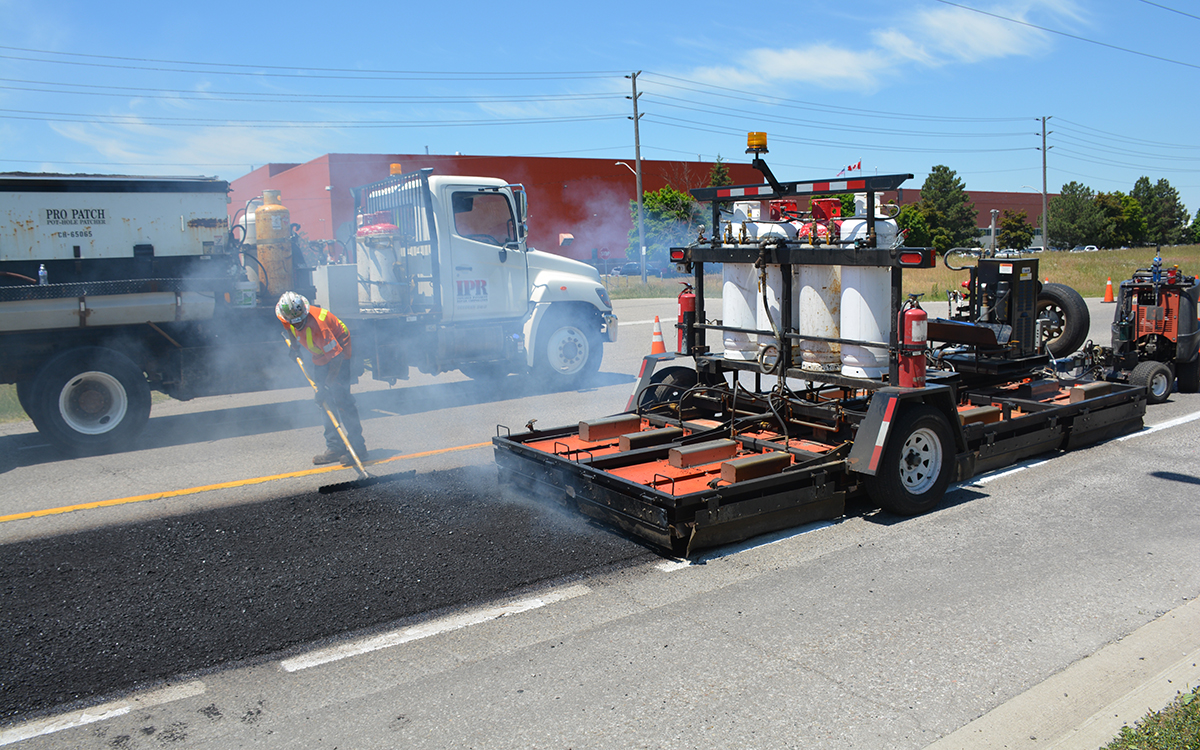
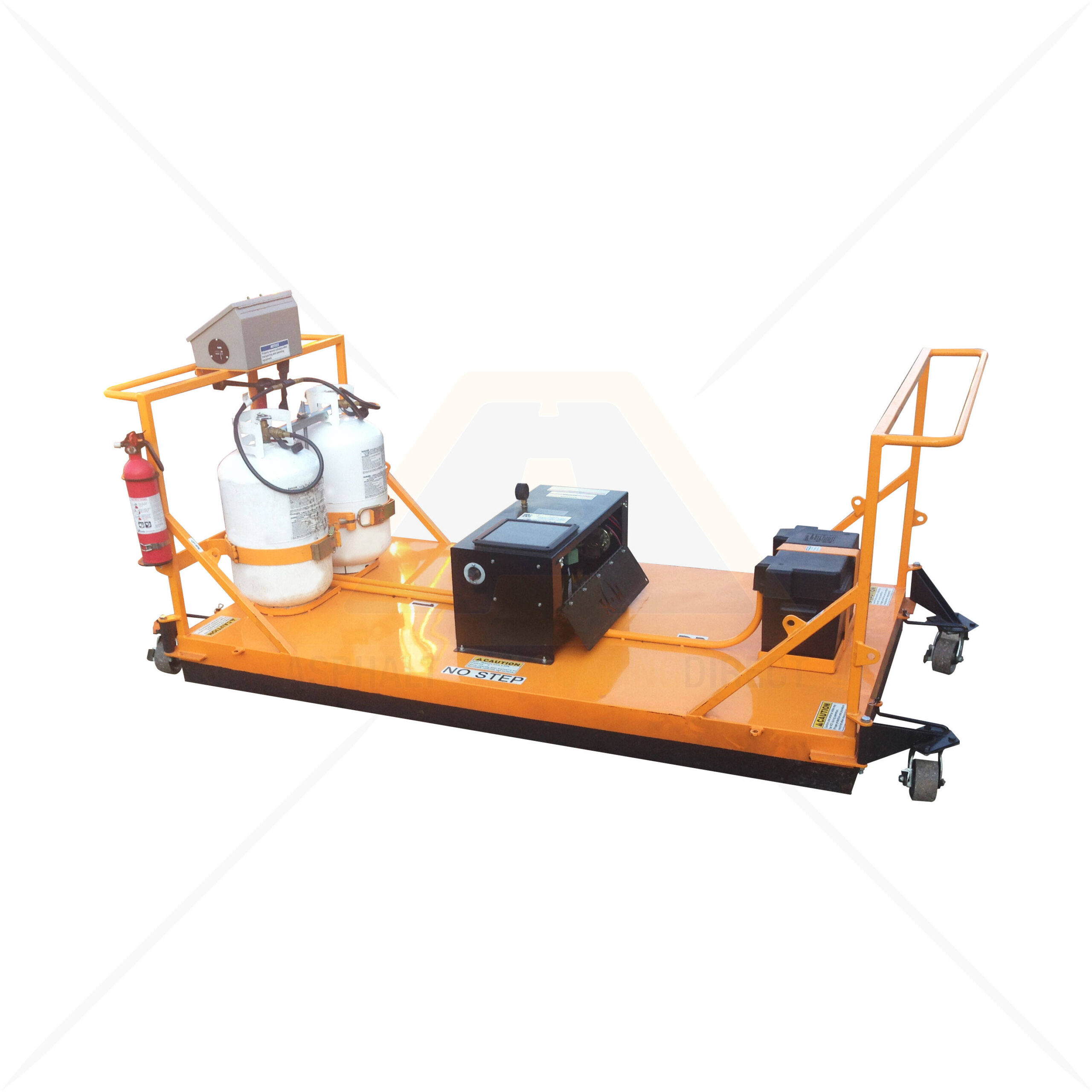
The global infrared asphalt heater market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand for energy-efficient, environmentally friendly road repair solutions. According to Grand View Research, the global road construction equipment market—of which infrared asphalt heaters are a growing segment—was valued at USD 47.8 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2% from 2023 to 2030. A key factor fueling this growth is the rising adoption of infrared technology in pavement maintenance, which allows for seamless, cold-weather paving and reduced material waste. Mordor Intelligence projects similar momentum, noting that advancements in heating efficiency and stricter environmental regulations are accelerating the shift toward infrared-based repair systems, particularly in North America and Europe. As municipalities and contractors prioritize faster, more sustainable road rehabilitation methods, the demand for high-performance infrared asphalt heaters