The global infant catheter market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) admissions, increasing prevalence of congenital urological disorders, and advancements in pediatric medical devices. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global pediatric catheters market was valued at USD 1.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.8% from 2024 to 2029. This expansion is further supported by Grand View Research, which highlights increasing demand for minimally invasive procedures and the development of specialty catheters tailored for neonatal and infant use. As healthcare systems prioritize precise, atraumatic solutions for vulnerable pediatric patients, innovation in infant catheter design and material safety has become a key focus. In this evolving landscape, a select group of manufacturers are leading the way in product development, compliance, and global distribution. Here are the top 8 infant catheter manufacturers shaping the future of neonatal urological care.
Top 8 Infant Catheter Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laborie Medical Technologies
Domain Est. 1995
Website: laborie.com
Key Highlights: Laborie is a medical technology company. We specialize in Gastroenterology, Gynecology, Urology, Obstetrics, Neonatal & Urogynecology. Learn more….
#2 Foley Catheter manufacturer, Microporous Tapes, Endotracheal …
Domain Est. 2009
Website: sterimedgroup.com
Key Highlights: Sterimed Group has one of the largest manufacturing capacities for Foley Balloon Catheter, Endotracheal Tubes (ET Tubes) and other medical disposable products ……
#3 Umbilical Catheter Manufacturer & Supplier
Domain Est. 2021
Website: haolangmedical.com
Key Highlights: Umbilical catheters are modern medical tools designed for neonates and infants who require medical intervention….
#4 Continence Care
Domain Est. 1995
Website: convatec.com
Key Highlights: Explore Continence Care resources to help make life as an intermittent catheter user completely your own. Request free product samples and information, discover ……
#5 Neonatal Intensive Care Medical Equipment
Domain Est. 1996
Website: cardinalhealth.com
Key Highlights: We offer a full line of neonatal products including umbilical vessel catheters and peripherally inserted central catheters for vascular access….
#6 Neonatal PICC catheters
Domain Est. 1997
Website: us.vygon.com
Key Highlights: These Peripherally Inserted Central Catheters (PICCs), made of biocompatible polyurethane or silicone, are indicated for premature babies, newborns and infants….
#7
Domain Est. 1999
Website: liberatormedical.com
Key Highlights: We have the right intermittent self-catheter for you. Choose from a wide variety of intermittent self-catheters, plus FREE samples from many suppliers….
#8 Pediatric Catheters
Domain Est. 2002
Website: 180medical.com
Key Highlights: If you need pediatric catheters for your child, 180 Medical is one of the leading providers of catheter supplies for children. Contact us!…
