The global industrial magnets market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by rising demand across sectors such as automotive, renewable energy, electronics, and manufacturing automation. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 19.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.6% through 2028, reaching an estimated USD 30.7 billion. This growth is fueled by the increasing adoption of high-performance rare-earth magnets in electric vehicles (EVs) and wind turbine generators, coupled with advancements in industrial automation. Additionally, Grand View Research highlights that the Asia Pacific region dominates both production and consumption, led by strong manufacturing bases in China and Japan. As industries prioritize efficiency and miniaturization, the demand for reliable, high-strength industrial magnets continues to rise—making the choice of manufacturer more critical than ever. In this context, identifying the top nine industrial magnets manufacturers provides key insights into innovation, quality, and market leadership shaping the future of this essential component sector.
Top 9 Industrial Magnets Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Industrial Magnetics, Inc.
Domain Est. 1995
Website: magnetics.com
Key Highlights: We design, engineer, and manufacture magnetic solutions to help improve productivity, purify products, protect processing equipment, increase profits….
#2 Arnold Magnetic Technologies
Domain Est. 2001
Website: arnoldmagnetics.com
Key Highlights: We are a leading magnet manufacturer of high-quality permanent magnets, magnetic assemblies, precision thin metals, flexible composites, and electromagnets….
#3 Magnum Magnetics
Domain Est. 1997
Website: magnummagnetics.com
Key Highlights: Magnum Magnetics is the largest flexible magnet manufacturer in the United States, including printable magnetic sheeting and magnetic rolls, magnetic strips, ……
#4 Walker Magnetics
Domain Est. 1997
Website: walkermagnet.com