continues to rise—spurring innovation among leading equipment manufacturers. This growing market landscape sets the stage for a closer look at the top 10 companies shaping the future of infrared asphalt heating technology.
Top 10 Infrared Asphalt Heater Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Heat Design Equipment Inc.
Domain Est. 2000
Website: asphaltheater.com
Key Highlights: Heat Design Equipment manufactures infrared heaters for asphalt construction and repair, using patented, state of the art technology….
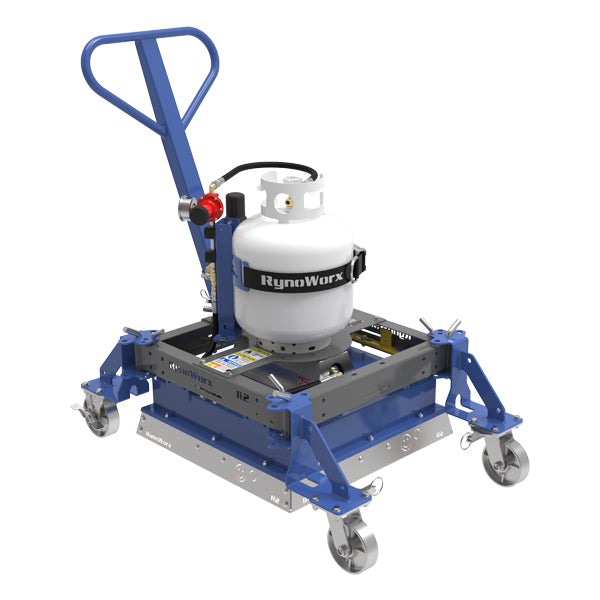
#2 Rynoworx Infrared Heater Model R2
Domain Est. 2021
Website: asphaltindustrial.com
Key Highlights: In stock $15 deliveryRynoWorx® Infrared Asphalt Heaters will bring distressed asphalt back to life. Infrared technology allows you to heat up and soften damaged areas so that they …
#3 ENNIS
Domain Est. 1990
Website: ppg.com
Key Highlights: Ennis-Flint by PPG StreetHeat infrared heaters give certified applicators or regulatory users the ability to easily apply preformed thermoplastic markings….
