The global industrial metal detector market is experiencing robust growth, driven by stringent food safety regulations, increasing automation in manufacturing, and rising demand for product purity across sectors such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 1.27 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.8% from 2023 to 2028. Similarly, Grand View Research forecasts rising adoption of advanced detection technologies, including multi-frequency and digital signal processing systems, to further fuel expansion. As quality control becomes a non-negotiable standard across supply chains, manufacturers are turning to leading industrial metal detector companies for reliable, high-performance solutions. In this landscape of increasing demand and technological innovation, the following ten manufacturers have emerged as key players globally, setting benchmarks in accuracy, durability, and integration capabilities.
Top 10 Industrial Metal Detector Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Tectron Engineering
Domain Est. 1999
Website: tectron.net
Key Highlights: A Metal Detection Equipment manufacturer specializing in industrial metal detectors that can detect ferrous, non ferrous and or tramp metal….
#2 Metal Detectors Inc.
Domain Est. 2005
Website: mdiblue.com
Key Highlights: With 60 years of experience manufacturing industrial metal detector equipment, MDI has a reputation you can trust, quality products that are top of the line, ……
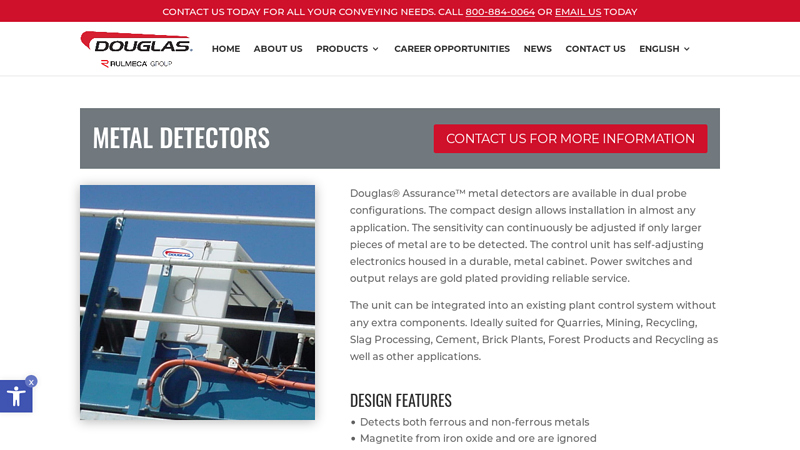
#3 Industrial Metal Detectors
Domain Est. 1996
Website: douglasmanufacturing.com
Key Highlights: Douglas manufactures metal detectors that are suitable for a variety of industrial applications, including mining, recycling, slag processing, cement, quarries ……
#4 Garrett Metal Detector Manufacturer for Sport, Security & More
Domain Est. 1997
Website: garrett.com
Key Highlights: Garrett designs and manufactures sport, security and countermine metal detectors, including hand-held, ground-search and walk-through detectors….
#5 CEIA Electromagnetic Inspection Systems
Domain Est. 1998
Website: ceia.net
Key Highlights: CEIA is an Industrial Company focused on the design and manufacturing of Electromagnetic Inspection Systems and Induction Heating Systems….
#6 Industrial Metal Detectors
Domain Est. 1999
Website: adsdetection.com
Key Highlights: (414) 672-0553 – Advanced Detection Systems offers top-quality, reliable metal detection systems to fit any application and serve many industries….
#7 VALLON GmbH
Founded: 1965
Website: vallon.de
Key Highlights: Innovative detection systems for explosive ordnance disposal and customized demagnetization solutions for industry. Technical excellence since 1965….
#8 Metal Detection Systems for Food, Pharma, & More
Domain Est. 1993
Website: mt.com
Key Highlights: Our portfolio includes tunnel and throat metal detectors, and gravity fall, pipeline, pharmaceutical and conveyorized metal detection systems….
#9 Metal Detection
Domain Est. 1995
Website: eriez.com
Key Highlights: Detect and Eliminate Metal Contamination. Eriez Metal Detectors and Separators can help safeguard product integrity in a vast assortment of industries….
#10 Smiths Detection
Domain Est. 2002
Website: smithsdetection.com
Key Highlights: Exceptional detection of powders, liquids, and solids. Open Architecture. Leading the development of responsible open architecture in the security industry….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Industrial Metal Detector

H2: Industrial Metal Detector Market Trends Forecast for 2026
The industrial metal detector market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, evolving regulatory landscapes, and increasing demands for product safety and automation across key end-use industries. Here’s an analysis of the dominant trends shaping the market:
1. Integration with Industry 4.0 and Smart Manufacturing (H2):
By 2026, metal detectors will increasingly become integral components of smart factories. Integration with IoT platforms, MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems), and cloud-based analytics will enable real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and data-driven decision-making. This connectivity allows for remote diagnostics, automated reporting, and seamless traceability—meeting the demands of digitalized production lines in food & beverage, pharmaceuticals, and automotive sectors.
