The global industrial laser welding market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by rising demand for high-precision, efficient, and automated manufacturing solutions across automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global laser welding market size was valued at USD 1.37 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.4% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is further fueled by advancements in fiber laser technology, increased adoption of Industry 4.0 practices, and the need for superior weld quality with minimal thermal distortion. As manufacturing operations continue to prioritize speed, accuracy, and scalability, industrial laser welding tools have become indispensable. In this competitive landscape, a select group of manufacturers leads innovation, offering advanced solutions that meet evolving production demands. Here’s a look at the top 10 industrial laser welding tools manufacturers shaping the future of modern fabrication.
Top 10 Industrial Laser Welding Tools Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Focus on laser
Website: hanslaser.net
Key Highlights: Laser marking machines Laser cutting machines Laser welding machines Automation Laser generator Semiconductor packaging equipment 3D printers Motor….
#2 LaserStar Technologies
Website: laserstar.net
Key Highlights: LaserStar Technologies designs and manufactures high-performance laser welding, marking, and cutting systems for industrial, jewelry, ……
#3 Laserax
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Laserax works with the world’s leading manufacturers to implement laser cleaning, welding, texturing, and marking solutions….
#4 HobartWelders
Website: hobartwelders.com
Key Highlights: Hobart Welders is a leading welding manufacturer in the U.S. Browse a variety of welders, welding equipment, gear and projects to find the best match for ……
#5 Denaliweld
Website: denaliweld.com
Key Highlights: We Specialize in Laser Welding & Cleaning. DenaliWeld INC, is a proud employee-owned fiber laser welding machine manufacturer based in Chicago, USA. Bolstered ……
#6 Laser Company for Industrial Laser Solutions
Website: laserline.com
Key Highlights: The leading laser company for integrated & customized diode laser manufacturing solutions for various industries & applications….
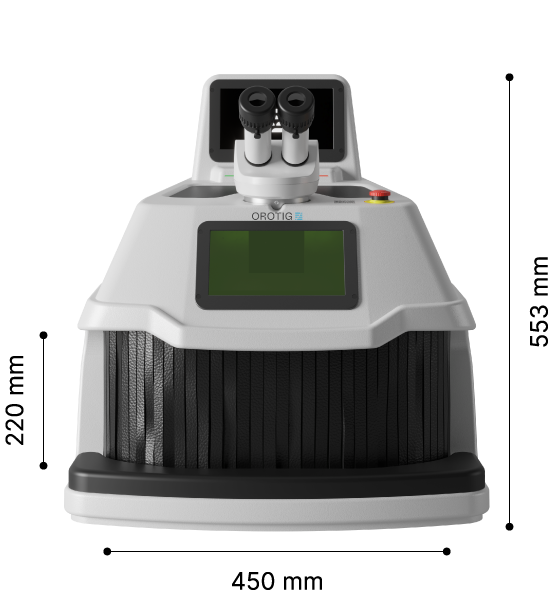
#7 Orotig: Laser Machinery
Website: orotig.com
Key Highlights: Orotig, with +30 years of experience, specializes in engineering and manufacturing laser solutions for welding engraving and casting metals….
#8 IPG Photonics
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: IPG Photonics manufactures high-performance fiber lasers, amplifiers, and laser systems for diverse applications and industries. Discover your solution….
#9 Branson
Website: emerson.com
Key Highlights: Branson offers state of the art plastic and metal welding and precision cleaning technologies and equipment….
