The global static mixer market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand across industries such as chemical processing, water treatment, pharmaceuticals, and food & beverage. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at approximately USD 3.2 billion in 2021 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 4.8% from 2023 to 2028. Similarly, Grand View Research estimates that the market size could exceed USD 4.5 billion by 2030, fueled by advancements in mixer design, energy efficiency, and process automation. Inline static mixers—valued for their low maintenance, consistent performance, and ability to handle continuous flow processes—are particularly in demand as manufacturers seek scalable and sustainable mixing solutions. With competitive dynamics intensifying and innovation accelerating, identifying the leading manufacturers in this space is critical for procurement professionals and engineering teams evaluating reliable supply partners.
Top 10 Inline Static Mixer Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Komax Systems
Domain Est. 1996 | Founded: 1973
Website: komax.com
Key Highlights: We have been a manufacturer of static inline mixers, steam heaters, and heat exchangers since 1973 with our technologies being applied to projects worldwide….
#2 Kenics
Domain Est. 1995
Website: nov.com
Key Highlights: Kenics static mixers have set the standard for inline mixing and heat transfer performance. We incorporate advanced technology into every static mixer….
#3 Industrial Mixers: Inline, In
Domain Est. 1997
Website: admix.com
Key Highlights: We pride ourselves on being the gold standard in industrial mixing solutions. Our fully scalable systems are designed to grow with your business….
#4 Koflo Corporation
Domain Est. 2000
Website: koflo.com
Key Highlights: Koflo designs and manufactures custom static mixers of all sizes for every industry and application. Let us design a mixer to meet your needs….
#5 Statiflo
Domain Est. 1996
Website: statiflo.com
Key Highlights: Statiflo is a world leader in the development and application of static pipe mixers, inline static mixers, channel mixers, duct mixers, gas dispersion systems….
#6 Static mixers
Domain Est. 1996
Website: sulzer.com
Key Highlights: With Sulzer’s static mixers you can produce small volumes with an excellent mixing reliability. They can be easily installed, cleaned and maintained….
#7 In-Line Static Mixers
Domain Est. 1999
Website: rhfs.com
Key Highlights: $1,000 deliveryClear PVC in-line static mixers in 3/8” to 2” sizes. Schedule 80 PVC inline mixers with injection ports in 1” to 6” sizes….
#8 Static Inline Mixer
Domain Est. 1999
Website: pulsafeeder.com
Key Highlights: The Pulsafeeder Inline Mixer utilizes a unique internal design, which uses ordinary line pressure to create high levels of turbulence….