Key Highlights: We design and manufacture a wide range of permanent, electromagnetic, electro-permanent magnet products and systems for industrial applications….
#5 Stanford Magnets
Domain Est. 1998
Website: stanfordmagnets.com
Key Highlights: Stanford Magnets is a rare earth magnet manufacturer including various custom magnets, specializes in the design, engineering, and manufacture of custom ……
#6 MP Materials
Domain Est. 2017
Website: mpmaterials.com
Key Highlights: MP Materials champions America’s rare earth magnet supply, powering sectors like EVs, robotics, defense, and renewable energy….
#7 Dura Magnetics
Domain Est. 1995
Website: duramag.com
Key Highlights: Dura Magnetics is a leader in custom magnet engineering. We design and manufacture custom magnet solutions and magnet assemblies to help your project succeed….
#8 Magnets
Domain Est. 1998
Website: magnetshop.com
Key Highlights: Magnet shop is an industry leading magnets supplier for high-quality, rare-earth and permanent magnets in assorted shapes, sizes and premium grades….
#9 Noveon Magnetics
Domain Est. 2021
Website: noveon.co
Key Highlights: Our powerful, next-generation EcoFlux magnets are changing the way we electrify the world, ushering in a new era of mobility and high-efficiency, low-carbon ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Industrial Magnets
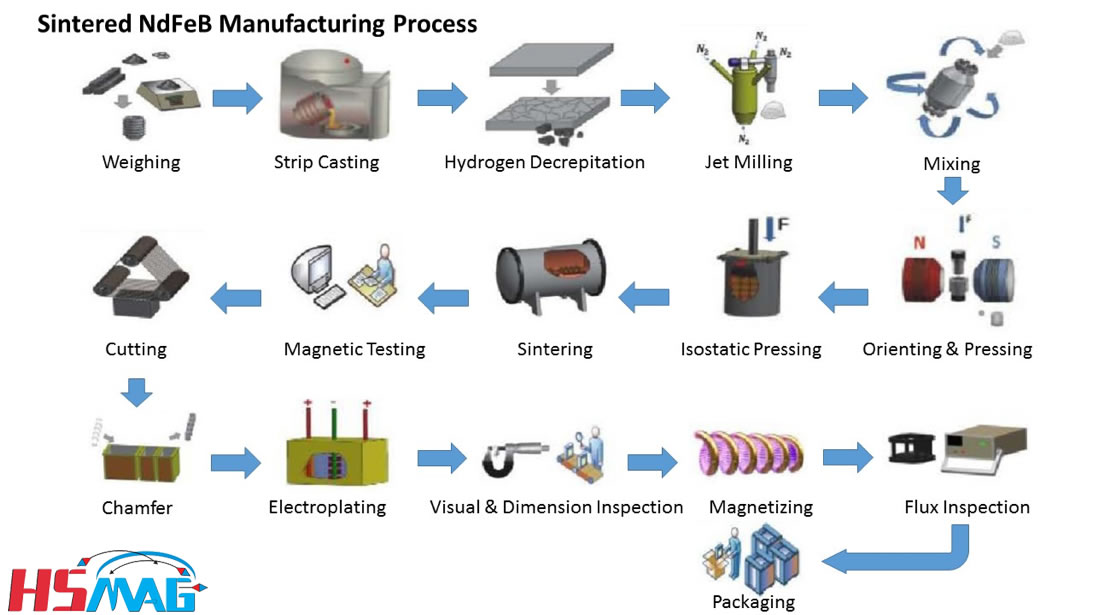
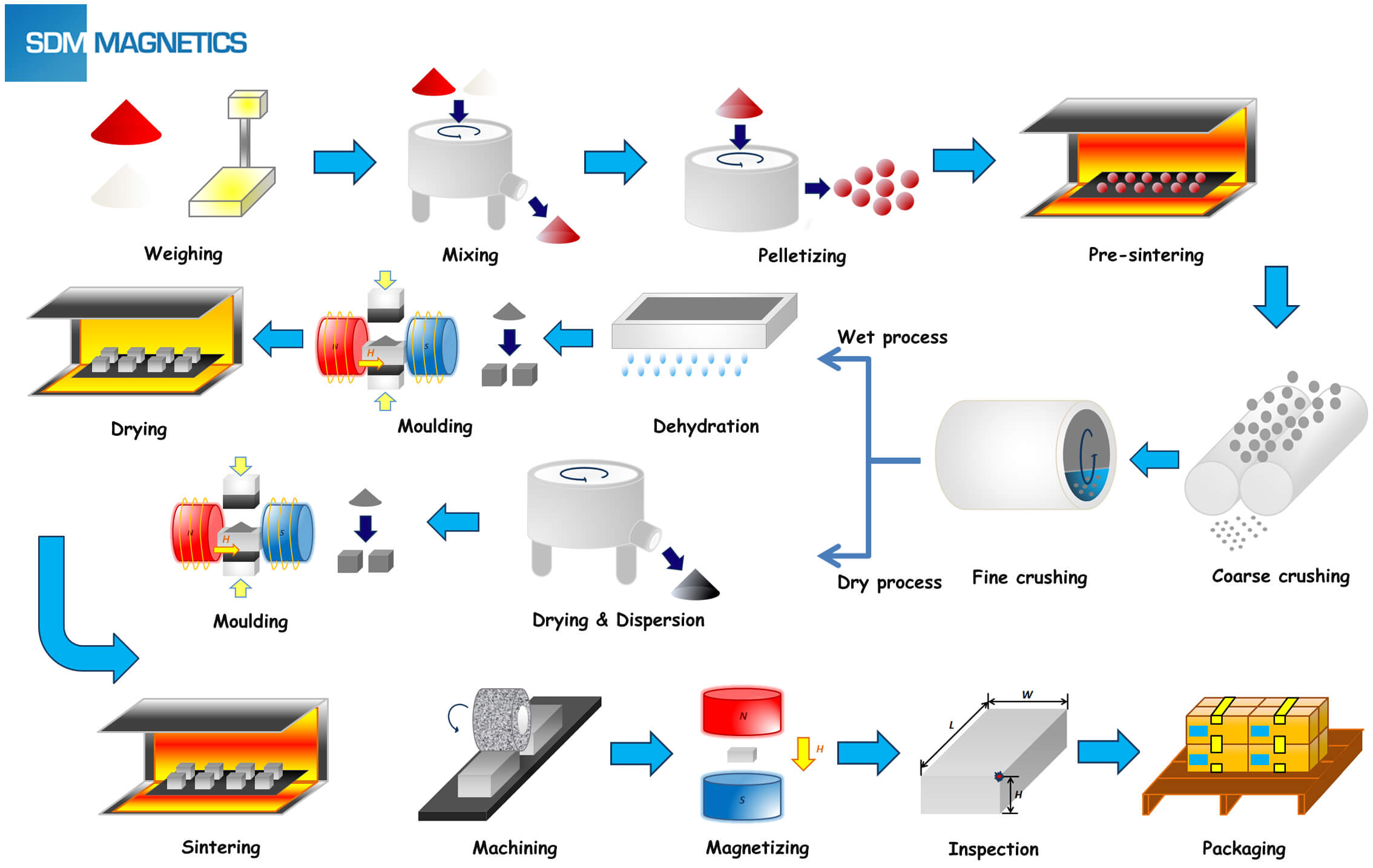
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Industrial Magnets
The industrial magnets market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, evolving industry demands, and global sustainability goals. Here’s a detailed analysis of key trends shaping the landscape:
1. Soaring Demand in Renewable Energy & Electrification:
* Wind Power Dominance: The continued global expansion of offshore and onshore wind farms will remain the single largest driver. High-performance neodymium-iron-boron (NdFeB) permanent magnets are critical for direct-drive and hybrid wind turbine generators due to their power density and efficiency. Demand will surge as turbine sizes increase, requiring larger, more powerful magnets.