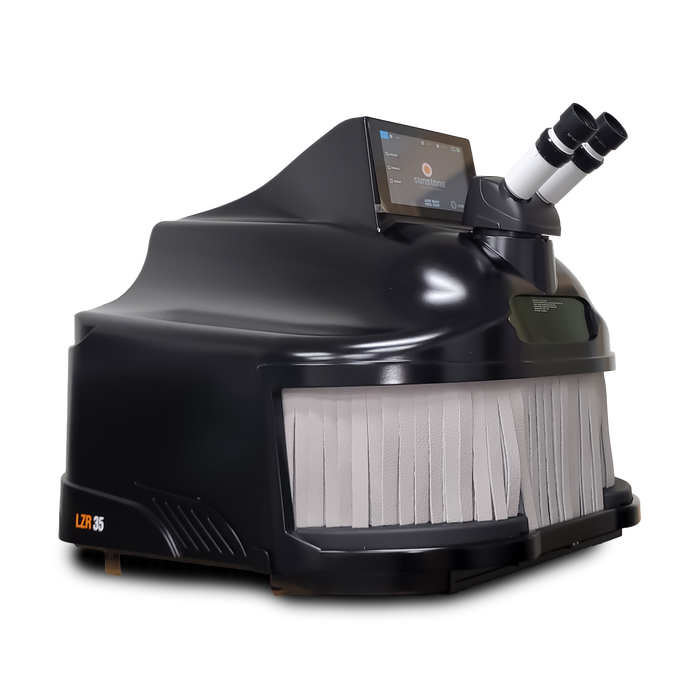
#10 Sunstone Welders
Website: sunstonewelders.com
Key Highlights: Sunstone designs and manufactures high-tech micro welding and engraving solutions for many different industries. In short, wherever a very small spot weld ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Industrial Laser Welding Tools
2026 Market Trends for Industrial Laser Welding Tools
The industrial laser welding tools market is poised for transformative growth and technological refinement by 2026, driven by automation demands, material advancements, and the pursuit of sustainable manufacturing. Key trends shaping the landscape include:
1. Dominance of Fiber Lasers and Power Scaling: Fiber lasers will solidify their position as the technology of choice, surpassing traditional CO2 and lamp-pumped lasers. By 2026, high-power fiber lasers (exceeding 10 kW, with increasing adoption of 20-30 kW systems) will become standard for deep-penetration welding in heavy industries like automotive chassis, shipbuilding, and energy. Key drivers include superior wall-plug efficiency (>40%), lower maintenance, compact footprints, and excellent beam quality enabling faster processing speeds and higher throughput.
2. Proliferation of Hybrid and Adaptive Welding Systems: Standalone laser tools will increasingly integrate into intelligent, multi-functional systems. Hybrid laser-arc welding (combining laser precision with arc process tolerance and gap bridging) will gain significant traction, particularly in automotive and heavy machinery for cost-effective, robust joints. Furthermore, adaptive welding systems incorporating real-time process monitoring (via integrated cameras, spectrometers, or photodiodes) and closed-loop control will become mainstream. These systems use AI/ML algorithms to detect defects (porosity, spatter, undercut) instantly and automatically adjust parameters (power, focus, speed) mid-process, ensuring consistent, high-quality welds with minimal rework.
3. Automation, Robotics, and Smart Factory Integration: Laser welding tools will be deeply embedded within automated production lines. Collaboration between high-precision robotic arms and laser sources will increase, enabling complex 3D welding paths with greater flexibility. Seamless integration with Industry 4.0 platforms via IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) protocols will be standard. This allows for remote monitoring, predictive maintenance (analyzing laser source health, consumable wear), production data analytics, and seamless data flow between CAD/CAM, MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems), and ERP systems, optimizing overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
4. Growth in Battery and Electric Vehicle (EV) Manufacturing: The explosive growth of the EV market will be a primary growth engine. Laser welding tools are critical for manufacturing battery cells (e.g., foil tab welding, busbar connections, cell-to-pack/module welding), power electronics (copper busbar welding), and lightweight EV components (e.g., aluminum subframes, motor housings). Demand will focus on ultra-high-precision, high-speed, low-heat-input processes (like pulsed lasers and blue lasers for copper) to ensure battery safety, performance, and longevity. This segment will drive innovation in specialized tooling and process reliability.
5. Expansion into New Materials and Applications: While steel and aluminum remain dominant, demand for welding advanced materials will grow. This includes:
* Copper and Copper Alloys: Driven by EVs and electronics, requiring specialized high-reflectivity handling (e.g., green or blue wavelength lasers).
* Dissimilar Metals: Joining combinations like aluminum-to-steel or copper-to-aluminum for lightweighting and multi-material designs, necessitating precise control and often hybrid techniques.
* High-Strength Steels and Lightweight Alloys: In aerospace and automotive, demanding precise heat control to maintain material properties.
* Additive Manufacturing (AM) Support: Laser welding tools for post-processing (stress relieving, repair, HIP-like processes) and hybrid manufacturing (adding features to AM parts).
6. Focus on Sustainability and Energy Efficiency: Regulatory pressures and corporate ESG goals will amplify the demand for energy-efficient technologies. The inherent efficiency of fiber lasers, coupled with systems optimized for lower energy consumption per weld (through faster speeds and reduced scrap/rework), will be a significant selling point. Reduced consumable waste (vs. arc welding) and the ability to enable lightweighting (reducing overall product energy footprint) further enhance the sustainability profile.