#9 High Performance Static Mixers Custom Made By Westfall
Domain Est. 2016
Website: westfallstaticmixers.com
Key Highlights: High performance drop-in Static Mixers are engineered to order for the water, wastewater, oil, gas, chemical, aerospace and insulation industries….
#10 Static Mixer (SM)
Website: noritake.co.jp
Key Highlights: The static mixer (SM) is a unique line mixer that does not require an actuator. It uniformly mixes liquids and gases, with various applications in foods, ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Inline Static Mixer
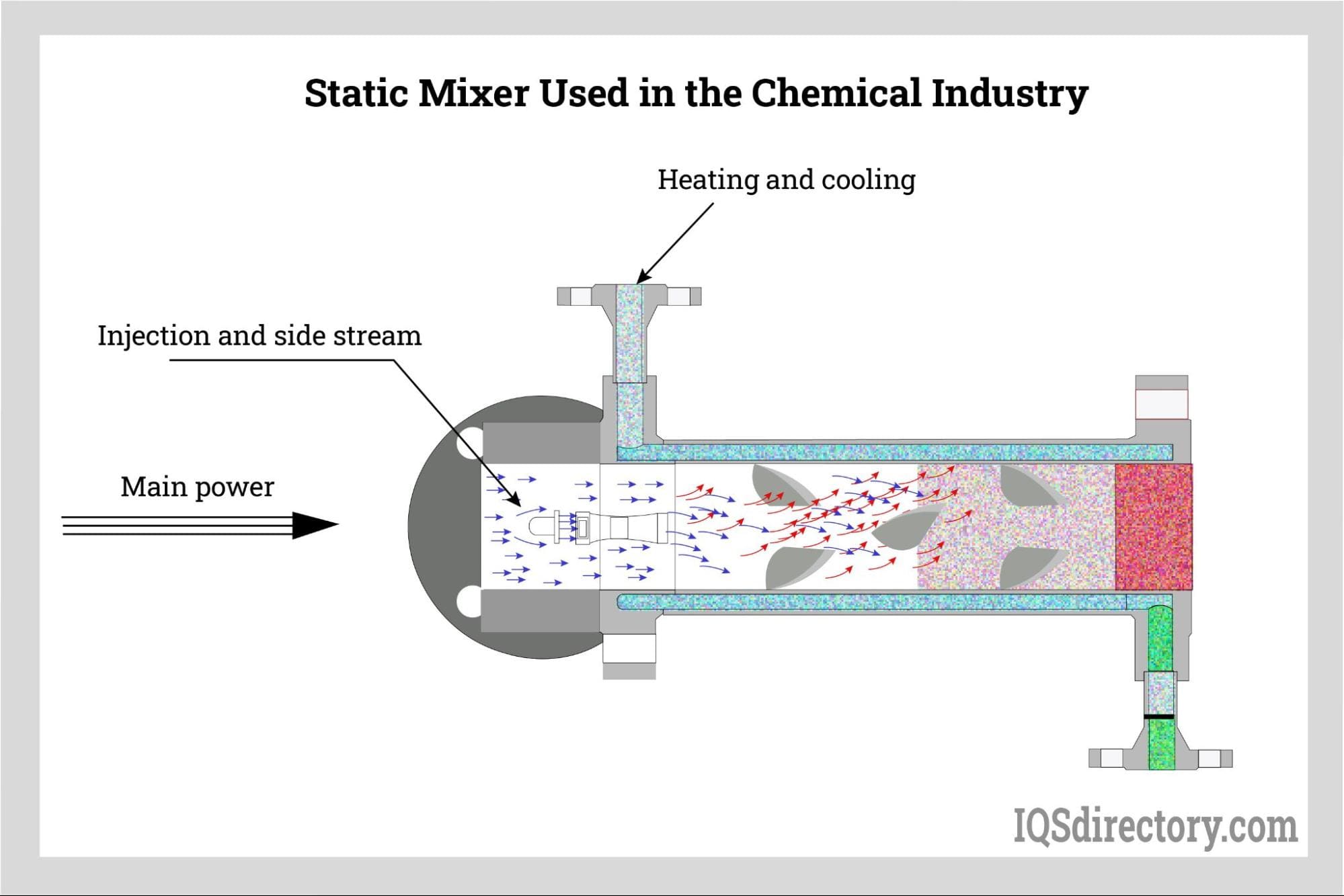
2026 Market Trends for Inline Static Mixers
The inline static mixer market is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by technological advancements, expanding industrial applications, and growing emphasis on process efficiency and sustainability. Key trends shaping the market landscape include:
Increasing Demand for Process Efficiency and Energy Savings
Industries across chemicals, pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, and water treatment are prioritizing operational efficiency and reduced energy consumption. Inline static mixers, with their no-moving-parts design, offer low pressure drop and minimal maintenance, aligning with these goals. By 2026, demand will grow for high-efficiency mixer designs that optimize mixing performance while minimizing energy use, particularly in large-scale continuous processes.
Expansion in Emerging Applications and Industries
Beyond traditional sectors, static mixers are finding new utility in emerging fields such as renewable energy (e.g., biodiesel production), advanced materials (nanocomposites, battery slurries), and biotechnology. The trend toward modular and continuous manufacturing in pharmaceuticals and specialty chemicals will further drive adoption, as inline mixers support precise, repeatable mixing in compact systems.
Advancements in Material Science and Customization
Developments in high-performance polymers, corrosion-resistant alloys, and 3D-printed components are enabling mixers suited for aggressive chemicals, high-temperature environments, and hygienic applications. By 2026, manufacturers will increasingly offer customized solutions tailored to specific fluid dynamics, viscosity profiles, and sanitary standards—especially in life sciences and food processing—enhancing performance and compliance.
Integration with Digitalization and Industry 4.0
Smart manufacturing trends are pushing integration of inline mixers with digital monitoring and control systems. Sensors for flow rate, pressure, and temperature, combined with data analytics, allow real-time performance optimization and predictive maintenance. By 2026, expect wider adoption of “smart mixers” connected to industrial IoT platforms, improving process visibility and reducing downtime.
