The global laser cleaning machine market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for eco-friendly, non-abrasive surface treatment solutions across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 720 million in 2022 and is projected to reach USD 1.68 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of approximately 14.9% during the forecast period. Similarly, Grand View Research estimates a CAGR of 15.2% from 2023 to 2030, citing advancements in fiber laser technology and rising adoption in maintenance and restoration applications. With this expansion, a growing number of manufacturers are competing on price, performance, and innovation. This dynamic landscape has made it essential for buyers to evaluate leading industrial laser cleaning machine suppliers not just on upfront cost, but on total value—including durability, cleaning efficiency, and service support. Below is a data-informed analysis of the top 10 manufacturers offering competitive pricing without compromising technical excellence.
Top 10 Industrial Laser Cleaning Machine Price Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: we engineer and manufacture the most advanced—and most powerful—pulsed industrial laser cleaning systems on the market, built for both manual and automated ……
#2 SHARK P CL Industrial Laser Cleaning Machines (100
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: SHARK P CL is an industrial pulsed laser cleaning machine series by PULSAR Laser with outputs from 100 W to 1000 W, air-cooled up to 500 W….
#3 Industrial 1500W 2000W CW Laser Cleaning Machine Rusty Remove
Website: xinglaser.com
Key Highlights: XING Laser (6am Life LLC, DBA XING Laser) specializes in the development and manufacture of high-performance handheld laser cleaning and rust removal equipment….
#4 Laserax
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Laserax works with the world’s leading manufacturers to implement laser cleaning, welding, texturing, and marking solutions….
#5 Laser Cleaning Machine Manufacturer
Website: hantencnc.com
Key Highlights: We offer a wide range of laser cleaners, from 100W to 3000W. Our lineup includes handheld, backpack, and trolley-type products to meet diverse cleaning needs….
#6 Argento Lux
Website: argentolux.com
Key Highlights: Our company provides state-of-the-art Industrial Laser Equipment Sales and Mobile Laser Cleaning Services for a wide range of applications and industries….
#7 Industrial Laser Machines & Solutions
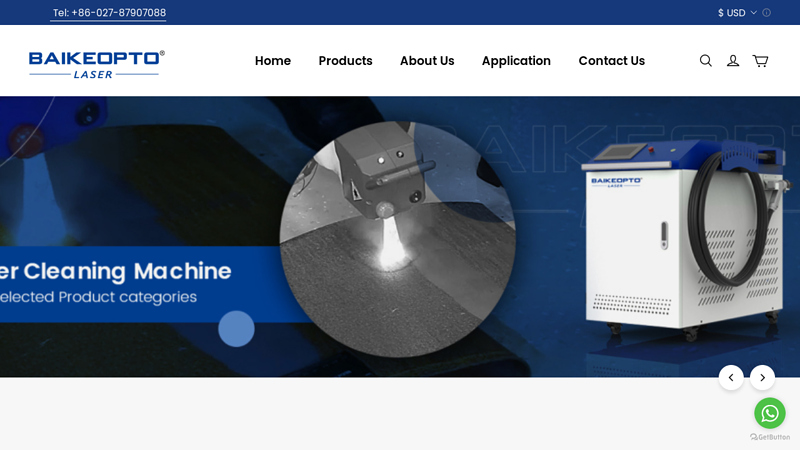
#8 Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: baikeopto.com
Key Highlights: BK-FLC300SL Suitcase 300W Multi-Module Industrial Rust Pulsed Laser Cleaning Machine for Metal Rust Oil Painting Price. BAIKEOPTO laser cleaning machines ……
#9 Laser Cleaning and Laser Ablation Systems
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Remove rust and surface contaminants with our laser cleaning & laser ablation systems. Experience superior cleaning tech, automation, and eco-friendly ……
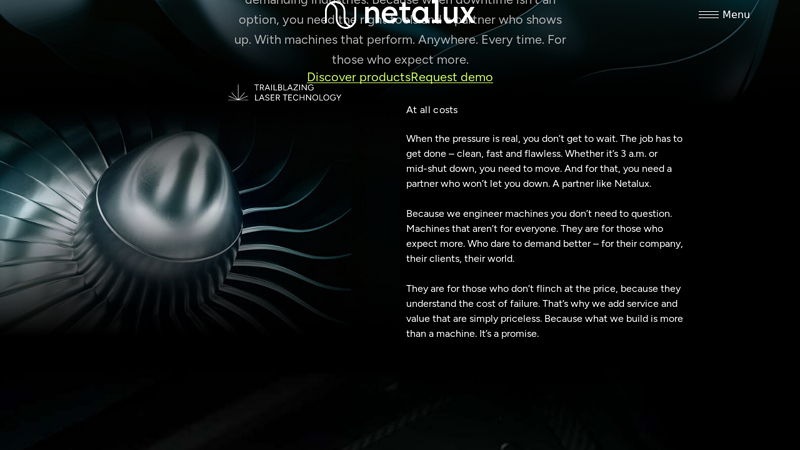
#10 Netalux
Website: netalux.com
Key Highlights: Discover our award-winning Laser Cleaning Solutions for the world’s most demanding industries. Discover our products and global service now….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Industrial Laser Cleaning Machine Price

2026 Market Trends Forecast for Industrial Laser Cleaning Machine Prices
The industrial laser cleaning machine market is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by technological advancements, increasing environmental regulations, and expanding industrial adoption. Price trends will be shaped by a complex interplay of cost pressures, demand growth, and competitive dynamics.