Expert Sourcing Insights for Infant Catheter
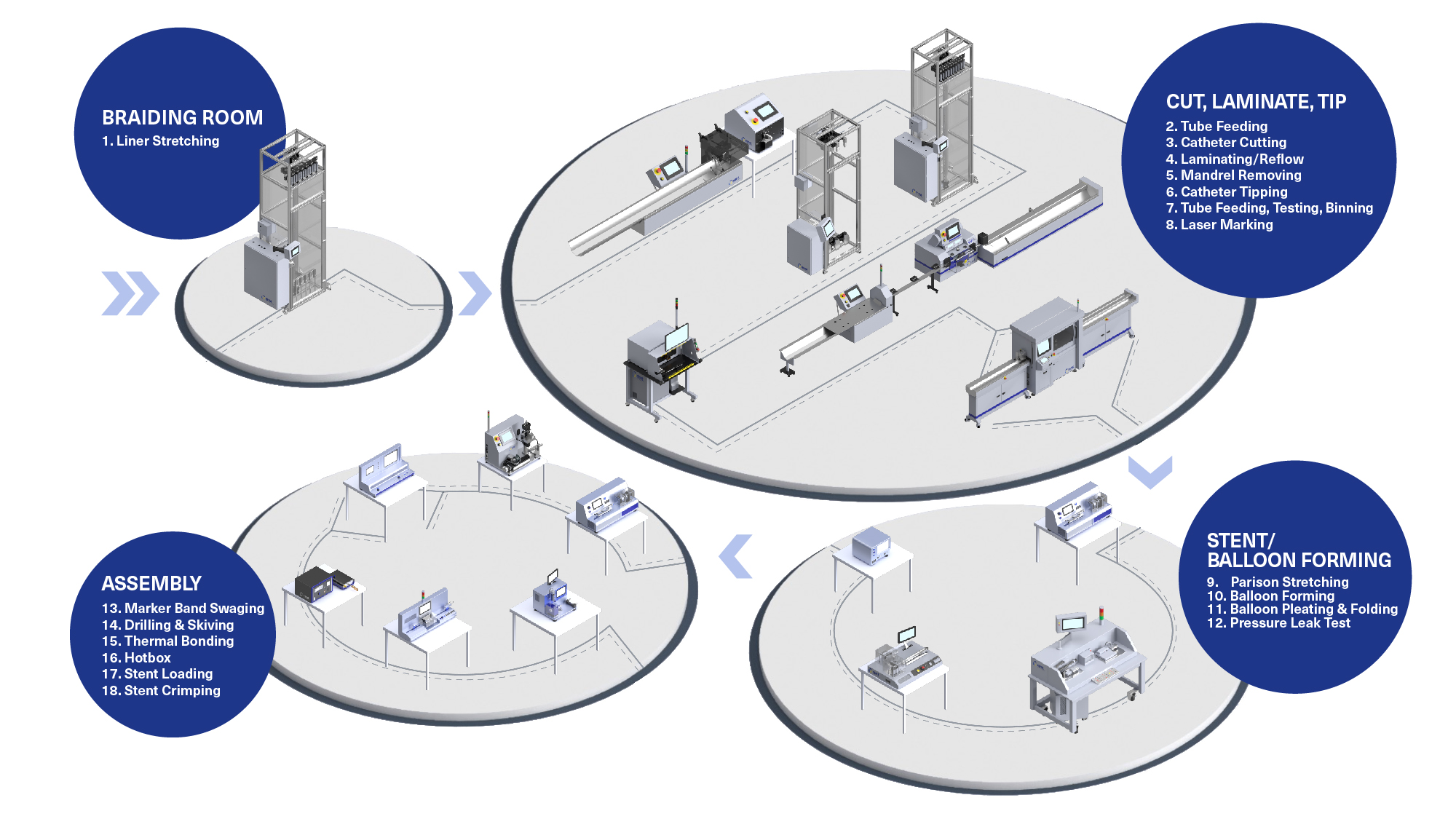
H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for Infant Catheters
The infant catheter market in 2026 is anticipated to be shaped by a convergence of demographic, technological, regulatory, and healthcare delivery trends. Driven primarily by the need for safer, more effective, and less invasive solutions for vulnerable neonatal and pediatric patients, key developments are expected across several dimensions:
1. Technological Innovation & Product Advancements:
* Miniaturization & Material Science: Continued development of ultra-thin, highly flexible catheters made from biocompatible, non-irritating materials (e.g., advanced silicones, hydrophilic coatings) will dominate. Focus will be on reducing urethral trauma, infection risk (CAUTI), and encrustation.
* Smart Catheters & Integration: Emerging integration of sensors for real-time monitoring of parameters like urine flow rate, bladder pressure, temperature, and early infection markers (e.g., pH, specific gravity) is expected to gain traction, enabling proactive interventions.
* Closed-System & Safety Features: Adoption of pre-lubricated, closed-system catheterization kits with integrated collection bags will increase, minimizing contamination risk during insertion and handling. Enhanced safety features like anti-reflux valves and secure leg-bag connectors will be standard.
* Specialized Designs: Growth in catheters specifically designed for unique neonatal anatomies (e.g., preterm infants, infants with urogenital anomalies) and specific clinical needs (e.g., long-term indwelling, intermittent catheterization in NICU settings).
2. Rising Prevalence of Underlying Conditions & Prematurity:
* Increasing global rates of preterm births and low birth weight infants, particularly in developing regions, will drive demand for specialized NICU catheters.
* Growing diagnosis and management of congenital urological disorders (e.g., posterior urethral valves, spina bifida, neurogenic bladder) will sustain the need for reliable infant catheterization solutions.
3. Focus on Infection Prevention & Patient Safety:
* CAUTI Reduction Imperative: Stringent hospital protocols and regulatory pressures (e.g., CMS non-payment for CAUTIs) will accelerate adoption of antimicrobial-coated catheters (e.g., silver alloy, nitrofurazone) and strict adherence to aseptic techniques facilitated by closed systems.
* Emphasis on Minimally Invasive Procedures: Surgeons and clinicians will increasingly favor catheters that support less traumatic insertion and reduce the need for repeated catheterizations, aligning with enhanced recovery protocols.
4. Regulatory Landscape & Reimbursement:
* Stricter Regulatory Scrutiny: Agencies like the FDA (US) and EMA (EU) will likely impose more rigorous requirements for biocompatibility, sterility, and clinical evidence, particularly for novel materials and smart devices, potentially increasing time-to-market.