* EV Revolution Acceleration: The exponential growth of electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrids will significantly boost demand for high-grade NdFeB magnets used in traction motors, power steering, and auxiliary systems. Advancements in motor efficiency and power density will push demand for optimized magnet grades.
* Grid & Infrastructure: Growth in energy storage systems (batteries, flywheels) and smart grid technologies will increase demand for magnets in sensors, actuators, and power conversion components.
2. Supply Chain Resilience & Geopolitical Shifts:
* Diversification Away from China: Heightened geopolitical tensions and supply chain vulnerabilities will accelerate efforts to diversify rare earth element (REE) mining, separation, and magnet manufacturing outside of China. Expect increased investment in projects in Australia, the US, Canada, Europe, and Southeast Asia.
* Vertical Integration & Onshoring: Major end-users (automotive OEMs, wind turbine manufacturers) and governments will push for greater vertical integration and onshoring/nearshoring of magnet production to secure critical supply chains, especially in North America and Europe (driven by initiatives like the US Inflation Reduction Act and EU Critical Raw Materials Act).
* Recycling Focus: Industrial magnet recycling (particularly NdFeB) will gain significant traction as a strategic supply source, driven by cost, sustainability, and supply security concerns. Advanced recycling technologies will mature and scale.
3. Technological Innovation & Material Advancements:
* Higher Performance & Efficiency: R&D will focus on developing NdFeB magnets with higher maximum energy products (BHmax), improved coercivity (especially at high temperatures), and better corrosion resistance to meet the demands of more compact, efficient motors and generators.
* Reduced Heavy Rare Earths (HRE): Intense efforts will continue to minimize or eliminate the need for critical HREs like Dysprosium (Dy) and Terbium (Tb) through grain boundary diffusion processes, novel microstructures, and alternative compositions, reducing cost and supply risk.
* Alternative Magnet Materials: While NdFeB dominates high-performance applications, research into alternatives like:
* Samarium-Cobalt (SmCo): For high-temperature applications (aerospace, defense) where its stability is crucial.
* Manganese-based alloys (e.g., MnAl, MnBi): Promising lower-cost, REE-free options, though performance and scalability challenges remain significant hurdles by 2026.
* Ferrite Advancements: Improved grades for cost-sensitive applications where ultimate performance isn’t critical.
* Additive Manufacturing: 3D printing of magnets (binder jetting, fused filament fabrication) will move beyond prototyping towards niche, complex-shaped magnet production, enabling novel motor designs.
4. Sustainability & Regulatory Pressure:
* ESG Compliance: Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria will be paramount. Manufacturers and users will prioritize magnets from suppliers with transparent, ethical, and low-environmental-impact sourcing and production processes (low carbon footprint, responsible mining).
* Circular Economy: Regulations and corporate commitments will push for increased magnet recycling rates and the design of products for easier magnet recovery at end-of-life.
* Carbon Neutrality Goals: The entire value chain, from mining to manufacturing, will face pressure to reduce emissions, influencing production location and energy sources.
5. Application Diversification & Emerging Sectors:
* Industrial Automation & Robotics: Growth in automation, collaborative robots (cobots), and precision manufacturing will increase demand for magnets in servo motors, linear motors, and sensors.
* Medical Technology: Advanced medical imaging (MRI), surgical robotics, and implantable devices will require high-reliability, biocompatible magnets.
* Aerospace & Defense: Demand for lightweight, high-performance, and high-temperature stable magnets (SmCo, advanced NdFeB) in actuators, sensors, and power systems will remain strong.
* Consumer Electronics: While mature, demand for smaller, more powerful magnets in speakers, haptics, and sensors in smartphones, wearables, and AR/VR will persist.
6. Market Consolidation & Strategic Partnerships:
* Vertical Integration: Expect increased M&A activity and strategic partnerships between mining companies, chemical processors, magnet manufacturers, and end-users to secure the supply chain.
* Technology Licensing: Collaboration on advanced magnet manufacturing and recycling technologies will be common.