2. Advancement in Detection Technology and Sensitivity (H2):
Demand for higher sensitivity and the ability to detect smaller contaminants—especially in wet or conductive products—will drive innovation. Manufacturers will focus on advanced signal processing algorithms, multi-frequency detection, and phased array technologies. These improvements will reduce false rejects, enhance reliability, and expand applicability in challenging environments such as frozen foods or bulk powder handling.
3. Regulatory Compliance Driving Market Growth (H2):
Stringent food safety regulations (e.g., FSMA in the U.S., EU Food Safety Standards) and pharmaceutical GMP guidelines will continue to mandate metal detection in production processes. By 2026, compliance will not only be a legal requirement but also a competitive advantage, pushing companies to adopt higher-grade detection systems. This regulatory pressure is particularly strong in emerging markets undergoing modernization of food safety infrastructure.
4. Expansion in Emerging Applications and Geographies (H2):
While food & beverage and pharmaceuticals remain dominant, growth will accelerate in non-traditional sectors such as recycling, plastics, textiles, and ceramics. Additionally, Asia-Pacific—led by China, India, and Southeast Asia—will emerge as a high-growth region due to rising industrialization, urbanization, and consumer safety awareness. Local manufacturing and cost-optimized solutions will be key to capturing market share.
5. Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Focus (H2):
Sustainability will influence product design, with manufacturers developing energy-efficient metal detectors featuring lower power consumption and longer operational life. The industry will also emphasize recyclability of components and reduced electronic waste. These factors will appeal to environmentally conscious enterprises seeking to meet ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals.
6. Rise of Automated and Hygienic Designs (H2):
With labor costs rising and hygiene standards tightening, especially post-pandemic, demand for fully automated, CIP (Clean-in-Place), and IP69K-rated metal detectors will grow. Systems designed for minimal human intervention, easy cleaning, and resistance to harsh environments will dominate in high-sanitation industries like dairy and meat processing.
Conclusion (H2):
By 2026, the industrial metal detector market will be characterized by smarter, more connected, and highly precise systems. Success will depend on innovation in digital integration, compliance readiness, and adaptability to diverse industrial needs. Companies investing in AI-enhanced detection, global regulatory alignment, and sustainable engineering will lead the market in this next phase of industrial safety and efficiency.
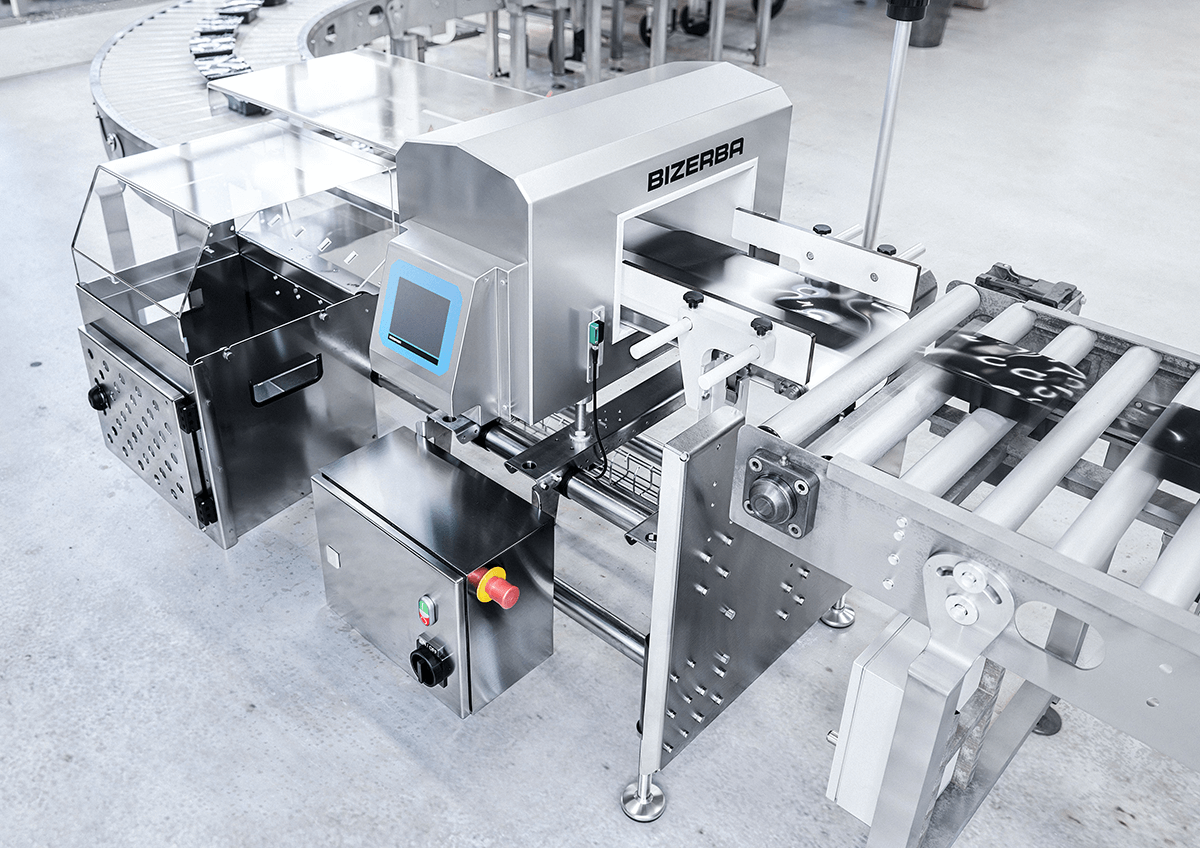
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Industrial Metal Detectors (Quality, IP)
Sourcing industrial metal detectors requires careful evaluation to avoid costly mistakes related to performance, reliability, and compliance. Overlooking key quality and Ingress Protection (IP) factors can lead to product contamination, production downtime, and safety hazards. Below are common pitfalls to watch for:
Inadequate IP Rating for the Environment
Choosing a metal detector with an insufficient IP rating for its operating environment is a frequent error. For example, using an IP54-rated unit in a washdown area where high-pressure water and cleaning chemicals are used can result in water ingress, electrical failure, and contamination risks. Always match the IP rating (e.g., IP65, IP66, IP69K) to the specific environmental demands—especially in food, pharmaceutical, or outdoor applications.
Compromised Build Quality and Materials
