 Insulation Fiber Glass Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Knauf Insulation
Domain Est. 2000
Website: knaufinsulation.com
Key Highlights: Knauf Insulation is one of the world’s largest manufacturers of insulation products and solutions. We are present in more than 40 countries and have 29 ……
#2 Innovative Fibreglass Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2013
Website: valmiera-glass.com
Key Highlights: Glass fibre for further processing, building, thermal insulation and aviation. Improving the quality of life worldwide for millions of people together!…
#3 ISOVER
Domain Est. 1995 | Founded: 1937
Website: saint-gobain.com
Key Highlights: Since 1937, we imagine, manufacture and deliver a broad range of insulation solutions made of different materials. A MULTI-MATERIAL OFFER….
#4 Fiberglass Insulation
Domain Est. 1995
Website: certainteed.com
Key Highlights: Fiberglass insulation can reduce energy costs, provide interior and exterior sound control, and it’s safe to manufacture and install….
#5 PINK Next Gen® Fiberglas™ Insulation
Domain Est. 1996
Website: owenscorning.com
Key Highlights: Owens Corning PINK Next Gen Fiberglas insulation fits perfectly in the cavity and does not settle over time. It glides easily, splits cleanly and fills ……
#6 Fiberglass Insulation
Domain Est. 1997
Website: jm.com
Key Highlights: Johns Manville Formaldehyde-free™ fiberglass insulation provides thermal and accoustical control for both vertical and horizontal applications….
#7 About Us
Domain Est. 1998
Website: insulfab.net
Key Highlights: Insul-Fab has been considered a premier converter of foams, fiberglass, and plastics, using a wide array of cutting and fabrication techniques….
#8 General Insulation Company
Domain Est. 2001
Website: generalinsulation.com
Key Highlights: A wholesale distributor, providing a full line of sustainable products and solutions for thermal efficiency, condensation/moisture control, and life safety….
#9 Greenfiber
Domain Est. 2001
Website: greenfiber.com
Key Highlights: Greenfiber cellulose insulation helps create energy-efficient, quiet, and comfortable homes with sustainable materials that protect what matters most….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Insulation Fiber Glass

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Insulation Fiberglass
The global insulation fiberglass market is expected to experience significant transformation by 2026, driven by rising environmental regulations, advancements in building efficiency standards, and growing demand for energy conservation. As governments and industries prioritize sustainability and carbon reduction, fiberglass insulation—known for its thermal performance, fire resistance, and cost efficiency—is poised to play a key role in both residential and commercial construction sectors.
One of the dominant trends shaping the 2026 market is the increasing adoption of green building certifications such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) and BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method). These standards encourage the use of high-performance insulation materials, including fiberglass, to reduce building energy consumption. As a result, demand for low-emission, formaldehyde-free fiberglass variants is growing, particularly in North America and Europe.
Another key trend is the expansion of the construction industry in emerging economies, especially in Asia-Pacific and the Middle East. Countries like India, China, and Saudi Arabia are investing heavily in infrastructure and smart city development, creating robust opportunities for fiberglass insulation manufacturers. Urbanization and rising awareness of indoor air quality are further fueling demand for advanced insulation solutions.
Technological innovation is also influencing the market. By 2026, manufacturers are expected to focus on enhancing product performance through finer glass fibers, improved binders, and integration with smart building systems. Additionally, the push for circular economy principles is driving research into recyclable fiberglass products and closed-loop manufacturing processes.
Lastly, supply chain resilience and raw material availability will remain critical issues. Fluctuations in energy prices and silica sand supply may impact production costs. However, strategic partnerships and regional manufacturing hubs are expected to mitigate these challenges.
In conclusion, the 2026 insulation fiberglass market will be characterized by sustainability-driven innovation, regulatory support, and geographic expansion, positioning fiberglass as a cornerstone material in the global shift toward energy-efficient construction.
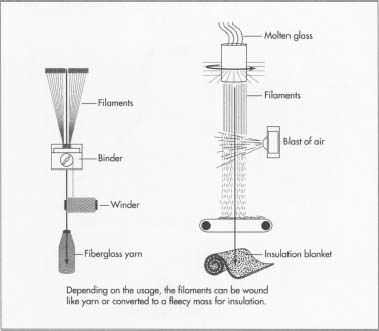
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Insulation Fiberglass (Quality, IP)
Sourcing insulation fiberglass involves navigating several critical challenges that can significantly impact product performance, compliance, and long-term project success. Overlooking these pitfalls—especially concerning quality and intellectual property (IP)—can lead to costly rework, safety hazards, or legal exposure.