1. Downward Price Pressure from Technological Advancements and Economies of Scale
A primary trend influencing 2026 pricing will be a gradual but steady decline in average machine costs. This is primarily driven by maturing fiber laser technology, which is becoming more efficient and less expensive to produce. As key components like high-power fiber lasers, beam delivery systems, and control software benefit from mass production and improved manufacturing processes, the overall bill of materials (BOM) for laser cleaning systems will decrease. Additionally, manufacturers are achieving greater economies of scale as global demand rises, further enabling cost reductions that can be passed on to customers. This trend will make laser cleaning more accessible to mid-sized and smaller enterprises.
2. Increased Competition Intensifying Price Sensitivity
The market is witnessing a surge in both established industrial equipment providers and new entrants, particularly from Asia. By 2026, this heightened competition is expected to intensify price competition, especially in the mid-range power segment (500W–2000W). Chinese manufacturers, in particular, are likely to maintain aggressive pricing strategies to capture market share, putting downward pressure on global price benchmarks. While premium brands will retain pricing power through advanced features, superior service, and reliability, the overall market will see a widening range of price points, with more budget-friendly options becoming available.
3. Demand Growth in New Sectors Supporting Volume and Price Stability
Despite downward pressures, strong demand across emerging and traditional sectors will help stabilize prices and prevent a freefall. Industries such as automotive (for paint stripping and weld prep), aerospace (composite and turbine cleaning), heritage restoration, and offshore oil & gas are increasingly adopting laser cleaning due to its precision, chemical-free operation, and environmental compliance. The growing emphasis on sustainable manufacturing and regulations restricting chemical cleaning (e.g., VOC emissions) will further boost adoption. This rising demand will absorb increased production volumes, allowing manufacturers to maintain healthy margins even as prices decrease incrementally.
4. Premium Pricing for Advanced and Integrated Systems
While basic laser cleaning units may see price reductions, high-end systems featuring automation (robotic integration), real-time monitoring, AI-based process optimization, and higher power outputs (3000W+) are likely to command premium prices. These advanced solutions cater to high-precision applications in aerospace, nuclear, and medical device manufacturing, where performance, repeatability, and safety justify higher costs. Customization for specific industrial workflows will also support value-based pricing models rather than pure commoditization.
5. Regional Price Variations Influenced by Local Factors
Pricing in 2026 will remain regionally differentiated. North America and Western Europe will generally exhibit higher prices due to service expectations, compliance with stringent safety standards, and the presence of premium brands. In contrast, Asia-Pacific—especially China and India—will lead in lower-cost solutions, fueled by local manufacturing and price-sensitive markets. However, as technology diffuses and local service networks improve globally, price disparities are expected to narrow slightly by 2026.