#4 Kasi Infrared
Domain Est. 1998
Website: kasiinfrared.com
Key Highlights: Infrared asphalt repair offers a highly efficient solution, with most repairs completed within just 25 minutes. This rapid turnaround minimizes disruption….
#5
Domain Est. 2000
Website: raytechinfrared.com
Key Highlights: Ray-Tech Infrared is the industry leader in high-performance infrared asphalt equipment, delivering unmatched efficiency, durability, and quality. Our ……
#6 ARS
Domain Est. 2000
Website: asphaltreheat.com
Key Highlights: From asphalt repairs, traditional paving, thermoplastic, or stamped and decorative asphalt, Asphalt Reheating Systems has the infrared heater for you!…
#7 Infrared Asphalt Heater
Domain Est. 2000
Website: tracklessvehicles.com
Key Highlights: The Trackless Infrared Asphalt Heater was designed to replace traditional propane fueled asphalt heaters with a PTO driven portable generator ……
#8 Asphalt Infrared Patching Equipment and Supplies
Domain Est. 2002
#9 KM 4
Domain Est. 2011
Website: kminternational.com
Key Highlights: KM 4-48: Heavy Duty Infrared Asphalt Heater. With 48 square feet of infrared heating area, the KM 4-48 is KM International’s largest infrared asphalt recycler….
#10 Infrared Asphalt Heaters
Domain Est. 2017
Website: ticabltd.com
Key Highlights: Our infrared asphalt heaters are perfect for urgent repairs to remove defects. They provide an expedited working process and a better result than traditional ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Infrared Asphalt Heater
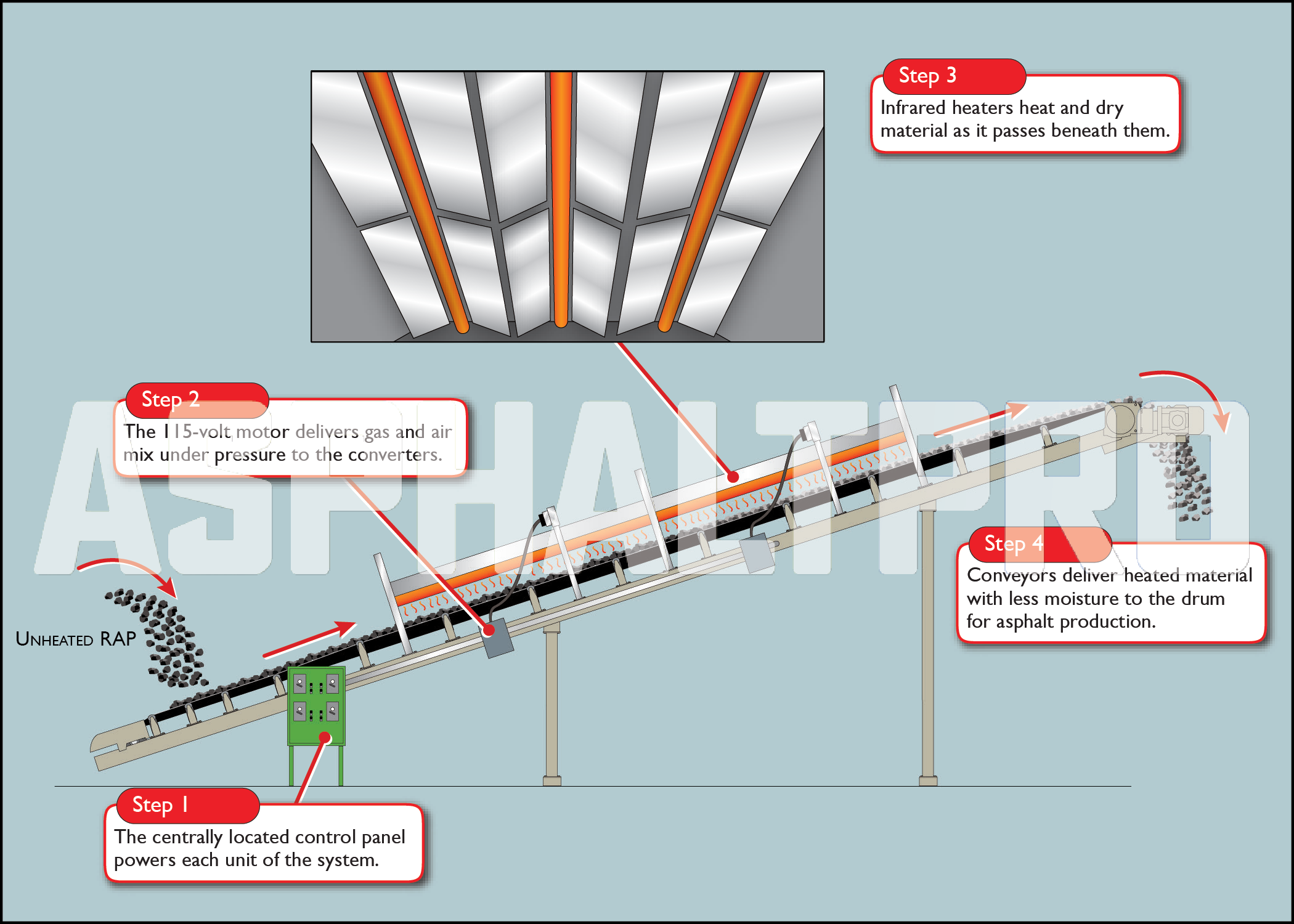
2026 Market Trends for Infrared Asphalt Heater
The global infrared asphalt heater market is poised for significant transformation and growth by 2026, driven by evolving infrastructure demands, technological advancements, and increasing emphasis on sustainability. Here’s an analysis of the key trends shaping this sector:
1. Accelerated Adoption of Smart and Connected Technologies: By 2026, infrared asphalt heaters will increasingly integrate IoT (Internet of Things) sensors and telematics. This enables real-time monitoring of heater performance, fuel consumption, pavement temperature, and maintenance needs. Fleet managers will leverage this data for predictive maintenance, optimizing repair schedules, improving fuel efficiency, and ensuring consistent, high-quality patching – directly enhancing operational efficiency and reducing downtime.
2. Heightened Focus on Fuel Efficiency and Emissions Reduction: Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals will drive innovation in fuel systems. Manufacturers will prioritize developing heaters with improved combustion efficiency, utilizing cleaner-burning fuels (like propane or renewable natural gas), and exploring hybrid or electric-assist models. This trend aligns with broader decarbonization efforts in road maintenance, making infrared repair a more environmentally viable alternative to traditional mill-and-fill methods.