Focus on Sustainability and Green Manufacturing
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals are influencing mixer design and deployment. Static mixers contribute to reduced waste, lower solvent use, and improved reaction yields. The trend toward eco-friendly processing—such as solvent-free coating applications and water-based formulations—will favor inline mixing technologies that enable precise, homogeneous blending with minimal environmental impact.
Regional Growth Dynamics
While North America and Europe remain strong markets due to mature process industries and regulatory standards, Asia-Pacific is expected to witness the fastest growth by 2026, driven by industrialization in China, India, and Southeast Asia. Investments in infrastructure, chemical production, and water treatment will fuel demand for cost-effective and reliable mixing solutions.
In summary, the 2026 inline static mixer market will be characterized by innovation in materials and design, deeper integration with digital systems, and expanding use across high-growth sectors—all underpinned by the global push for efficiency, sustainability, and process intensification.
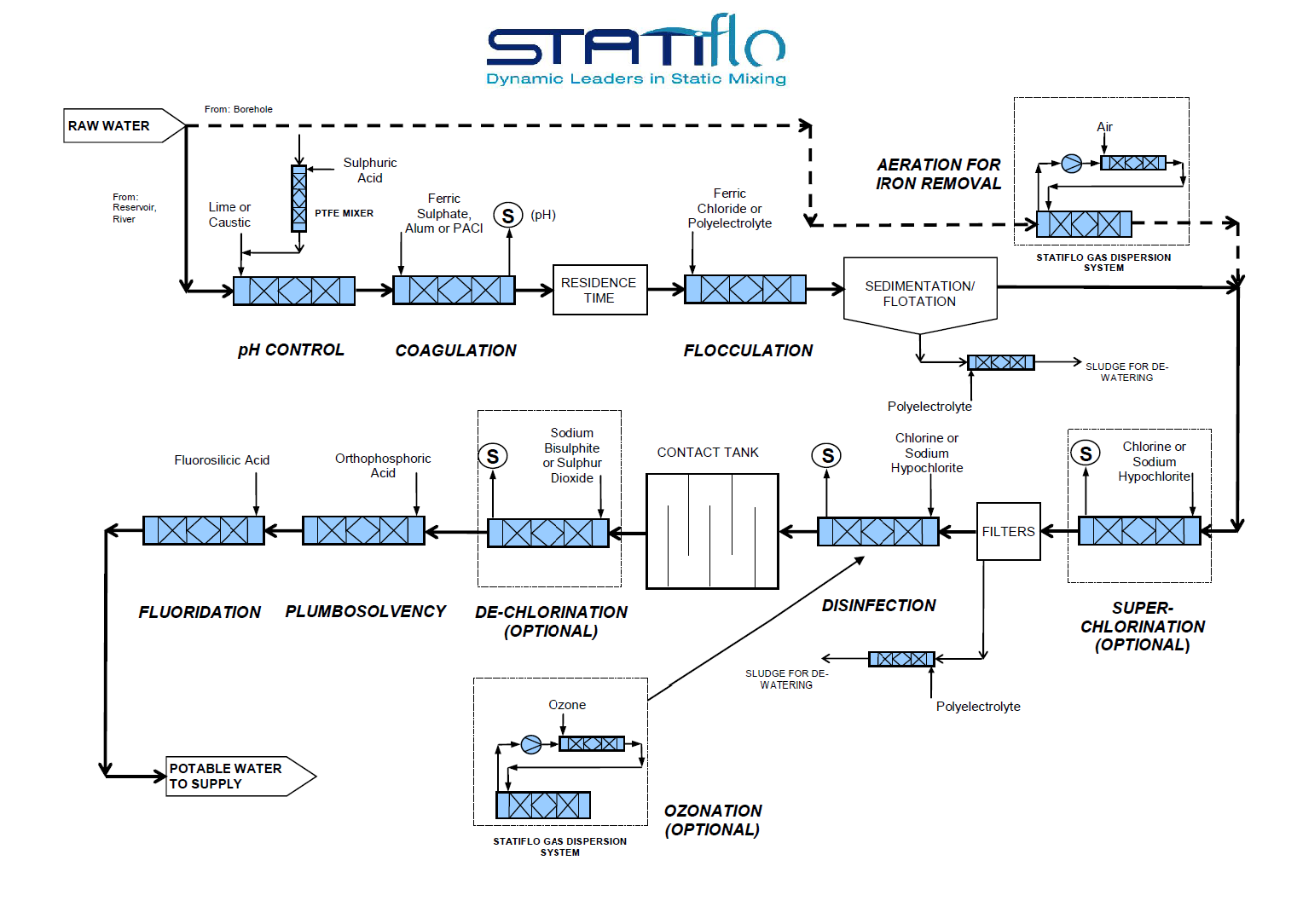
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Inline Static Mixers (Quality, IP)
Sourcing inline static mixers requires careful evaluation to ensure performance, durability, and compliance. Overlooking key factors can lead to operational inefficiencies, contamination risks, or intellectual property (IP) issues. Below are common pitfalls in quality and IP considerations:
Poor Material Quality and Construction
One of the most frequent issues is selecting mixers made from substandard materials. Low-grade plastics or metals may degrade when exposed to aggressive chemicals, high temperatures, or pressure fluctuations. This can result in premature failure, contamination of the process stream, or safety hazards. Always verify material certifications (e.g., ASTM, FDA, USP Class VI) and ensure compatibility with your process media.