Conclusion
By 2026, the industrial laser cleaning machine market will experience a general trend of moderate price decline due to technological improvements and competition, particularly in the mid-tier segment. However, robust demand from environmentally conscious industries and premium features in advanced systems will prevent steep price drops. The market will likely bifurcate, with cost-effective models driving mass adoption and high-performance systems sustaining higher price points. Buyers can expect greater affordability and choice, making laser cleaning a more viable and economical alternative to traditional cleaning methods.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Industrial Laser Cleaning Machine Prices (Quality, IP)
When sourcing industrial laser cleaning machines, focusing solely on price can lead to significant long-term costs and operational issues. Buyers often overlook critical factors related to quality and intellectual property (IP), resulting in subpar performance, safety risks, and legal complications. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Overlooking Build Quality and Component Standards
Many suppliers offer lower-priced machines that cut corners on materials and engineering. These may use inferior optical components, under-spec cooling systems, or non-industrial-grade housings, leading to frequent breakdowns, reduced cleaning efficiency, and shorter lifespans. Always verify the quality of core components—such as the laser source, scanner heads, and cooling units—and request third-party certifications or test reports.
Ignoring Safety and Compliance Certifications
Low-cost machines may lack essential safety features or fail to meet international standards (e.g., CE, FDA, IEC 60825). This not only poses risks to operators but can also result in workplace violations or insurance issues. Ensure the supplier provides full compliance documentation and that safety interlocks, protective enclosures, and emergency shutoffs are properly integrated.
Falling for Inflated or Misleading Specifications
Some vendors exaggerate laser power, cleaning speed, or duty cycle to appear competitive. For example, a machine advertised as “1000W” might refer to peak power rather than continuous output. Always request verified performance data under real-world conditions and, if possible, conduct on-site or video demonstrations to validate claims.
Underestimating After-Sales Support and Serviceability
Cheaper machines from unknown manufacturers often come with limited or non-existent technical support, spare parts availability, or service networks. Downtime due to lack of maintenance or repair options can far outweigh initial cost savings. Evaluate the supplier’s service infrastructure, warranty terms, and responsiveness before making a purchase.
Neglecting Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Purchasing from suppliers that use cloned or reverse-engineered technology can expose your business to legal liability. Machines lacking proper IP clearance might infringe on patents or copyrights, leading to shipment seizures, fines, or forced equipment removal. Always verify that the manufacturer holds legitimate IP rights or proper licensing for their technology.
Assuming All Software and Control Systems Are Equal
Low-cost machines may use outdated or unlicensed control software with limited functionality, poor user interfaces, or no update path. This can hinder integration with existing systems and reduce operational efficiency. Confirm software authenticity, update policies, and compatibility with automation or data logging requirements.
Failing to Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership
The upfront price is just one part of the equation. Consider maintenance costs, energy consumption, consumables (e.g., protective lenses), training, and expected machine lifetime. A slightly more expensive, high-quality machine often delivers better ROI through reliability and lower downtime.
By addressing these pitfalls, buyers can make informed decisions that balance cost with quality, safety, and legal compliance—ensuring a successful and sustainable investment in industrial laser cleaning technology.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Industrial Laser Cleaning Machine Price
When evaluating the price of an industrial laser cleaning machine, it’s essential to consider not only the base cost but also the logistics and compliance factors that can significantly impact total expenses and delivery timelines. Understanding these elements ensures a smooth procurement, shipment, and deployment process while avoiding unexpected fees or delays.
Shipping and Freight Costs
The physical size, weight, and packaging requirements of industrial laser cleaning machines influence shipping methods and costs. Most units are heavy (ranging from 100 kg to over 1,000 kg) and may require specialized crating. Costs vary depending on:
- Shipping method: Air freight (faster but expensive) vs. sea freight (cost-effective for heavy equipment but slower).
- Origin and destination: Import/export between countries affects freight rates and transit time.
- Insurance: High-value machinery should be fully insured during transit.
- Incoterms: Clearly define responsibilities (e.g., FOB, CIF, DDP) to avoid misunderstandings about who pays for shipping, insurance, and customs.
Tip: Always request a landed cost quote that includes shipping, insurance, and estimated duties to compare suppliers accurately.
Import Duties and Taxes
Import duties, value-added tax (VAT), or goods and services tax (GST) can add 5%–25% or more to the machine’s price, depending on the destination country. Key considerations:
- Harmonized System (HS) Code: Industrial laser cleaning machines typically fall under HS Code 8515. This code determines the applicable duty rate. Confirm the correct classification with local customs.
- Free Trade Agreements: Some countries offer reduced or zero tariffs under trade agreements (e.g., USMCA, ASEAN).
- VAT/GST Exemptions: Certain industrial equipment may qualify for tax relief if used for manufacturing or R&D—verify eligibility with a local tax advisor.