* Reimbursement Pressures: Healthcare systems focused on cost containment will demand robust health economic data demonstrating that advanced (often higher-cost) catheters reduce overall costs by preventing complications (CAUTIs, readmissions).
5. Shifting Healthcare Delivery & Market Dynamics:
* Home Care Expansion: Growth in home-based care for infants with chronic conditions will increase demand for user-friendly, safe catheterization kits and supplies, along with comprehensive caregiver training programs.
* Consolidation & Competition: The market will likely see continued M&A activity among key players (e.g., B. Braun, Teleflex, Coloplast, Boston Scientific) seeking to broaden portfolios. Simultaneously, niche players focusing on innovation (e.g., smart catheters, specialized materials) will emerge, increasing competitive pressure.
* Emerging Market Growth: Significant market expansion is expected in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and parts of Africa due to improving healthcare infrastructure, rising awareness, and increasing neonatal care capacity.
6. Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing:
* Growing awareness will push manufacturers towards more sustainable practices, including reducing plastic waste (e.g., via reusable components where feasible, optimized packaging) and ensuring ethical sourcing of raw materials.
In summary, the 2026 infant catheter market will be characterized by a strong push towards innovation focused on safety, infection prevention, and patient-specific needs, driven by clinical demands and regulatory pressures. Success will depend on manufacturers’ ability to deliver technologically advanced, clinically proven, and cost-effective solutions while navigating a complex global landscape.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Infant Catheters (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing infant catheters requires extreme diligence due to the vulnerability of the patient population and the specialized nature of the devices. Overlooking critical aspects can lead to severe consequences, including patient harm, regulatory non-compliance, and legal liabilities. Here are the key pitfalls related to quality and intellectual property (IP):
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inadequate Supplier Qualification and Auditing
Failing to thoroughly vet suppliers—especially those in low-cost regions—can result in substandard products. Many manufacturers may claim compliance with ISO 13485 or FDA regulations but lack consistent quality systems. Without on-site audits, document reviews, and sample testing, sourcing teams risk receiving catheters with inconsistent materials, poor sterility, or faulty dimensions.
2. Non-Compliance with Pediatric-Specific Standards
Infant catheters have unique requirements (e.g., smaller diameters, biocompatible materials, flexibility). Sourcing generic or adult-sized catheters repackaged for infants without proper validation is a critical error. Suppliers must demonstrate compliance with pediatric-specific standards such as ISO 8536-13 (infusion sets) or IEC 60601-2-64 (for related medical electrical equipment).
3. Inconsistent Raw Material Sourcing and Traceability
Using substandard or untraceable materials (e.g., non-phthalate-free PVC, non-USP Class VI compliant polymers) can lead to toxicity or adverse reactions in infants. A lack of full supply chain transparency makes it difficult to ensure material consistency and respond to recalls or quality deviations.
4. Insufficient Sterilization Validation
Improper or undocumented sterilization processes (e.g., EO, gamma) can compromise sterility assurance levels (SAL). Suppliers may not provide valid sterilization dossiers or bioburden testing data, increasing the risk of infections in neonatal intensive care units (NICUs).
5. Inadequate Packaging and Shelf-Life Validation
Poor packaging design or lack of accelerated aging studies can lead to compromised integrity during transport or storage. Sourcing products without validated shelf life or real-time stability data risks using devices that degrade prematurely.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
1. Sourcing from Suppliers with Infringing Designs
Some manufacturers replicate patented catheter designs (e.g., specific tip configurations, anti-kink features) without licensing. Purchasing such products—even unknowingly—can expose the buyer to contributory infringement claims, especially in markets like the U.S. or EU with strong IP enforcement.
2. Lack of IP Due Diligence in Contracts
Purchase agreements that fail to include IP warranties, indemnification clauses, or statements of original design leave buyers vulnerable. If a supplier’s product is later found to infringe, the buyer may face litigation, product seizures, or costly redesigns.
3. Counterfeit or Gray Market Products
Infant catheters are sometimes counterfeited or diverted through unauthorized distribution channels. These products bypass quality controls and may use stolen IP. Relying on third-party distributors without verifying authenticity increases exposure to both safety and IP risks.
4. Unclear Ownership of Custom Designs
When working with contract manufacturers on custom pediatric catheters, failure to define IP ownership in writing can lead to disputes. Suppliers may claim rights to design improvements or tooling, limiting the buyer’s ability to switch manufacturers or protect innovations.
Mitigating these pitfalls requires a robust sourcing strategy that includes rigorous supplier audits, technical validation, legal review of IP status, and clear contractual safeguards—ensuring both patient safety and regulatory compliance.