Opting for lower-cost detectors made with substandard materials (e.g., non-stainless steel housings, flimsy casings) can lead to rapid deterioration in harsh environments. Poorly constructed units may corrode, warp, or fail mechanically, impacting detection accuracy and requiring frequent replacements. Ensure housings are made from durable, food-grade stainless steel (e.g., AISI 304 or 316) and that internal components are adequately sealed and protected.
Lack of Proper Certification and Compliance
Failing to verify that the metal detector meets industry-specific standards (e.g., HACCP, FDA, EHEDG, 3A) can result in non-compliance during audits. In regulated industries like food and pharma, using uncertified equipment may lead to rejected shipments or regulatory penalties. Always confirm relevant certifications and documentation before purchase.
Inconsistent Detection Sensitivity and Calibration
Some low-quality detectors exhibit inconsistent sensitivity across different product types or environmental conditions. Poorly calibrated or untested units may miss contaminants or generate false rejections, disrupting production. Verify that the detector is tested and calibrated for your specific product (e.g., wet, dry, hot, or conductive) and operating speed.
Poor Sealing and Vulnerability to Contamination
Even with a high IP rating, poorly designed seals around doors, cable entries, and joints can compromise integrity. Gaps or low-quality gaskets allow moisture, dust, and product residue to enter, fostering bacterial growth and damaging electronics. Inspect sealing mechanisms thoroughly and request validation data or third-party testing reports.
Inadequate Supplier Support and Documentation
Choosing a supplier that lacks technical support, fails to provide detailed IP certification documentation, or offers limited warranty and service can leave you stranded during failures. Ensure the supplier offers responsive support, clear installation guidance, and accessible spare parts—critical for minimizing downtime.
Overlooking Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Shielding
Industrial environments often contain sources of EMI (e.g., motors, welders), which can interfere with detector performance. Detectors without proper shielding or filtering may produce inaccurate readings. Confirm that the unit includes EMI protection measures appropriate for your facility’s electrical environment.
Avoiding these pitfalls ensures reliable contaminant detection, regulatory compliance, and long-term operational efficiency. Always conduct thorough due diligence on product specifications, certifications, and supplier reputation before finalizing procurement.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Industrial Metal Detector
Product Overview and Intended Use
Industrial metal detectors are critical inspection systems used across food processing, pharmaceuticals, textiles, and manufacturing to detect ferrous, non-ferrous, and stainless-steel contaminants in raw materials, packaging, or finished goods. Ensuring proper logistics handling and regulatory compliance is essential for operational safety, product quality, and legal adherence.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Industrial metal detectors must comply with various international, national, and industry-specific regulations. Key compliance standards include:
– CE Marking (EU): Compliance with the Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC), Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive (2014/30/EU), and RoHS Directive (2011/65/EU) is mandatory for sale in the European Union.
– FCC Regulations (USA): Metal detectors must meet FCC Part 15 Class A or B emission standards to prevent electromagnetic interference.
– FDA & USDA (USA): In food and pharmaceutical applications, equipment must support compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) and be suitable for sanitary environments (e.g., IP69K-rated housings).