3. Expansion Driven by Preventive Maintenance Strategies: Municipalities and highway agencies are shifting focus from reactive repairs to proactive, preventive pavement maintenance. Infrared asphalt heating, enabling seamless, full-depth recycling of localized damage, perfectly fits this strategy. Its ability to extend pavement life cost-effectively will fuel adoption, particularly in regions with extensive aging road networks, making it a standard tool in routine maintenance fleets.
4. Growth in Rental and Service-Based Models: The high initial cost of advanced infrared heater units will encourage the growth of rental markets and on-demand repair services. Contractors and smaller municipalities will increasingly opt to rent equipment or hire specialized subcontractors, lowering the barrier to entry and increasing market penetration without requiring significant capital investment.
5. Technological Refinements for Performance and Usability: Expect continued improvements in heating uniformity, depth control, and cycle time. Advancements in emitter design (e.g., more efficient ceramic or quartz elements) and control systems will allow for faster, more precise heating, better integration with different asphalt mixtures, and easier operation, reducing operator skill requirements and improving repair quality consistency.
6. Regional Growth Variations: Growth will be robust in North America and Europe, driven by aging infrastructure and stringent environmental standards. Significant growth is also anticipated in the Asia-Pacific region, particularly in China and India, fueled by massive infrastructure development and urbanization projects. Government spending on road maintenance will be a critical driver globally.
7. Integration with Sustainable Materials: The compatibility of infrared repair with recycled asphalt pavement (RAP) will be a major selling point. As the use of RAP in new mixes increases, the ability of infrared technology to seamlessly integrate recycled materials into existing pavement will bolster its position as a sustainable solution, appealing to environmentally conscious stakeholders.
In conclusion, the 2026 infrared asphalt heater market will be characterized by smarter, cleaner, and more efficient equipment, deeply integrated into preventative maintenance programs and supported by evolving service models. Driven by technological innovation and the imperative for sustainable infrastructure, the market is set for sustained growth, solidifying infrared heating as a cornerstone technology in modern road preservation.