7. Software-Defined Welding and Digital Twins: Advanced software will become as crucial as the hardware. User-friendly interfaces, simulation software for virtual process design and optimization (reducing physical trials), and digital twin technology (creating virtual replicas of the welding cell for monitoring, simulation, and predictive optimization) will be increasingly adopted, lowering skill barriers and improving process development speed.
In conclusion, by 2026, the industrial laser welding tools market will be characterized by smarter, faster, more integrated, and more efficient systems. Driven by electrification, automation, and digitalization, these tools will move beyond simple joining to become intelligent components of optimized, sustainable manufacturing ecosystems, particularly in high-growth sectors like EVs and advanced battery production.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Industrial Laser Welding Tools: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing industrial laser welding tools involves significant technical, financial, and legal considerations. Overlooking key aspects related to quality and intellectual property (IP) can lead to production delays, safety hazards, legal disputes, and lost competitiveness. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Inadequate Quality Verification and Testing
Many buyers focus on initial cost and delivery timelines while underestimating the importance of rigorous quality validation. Purchasing tools without thorough performance testing—especially under real-world operating conditions—can result in inconsistent weld quality, frequent downtime, and higher total cost of ownership. Beware of suppliers who provide only generic certifications (e.g., CE or ISO) without detailed test reports, beam profiling data, or traceable calibration records.
Overlooking Component Longevity and Serviceability
Industrial laser systems often include critical components like laser sources, optics, cooling units, and control software. Sourcing tools with proprietary or poorly documented subsystems can lead to long-term maintenance challenges. If replacement parts are unavailable or require extended lead times, production lines may face costly interruptions. Always assess the availability of spare parts, technical documentation, and access to repair services before procurement.
Insufficient Due Diligence on Supplier IP Compliance
A major risk in sourcing laser tools—especially from emerging manufacturers—is the potential use of unlicensed or copied technology. Some suppliers may integrate third-party optics, software algorithms, or laser sources without proper licensing, exposing the end user to IP infringement claims. This is particularly concerning when sourcing from regions with less stringent IP enforcement. Conduct IP audits or require suppliers to provide proof of legitimate licensing for core technologies.
Ambiguous Ownership of Customizations and Integrations
When modifying or integrating laser tools into proprietary production systems, unclear contractual terms can lead to disputes over IP ownership. If a supplier develops a custom solution based on your specifications, ensure the contract explicitly states whether you retain sole rights to the design, software, or process improvements. Without clear agreements, the supplier may claim ownership or restrict your use of the modified tool.
Relying on Incomplete or Misleading Specifications
Some suppliers provide optimistic or vague performance data (e.g., power output, beam quality, duty cycle) that do not reflect actual operating conditions. This can result in underperforming tools that fail to meet production requirements. Always request independent verification, on-site demonstrations, or trial periods before full procurement. Avoid contracts that lack performance warranties or measurable acceptance criteria.
Neglecting Software and Firmware Licensing
Modern laser welding systems depend heavily on software for control, monitoring, and diagnostics. Hidden licensing fees, restrictive usage terms, or embedded third-party code with unclear IP status can create compliance risks. Ensure software licenses permit necessary usage, updates, and integration with factory systems. Audit firmware for open-source components that may require disclosure or impose redistribution obligations.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP-related pitfalls, businesses can mitigate risks, ensure reliable manufacturing performance, and protect their innovation investments when sourcing industrial laser welding tools.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Industrial Laser Welding Tools
Overview and Purpose
This guide provides essential information for the safe, efficient, and compliant handling, transportation, import/export, and operation of industrial laser welding tools. These high-precision systems pose unique logistical and regulatory challenges due to their technical complexity, high energy output, and international regulatory oversight. Adherence to the guidelines below ensures regulatory compliance, operator safety, and supply chain integrity.
Regulatory Classification and Documentation
Industrial laser welding tools are subject to multiple regulatory frameworks depending on jurisdiction. Key classifications include:
– Laser Safety Class: Typically Class 4 (highest hazard level), requiring strict controls under IEC 60825-1 and FDA 21 CFR 1040.10/1040.11.
– Export Controls: Subject to EAR (Export Administration Regulations) or ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations) if applicable technologies meet defense-related criteria.
– Customs Tariff Codes: Classified under HS Code 8515.21 (Laser Welding Machines) for global trade. Ensure accurate classification to avoid delays or penalties.
– Required Documentation: Commercial invoices, packing lists, certificates of origin, technical specifications, FDA laser product reports (U.S.), and CE/UKCA declarations of conformity (Europe/UK).
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Proper packaging is critical to prevent damage during transit:
– Use shock-absorbent materials and custom crating to protect sensitive optics, power supplies, and robotic components.