Tip: Work with a customs broker to calculate total landed cost and ensure accurate documentation.
Regulatory and Safety Compliance
Industrial laser systems must comply with health, safety, and environmental regulations in both the exporting and importing countries. Non-compliance can result in shipment delays, fines, or equipment rejection.
- Laser Safety Standards:
- IEC 60825-1: International standard for laser product safety. Machines must have proper classification (typically Class 1 or Class 4 with safety interlocks).
- FDA/CDRH (USA): Requires manufacturers to file a product report and comply with 21 CFR 1040.10 regulations.
-
CE Marking (EU): Requires conformity with the Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC) and EMC Directive (2014/30/EU).
-
Electrical Standards:
- UL/CSA (North America)
- CE/UKCA (Europe/UK)
- CCC (China)
Tip: Confirm that the supplier provides full compliance documentation (e.g., Declaration of Conformity, laser safety certification) before purchase.
Customs Documentation and Export Controls
Proper documentation is critical for international shipments:
- Commercial Invoice: Must detail the machine description, value, and HS code.
- Packing List: Includes weight, dimensions, and packaging details.
- Bill of Lading/Air Waybill: Proof of shipment and contract of carriage.
- Certificate of Origin: May be required to qualify for tariff reductions.
- Export Licenses: Some high-powered laser systems may be subject to export controls (e.g., under the Wassenaar Arrangement). Verify if an export license is needed from the supplier’s country.
Tip: Delays often occur due to incomplete or inaccurate paperwork—double-check all documents with your freight forwarder.
Installation and On-Site Compliance
After delivery, local regulations may require additional steps before operation:
- Electrical Installation: Must meet local codes (e.g., NEC in the U.S., IEC in Europe). Voltage and plug types must match local standards.
- Laser Safety Program: Facilities using Class 3B or Class 4 lasers may need to appoint a Laser Safety Officer (LSO) and implement safety controls (e.g., interlocks, warning signs, training).
- Environmental Permits: In some regions, industrial processes involving lasers may require environmental notifications.
Tip: Budget for site preparation, training, and any required modifications to meet local safety codes.
Warranty and After-Sales Service Logistics
Consider the logistics of maintenance and support:
- Spare Parts Availability: Determine if critical components are stocked locally or require international shipping.
- Service Response Time: Understand how quickly the supplier or distributor can respond to breakdowns.
- Warranty Terms: Clarify whether warranty service includes labor, parts, and return shipping—especially for cross-border support.
Tip: Choose suppliers with regional service centers or authorized partners to reduce downtime.
Summary: Total Cost of Ownership
When calculating the industrial laser cleaning machine price, include:
- Base machine cost
- Shipping and insurance
- Import duties and taxes
- Compliance certification and documentation
- Installation and safety setup
- Training and after-sales support
By accounting for logistics and compliance early in the procurement process, businesses can avoid surprises, ensure regulatory adherence, and make more accurate investment decisions.
Conclusion on Sourcing Industrial Laser Cleaning Machine Prices
Sourcing an industrial laser cleaning machine requires a strategic approach that balances cost, performance, and long-term value. While initial price is a significant factor, it should not be the sole determinant in the purchasing decision. Market research shows a wide price range—typically from $20,000 to over $100,000—depending on laser power, automation level, brand reputation, and customization.
Key factors influencing price include laser wattage (e.g., 500W to 2000W+), beam quality, portability, integrated safety features, and after-sales support. Machines from established manufacturers in Europe and North America tend to be more expensive but offer higher reliability and compliance with international standards. Meanwhile, suppliers from China and other Asian markets often provide cost-competitive options, though due diligence on quality control and technical support is essential.
To optimize sourcing, it is recommended to:
– Clearly define application requirements (material type, cleaning speed, surface area).
– Request detailed quotations with specifications and warranty terms.
– Evaluate total cost of ownership, including maintenance, training, and energy consumption.
– Consider pilot testing or site visits to assess machine performance.
– Explore leasing or financing options to manage upfront investment.
Ultimately, the most cost-effective solution is not always the cheapest—but the one that delivers consistent performance, durability, and strong technical support, ensuring a faster return on investment and minimal operational downtime. Working with reputable suppliers and performing thorough comparative analysis will lead to a well-informed procurement decision tailored to specific industrial needs.