Inadequate Mixing Performance Validation
Suppliers may provide generic performance data that doesn’t reflect real-world conditions. Without proper validation—such as CFD (computational fluid dynamics) analysis or third-party testing—there’s a risk the mixer won’t achieve the required homogeneity. Always request application-specific performance data and, if possible, pilot testing before full-scale procurement.
Lack of Traceability and Documentation
Poor documentation of manufacturing processes, material lots, or quality control tests can pose serious risks, especially in regulated industries (e.g., pharmaceuticals, food & beverage). Without full traceability, it becomes difficult to investigate failures or meet audit requirements. Ensure suppliers provide complete documentation, including certificates of conformance and material test reports.
Ignoring Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Using a static mixer design that infringes on patented technology can lead to legal disputes, production delays, or forced redesigns. Some suppliers may replicate proprietary geometries without licensing. Always verify that the mixer design does not violate existing patents, and consider working with suppliers who hold their own IP or offer licensed solutions.
Insufficient Protection of Custom Designs
If you’ve developed a proprietary mixer configuration for a specific application, failing to secure IP rights (e.g., through patents or trade secrets) leaves your innovation vulnerable. When sourcing custom mixers, ensure contracts include clauses on IP ownership, non-disclosure, and restrictions on reuse of your design by the supplier.
Inconsistent Manufacturing Tolerances
Static mixers rely on precise internal geometries to function effectively. Suppliers with poor quality control may produce units with inconsistent tolerances, leading to flow imbalances and reduced mixing efficiency. Audit the supplier’s manufacturing processes and request evidence of in-process inspections and dimensional verification.
Overlooking Regulatory Compliance
Depending on the industry, mixers may need to comply with standards such as 3A, EHEDG, or ATEX. Sourcing a mixer without the appropriate certifications can prevent installation or lead to non-compliance during inspections. Confirm that the mixer meets all relevant regulatory and hygiene standards for your application.