– Clearly label packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Protect from Moisture.”
– Include desiccants in sealed enclosures to prevent condensation during air or sea transport.
– Secure all moving parts and remove or lock robotic arms during shipment.
– Follow manufacturer-specific disassembly and reassembly protocols.
Transportation and Shipping Considerations
- Mode of Transport: Air freight is preferred for time-sensitive deliveries but may require special approvals due to battery or high-value components. Sea freight is cost-effective for heavy equipment but requires longer planning and climate control.
- Hazardous Components: Some laser tools contain lithium batteries (e.g., for backup systems) or cooling liquids. Declare and package per IATA/IMDG regulations if applicable.
- Insurance: Obtain comprehensive cargo insurance covering full replacement value, including high-cost optical elements.
- Carrier Qualifications: Use freight carriers experienced in handling high-tech industrial machinery with tracking and climate monitoring capabilities.
Import/Export Compliance
- Export Licenses: Determine EAR99 status or obtain required licenses (e.g., from BIS in the U.S.) for controlled technology.
- Import Duties and Taxes: Research local VAT, GST, or import tariffs. Use Incoterms (e.g., DDP, EXW) clearly in contracts to define responsibility.
- Customs Inspections: Prepare for potential delays; provide complete technical documentation, including block diagrams and power ratings.
- Restricted Destinations: Verify recipient country is not under trade sanctions or embargoes (e.g., OFAC compliance in the U.S.).
Installation and On-Site Compliance
Upon delivery:
– Conduct a full inspection for transit damage before unpacking.
– Follow manufacturer-recommended installation procedures, including grounding, ventilation, and cooling system setup.
– Verify compliance with local electrical codes (e.g., NEC in the U.S., IEC in Europe).
– Install appropriate laser interlocks, warning signs, and beam enclosures per ANSI Z136.1 or equivalent standards.
Safety and Operational Compliance
- Laser Safety Officer (LSO): Appoint an LSO to oversee compliance with laser safety programs.
- Protective Equipment: Provide appropriate laser safety eyewear (wavelength-specific), protective enclosures, and fume extraction systems.
- Training: Ensure operators are trained in laser safety, emergency shutdown, and maintenance procedures. Maintain training records.
- Audits and Inspections: Conduct regular safety audits and equipment inspections to maintain compliance with OSHA, EU Machinery Directive, or other local regulations.
Maintenance and Lifecycle Management
- Schedule routine maintenance per manufacturer guidelines to prevent performance degradation and safety hazards.
- Track calibration of optical components and laser power output.
- Dispose of obsolete or damaged units in accordance with environmental regulations (e.g., WEEE in the EU, EPA rules in the U.S.).
- Retain compliance documentation throughout the equipment lifecycle for audits or resale.
Emergency Response and Incident Reporting
- Develop an emergency response plan for laser fires, beam exposure, or electrical faults.
- Report accidental exposures or system malfunctions to relevant authorities (e.g., FDA for U.S. manufacturers, HSE in the UK).
- Maintain an incident log and conduct root cause analysis to prevent recurrence.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance management for industrial laser welding tools is essential for operational safety, legal adherence, and supply chain reliability. By following this guide, organizations can mitigate risks, ensure regulatory alignment, and maximize the lifespan and performance of their laser systems. Always consult with legal, safety, and logistics experts when expanding into new markets or transporting high-value laser equipment.
Conclusion: Sourcing Industrial Laser Welding Tools
Sourcing industrial laser welding tools is a strategic decision that significantly impacts manufacturing efficiency, product quality, and long-term operational costs. As industries increasingly demand precision, speed, and automation, selecting the right laser welding equipment—paired with reliable suppliers—is paramount. A comprehensive sourcing approach should evaluate not only technical specifications such as laser power, beam quality, and compatibility with materials, but also supplier reputation, after-sales support, training, and total cost of ownership.
Global market dynamics offer a range of options, from established European and North American manufacturers known for precision and durability, to competitive Asian suppliers providing cost-effective solutions. However, the lowest upfront price should not overshadow critical factors like system integration capabilities, maintenance requirements, and scalability for future production needs.
Ultimately, successful sourcing involves aligning technological capabilities with business objectives. Investing in high-quality, well-supported industrial laser welding tools leads to improved weld integrity, reduced waste, and enhanced productivity. By conducting thorough supplier due diligence and considering lifecycle costs, manufacturers can ensure a robust return on investment and maintain a competitive edge in advanced manufacturing environments.