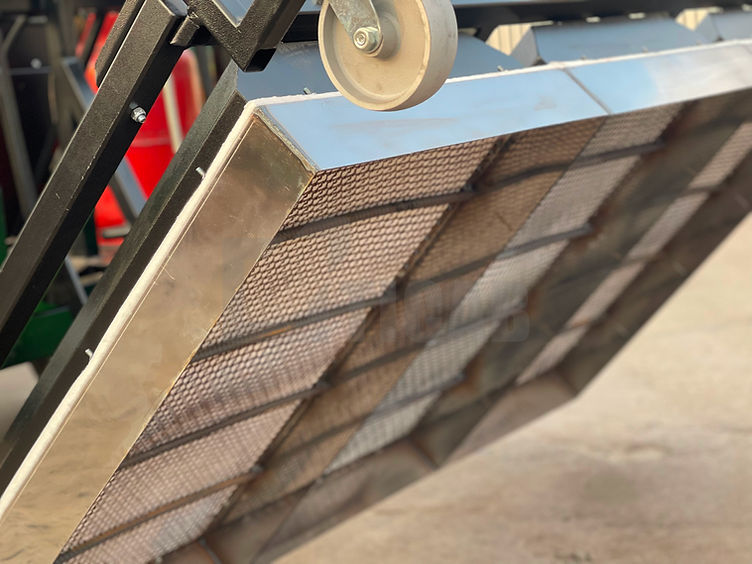

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Infrared Asphalt Heaters (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing infrared asphalt heaters involves navigating several critical challenges related to both product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these pitfalls can lead to equipment failure, safety hazards, legal disputes, and financial losses.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Heating Performance and Efficiency
A common issue is sourcing heaters that fail to deliver consistent, uniform heat required for effective asphalt repair. Low-quality units may have poorly calibrated infrared emitters or insufficient power output, leading to incomplete softening of asphalt. This results in substandard patching, reduced pavement lifespan, and increased rework. Buyers should verify technical specifications, such as radiant efficiency, heating depth, and temperature control mechanisms, through third-party testing or field demonstrations.
Poor Build Quality and Durability
Many low-cost infrared heaters use substandard materials—such as thin-gauge steel, inferior reflectors, or low-grade electrical components—that degrade quickly under high-temperature operation and harsh job site conditions. This leads to frequent breakdowns, higher maintenance costs, and potential safety risks. Insist on detailed material specifications, corrosion-resistant coatings, and evidence of rigorous stress testing before purchase.
Lack of Safety Features and Compliance
Inferior heaters may lack essential safety mechanisms like overheat protection, emergency shut-offs, or proper grounding. They may also fail to meet regional safety standards (e.g., CE, UL, or CSA). Using non-compliant equipment can expose contractors to liability, regulatory penalties, and workplace accidents. Always confirm certification documents and conduct an on-site inspection of safety systems.
Inaccurate or Missing Technical Documentation
Suppliers of low-quality units often provide incomplete or vague technical manuals, making installation, operation, and troubleshooting difficult. Missing calibration data or maintenance schedules can impair performance and void warranties. Demand comprehensive, well-documented technical packages before finalizing procurement.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
Sourcing Counterfeit or Copycat Equipment
The market includes counterfeit versions of reputable infrared heaters, which mimic branding and design but use inferior engineering. These copies often infringe on patents and trademarks, exposing buyers to legal risk if used commercially. Verify the authenticity of suppliers through official manufacturer channels and validate model numbers and serials.
Unlicensed Use of Proprietary Technology
Some manufacturers reverse-engineer patented infrared emitter designs, reflector geometries, or control systems without licensing. Purchasing such equipment may inadvertently support IP theft and leave users vulnerable to legal action—especially in regions with strong IP enforcement. Conduct due diligence by reviewing patent databases and requesting proof of IP compliance from suppliers.
Ambiguous Warranty and Support Terms
Infringing products typically lack proper manufacturer support and offer limited or voidable warranties. If a heater is found to violate IP rights, the supplier may disappear or refuse service. Ensure warranty terms are backed by a legally registered entity and include clear clauses on repairs, replacements, and liability.
Reputational and Contractual Risk
Using equipment with questionable IP status can damage a contractor’s reputation, especially when working on public or government-funded projects where compliance is scrutinized. Some contracts explicitly require the use of IP-compliant tools. Always review procurement agreements and confirm equipment legitimacy to avoid disqualification or breach of contract.
To mitigate these risks, buyers should prioritize suppliers with proven track records, transparent manufacturing processes, and verifiable IP rights. Third-party audits, site visits, and legal reviews of supply agreements can further safeguard procurement decisions.
