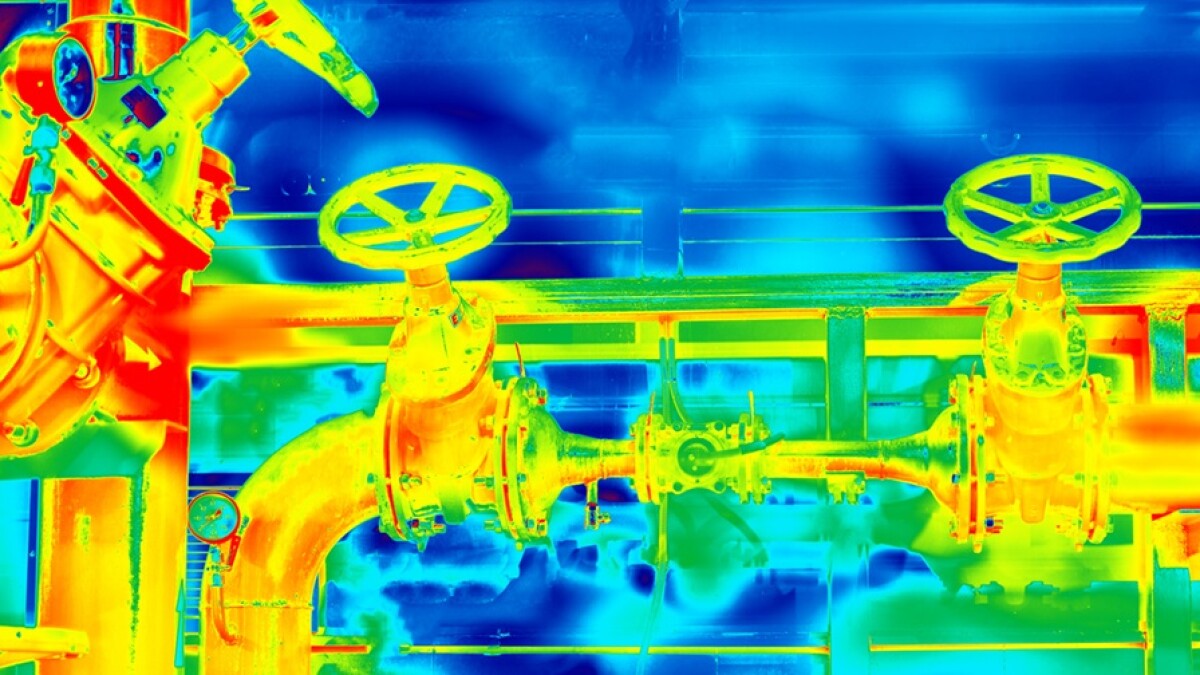
The global infrared leak detection market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by increasing regulatory emphasis on emission control, rising infrastructure investments, and growing demand for predictive maintenance across oil & gas, chemical, and industrial manufacturing sectors. According to Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at approximately USD 1.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 7.5% through 2029. This growth is further supported by advancements in optical imaging technologies and the adoption of real-time monitoring solutions that enhance safety and operational efficiency. As industries prioritize environmental compliance and asset integrity, infrared-based systems have emerged as a critical tool for rapid, non-contact, and accurate detection of gas and refrigerant leaks. With innovation accelerating across the sector, a select group of manufacturers is leading the charge in developing high-performance, scalable solutions. Based on technological leadership, market reach, and product innovation, the following nine companies represent the forefront of infrared leak detection manufacturing.