Conclusion for H2 2026:
By the second half of 2026, the industrial magnets market will be characterized by accelerated growth driven by the green energy transition, intense focus on supply chain security and diversification, significant technological innovation focused on performance and reduced critical material dependence, and heightened regulatory and sustainability pressures. Companies that successfully navigate these trends—securing reliable, ethical raw materials, investing in advanced manufacturing and recycling, and developing high-performance, sustainable magnet solutions—will be best positioned to capture value in this dynamic and strategically critical market. The dominance of NdFeB will continue, but the push for alternatives and reduced HRE content will be a defining theme.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Industrial Magnets (Quality, IP)
Sourcing industrial magnets involves navigating complex technical requirements and potential risks, particularly concerning quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to performance failures, supply chain disruptions, and legal exposure.
Inadequate Quality Control and Material Verification
One of the most frequent pitfalls is assuming supplier-provided specifications without independent verification. Industrial magnets—especially rare-earth types like neodymium—require tight tolerances in composition, coating, and magnetic properties. Purchasers may receive batches with inconsistent magnetic strength (gauss or BHmax), improper plating (leading to corrosion), or substandard sintering processes that reduce longevity. Without third-party testing or on-site audits, counterfeit or downgraded materials can infiltrate the supply chain.
Lack of Traceability and Certification
Reputable industrial applications demand full material traceability and compliance certifications (e.g., RoHS, REACH, ISO 9001). Many suppliers, particularly in competitive low-cost regions, fail to provide documented proof of origin or process controls. This absence makes it difficult to verify ethical sourcing (e.g., conflict minerals) or ensure batch-to-batch consistency, increasing liability and operational risk.
Intellectual Property Exposure During Custom Design
When sourcing custom magnet shapes or proprietary magnetic assemblies, companies often share detailed engineering drawings and performance requirements. Without robust Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) and clear IP ownership clauses in contracts, suppliers may replicate designs for competing customers or reverse-engineer innovations. This is especially prevalent in regions with weak IP enforcement, leading to loss of competitive advantage.
Overlooking Geopolitical and Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
The production of high-performance magnets is heavily concentrated in specific regions, particularly China, which dominates rare-earth element processing. Relying on single-source suppliers exposes buyers to export restrictions, tariffs, and geopolitical instability. Additionally, unverified subcontracting by suppliers can further obscure the actual manufacturing location, increasing both IP and quality risks.
Insufficient Testing and Performance Validation
Procurement teams may accept magnets based solely on datasheets without conducting in-house performance testing under real-world conditions (e.g., temperature cycling, exposure to demagnetizing fields). This can result in field failures, especially in demanding environments such as electric motors, medical devices, or aerospace systems where magnet reliability is critical.
Failure to Audit Manufacturing Processes
Many buyers focus on the final product without auditing the supplier’s production methods. Poor process controls in magnetization, heat treatment, or coating application can degrade performance over time. Without access to process validation data or regular audits, companies risk long-term reliability issues that may not surface until after deployment.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Industrial Magnets
Overview
Industrial magnets—such as neodymium (rare earth), ferrite, alnico, and samarium cobalt—are essential components in numerous sectors, including manufacturing, automotive, electronics, and renewable energy. However, their unique physical properties, material composition, and potential hazards (e.g., strong magnetic fields, brittleness, and rare earth content) necessitate strict logistics and compliance protocols. This guide outlines key considerations for the safe, legal, and efficient handling, storage, transportation, and regulatory compliance of industrial magnets.
Classification & Regulatory Framework
Industrial magnets are subject to various international and national regulations depending on their type, strength, material composition, and intended use. Key regulatory frameworks include:
– UN Dangerous Goods Regulations (UN Model Regulations): Magnets exceeding specific magnetic field strength thresholds (typically 0.159 A/m at 2.1 meters from the package) are classified as Class 9 Miscellaneous Dangerous Goods (UN2807 or UN3480 for lithium-ion batteries if integrated).
– International Air Transport Association (IATA) Dangerous Goods Regulations: Governs air transport; magnets meeting Class 9 criteria require special packaging, labeling, and documentation.
– International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code: Regulates sea transport; similar classification and handling requirements apply.
– U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT) 49 CFR: Enforces hazardous materials transportation regulations domestically and internationally.
– REACH & RoHS (EU Regulations): Restrict hazardous substances (e.g., cobalt, nickel) in magnets and require substance registration and reporting.
– Export Control Regulations (e.g., ITAR, EAR): Rare earth magnets may be subject to export controls due to strategic material content (e.g., neodymium, dysprosium).
Packaging & Handling Requirements
Proper packaging is critical to prevent damage, demagnetization, and safety hazards:
– Shielding: Use ferromagnetic shielding (e.g., steel plates) to contain magnetic fields and avoid interference with navigation, medical devices, or data storage.