Poor Material Quality and Performance
One of the most frequent issues is receiving fiberglass insulation that does not meet specified performance standards. Substandard products may have inconsistent fiber density, improper binder content, or inadequate thermal and acoustic properties. This can result in reduced energy efficiency, increased HVAC loads, and non-compliance with building codes. Buyers must verify third-party certifications (e.g., ASTM, ISO) and request material test reports to ensure consistency and reliability.
Misrepresentation of R-Value and Thermal Performance
Suppliers may exaggerate or inaccurately state the R-value (thermal resistance) of fiberglass insulation. Since R-value is critical to energy code compliance and building efficiency, relying on unsubstantiated claims can lead to underperforming installations. Always demand independent lab testing data and ensure performance metrics are based on standardized test methods (e.g., ASTM C518).
Inconsistent Product Dimensions and Fit
Fiberglass batts or rolls that vary in thickness, width, or compressive strength can create gaps, compression, or improper fit during installation. Poor fit reduces effective R-value and allows air leakage, undermining the insulation’s purpose. Specify tight manufacturing tolerances and conduct random on-site inspections to verify dimensional accuracy.
Lack of Fire and Safety Compliance
Some sourced fiberglass fails to meet required fire resistance, smoke development, or toxicity standards (e.g., ASTM E84, UL 723). Especially in commercial or high-occupancy buildings, non-compliant materials can pose serious safety risks and violate fire codes. Insist on up-to-date fire safety certifications and ensure labeling matches regulatory requirements for the project’s jurisdiction.
Inadequate Environmental and Health Standards
Low-quality fiberglass may emit excessive formaldehyde or other volatile organic compounds (VOCs), raising indoor air quality concerns and potentially violating green building standards (e.g., LEED, WELL). Source products labeled as low-emission or formaldehyde-free, and verify compliance through environmental product declarations (EPDs) or Health Product Declarations (HPDs).
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Sourcing from manufacturers or distributors that replicate patented fiberglass technologies—such as specific fiber formulations, binder systems, or installation methods—can expose buyers to IP litigation. Unlicensed use of proprietary processes (e.g., Owens Corning’s FOAMGLAS®-related IP or CertainTeed’s patented bonding techniques) may result in legal liability, even if unintentional. Conduct supplier due diligence and require written assurance of IP compliance.
Counterfeit or Gray Market Products
The market includes counterfeit or diverted “gray market” insulation products that mimic reputable brands but lack quality control and warranty coverage. These products often bypass official distribution channels and may not meet regional standards. Always purchase through authorized distributors and verify product authenticity via batch numbers, holograms, or manufacturer verification tools.
Insufficient Warranty and Technical Support
Low-cost suppliers may offer limited or voidable warranties, leaving buyers exposed if performance issues arise. Additionally, lack of technical support can hinder proper installation and troubleshooting. Prioritize suppliers who provide comprehensive warranties, installation guidelines, and access to engineering support.
Failure to Verify Regional Standards and Approvals
Insulation requirements vary by region, climate zone, and application (e.g., residential vs. industrial). Sourcing products without confirming local building code approvals (e.g., IRC, IBC, or EU CE marking) can result in rejected materials or failed inspections. Ensure all fiberglass insulation is certified for use in the target market.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls—through rigorous supplier vetting, independent testing, and IP compliance checks—buyers can ensure they source high-quality, legally sound, and high-performing insulation fiberglass.