Top 9 Infrared Leak Detection Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 VIGO Photonics
Domain Est. 2021
Website: vigophotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser Gas Leak Detection with Infrared. VIGO Photonics has developed a unique technology of manufacturing instruments for a quick and convenient detection of ……
#2 INFICON
Domain Est. 1995
Website: inficon.com
Key Highlights: Transforming Gas Leak Detection with Infrared and Digital Technology. Next-generation leak detection tools and digital gas leak detection are helping ……
#3 Flir
Domain Est. 1993
Website: flir.com
Key Highlights: Electrical Inspection · Asset Troubleshooting · Energy Audit · Building Diagnostics & Indoor Air Quality · Liquid Leak Detection · Compressed Air & Gas Leak ……
#4 Seek Thermal
Domain Est. 1993
Website: thermal.com
Key Highlights: Assess. Direct. Attack. · Your lifeline to get home. ; Professional tool. Personal budget. · Your all-in-one thermal monitoring solution. ; Durable, reliable, safe….
#5 Infrared Leak Detection Company in Gainesville
Domain Est. 2000
Website: americanleakdetection.com
Key Highlights: We offer advanced infrared leak detection services that quickly and efficiently identify leaks without causing damage to your property….
#6 Refrigerant Leak Detection
Domain Est. 2004
Website: us.msasafety.com
Key Highlights: The Chillgard 5000 Refrigerant Leak Monitor provides the earliest level of detection of costly refrigerant gas leaks in mechanical equipment rooms….
#7 FOTRIC
Domain Est. 2015
Website: fotric.com
Key Highlights: FOTRIC leads in innovating and manufacturing advanced thermal and acoustic imaging cameras, redefining reliability testing and maintenance….
#8 Gas Detection Systems
Domain Est. 2019
Website: teledynegasandflamedetection.com
Key Highlights: Teledyne Gas and Flame Detection offers high-performance flame detection solutions that precisely meet the needs of the most demanding professionals….
#9 Best Thermal Imaging Cameras
Domain Est. 1986
Website: fluke.com
Key Highlights: Thermal imaging cameras capture infrared energy to create images, ideal for industrial inspections, maintenance, leak detection, ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Infrared Leak Detection
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Infrared Leak Detection
The global market for infrared (IR) leak detection is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, regulatory pressures, and growing demand across key industries. As environmental sustainability and operational efficiency become central priorities, infrared leak detection systems are increasingly recognized for their non-contact, real-time, and highly accurate capabilities in identifying gas and refrigerant leaks.
1. Technological Advancements Driving Adoption
By 2026, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning with infrared imaging is expected to enhance diagnostic precision, enabling predictive maintenance and automated anomaly detection. Portable and drone-mounted IR cameras are becoming more compact and affordable, expanding their use in hard-to-reach areas such as offshore platforms, pipelines, and industrial rooftops. Additionally, improvements in detector sensitivity—especially in the mid-wave (MWIR) and long-wave (LWIR) infrared spectrum—are allowing systems to detect lower concentrations of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and greenhouse gases like methane and sulfur hexafluoride (SF6).
2. Regulatory and Environmental Compliance
Stringent environmental regulations from agencies such as the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), the European Union’s F-Gas Regulation, and the Paris Agreement are compelling industries to adopt advanced leak detection technologies. Methane emissions monitoring, in particular, is a key growth driver in the oil and gas sector. By 2026, mandatory leak detection and repair (LDAR) programs are expected to be more rigorously enforced, increasing demand for IR solutions that offer faster, more reliable compliance reporting.
3. Expansion in Key Industry Verticals
The oil and gas industry will remain the largest end-user of IR leak detection, especially in upstream and midstream operations where fugitive emissions are prevalent. However, the HVAC/R (Heating, Ventilation, Air Conditioning, and Refrigeration) and automotive sectors are emerging as high-growth markets. With the phase-down of high-GWP refrigerants under the Kigali Amendment, IR cameras are being used more frequently during installation, servicing, and decommissioning of cooling systems.
4. Geographic Market Dynamics
North America is expected to maintain its leadership in the IR leak detection market, supported by robust regulatory frameworks and widespread adoption in shale gas operations. Meanwhile, the Asia-Pacific region—particularly China, India, and South Korea—is projected to witness the highest compound annual growth rate (CAGR) through 2026 due to rapid industrialization, urban infrastructure development, and increasing environmental awareness.
5. Competitive Landscape and Innovation
Major players such as FLIR Systems (now part of Teledyne Technologies), Fluke Corporation, and Honeywell are investing heavily in R&D to differentiate their offerings through features like wireless connectivity, cloud-based data analytics, and integration with IoT platforms. Smaller innovators are also entering the space with cost-effective, AI-powered solutions targeting niche applications, fostering a dynamic and competitive market environment.
Conclusion
By 2026, the infrared leak detection market is expected to be characterized by smarter, more connected systems that deliver actionable insights with minimal human intervention. As industries prioritize safety, compliance, and sustainability, IR technology will play a pivotal role in reducing emissions, preventing equipment failures, and optimizing maintenance operations—solidifying its position as a cornerstone of modern industrial monitoring.
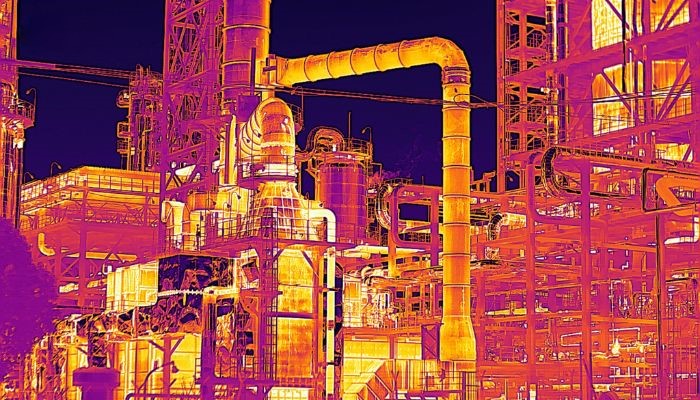

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Infrared Leak Detection (Quality, IP)
When sourcing infrared (IR) leak detection equipment, companies often face challenges that can compromise performance, reliability, and return on investment. Understanding these pitfalls—particularly concerning quality and intellectual property (IP)—is critical for making informed procurement decisions.
Poor Image Quality and Sensor Performance
Low-cost IR cameras may use inferior sensors or outdated technology, resulting in poor thermal resolution, inaccurate temperature readings, or reduced sensitivity. This can lead to missed leaks or false positives, undermining the effectiveness of leak detection programs. Always verify sensor specifications (e.g., NETD, resolution, thermal sensitivity) and request real-world demo footage.
Inadequate Environmental Protection (IP Rating)
Many IR cameras are used in harsh industrial environments. Sourcing devices without appropriate Ingress Protection (IP) ratings (e.g., IP54 or higher) risks damage from dust, moisture, or chemicals. Ensure the IP rating meets the operational environment requirements—especially for outdoor or high-humidity applications.
Lack of Calibration and Traceability
Some suppliers provide equipment without valid calibration certificates or metrological traceability. This affects measurement accuracy and compliance with regulatory or quality standards (e.g., ISO 17025). Insist on factory calibration reports and regular recalibration services.
Hidden Software Limitations and Licensing Costs
Entry-level IR cameras may come with bundled software that lacks advanced analytics, reporting features, or multi-camera support. Additional features are often offered as costly add-ons. Evaluate software capabilities upfront and clarify licensing models to avoid unexpected expenses.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks in Custom Solutions
When sourcing custom or OEM IR systems, unclear IP ownership agreements can lead to disputes. Suppliers may retain rights to firmware, algorithms, or design modifications, limiting your ability to maintain, upgrade, or resell the solution. Always define IP ownership in contracts and ensure transfer of relevant rights.
Short Product Lifespan and Obsolescence
Some manufacturers discontinue models quickly or lack long-term support. This can leave users without spare parts, firmware updates, or technical assistance. Prioritize suppliers with a proven track record of product longevity and backward compatibility.
Inadequate Training and Support
Even high-quality IR equipment underperforms without proper training. Suppliers may offer minimal onboarding or lack local technical support. Confirm availability of training programs, user documentation, and responsive technical assistance before purchase.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires thorough due diligence, clear specifications, and strong contractual terms—especially regarding quality assurance and IP rights.
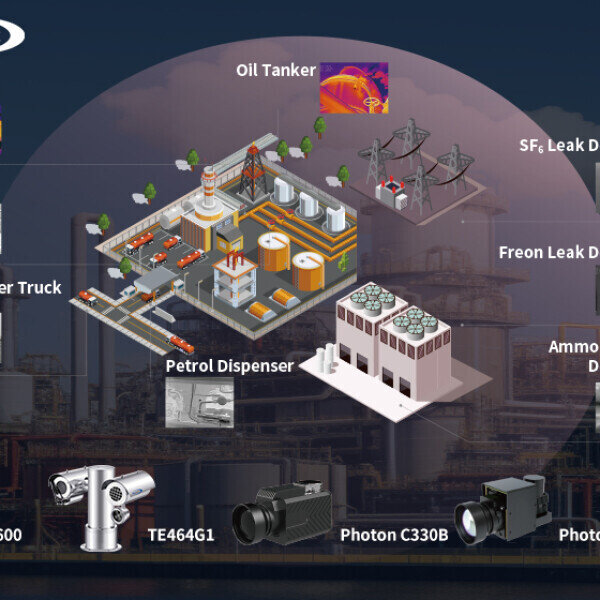
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Infrared Leak Detection
Scope and Purpose
This guide outlines the logistical considerations and compliance requirements for conducting Infrared (IR) Leak Detection operations, particularly in industrial, environmental, and safety-critical applications such as oil and gas, chemical processing, and HVAC systems. It ensures safe, effective, and legally compliant deployment of IR technology for detecting fugitive emissions and leaks.
Regulatory and Compliance Framework
Environmental Regulations
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Standards
- Compliance with 40 CFR Part 60, Subparts VV, VVa, and VVb (NSPS for petroleum refineries and VOC sources) requires periodic monitoring using Method 21 or equivalent technologies.
-
OTM-33A (Optical Gas Imaging – Qualification Method) establishes performance criteria for IR cameras used in detecting VOCs. Only EPA-qualified instruments may be used for compliance monitoring.
-
European Union Industrial Emissions Directive (IED) 2010/75/EU
-
Mandates regular leak detection and repair (LDAR) programs. IR cameras may be used as part of Best Available Techniques (BAT) for monitoring, provided they meet EN standards and are properly calibrated.
-
Canadian Environmental Protection Act (CEPA)
- Requires LDAR programs for specified facilities. Use of IR cameras must align with provincial and federal guidelines, including proper documentation and reporting.
Safety Standards
- OSHA Regulations (29 CFR 1910)
- Personnel conducting IR inspections must be trained in hazardous area safety, PPE usage, and confined space protocols where applicable.
- ATEX/IECEx Directives (EU/Global)
- IR equipment used in explosive atmospheres must carry appropriate certification (e.g., ATEX for EU, IECEx internationally) to prevent ignition hazards.
Industry Standards
- API 1584 – Recommended Practice for Leak Detection Using Optical Gas Imaging.
- ISO 18434-1 – Condition monitoring and diagnostics of machines — Thermography — Part 1: General procedures.
- ASTM E1934-99 – Standard Guide for Examining Electrical and Mechanical Equipment with Infrared Thermography.
Equipment Requirements
IR Camera Specifications
- Use EPA OTM-33A-qualified cameras for VOC detection in regulated environments.
- Ensure spectral range is appropriate for target gases (e.g., MWIR 3–5 μm for hydrocarbons).
- Cameras must be calibrated annually by an accredited lab; calibration records must be maintained.
- Intrinsically safe (IS) or explosion-proof models required in hazardous zones (Class I, Div 1/2).
Ancillary Equipment
- Portable gas detectors (for confirmation and safety).
- Wind speed/direction meter (anemometer) to assess detection conditions.
- Radiometric temperature measurement tools (if thermographic analysis is needed).
- Protective cases and cleaning kits for lens maintenance.
Personnel Qualifications and Training
- Certification: Technicians must be certified in OGI (Optical Gas Imaging) per API 1584 or equivalent.
- Training Requirements:
- Operation of IR equipment in various environmental conditions.
- Understanding of fluid dynamics and vapor plume behavior.
- Regulatory compliance procedures and reporting.
- Safety protocols for working in industrial environments.
- Refresher Training: Required annually or after significant regulatory updates.
Operational Logistics
Pre-Inspection Planning
- Develop inspection route maps and schedules based on process units and emission sources.
- Review P&IDs and equipment lists to identify high-risk components (valves, flanges, pumps, connectors).
- Coordinate with site operators to ensure process stability during inspection (e.g., avoid startups/shutdowns).
- Confirm weather suitability: avoid heavy rain, fog, or high winds (>15 mph) that impair detection.
On-Site Execution
- Perform pre-use camera checks (battery, focus, calibration status).
- Conduct a functional check using a known emission source (e.g., methane test cell).
- Scan components systematically, maintaining optimal distance (typically 5–30 meters) and angles.
- Document all suspected leaks with timestamped images, GPS coordinates, and component identifiers.
Post-Inspection Procedures
- Upload data to LDAR management software (e.g., ENVIRON, Sphera, or custom platforms).
- Generate compliance reports including:
- Date, time, and location of inspection.
- Equipment used and operator credentials.
- List of detected leaks with severity estimates.
- Corrective action recommendations and repair deadlines.
- Retain digital records for minimum 5 years (per EPA and most regulatory bodies).
Data Management and Reporting
- Electronic Recordkeeping: Use secure, auditable systems that support regulatory submission formats.
- Leak Classification: Categorize leaks per regulatory thresholds (e.g., >500 ppm for EPA NSPS).
- Reporting Deadlines:
- Initial leak identification: Within 1–5 days, depending on jurisdiction.
- Repair verification: Within 15 days (first attempt), with follow-up within 30 days.
- Annual summary reports to regulatory agencies as required.
Safety and Risk Mitigation
- Conduct a Job Safety Analysis (JSA) before each inspection.
- Equip personnel with appropriate PPE: flame-resistant clothing, safety glasses, gloves, and gas monitors.
- Establish communication protocols with site emergency response teams.
- Avoid direct beam exposure to eyes; never point IR camera at reflective surfaces near personnel.
Quality Assurance and Continuous Improvement
- Perform quarterly internal audits of inspection procedures and records.
- Participate in proficiency testing programs for OGI technicians.
- Update procedures in response to regulatory changes, technological advances, or audit findings.
Conclusion
Effective infrared leak detection requires meticulous planning, regulatory adherence, and skilled execution. By following this logistics and compliance guide, organizations can ensure environmental protection, regulatory compliance, and operational safety while minimizing emissions and associated liabilities.
Conclusion for Sourcing Infrared Leak Detection:
Sourcing infrared leak detection technology represents a strategic investment in improving operational efficiency, safety, and environmental compliance across various industries—particularly in oil and gas, chemical processing, and utilities. Infrared (IR) leak detection systems offer non-contact, real-time monitoring capabilities that enable early identification of gas leaks, minimizing fugitive emissions and reducing potential hazards. These advanced systems outperform traditional detection methods in terms of speed, sensitivity, and coverage, especially in large or hard-to-reach areas.
When sourcing infrared leak detection equipment, it is essential to consider factors such as detection sensitivity, spectral range, environmental resilience, integration capabilities with existing monitoring systems, and total cost of ownership. Partnering with reputable suppliers offering proven technology, reliable support, and compliance with international standards (e.g., EPA OOOOa, ISO 20480) ensures long-term effectiveness and regulatory compliance.
In conclusion, adopting infrared leak detection not only enhances safety and sustainability but also supports regulatory adherence and cost savings through reduced product loss and maintenance downtime. Organizations that prioritize the strategic sourcing of advanced IR detection solutions position themselves as leaders in operational excellence and environmental stewardship.