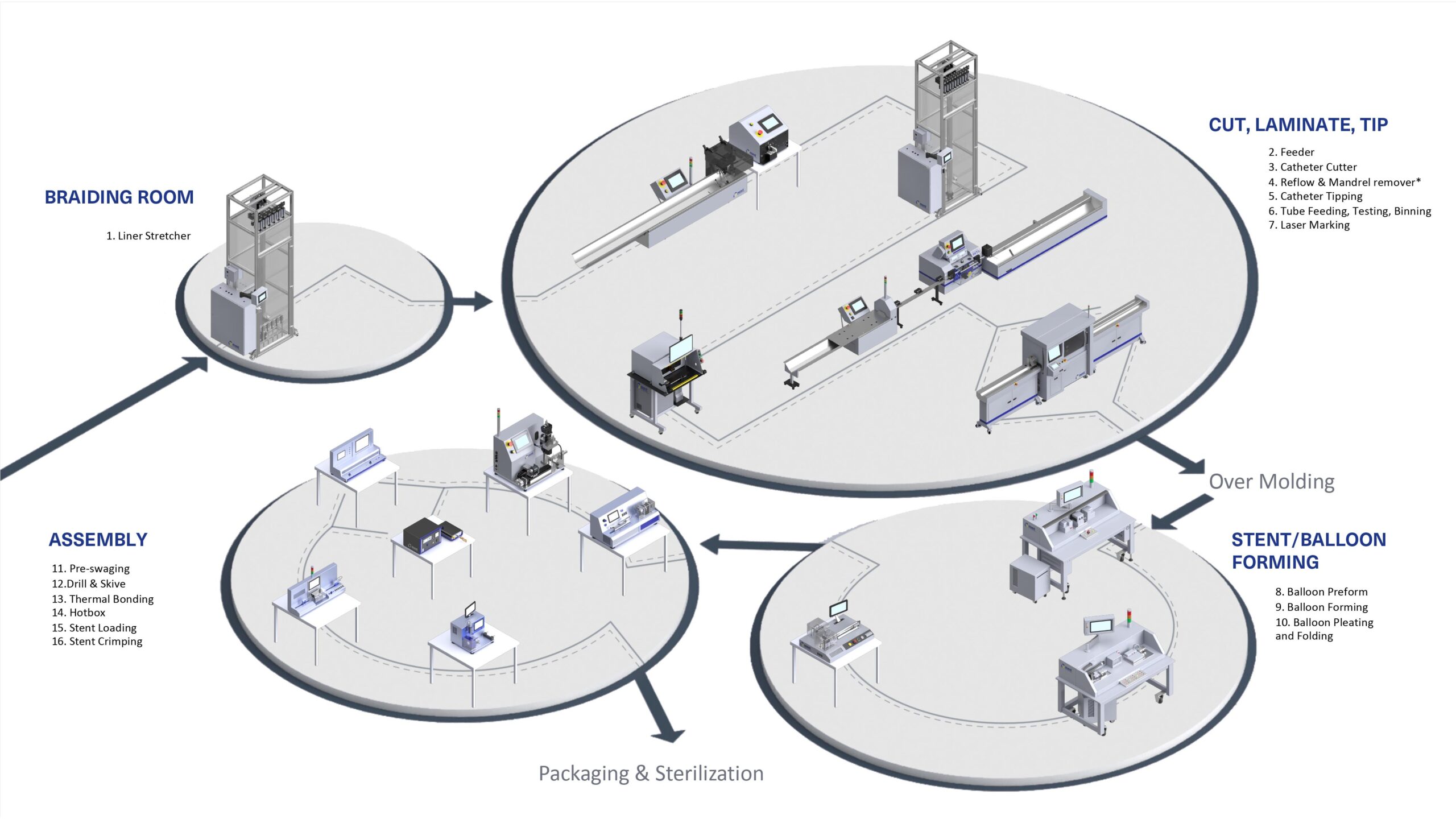
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Infant Catheters
Overview
Infant catheters are medical devices used for urinary drainage in neonatal and pediatric patients. Due to their sensitive application and vulnerable patient population, the logistics and compliance requirements for infant catheters are stringent and must adhere to international regulatory standards, temperature control protocols, and traceability mandates.
Regulatory Compliance
Infant catheters are classified as medical devices and are subject to regulatory oversight in all major markets. Key compliance frameworks include:
- FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration): Must comply with 21 CFR Part 800–892, including premarket notification (510(k)) clearance or approval, Quality System Regulation (QSR), and Unique Device Identification (UDI) requirements.