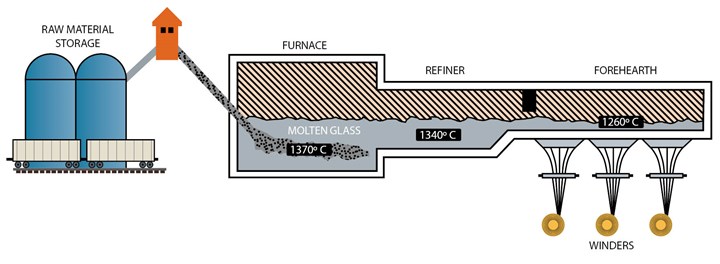
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Insulation Fiberglass
Overview of Insulation Fiberglass
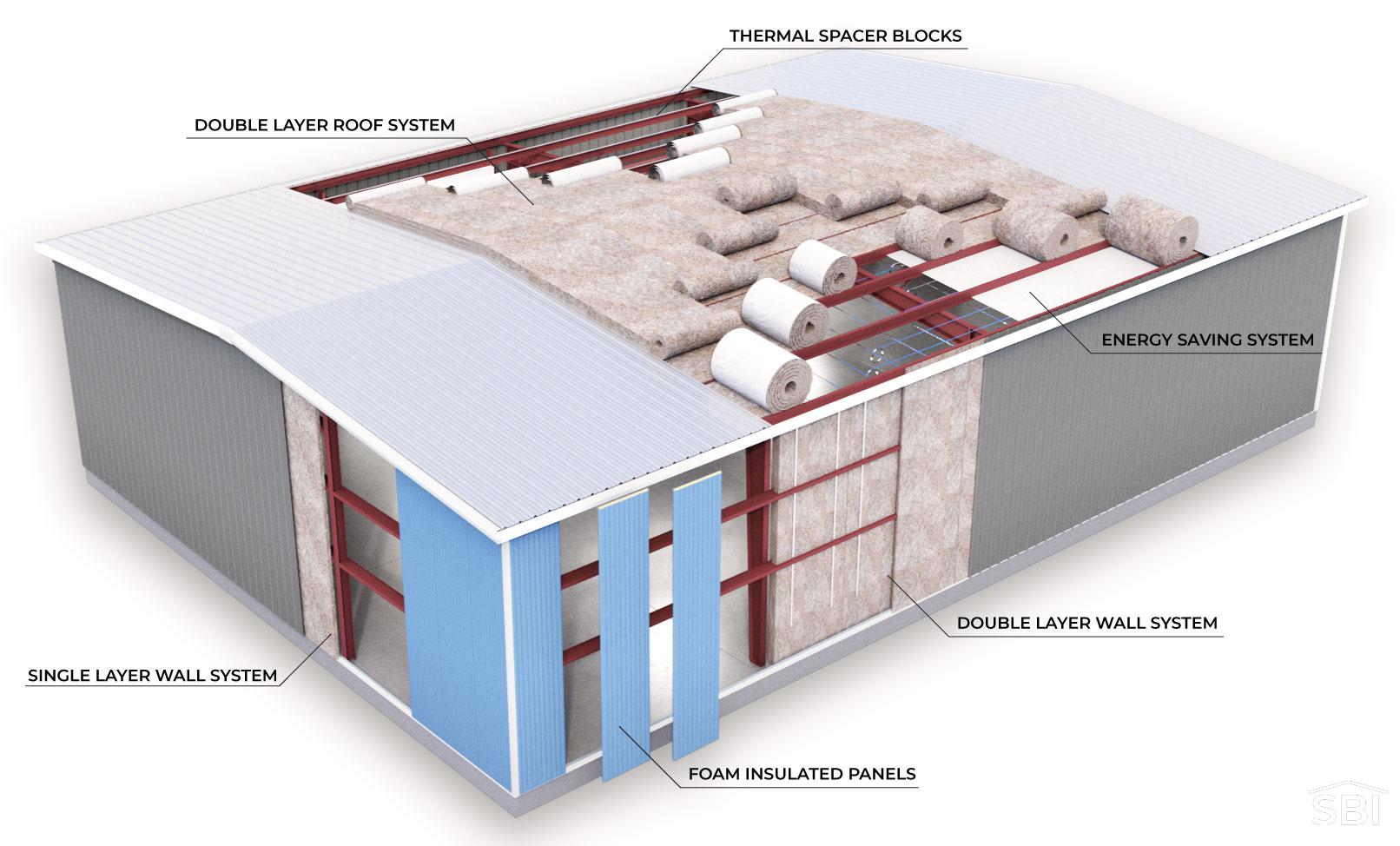
Insulation fiberglass is a widely used thermal and acoustic insulation material composed of fine glass fibers. It is commonly used in residential, commercial, and industrial construction to improve energy efficiency and reduce noise transmission. Due to its physical properties and potential health and environmental impacts, the logistics and compliance requirements for handling, transporting, and storing fiberglass insulation are specific and must be strictly followed.
Classification and Regulatory Framework
Insulation fiberglass is generally classified as a non-hazardous material under most international transport regulations, including the UN Model Regulations and the U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT) guidelines. However, it may be subject to certain handling and labeling requirements due to its fibrous nature.
- UN Number: Not applicable (typically non-hazardous)
- IMO/IMDG Code: Not classified as dangerous goods
- IATA/ICAO: Not restricted as hazardous for air transport
- OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration): Regulates worker exposure under general industry standards (29 CFR 1910.1001 for mineral wool fibers, often referenced for fiberglass)
- REACH (EU): Registered substance; no SVHCs (Substances of Very High Concern) currently listed for standard fiberglass
- CLP Regulation (EU): Labeling not required for standard forms, but may apply to certain additives or binders
Packaging and Containment
Proper packaging is essential to prevent fiber release, physical damage, and moisture exposure during logistics operations.