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence in supplier qualification, clear technical specifications, and attention to both quality assurance and intellectual property protection throughout the sourcing process.
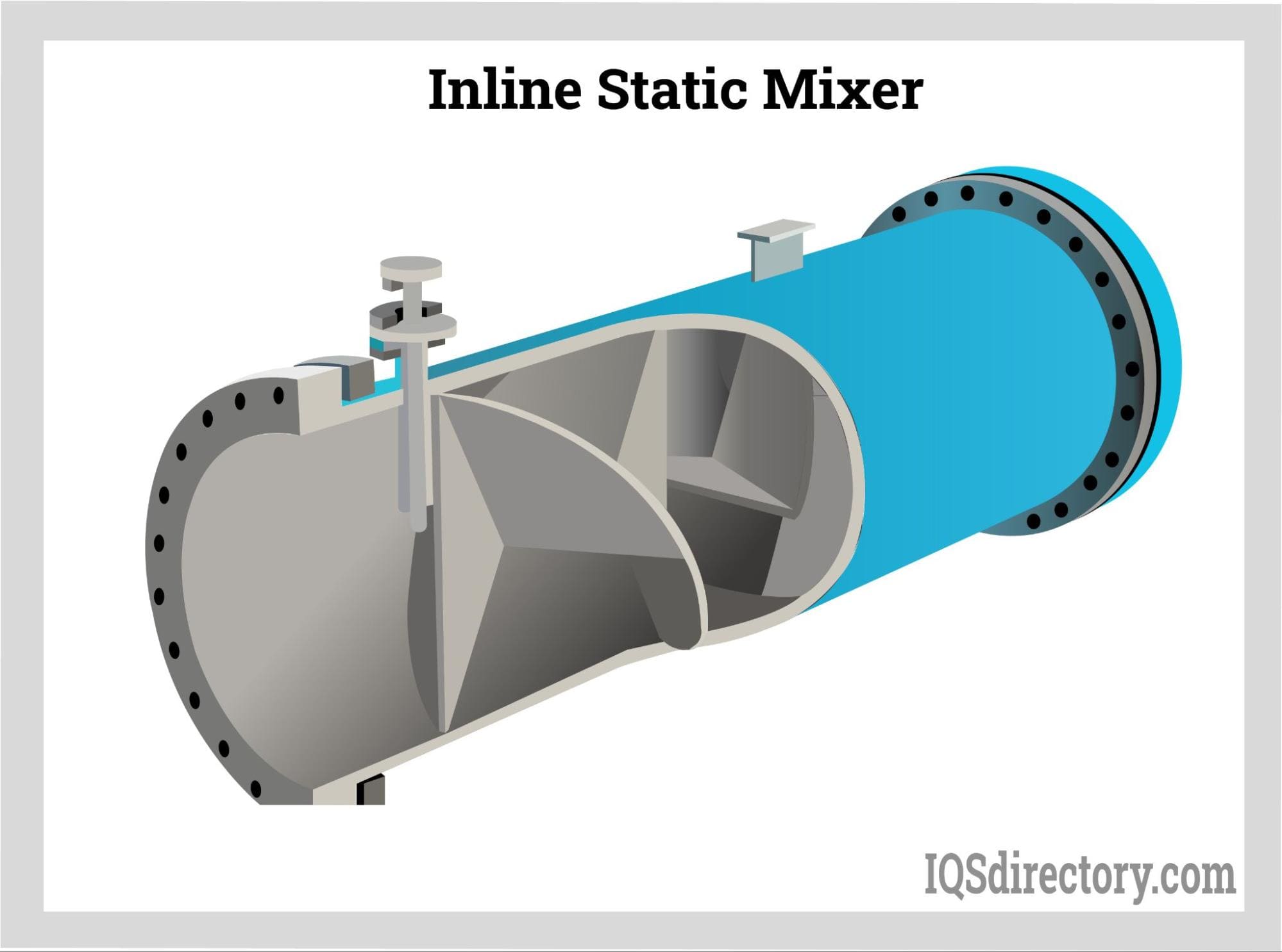
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Inline Static Mixer
This guide provides essential information for the safe, efficient, and compliant handling, transportation, and use of inline static mixers across various industries.
Product Overview
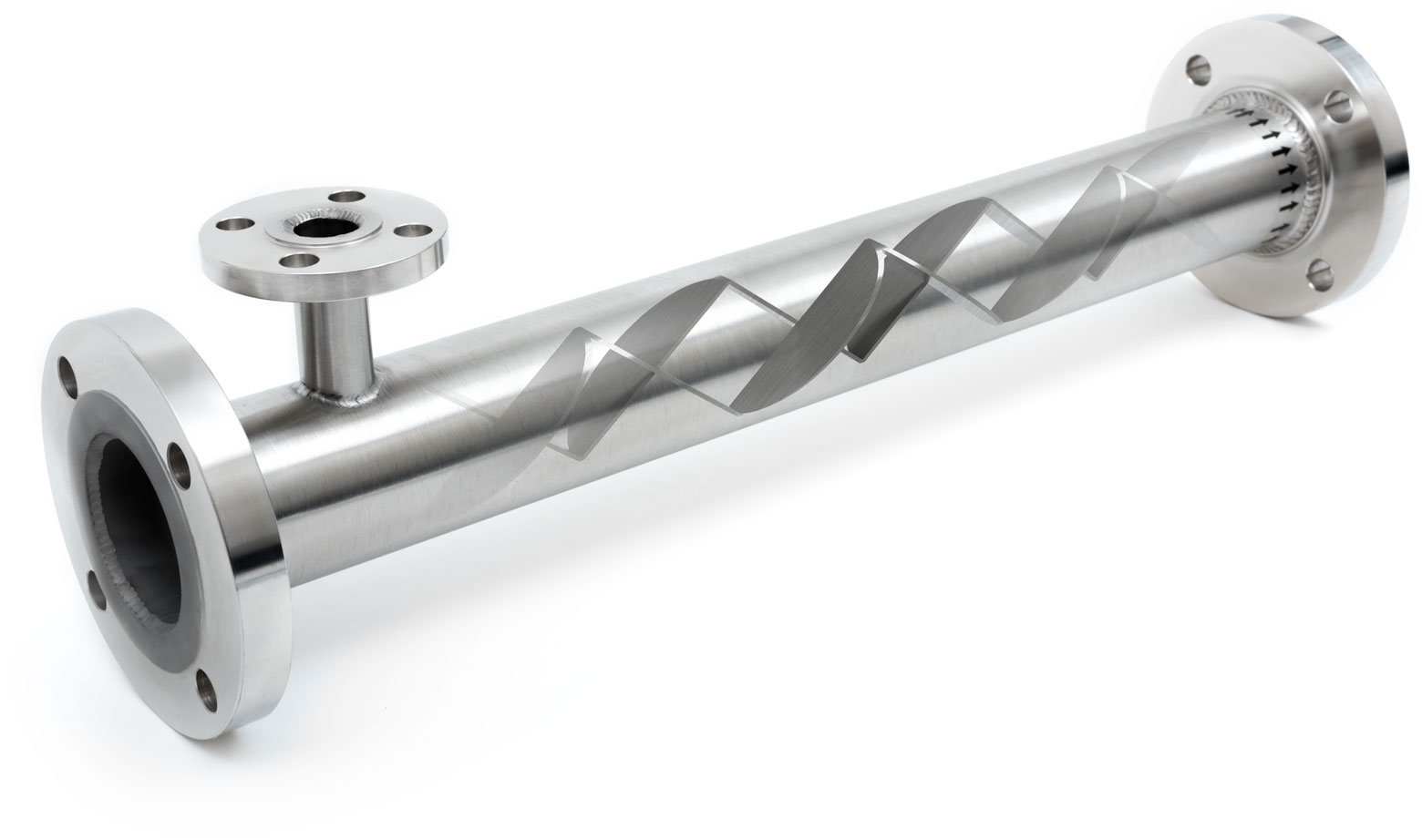
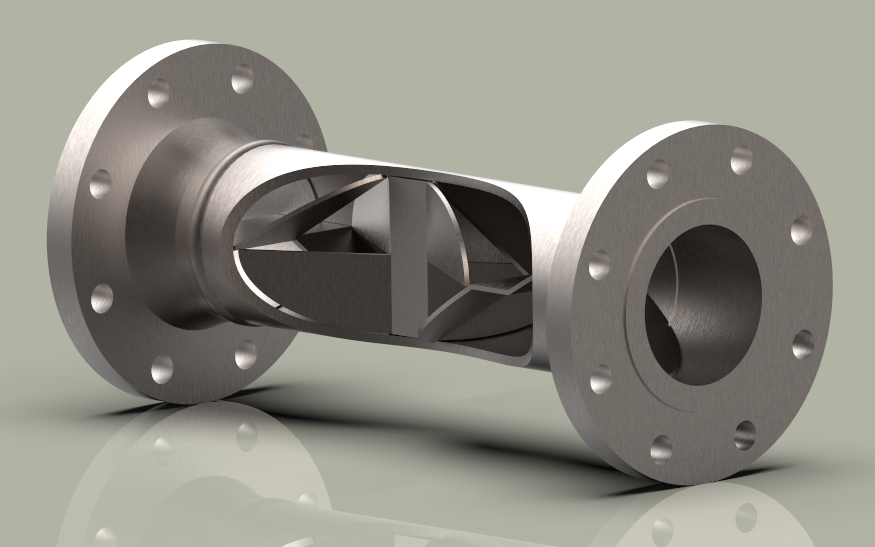
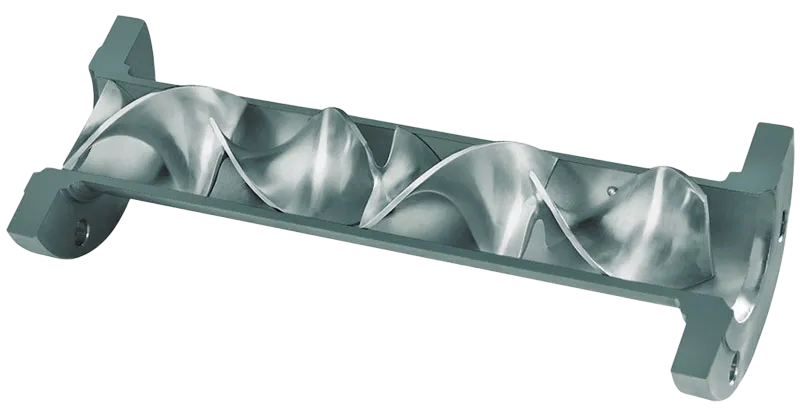
An inline static mixer is a maintenance-free device installed within a pipeline to mix fluids without moving parts. It uses specially engineered internal elements to divide, redirect, and recombine fluid streams, ensuring homogeneous mixing through laminar or turbulent flow. Common applications include chemical processing, water treatment, food and beverage, and pharmaceuticals.