– ATEX/IECEx (Hazardous Areas): If used in explosive atmospheres, detectors must be certified under ATEX (EU) or IECEx (international) standards.
– Local Electrical Codes: Compliance with national electrical safety standards (e.g., UL in North America, CCC in China) is required for installation and operation.
Packaging and Shipping Considerations
Proper packaging ensures the metal detector arrives undamaged and ready for use:
– Use reinforced, moisture-resistant wooden crates or heavy-duty corrugated containers with internal foam or custom-fit padding.
– Clearly label packages with handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” “Do Not Stack”).
– Include desiccant packs to prevent condensation during transit, especially in humid climates.
– Secure all removable components (conveyor belts, control panels, probes) separately to prevent internal damage.
Transportation and Handling Guidelines
Follow these best practices during transport and delivery:
– Use forklifts or pallet jacks with appropriate load capacity; avoid dragging or tilting the unit beyond manufacturer specifications.
– Protect the aperture and sensor coils from impacts—these are sensitive components critical to detection accuracy.
– Maintain a clean, dry environment during transit to prevent dust or moisture ingress.
– For international shipments, ensure all customs documentation (commercial invoice, packing list, certificates of conformity) are complete and accurate.
Import/Export Documentation and Duties
Cross-border shipments require thorough documentation:
– Prepare a commercial invoice detailing product description, value, country of origin, and HS (Harmonized System) code—typically 9022.90 for industrial inspection equipment.
– Include certificates of conformity (CE, FCC, etc.) and a packing list with weight and dimensions.
– Verify import duties, taxes, and any restricted goods classifications in the destination country.
– For destinations with strict regulatory environments (e.g., EU, Australia, Japan), pre-approval or local representation may be necessary.
Installation and Site Preparation Compliance
Ensure the installation site meets technical and safety standards:
– Verify power supply compatibility (voltage, frequency, grounding) per local electrical codes.
– Maintain recommended clearances around the unit for ventilation, access, and electromagnetic isolation.
– Install in a stable, vibration-free environment to prevent false detections.
– Confirm that the installation complies with workplace safety regulations (e.g., OSHA in the U.S., HSE in the UK).
Calibration and Validation Requirements
Post-installation, metal detectors must be calibrated and validated:
– Perform initial sensitivity testing using certified test samples (e.g., Fe, Non-Fe, and SUS spheres).
– Document calibration results and maintain logs as part of quality assurance (e.g., ISO 22000, HACCP, IFS, BRCGS).
– Schedule periodic revalidation (daily, weekly) as per food safety or industry standards.
– Use only manufacturer-approved calibration tools and procedures.
Maintenance and Recordkeeping
Maintaining compliance throughout the product lifecycle requires:
– Routine cleaning with approved, non-abrasive agents—especially in food-grade environments.
– Scheduled inspections of belts, rollers, and seals for wear or contamination.
– Retention of service records, calibration logs, and compliance certifications for audits.
– Software/firmware updates to ensure continued compliance with evolving standards.
End-of-Life and Environmental Compliance
When decommissioning a metal detector:
– Follow WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directives in the EU for proper recycling.
– Safely dispose of electronic components and batteries in accordance with local environmental regulations.
– Remove and securely store any data-containing modules to protect sensitive information.
Summary and Best Practices
To ensure seamless logistics and full compliance:
– Work with certified suppliers who provide complete documentation.
– Train personnel on proper handling, operation, and regulatory requirements.
– Maintain an audit-ready file of all compliance and maintenance records.
– Regularly review regulatory updates affecting industrial inspection equipment.
Adhering to this guide supports safe, efficient deployment of industrial metal detectors while minimizing compliance risks and operational downtime.
Conclusion for Sourcing an Industrial Metal Detector
Sourcing an industrial metal detector is a critical decision that directly impacts product safety, quality control, and regulatory compliance in manufacturing and processing environments. The selection process must be guided by a thorough understanding of operational requirements, including the type of product being inspected (dry, wet, hot, frozen, etc.), production speed, contamination risks, and industry standards such as HACCP, FDA, or BRCGS.
Key factors to consider when sourcing include detection sensitivity, ease of integration into existing production lines, durability, hygiene design (especially for food and pharmaceutical applications), and the level of after-sales support and service. It is also essential to evaluate both initial costs and long-term value, including maintenance, uptime, and potential recalls avoided through reliable detection.
Opting for a reputable supplier with proven expertise, certifications, and responsive technical support ensures reliability and performance over time. Investing in the right industrial metal detector not only safeguards consumers and protects brand reputation but also enhances operational efficiency and supports compliance with stringent safety regulations.
In conclusion, a well-informed sourcing strategy—balancing technical specifications, total cost of ownership, and supplier reliability—will lead to a successful implementation that delivers lasting benefits across safety, quality, and productivity.