- Primary Packaging: Fiberglass batts, rolls, or loose-fill are typically wrapped in plastic film (e.g., polyethylene) to protect from moisture and limit fiber dispersion.
- Secondary Packaging: Bundled and secured on pallets using stretch wrap or strapping.
- Labeling: Packages should be labeled with product identification, batch number, manufacturer details, and handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” “Protect from Moisture”).
- Fiber Containment: Ensure packaging remains intact to minimize airborne fiber release during handling.
Storage Requirements
- Indoor Storage: Store in a dry, well-ventilated area away from direct weather exposure.
- Elevation: Keep pallets off the ground using pallet racks or skids to prevent moisture absorption.
- Stacking: Limit stack height per manufacturer recommendations to prevent compression damage.
- Segregation: Store away from chemicals, solvents, or abrasive materials that could degrade packaging or the product.
Transportation Guidelines
- Mode of Transport: Suitable for road, rail, sea, and air freight as non-hazardous cargo.
- Load Securing: Use straps, bracing, or dunnage to prevent shifting during transit.
- Moisture Protection: Use weather-resistant tarps or enclosed trailers for open-bed transport.
- Temperature Considerations: Avoid prolonged exposure to extreme heat or freezing conditions that may affect binder integrity.
Handling and Worker Safety
While fiberglass is not classified as a carcinogen (IARC Group 3), inhalation of fibers can cause respiratory and skin irritation.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
- NIOSH-approved respirator (N95 or equivalent) for dusty environments
- Long-sleeved clothing, gloves, and safety goggles
- Ventilation: Ensure adequate airflow in enclosed handling areas.
- Hygiene: Provide washing facilities; prohibit eating, drinking, or smoking in handling zones.
- Training: Employees must be trained on safe handling, emergency procedures, and proper disposal.
Environmental and Disposal Compliance
- Recyclability: Fiberglass insulation can often be recycled or reused; check with local facilities.
- Waste Disposal: Dispose of damaged or excess material in accordance with local solid waste regulations.
- Landfill: If landfilling is required, ensure compliance with municipal or regional waste directives.
- Spill Management: In case of packaging failure, clean up using wet methods or HEPA-filter vacuuming—avoid dry sweeping.
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Maintain accurate documentation throughout the supply chain:
– Safety Data Sheet (SDS): Provide updated SDS (Section 14 includes transport information) to all stakeholders.
– Bill of Lading / Air Waybill: Include proper product description and handling notes.
– Certificates of Compliance: Retain records of regulatory compliance (e.g., REACH, OSHA training logs).
– Shipping Labels: Ensure all labels reflect manufacturer and handling instructions.
International Considerations
- Import/Export Controls: Verify no restrictions apply in destination countries; some may require conformity assessment (e.g., CE marking in the EU).
- Customs Declarations: Accurately classify under HS Code (e.g., 7019.31 or 7019.32 for glass wool).
- Language Requirements: Provide SDS and labels in the local language where required.
Emergency Response
- Fiber Release: Isolate area, wear PPE, and clean with wet methods or HEPA vacuum.
- Eye Contact: Flush with water for at least 15 minutes; seek medical attention if irritation persists.
- Inhalation: Move to fresh air; seek medical advice if coughing or breathing difficulty occurs.
- Spill Kits: Maintain kits with PPE, containment materials, and cleanup tools at handling sites.
Conclusion
Insulation fiberglass requires careful logistics management and compliance with health, safety, and environmental regulations despite its non-hazardous classification. Adhering to proper packaging, handling, transportation, and documentation standards ensures product integrity, regulatory compliance, and worker safety throughout the supply chain. Always consult the manufacturer’s guidelines and local regulatory authorities for region-specific requirements.
Conclusion for Sourcing Fiberglass Insulation
In conclusion, sourcing fiberglass insulation requires a careful evaluation of quality, cost, sustainability, and supplier reliability. As a widely used thermal and acoustic insulation material, fiberglass offers excellent energy efficiency, fire resistance, and durability when sourced from reputable manufacturers. Key considerations in the procurement process include compliance with industry standards (such as ASTM and ISO), environmental certifications (like formaldehyde-free or recycled content), and long-term performance in specific applications.
Strategic sourcing should involve comparing multiple suppliers based on product specifications, delivery capabilities, and technical support. Additionally, evaluating the total cost of ownership—factoring in insulation performance, installation ease, and lifecycle savings—can lead to more informed and cost-effective decisions. Emphasis on sustainable sourcing practices not only supports environmental goals but also aligns with increasing regulatory and consumer demands for green building materials.
Ultimately, a well-structured fiberglass insulation sourcing strategy contributes to improved building performance, energy conservation, and project success across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors.