The global infrared detectors market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by rising demand across defense, industrial, and healthcare sectors. According to Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 11.3 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 7.2% from 2024 to 2029. This growth is fueled by advancements in thermal imaging technology, increasing adoption in autonomous vehicles, and expanding applications in surveillance and predictive maintenance. As innovation accelerates, a select group of manufacturers are leading the charge in developing high-performance, cost-effective infrared detection solutions. Below, we spotlight the top 9 infrared detectors manufacturers shaping the industry’s future through technological leadership and strategic market presence.
Top 9 Infrared Detectors Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Global Sensor Technology
Domain Est. 2021
Website: gst-ir.net
Key Highlights: Global Sensor Technology Co., Ltd (GST) specializes in the design, manufacture, sales and marketing of infrared thermal imaging detectors and modules….
#2 Infrared Sensors
Domain Est. 1994
Website: murata.com
Key Highlights: Murata’s pyroelectric infrared sensors are the best sensors for detecting human movement. They utilize the pyroelectric effect of pyroelectric ceramics as ……
#3 Optris
Domain Est. 2004
Website: optris.com
Key Highlights: Optris has been developing and manufacturing affordable innovative infrared measurement devices for non-contact temperature measurement….
#4 Infrared sensor technology – Infrared detectors
Domain Est. 2007
Website: infratec-infrared.com
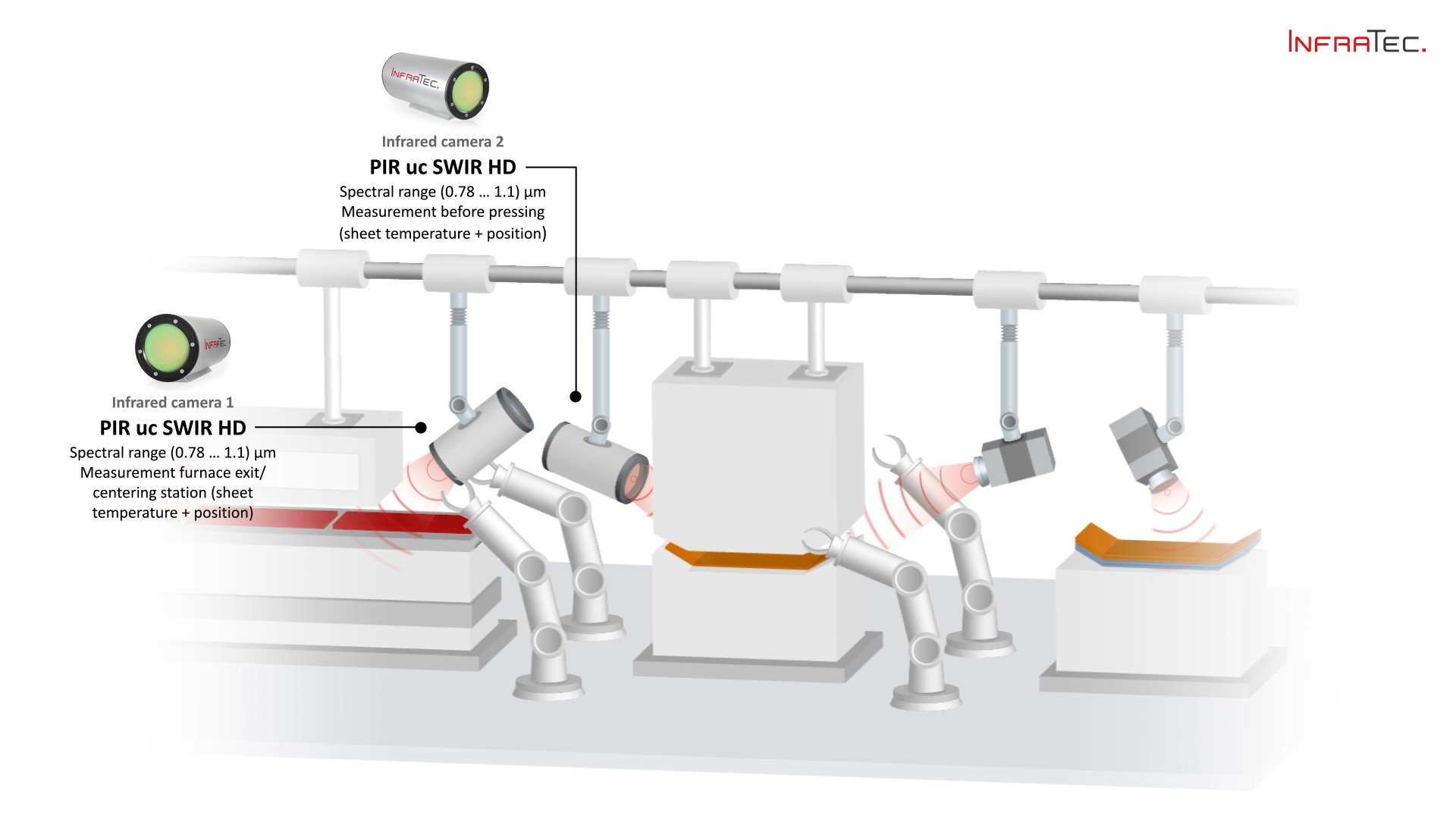
Key Highlights: InfraTec develops and produces many different high-quality pyroelectric infrared detectors. Get further information about infrared sensor technology….
#5 Infrared Systems
Domain Est. 2018
Website: leonardo.us
Key Highlights: Leonardo Electronics US Inc. has extensive experience developing infrared systems for airborne, land, and naval surveillance and targeting missions….
#6 VIGO Photonics
Domain Est. 2021
Website: vigophotonics.com
Key Highlights: VIGO Photonics SA is a world-leading manufacturer of uncooled infrared photon detectors. In the 1980’s, a team led by Professor Józef Piotrowski, Ph.D., ……
#7 Flir
Domain Est. 1993
Website: flir.com
Key Highlights: Handheld Gas Detection Cameras · Infrared Guided Measurement · Flir One® · Portable Inspection Software · callout block image. NEW iXX-Series: Revolutionizing ……
#8 Infrared Sensors
Domain Est. 2017
Website: leonardodrs.com
Key Highlights: Leonardo DRS is the industry leader for cooled and uncooled infrared sensors. For over 50 years, we have built our products from the ground up with state-of- ……
#9 Guide Infrared
Domain Est. 2002
Website: guide-infrared.com
Key Highlights: We specialize in the design, manufacture, sales, and marketing of infrared thermal imaging detectors and modules, and advanced integrated electro-optical ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Infrared Detectors
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Infrared Detectors
The global infrared (IR) detector market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, expanding applications, and growing demand across defense, industrial, automotive, and consumer electronics sectors. Several key trends are expected to shape the market landscape in the coming years:
-
Rising Demand in Defense and Security Applications
Defense and homeland security remain dominant end-users of IR detectors, particularly uncooled microbolometers and cooled photodetectors. By 2026, increased military modernization efforts—especially in Asia-Pacific and North America—are fueling demand for advanced thermal imaging systems in night vision, surveillance, missile guidance, and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). Governments are investing heavily in border security and reconnaissance, accelerating procurement of IR-enabled equipment. -
Growth in Automotive and ADAS Integration
The integration of infrared detectors in Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) and autonomous vehicles is a major growth catalyst. Thermal cameras enhance object detection in low-visibility conditions (e.g., fog, darkness), improving pedestrian and animal detection. By 2026, rising production of electric and autonomous vehicles, especially in Europe and China, is expected to boost demand for cost-effective IR sensors, particularly long-wave infrared (LWIR) detectors. -
Advancements in Uncooled Detector Technologies
Uncooled IR detectors, especially those based on vanadium oxide (VOx) and amorphous silicon (a-Si) microbolometer technology, are gaining traction due to their lower cost, reduced power consumption, and smaller form factors. Continued R&D is driving improvements in resolution (e.g., 640×480 and beyond), sensitivity, and miniaturization, enabling broader adoption in commercial and consumer applications. -
Expansion in Industrial and Commercial Applications
IR detectors are increasingly used in predictive maintenance, building diagnostics, gas detection, and process monitoring. The push toward Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing is spurring demand for thermal imaging in condition monitoring and automation. Additionally, post-pandemic health monitoring applications—such as fever screening—have created sustained interest in non-contact temperature measurement systems. -
Consumer Electronics and Smart Devices
Integration of IR sensors into smartphones, smart home systems, and wearable devices is expected to grow. Innovations such as low-cost IR sensors for facial recognition, gesture control, and environmental sensing are opening new markets. Companies are exploring wafer-level packaging (WLP) and CMOS-compatible processes to reduce costs and enable mass production. -
Regional Market Shifts and Supply Chain Dynamics
Asia-Pacific, led by China, Japan, and South Korea, is emerging as a key manufacturing and consumption hub for IR detectors. Local production of microbolometers and investment in domestic defense capabilities are reducing reliance on Western suppliers. Meanwhile, export controls on high-performance IR technology (especially from the U.S.) are prompting countries to develop indigenous capabilities. -
Material and Technological Innovation
Emerging materials such as quantum dots, Type-II superlattices (T2SLs), and strained-layer superlattices are being explored to replace traditional materials like mercury cadmium telluride (MCT) and indium antimonide (InSb). These next-generation detectors promise higher operating temperatures, improved performance, and lower manufacturing costs—critical for scaling in commercial applications. -
Sustainability and Environmental Monitoring
IR detectors are playing a growing role in climate monitoring, pollution detection, and agricultural management. Hyperspectral and multispectral IR imaging are being deployed in satellite and drone platforms for environmental observation. By 2026, regulatory focus on emissions and resource efficiency is expected to increase demand for IR-based remote sensing solutions.
In conclusion, the 2026 infrared detector market will be characterized by technological democratization, broader commercialization, and sector diversification. While defense remains a cornerstone, the convergence of cost reduction, performance enhancement, and new application frontiers will drive sustained growth, with the global market projected to expand at a CAGR of 7–9% through 2026.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Infrared Detectors: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing infrared (IR) detectors involves navigating complex technical and legal landscapes. Overlooking key quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations can lead to performance failures, supply chain disruptions, and legal liabilities. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Performance Specification Verification
Many suppliers provide optimistic or incomplete datasheets. Buyers often assume specifications like detectivity (D*), noise equivalent temperature difference (NETD), or response time are independently verified. However, discrepancies in test conditions (e.g., temperature, bias voltage, modulation frequency) can render comparisons misleading. Always request test reports under standardized conditions (e.g., MIL-STD or ISO) and validate performance with third-party testing when possible.
Lack of Long-Term Reliability Data
IR detectors are often deployed in harsh environments (e.g., aerospace, defense, industrial monitoring). Sourcing from suppliers who cannot provide accelerated life testing, thermal cycling results, or mean time to failure (MTTF) data increases the risk of premature field failures. Ensure reliability data aligns with your operational requirements.
Insufficient Screening and Qualification
Not all detectors undergo rigorous screening (e.g., burn-in, environmental stress screening). Sourcing unqualified components for mission-critical applications can result in high infant mortality rates. Verify that the supplier performs lot acceptance testing and adheres to industry qualification standards such as MIL-PRF-38534 or AEC-Q102 for automotive applications.
Counterfeit or Recycled Components
The high cost and limited availability of advanced IR detectors (e.g., InSb, MCT, or type-II superlattices) make them targets for counterfeiting. Be wary of unusually low prices or non-authorized distributors. Implement supply chain traceability measures and use trusted distribution channels.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
Unlicensed Use of Proprietary Technologies
Many IR detector technologies are protected by patents covering materials (e.g., HgCdTe growth methods), device architectures (e.g., avalanche photodiodes), or fabrication processes. Sourcing detectors from manufacturers who infringe on third-party IP can expose the buyer to legal action, especially in export-controlled or defense applications. Conduct due diligence on the supplier’s IP portfolio and freedom-to-operate (FTO) status.
Unclear IP Ownership in Custom Designs
When co-developing or customizing detectors, contracts often fail to clearly assign IP rights. Suppliers may retain ownership of design improvements or process innovations, limiting your ability to switch vendors or scale production. Ensure IP ownership, licensing terms, and background IP are explicitly defined in development agreements.
Export Control and ITAR Compliance Risks
Advanced IR detectors are subject to export controls such as the International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) or the Export Administration Regulations (EAR). Sourcing from non-compliant suppliers can result in regulatory penalties. Confirm that the supplier has proper export authorization and can provide necessary documentation (e.g., ECCN classification, license exceptions).
Reverse Engineering and Technology Leakage
Using offshore or low-cost manufacturers may expose sensitive designs to unauthorized replication. Without robust non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) and IP protection clauses, there is a risk of technology leakage, especially in regions with weak IP enforcement. Prioritize suppliers with strong security protocols and proven IP protection practices.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires thorough technical evaluation, legal due diligence, and strong supplier relationships. Engaging with reputable, transparent manufacturers and involving legal and compliance teams early in the sourcing process is essential for mitigating risks related to both quality and intellectual property.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Infrared Detectors
Infrared (IR) detectors are critical components in various industries, including defense, aerospace, industrial monitoring, medical imaging, and scientific research. Due to their advanced technology and potential dual-use applications, their international shipment and handling are subject to stringent logistics and compliance regulations. This guide outlines key considerations to ensure legal, safe, and efficient movement of IR detectors across borders and within supply chains.
Regulatory Classification & Export Controls
Infrared detectors are often classified under strict export control regimes due to their potential use in military or surveillance systems. Proper classification is the foundation of compliance.
- Export Control Classification Number (ECCN): In the United States, IR detectors are typically classified under ECCN 6A002 or 6A003 in the Commerce Control List (CCL), depending on performance specifications such as spectral range, pixel count, and cooling method. Exporters must determine the correct ECCN and verify if a license is required.
- International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR): Some high-performance IR detectors, particularly those designed for military applications (e.g., thermal imaging in targeting systems), may fall under the U.S. Department of State’s ITAR and be listed on the U.S. Munitions List (USML) Category XII. ITAR-controlled items require strict licensing and handling procedures.
- Wassenaar Arrangement: As a multilateral export control regime, the Wassenaar Arrangement guides national policies on dual-use goods and technologies. Many countries align their export controls with its guidelines, affecting the shipment of IR detectors to participating nations.
- End-Use and End-User Screening: Conduct thorough due diligence on end-users and destinations. Prohibited or restricted parties (e.g., sanctioned entities or embargoed countries) must be screened using official government lists (e.g., OFAC, BIS Denied Persons List).
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Proper packaging and handling are essential to maintain detector integrity and comply with transportation regulations.
- ESD Protection: Infrared detectors, especially those based on semiconductor materials (e.g., HgCdTe, InSb, or InGaAs), are highly sensitive to electrostatic discharge (ESD). Use anti-static packaging materials and grounded handling procedures.
- Environmental Protection: Detectors may require protection from moisture, temperature fluctuations, and mechanical shock. Use desiccants, sealed enclosures, and temperature-controlled packaging when necessary.
- Labeling: Clearly label packages with handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” “Static Sensitive”) and compliance markings if applicable (e.g., export license number, hazardous material indicators if coolants are included).
- Cooling Systems: If detectors include cryogenic coolers or contain hazardous coolants (e.g., Stirling coolers with refrigerants), additional regulations (e.g., IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations) may apply.
Transportation and Shipping Compliance
Shipping IR detectors across borders involves adherence to multiple international and national transport standards.
- Air Transport (IATA): Ensure compliance with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations if shipping with batteries, coolants, or pressurized components. Declare all hazardous materials properly and use certified packaging.
- Ground and Sea Freight (IMDG, ADR, etc.): Follow relevant modal regulations for non-air shipments. Include accurate shipping documents, including commercial invoices, packing lists, and export declarations.
- Customs Documentation: Provide complete and accurate documentation, including:
- Commercial invoice with detailed technical specifications
- Packing list
- Export license or license exception authorization (e.g., EAR99, NLR)
- Certificate of Origin
- End-User Statement (if required)
- Incoterms: Clearly define responsibilities between buyer and seller using appropriate Incoterms (e.g., FCA, DDP) to clarify who manages export/import clearance, insurance, and risk transfer.
Import Compliance and Duties
Import regulations vary by destination country and must be researched in advance.
- Import Licensing: Some countries require import licenses for dual-use or sensitive technology. Verify requirements with local customs authorities or trade representatives.
- Tariff Classification (HS Codes): Assign the correct Harmonized System (HS) code for the destination country to determine applicable duties and taxes. IR detectors often fall under headings such as 8543 or 9013.
- Local Regulations: Certain jurisdictions may impose additional requirements, such as technology transfer restrictions, cybersecurity assessments, or mandatory registration with national technology control agencies.
Recordkeeping and Audit Preparedness
Maintaining comprehensive records is critical for regulatory audits and enforcement actions.
- Export Documentation Retention: Retain all export records for a minimum of five years (or longer as required by jurisdiction), including licenses, correspondence, shipping records, and classification analyses.
- Internal Compliance Program (ICP): Establish a formal ICP that includes training, screening procedures, audits, and a point of contact for compliance issues.
- Audits and Self-Disclosures: Conduct regular internal audits. If violations are discovered, consider voluntary self-disclosure to relevant authorities (e.g., BIS in the U.S.) to mitigate penalties.
Conclusion
Shipping infrared detectors requires careful attention to export controls, proper handling, transportation regulations, and documentation. Non-compliance can result in severe penalties, shipment delays, or reputational damage. By understanding the regulatory landscape and implementing robust compliance procedures, organizations can ensure the secure and lawful distribution of these advanced technologies. Always consult with legal and compliance experts or government agencies when in doubt.
In conclusion, sourcing infrared detectors requires a comprehensive evaluation of technical specifications, application requirements, supplier reliability, and cost-effectiveness. Key factors such as spectral range, sensitivity (e.g., detectivity D*), response time, operating temperature, and form factor must align with the intended use—whether in industrial sensing, defense, medical imaging, or consumer electronics. Cooling requirements (cooled vs. uncooled detectors) significantly impact system complexity and cost, making the choice between technologies like MCT, InSb, InGaAs, or microbolometers crucial. Additionally, assessing supplier qualifications, manufacturing consistency, lead times, and after-sales support ensures long-term supply chain stability. As infrared technology advances, with growing miniaturization and integration into smart systems, strategic sourcing should also consider future scalability and compatibility with emerging platforms. Ultimately, a balanced approach that weighs performance, reliability, and total cost of ownership will enable optimal selection and integration of infrared detectors for any given application.