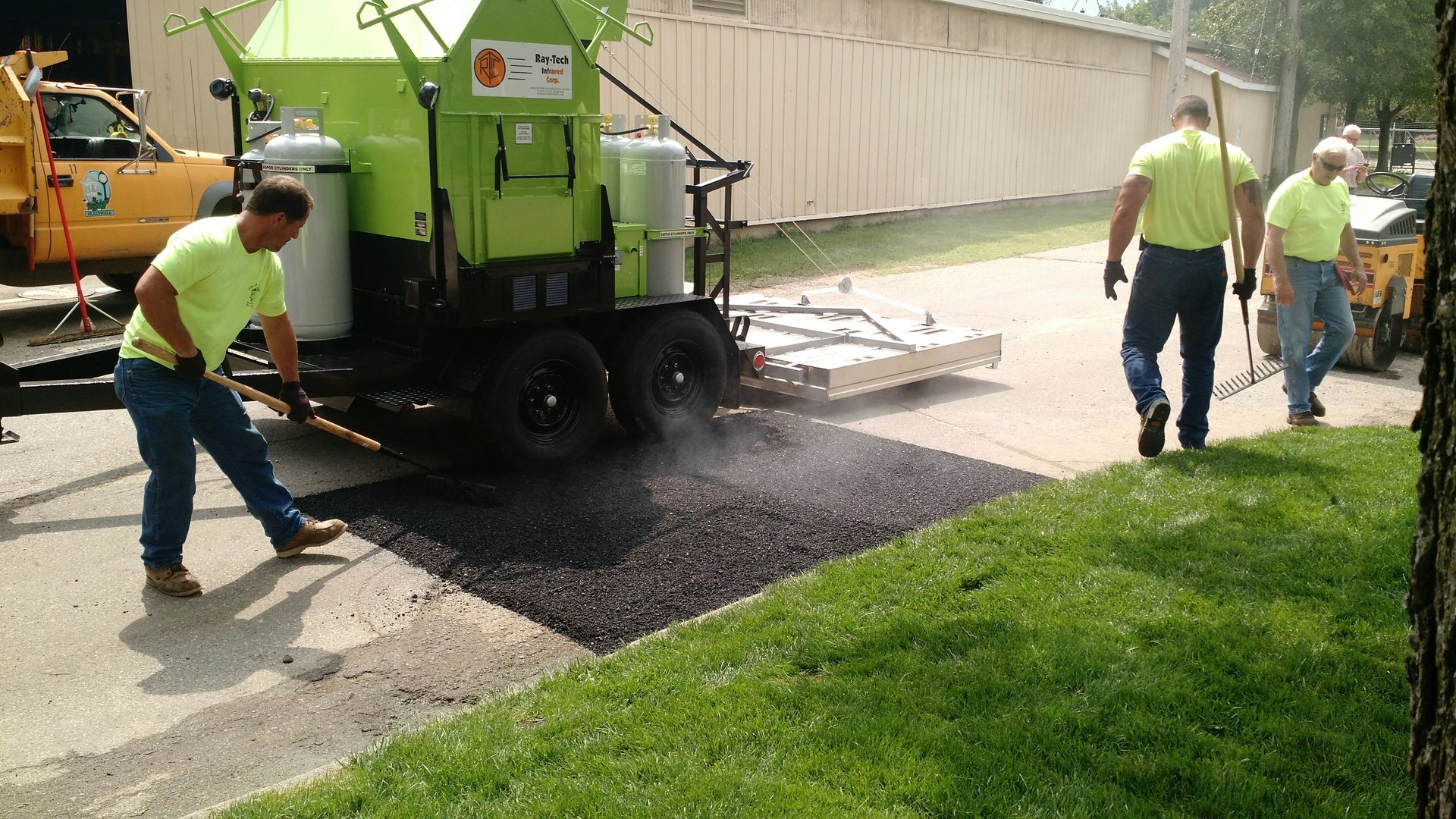

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Infrared Asphalt Heater
H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Infrared Asphalt Heater
1. Pre-Shipment Planning & Documentation
- Product Classification:
- HS Code: Obtain the correct Harmonized System (HS) code for the infrared asphalt heater (e.g., often falls under 8419.81.00 – “Other machinery, plant or laboratory equipment, for the treatment of materials by a process involving a change of temperature…”). Verify with your customs broker or local authority, as classifications can vary by country and specific heater design (e.g., trailer-mounted vs. skid-mounted).
- Export Control: Confirm the heater is not subject to export controls (e.g., no dual-use technology, specific power sources, or materials of concern). Check ITAR/EAR (US), Wassenaar Arrangement, or equivalent national regulations.