- EU MDR (Medical Device Regulation 2017/745): Requires CE marking, adherence to risk management (ISO 14971), Post-Market Surveillance (PMS), and UDI implementation.
- Health Canada: Must meet the Medical Devices Regulations (SOR/98-282), including licensing and adverse event reporting.
- Other Regions: Compliance with local regulations (e.g., TGA in Australia, PMDA in Japan, NMPA in China) may require additional certifications and labeling adaptations.
Manufacturers and distributors must maintain technical documentation, ensure sterile integrity, and comply with biocompatibility standards (e.g., ISO 10993).
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
Proper packaging and labeling are critical to ensure sterility and regulatory compliance:
- Sterile Barrier System: Must utilize validated packaging (e.g., peelable pouches) that maintains sterility throughout shelf life.
- Labeling: Must include UDI, lot number, expiration date, storage conditions, single-use designation, and appropriate symbols per ISO 15223-1.
- Language: Local language requirements for target markets (e.g., bilingual labels in Canada, French in EU member states).
- Child-Safe Packaging: Where applicable, comply with regional safety standards for tamper evidence.
Storage and Handling
Infant catheters require controlled storage conditions:
- Temperature: Store at 15–30°C (59–86°F), unless otherwise specified by the manufacturer. Avoid freezing and direct sunlight.
- Humidity: Maintain relative humidity below 60% to prevent packaging degradation.
- Shelf Life: Monitor expiration dates strictly; do not distribute expired devices. Typical shelf life ranges from 2 to 5 years.
- Handling: Use clean, dry hands or gloves; avoid crushing or puncturing packaging.
Transportation and Distribution
Transport logistics must ensure product integrity:
- Cold Chain (if required): Though most catheters are ambient-stable, verify manufacturer specifications. Use temperature-monitored shipments if needed.
- Validation: Conduct shipping validations (e.g., ISTA 3A) to ensure packaging withstands vibration, compression, and temperature fluctuations.
- Serialization and Traceability: Implement systems to track catheters from manufacturer to end-user using UDI and batch/lot numbers.
- Carrier Requirements: Use certified medical device couriers with GDP (Good Distribution Practice) compliance.
Import/Export Documentation
Cross-border movement requires accurate documentation:
- Commercial Invoice: Includes product description, value, and harmonized system (HS) code (e.g., 9018.39 for catheters).
- Packing List: Details quantity, weight, and dimensions.
- Certificate of Conformity: Issued by manufacturer, confirming compliance with destination country regulations.
- Bill of Lading/Air Waybill: Legal receipt of goods for transport.
- Customs Declarations: Required in all jurisdictions; may include FDA Prior Notice (U.S.) or EU Export Health Certificate.
- Import Permits: Some countries require medical device import licenses.
Post-Market Surveillance and Recall Preparedness
Proactive compliance continues after distribution:
- Adverse Event Reporting: Establish procedures to report incidents to regulatory bodies (e.g., FDA MAUDE, EUDAMED).
- Field Safety Notices: Issue alerts for product issues or recalls promptly.
- Recall Plan: Maintain a documented, tested recall procedure aligned with FDA 21 CFR Part 7 and EU MDR Article 87.
- Customer Feedback Loop: Monitor and analyze complaints for quality improvement.
Training and Documentation
All personnel involved in logistics and handling must be trained:
- GDP Training: Ensure staff understand Good Distribution Practices.
- SOPs (Standard Operating Procedures): Maintain documented processes for storage, handling, shipping, and incident response.
- Audit Readiness: Regular internal audits and preparation for regulatory inspections (e.g., FDA, Notified Body).
Conclusion
The logistics and compliance management of infant catheters demands a robust, integrated approach that spans regulatory adherence, sterile integrity, traceability, and responsive post-market systems. Adherence to global standards ensures patient safety and uninterrupted supply to critical care environments.
Conclusion on Sourcing Infant Catheters
Sourcing infant catheters requires careful consideration of multiple critical factors including biocompatibility, size accuracy, material safety, regulatory compliance, and clinical suitability for neonatal and pediatric patients. Given the fragility of infant patients, it is essential to procure catheters from reputable manufacturers that adhere to international quality standards such as ISO 13485 and FDA or CE regulations. Close collaboration with healthcare professionals, thorough evaluation of product specifications, and attention to sterile packaging and traceability are vital to ensure patient safety and effective clinical outcomes. Additionally, establishing reliable supply chains with transparent sourcing practices helps mitigate risks of shortages and ensures continuity of care. Ultimately, a strategic, quality-driven approach to sourcing infant catheters supports optimal neonatal treatment and aligns with best practices in pediatric healthcare delivery.