Regulatory Compliance
Ensure compliance with relevant international, national, and industry-specific standards:
- ASME B31.3 – For process piping design and installation.
- FDA 21 CFR – Required for mixers used in food, beverage, or pharmaceutical applications (e.g., compliant materials like 316L stainless steel or FDA-approved polymers).
- EU Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004 – For materials intended to come into contact with food.
- ATEX Directive 2014/34/EU – If used in potentially explosive atmospheres.
- Pressure Equipment Directive (PED) 2014/68/EU – Applies to mixers used under pressure in the European market.
- ISO 9001 – Quality management systems for manufacturing consistency.
Verify that the mixer material and construction meet the required certifications for your application and region.
Material Compatibility
Select mixer materials based on the fluids being processed:
- Stainless Steel (304, 316/L) – Suitable for corrosive chemicals, high temperatures, and sanitary applications.
- PVC, PVDF, PTFE – Ideal for aggressive chemicals and low-pressure systems.
- Confirm compatibility with process media using chemical resistance charts. Avoid materials that may degrade or contaminate the product.
Installation Requirements
- Install in-line with proper orientation (follow flow direction arrow).
- Ensure pipe supports are in place to prevent stress on mixer connections.
- Use appropriate gaskets and flange ratings to avoid leaks.
- Avoid installing near bends or valves that disrupt flow profile; maintain recommended upstream/downstream straight pipe lengths (typically 10–20 pipe diameters upstream).
Transportation & Handling
- Pack mixers in protective packaging to prevent mechanical damage.
- Handle with care; avoid dropping or impacting internal elements.
- Store in a dry, clean environment to prevent corrosion or contamination.
- For large or heavy units, use proper lifting equipment and slings around the body—not the connections.
Cleaning & Maintenance
- Clean regularly in CIP (Clean-in-Place) systems using approved agents.
- Inspect for clogging, erosion, or buildup, especially with viscous or particulate-laden fluids.
- Static mixers are generally maintenance-free but should be visually inspected during system shutdowns.
- Replace elements if damaged or if mixing efficiency declines.
Environmental & Safety Considerations
- Confirm mixer integrity to prevent leaks of hazardous materials.
- Follow local regulations for disposal of used mixers (especially those exposed to toxic or regulated substances).
- Use PPE when handling or installing mixers in industrial settings.
- Ensure system pressure and temperature remain within the mixer’s rated limits to prevent failure.
Documentation & Traceability
Maintain records including:
- Material Certificates (e.g., Mill Test Reports)
- Compliance Certifications (FDA, ATEX, PED, etc.)
- Installation Logs
- Maintenance and Inspection Reports
Proper documentation ensures regulatory audits can be passed and supports quality assurance programs.
Conclusion
Proper logistics and compliance practices are critical to the safe and effective use of inline static mixers. Always consult the manufacturer’s specifications and adhere to regional regulations to ensure optimal performance and regulatory compliance.
Conclusion for Sourcing Inline Static Mixer
In conclusion, sourcing an inline static mixer requires a thorough evaluation of application-specific requirements, including fluid properties, flow rates, mixing objectives, and compatibility with system pressure and temperature conditions. Key factors such as material of construction (e.g., stainless steel, PVC, or specialty alloys), mixer design (e.g., helical, baffle, or cross-flow elements), and ease of installation and maintenance should guide the selection process. Additionally, prioritizing suppliers with proven expertise, industry certifications, and strong technical support ensures reliability, performance, and long-term cost efficiency. By carefully aligning technical specifications with operational needs and engaging reputable vendors, organizations can effectively integrate inline static mixers to enhance process efficiency, improve product consistency, and reduce energy consumption—ultimately contributing to optimized production outcomes.