- Required Documentation:
- Commercial Invoice: Detailed description (make, model, serial number), value (FOB, CIF), quantity, harmonized code, country of origin, buyer/seller details. Must reflect true transaction value.
- Packing List: Itemized list per package, weights (gross/net), dimensions, packaging type, marks & numbers. Critical for handling and customs clearance.
- Bill of Lading (B/L) or Air Waybill (AWB): Contract of carriage. Specify Incoterms® 2020 (e.g., EXW, FOB, CIF, DDP) clearly defining responsibilities and costs. For sea freight, use a negotiable B/L if payment terms require it.
- Certificate of Origin (CoO): May be required for tariff preferences (e.g., USMCA, EU agreements) or general customs requirements. Can be generic or preferential (e.g., Form A, EUR.1).
- Technical Specifications & Manual: Essential for customs valuation, classification, and end-user compliance. Include electrical ratings, fuel type, safety features.
- Test Reports/Certificates: Copies of relevant safety and emissions certifications (see Compliance section below).
- Export License (if required): Based on destination country, value, or technology.
- Packaging & Marking:
- Robust Packaging: Use heavy-duty crates, skids, or containers suitable for long-distance transport. Secure all components, especially the heating elements and control panels. Use cushioning and moisture barriers.
- Clear Marking: Label each package with: Shipper/Consignee, PO Number, Model/Serial Number, Weight, Dimensions, “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” “Do Not Stack,” “Keep Dry,” and specific handling instructions (e.g., “Protect Heating Elements”). Include hazardous material labels only if applicable (e.g., fuel in tank – see below).
2. Transportation & Handling
- Mode Selection:
- Road: Common for regional/domestic or short-haul international (e.g., trailer-mounted units). Ensure vehicle capacity and permits for oversized loads if applicable. Securely tie down.
- Sea Freight (FCL/LCL): Standard for international shipments. FCL (Full Container Load) recommended for single units or full orders to minimize handling risk. LCL (Less than Container Load) possible but increases damage risk. 20ft or 40ft standard containers. Consider open-top containers for very tall units.
- Air Freight: Only for urgent, very high-value shipments or replacement parts due to extremely high cost. Requires disassembly or very compact units.
- Handling Procedures:
- Lifting Points: Use ONLY designated lifting points (forklift pockets, crane hooks). Never lift by the heating panels, controls, or fuel tank.
- Forklifts/Cranes: Use appropriate capacity equipment. Operators must be trained. Use spreader bars for crane lifts to prevent damage.
- Tilting: Avoid tilting beyond the manufacturer’s specified angle (usually minimal) to prevent fuel/oil leaks or internal component damage.
- Fuel & Fluids:
- Crucial: Drain ALL fuel (diesel, propane, LPG) and hydraulic oil BEFORE shipment. Transporting fuel is highly regulated (Dangerous Goods – Class 3 Flammable Liquids / Class 2.1 Flammable Gas), extremely costly, and poses significant fire/explosion risks and regulatory hurdles. Ship empty.
- Provide detailed instructions for the end-user on safe fueling procedures upon receipt.
- Transit Insurance: Obtain comprehensive marine (or all-risk) cargo insurance covering the full value (including freight and insurance – CIF basis) against loss, damage, and delay. Specify coverage for handling damage.
3. Import & Customs Clearance
- Engage Local Expertise: Use a reputable customs broker in the destination country.
- Duty & Tax Calculation: Based on HS code, declared value (Commercial Invoice), and destination country’s tariff schedules. Calculate:
- Import Duty (Ad Valorem, Specific, or Compound)
- Value-Added Tax (VAT) or Goods and Services Tax (GST)
- Any applicable customs processing fees
- Submission: Broker submits all required documents (Invoice, Packing List, B/L/AWB, CoO, Test Reports, Import License if needed) electronically or physically to customs authorities.
- Inspection: Be prepared for potential customs inspection. Ensure easy access to documentation and the unit. Delays may occur.
- Payment & Release: Pay assessed duties/taxes/fees. Customs will release the goods upon payment and verification.
4. Key Compliance Requirements
- Electrical Safety:
- CE Marking (Europe): Mandatory. Requires compliance with Low Voltage Directive (LVD 2014/35/EU) and Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive (EMCD 2014/30/EU). Involves risk assessment, technical file, Declaration of Conformity (DoC), and likely involvement of a Notified Body for testing/certification (e.g., TÜV, SGS, Intertek). Must meet EN standards (e.g., EN 60204-1 for machinery safety).
- UKCA Marking (UK): Required for Great Britain (post-Brexit). Similar requirements to CE, based on UK versions of EU directives (UK LVD, UK EMC). Northern Ireland may still require CE.