– Physical Protection: Employ rigid, non-magnetic containers (e.g., plastic or wood) with cushioning to prevent chipping or cracking—especially for brittle neodymium magnets.
– Separation: Keep individual magnets separated using spacers to prevent snapping together, which can cause injury or damage.
– Anti-Corrosion Measures: Apply protective coatings (e.g., nickel, epoxy) and use desiccants in packaging for moisture-sensitive magnets.
– Demagnetization Prevention: Avoid exposure to high temperatures, mechanical shocks, and opposing magnetic fields during storage and transit.
Transportation Guidelines
Different transport modes have specific requirements:
– Air Freight: Class 9 magnets must pass the “magnetic field strength test” (IATA Packing Instruction 953). Packages must display Class 9 hazard labels and “Magnetized Material” markings. Air carriers often require prior approval.
– Sea Freight: Follow IMDG Code; packages must be marked, labeled, and stowed away from sensitive cargo (e.g., medical equipment, navigation systems).
– Ground Transport (Road/Rail): Comply with national regulations (e.g., DOT 49 CFR in the U.S.). Secure loads to prevent shifting, and ensure vehicle compatibility with magnetic fields.
– Documentation: Include Safety Data Sheets (SDS), Shipper’s Declaration for Dangerous Goods (when applicable), and proper shipping names (e.g., “Magnetized Material, 9, UN2807”).
Storage Best Practices
- Environment: Store in a dry, temperature-controlled area away from direct sunlight and corrosive substances.
- Orientation: Arrange magnets to minimize attractive or repulsive forces (e.g., alternate poles, use keepers).
- Separation from Sensitive Devices: Keep at least 2 meters from pacemakers, credit cards, monitors, and other magnetic media.
- Stacking: Avoid stacking heavy loads on brittle magnets; use pallets and secure storage racks.
Compliance & Documentation
Maintain accurate records to ensure regulatory compliance:
– Safety Data Sheets (SDS): Required under GHS; include hazard statements for physical risks (e.g., pinching, flying debris) and chemical composition.
– Customs Documentation: Declare magnets accurately using correct HS codes (e.g., 8505.10 for permanent magnets). Note any rare earth content for import/export restrictions.
– Export Licenses: Obtain required permits for controlled materials under EAR (e.g., ECCN 1C997 for certain rare earth magnets).
– Labeling: Packages must display proper hazard labels, handling instructions (e.g., “Keep Away From Pacemakers”), and shipper/consignee details.
Safety & Risk Mitigation
- Personnel Training: Train staff on magnet hazards, PPE use (e.g., gloves, eye protection), and emergency procedures.
- Medical Device Warnings: Clearly label shipments and storage areas with warnings for individuals with implanted medical devices.
- Emergency Response: Establish procedures for magnet-related injuries (e.g., pinching) and magnetic field interference incidents.
Environmental & Disposal Considerations
- Recycling: Rare earth magnets should be recycled due to material scarcity and environmental impact. Partner with certified e-waste or metal recycling facilities.
- Waste Disposal: Follow local regulations for hazardous waste if magnets contain restricted substances (e.g., nickel, cobalt). Do not incinerate neodymium magnets—risk of toxic fumes.
Conclusion
Successful logistics and compliance for industrial magnets require a multidisciplinary approach integrating regulatory knowledge, proper packaging, and safety awareness. By adhering to international standards and maintaining thorough documentation, businesses can ensure the safe and legal movement of these powerful yet sensitive materials across global supply chains. Regular audits and staff training are recommended to stay compliant with evolving regulations.
Conclusion on Sourcing Industrial Magnets
Sourcing industrial magnets requires a strategic approach that balances performance, cost, reliability, and supplier expertise. As these magnets play a critical role in various applications—ranging from manufacturing and automation to renewable energy and medical devices—selecting the right type (such as neodymium, samarium-cobalt, alnico, or ferrite) based on required strength, temperature resistance, and environmental conditions is essential.
Key considerations in the sourcing process include material quality, customization capabilities, production capacity, and adherence to international standards (such as ISO and RoHS). Establishing relationships with reputable suppliers—whether domestic or international—can ensure consistent supply, technical support, and long-term cost efficiency. Additionally, evaluating total ownership costs, including shipping, tariffs, and lead times, helps avoid unforeseen disruptions.
In today’s competitive and technologically advancing market, effective supplier vetting, ongoing quality assurance, and staying informed about material innovations are crucial. By taking a comprehensive and informed approach to sourcing industrial magnets, businesses can enhance product performance, maintain operational continuity, and support sustainable growth.