- UL/CSA (North America): Highly recommended or required by many customers/insurers. UL 1741 (Inverters, Converters, Controllers) or UL 60950-1/62368-1 (Safety of IT/AV Equipment) might be applicable depending on controls, but often a risk-based assessment per UL 508A (Industrial Control Panels) or specific machinery standards is needed. CSA C22.2 No. 601-1 (Safety of Household and Similar Electrical Appliances) may also be considered. Third-party certification (UL, CSA, Intertek) is typical.
- Other Markets: Check local requirements (e.g., RCM in Australia/NZ, CCC in China, KC in South Korea, PSE in Japan).
- Emissions & Environmental:
- Air Quality Regulations: Ensure combustion emissions (if fuel-fired) comply with destination country standards (e.g., EPA Tier standards in the US, EU Stage V non-road engine directives if using a diesel generator). Provide emission test reports if required.
- RoHS (EU/China/UK/others): Restriction of Hazardous Substances. Applies to electrical/electronic components. Must declare compliance (usually via supplier DoCs for sub-components).
- WEEE (EU): Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment. Requires producer registration and financing take-back/recycling. Provide information to end-user.
- Machinery Safety (Global):
- ISO 12100: Risk assessment and risk reduction principles.
- ISO 13849-1: Safety of machinery – Safety-related parts of control systems.
- Specific Standards: May include ISO 2867 (Earth-moving machinery – Access systems), ISO 15870 (Road construction machinery – Pavers), or others depending on configuration. Requires safety guards, emergency stops, warning labels (in local language), and risk assessment documentation.
- Transportation of Dangerous Goods (If Applicable):
- STRICTLY AVOID SHIPPING WITH FUEL. If absolutely unavoidable (extremely rare and discouraged), it becomes a Class 3 (Flammable Liquid – Diesel) or Class 2.1 (Flammable Gas – Propane/LPG) shipment under ADR (Europe), IMDG Code (Sea), IATA DGR (Air), or 49 CFR (US). Requires:
- Specialized packaging (UN-certified pressure vessels for gas, approved cans/containers for liquid).
- Dangerous Goods Declaration.
- Proper labeling/placarding (Class 3 or 2.1 labels, UN number – e.g., UN1202 for Diesel).
- Trained personnel (shippers, handlers).
- Significant additional cost and regulatory burden. Draining fuel is the standard and expected practice.
- STRICTLY AVOID SHIPPING WITH FUEL. If absolutely unavoidable (extremely rare and discouraged), it becomes a Class 3 (Flammable Liquid – Diesel) or Class 2.1 (Flammable Gas – Propane/LPG) shipment under ADR (Europe), IMDG Code (Sea), IATA DGR (Air), or 49 CFR (US). Requires:
5. Post-Delivery & Final Steps
- Customer Handover: Provide complete documentation package (manual, safety instructions, compliance certificates – CE/UKCA/UL DoC, warranty).
- Training: Ensure the end-user receives proper operational and safety training, especially on fueling procedures, start-up, shutdown, and emergency stops.
- Compliance Record Keeping: Maintain copies of all export/import documents, test reports, certificates, and Declarations of Conformity for the legally required period (often 10 years for CE/UKCA).
Summary: Successful logistics and compliance for an infrared asphalt heater hinge on meticulous documentation, robust packaging, safe handling (especially draining all fuel), understanding destination-specific regulatory requirements (electrical, emissions, machinery safety), and utilizing expert partners (freight forwarders, customs brokers, certification bodies). Prioritize safety and regulatory adherence throughout the entire supply chain.
Conclusion for Sourcing an Infrared Asphalt Heater
In conclusion, sourcing an infrared asphalt heater is a strategic investment that offers numerous advantages for road maintenance and repair operations. Infrared heaters provide energy-efficient, precise, and uniform heating, enabling seamless asphalt repairs that enhance pavement longevity and reduce the likelihood of rework. When selecting a supplier, it is essential to consider factors such as heater performance, durability, ease of use, safety features, after-sales support, and compliance with environmental and industry standards.
After evaluating various options, partnering with a reputable manufacturer or distributor that offers reliable technology, proven field performance, and strong service networks ensures optimal return on investment. Additionally, sourcing heaters with adjustable temperature controls, portability, and low emissions aligns with sustainability goals and regulatory requirements.
Ultimately, implementing infrared asphalt heating technology through well-vetted sourcing enhances operational efficiency, reduces material waste, and supports high-quality road maintenance—making it a sound long-term solution for municipalities, contractors, and infrastructure maintenance teams.